Niclosamide for the treatment of cancer metastasis
a cancer metastasis and niclosamide technology, applied in the field of niclosamide, can solve the problems of aggressive tumor growth, difficult or impossible adjuvant treatment, difficult or impossible detection of metastatic lesions, etc., and achieve the effect of inhibiting s100a4-induced metastasis, inhibiting s100a4-induced metastasis formation, and reducing liver metastasis scor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
High-Throughput Screening for S100A4 Inhibitors
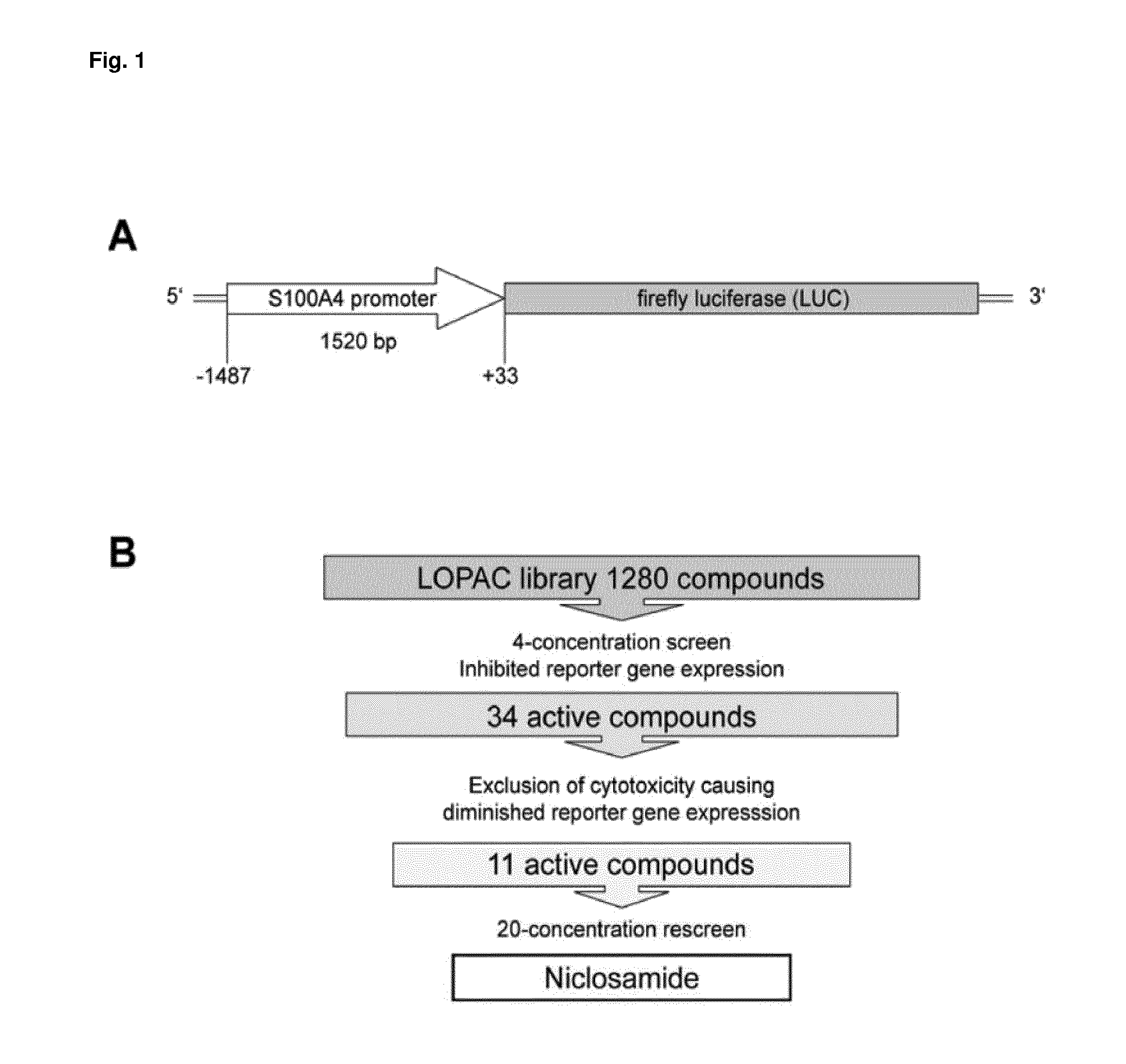
[0084]HCT116-S100A4p-LUC colon cancer cells stably expressing a human S100A4 promoter-driven luciferase reporter gene construct were screened with the Library of Pharmacologically Active Compounds (LOPAC; FIG. 1, A). The LOPAC Library represents a collection of 1280 well characterized small molecule inhibitors. In a primary 4-concentration screen, 34 compounds were found to inhibit S100A4 promoter-driven luciferase expression by greater than 50% compared with DMSO-treated control cells (FIG. 1, B). In parallel, cell viability was determined using the Alamar blue assay to evaluate whether some of the inhibitory effects were caused by cytotoxicity (data not shown). Of the 34 effective compounds, 11 compounds most efficiently inhibited reporter gene expression at concentrations that were non-toxic or only slightly affected cell viability. To confirm the inhibitory capacity of the selected compounds and to more accurately establish the conc...
