Systems and methods for capturing or replaying time-series data
a time-series data and time-series technology, applied in the field of data processing, can solve the problems of increasing difficulty in detecting malicious activity carried on the network, more difficult to assess whether any particular portion of the data conveyed will cause harm, and detection systems fail to assess network traffi
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
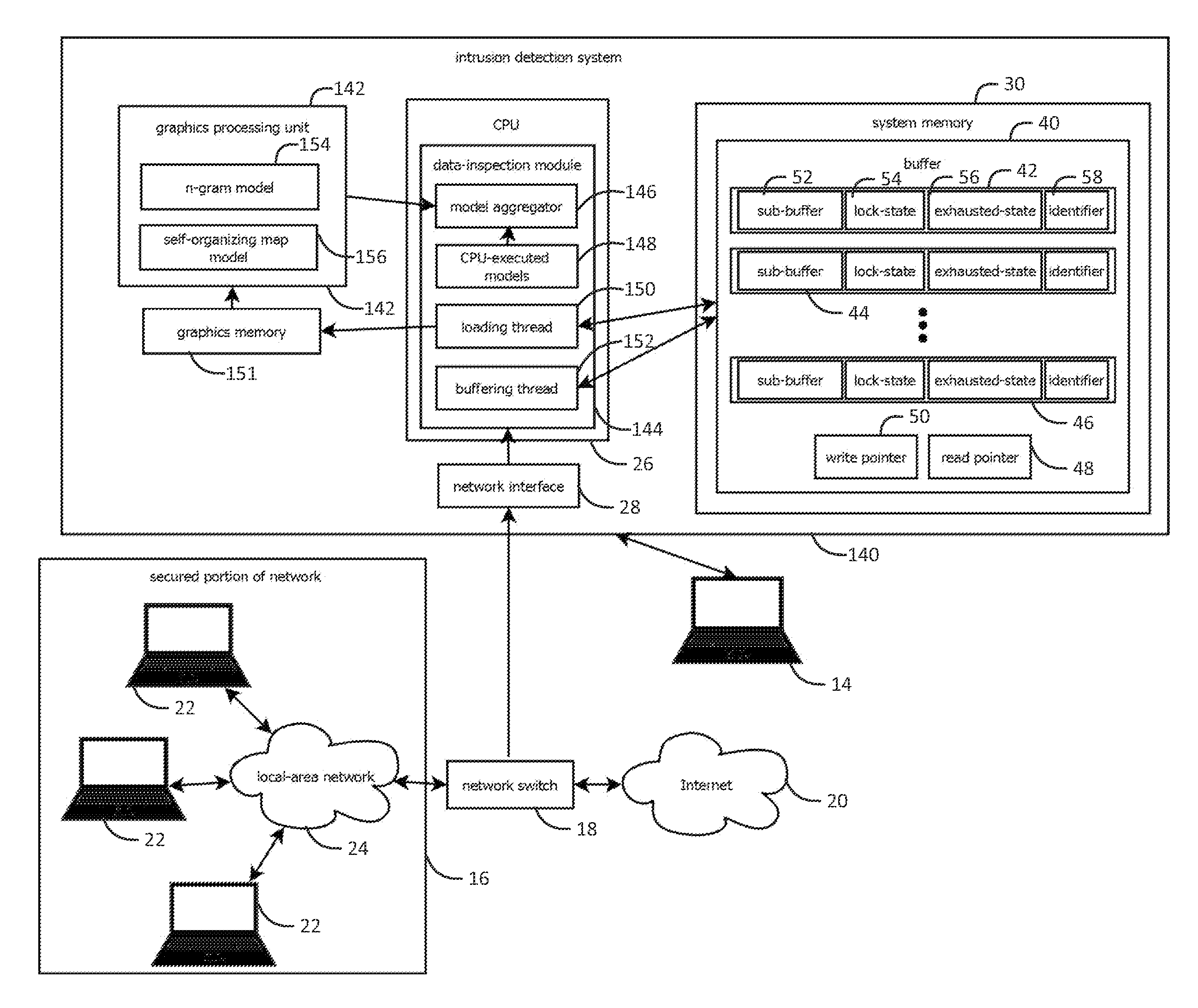
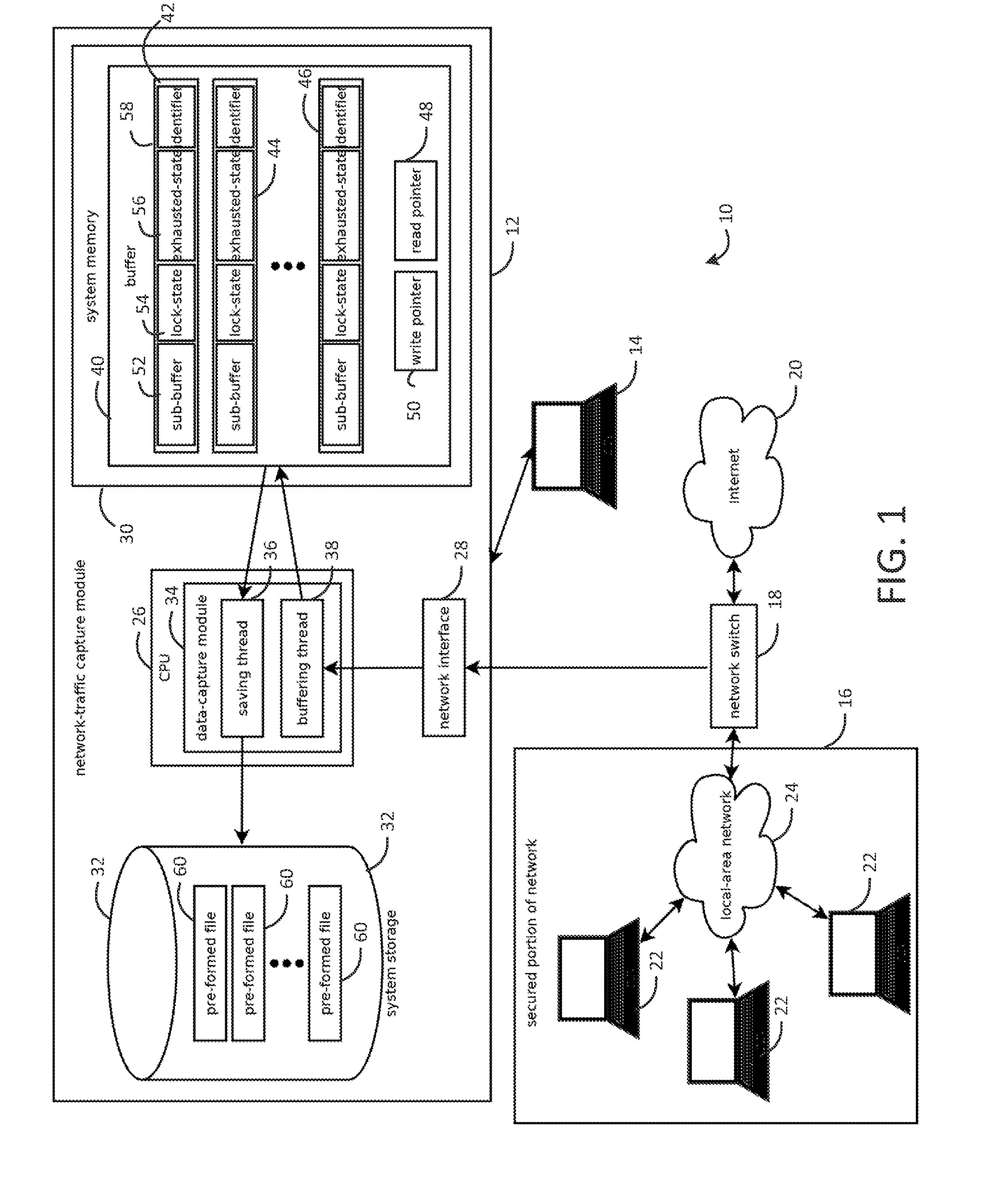
