Mobile Computing Based Railway Crossing Collision Avoidance System
a collision avoidance system and mobile computing technology, applied in the field of railroad crossing safety, can solve problems such as ineffective methods of preventing collisions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment one
Preferred Embodiment One
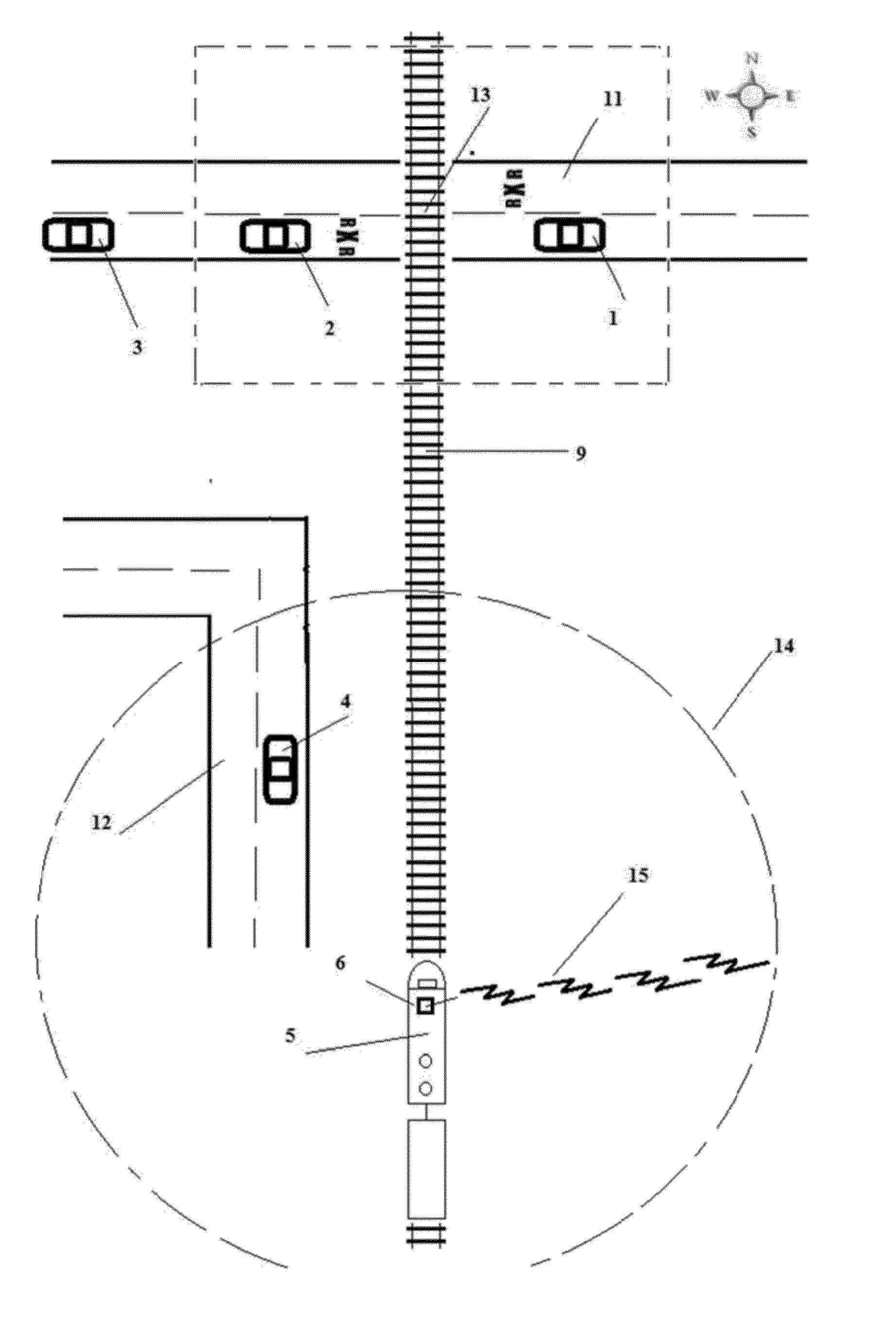
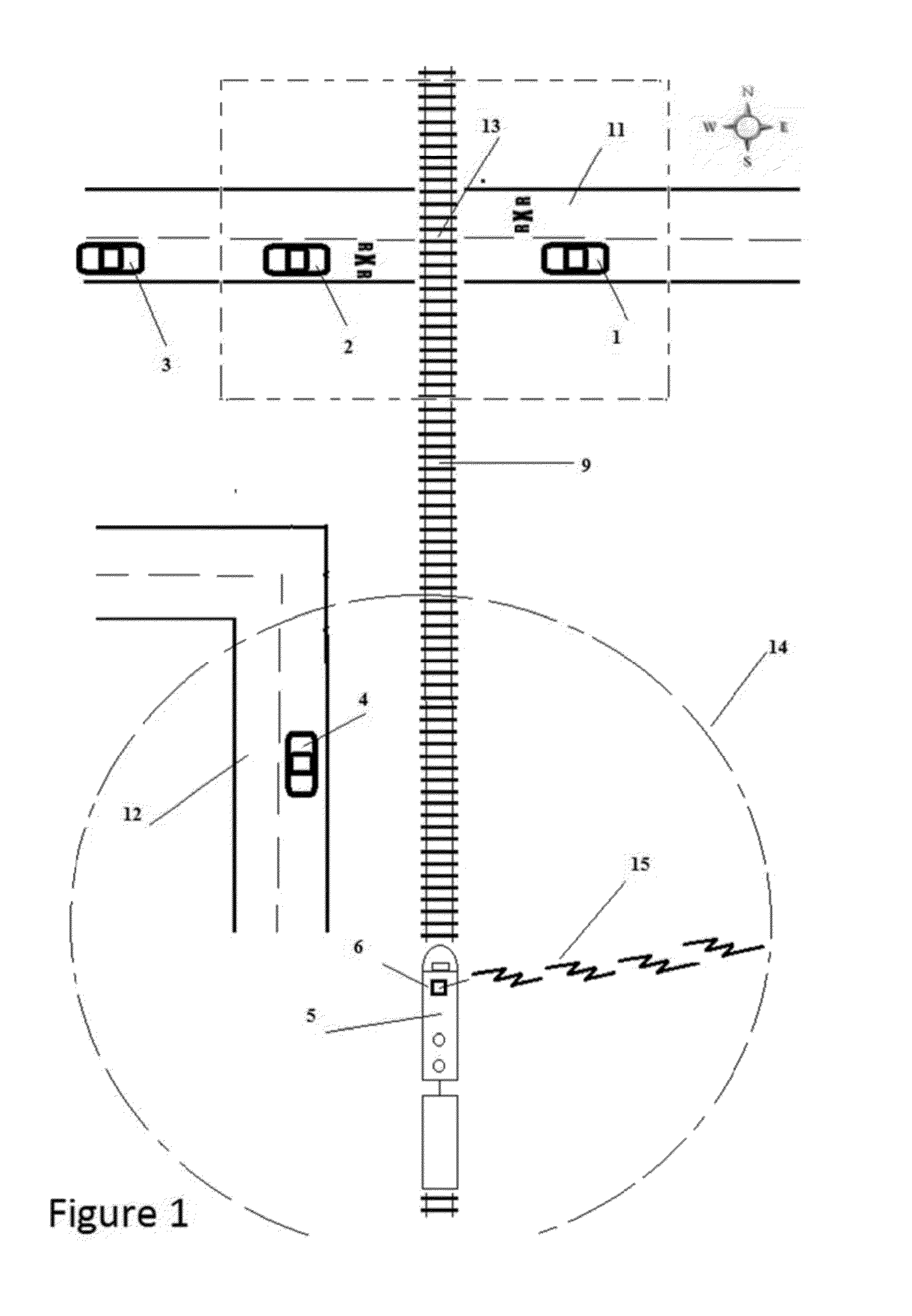
[0019]Referring to FIG. 1, a train 5 travelling on train tracks 9 (northward in this example) towards a railroad crossing 13 is equipped with an FM radio transmitter 6 that transmits an FM signal 15 at a set frequency at a nominal distance of 1 mile radius 14 in all directions around the train. Any available frequency can be used. Vehicles 1, 2, 3 (travelling eastward in this example) and 4 (travelling northward in this example) are all travelling in the vicinity of the railway crossing or train.
[0020]Each vehicle 1, 2, 3 and 4 are equipped with a mobile computing device 57 of FIG. 3 and an FM receiver 51 of FIG. 3 which can detect the presence of the FM signal 15 transmitting from the FM transmitter 6 of the train 5. Referring to of FIG. 3 the mobile computing device 57 is also equipped with a GPS receiver 52 that can detect the GPS coordinates of the mobile computing device 57.
[0021]The mobile computing device 57 is also equipped with a CPU 53 and a compute...
embodiment two
Preferred Embodiment Two
[0029]An improvement to the previous embodiment would be for the present invention to take into consideration the type and speed of the vehicle approaching the railway crossing 13 of FIG. 1. The type of vehicle information can be stored in an area 59 of FIG. 3 in the mobile computing device. The vehicle speed can be input into the mobile computing device from the vehicle speedometer or be calculated by the mobile computing device using GPS coordinate reading over a period of time. The method of operation for preferred embodiment two is the same as preferred embodiment one, except that the computer program 58 takes into consideration the vehicle type and speed. A semi-trailer, for example, takes longer to come to a stop than a small car, and therefore the area 7 of FIG. 1 would be increased when computing whether a the vehicle is in the danger zone area of the railway crossing and in need of being given an alert when the train 5 of FIG. 1 is also near the rail...
embodiment three
Preferred Embodiment Three
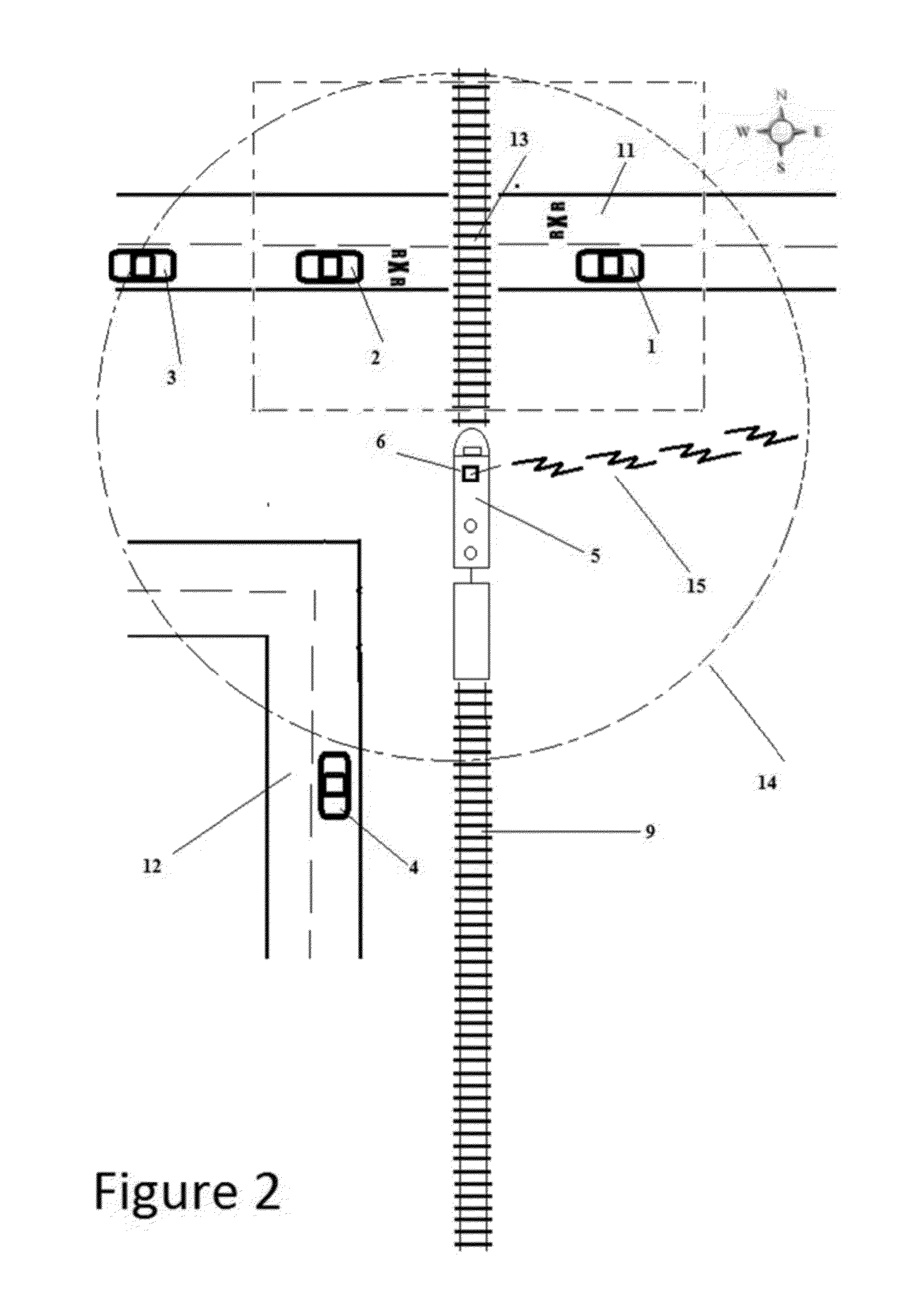
[0030]Referring to FIG. 5, a train 5 travelling on train tracks 9 (northward in this example) towards a railroad crossing 13 is equipped with an FM radio transmitter 6 that transmits an FM signal 14 at a set frequency at a nominal distance of a 4 mile radius 15 in all directions around the train. Any available frequency can be used. Preferred embodiment three functions identically to that of preferred embodiments 1 and 2 with the difference being that the train 5 encodes onto the FM radio signal the trains speed, distance to the railway crossing, and the length of the train. For example, a train traveling 5 MPH that, is 1 mile from the train crossing presents no real danger to vehicles 1, 2 or 3.
[0031]Referring to FIG. 4, preferred embodiment three receives the encoded FM radio signal 14 of FIG. 5 via the FM receiver 51 and the mobile computing device then decodes from the FM radio signal 14 of FIG. 5 the speed, distance from the railway crossing and length...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com