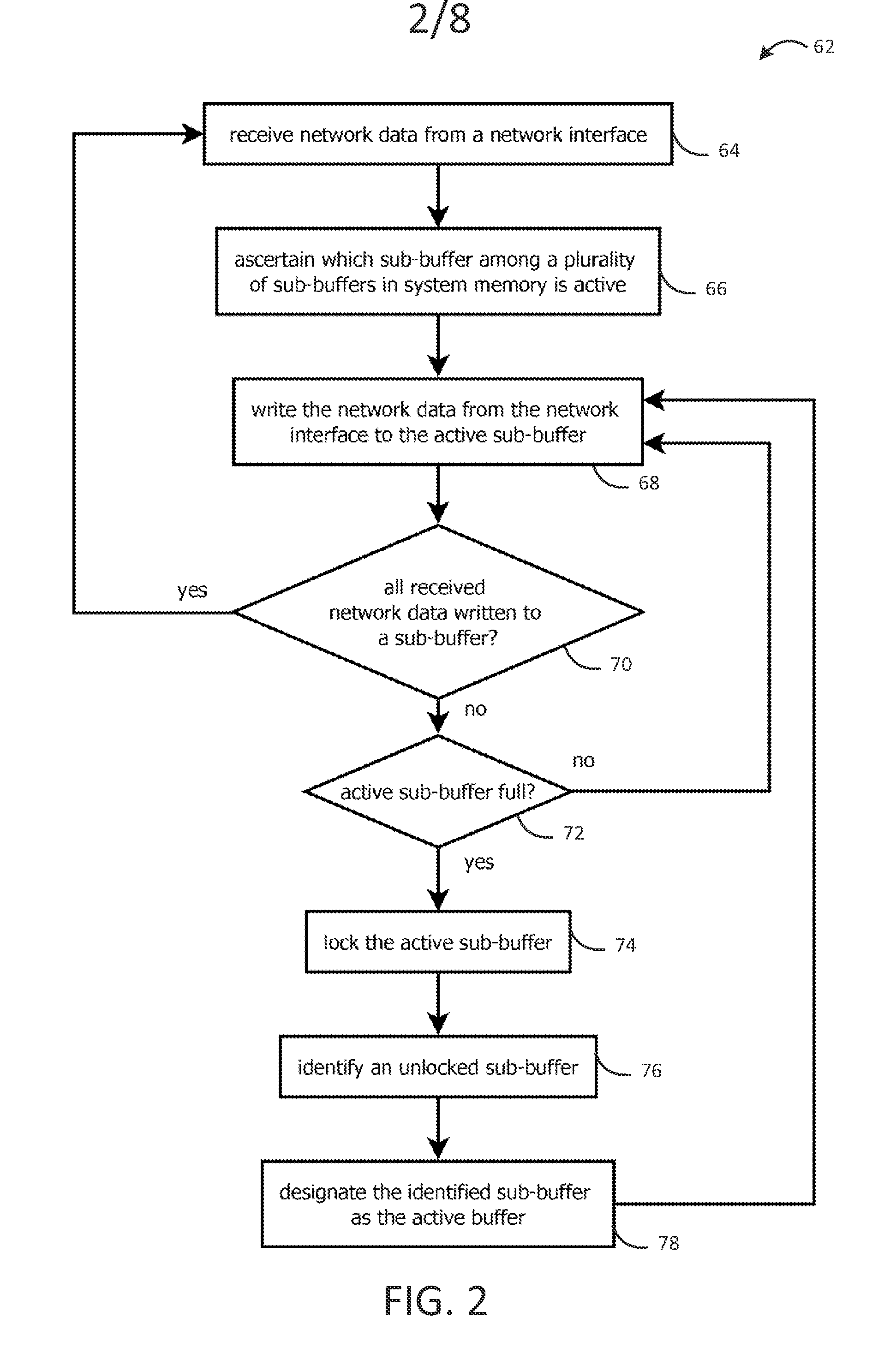
[0024]FIGS. 1-8 describe systems and processes for capturing, replaying, or analyzing time-series data (e.g., network data passing through a network node over time) at a relatively high rate (for example, 10 gigabit (Gb) per second or faster), using relatively inexpensive, off-the-shelf commodity computing components. These techniques may be combined in a single system, e.g., an intrusion detection system, having different modes of operation for capture, replay, and analysis. But, it should be noted that these techniques may be used separately in different systems and applications, e.g., for data capture or replay in contexts other than detecting intrusions in network traffic.
[0025]The techniques described herein are broadly applicable. In some use cases, the techniques may be used to capture, replay, or analyze various types of data other than network traffic between other computers, for example internal or externally originated application program interface (“API”) calls, such as ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com