example 2
Effect of Niclosamide on S100A4 mRNA and Protein Expression
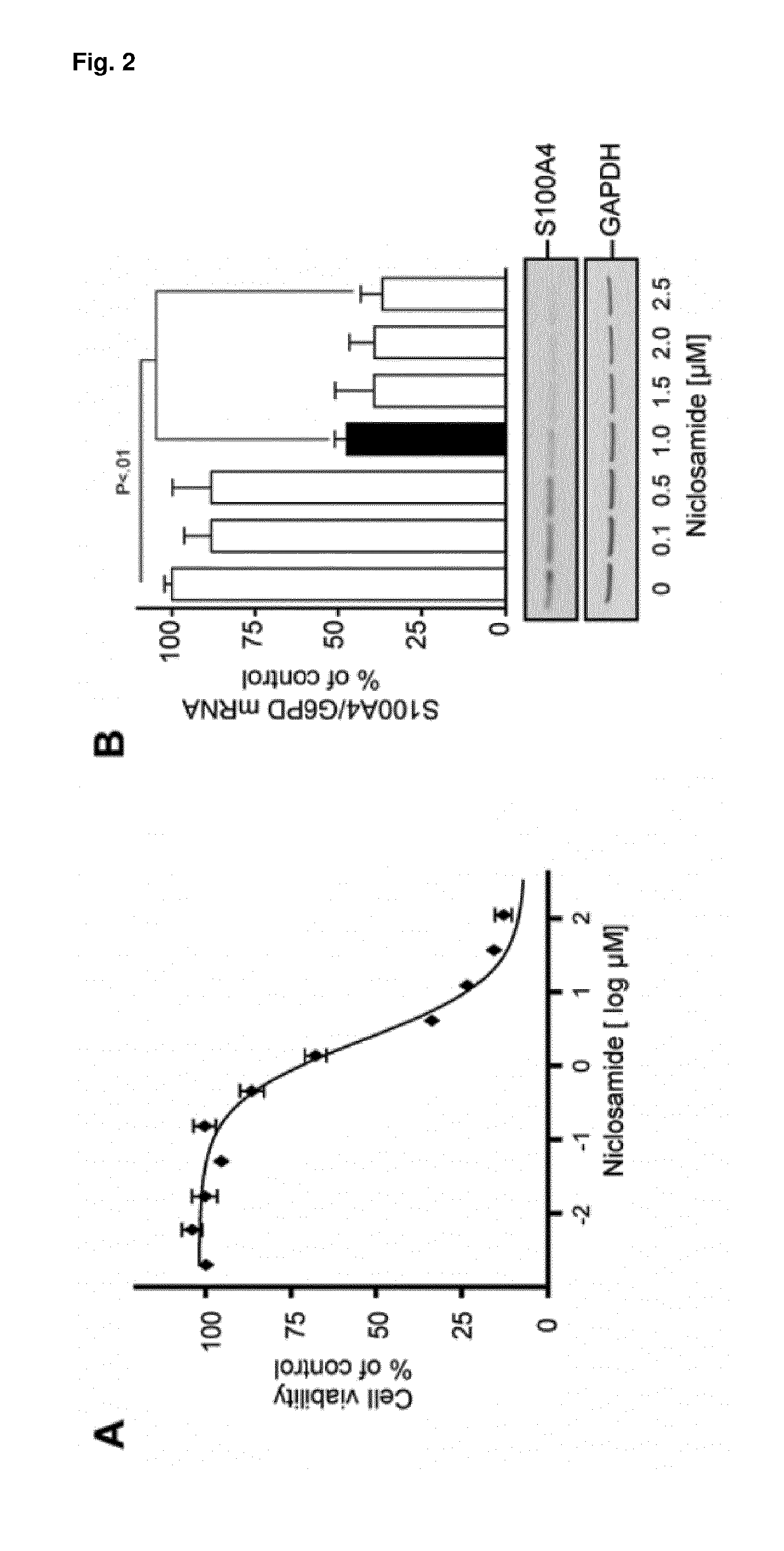
[0085]To determine an applicable niclosamide concentration, the cytotoxicity of niclosamide on HCT116 cells was analyzed. Exposure of HCT116 cells to increasing concentrations of niclosamide reduced cell viability in a concentration-dependent manner (EC50=2.2 μM; 95% Cl 1.87 to 2.92 μM) (FIG. 2, A). Choosing a concentration range from 0.1 μM to 2.5 μM niclosamide endogenous S100A4 expression in HCT116 cells was analyzed and found S100A4 mRNA and protein levels to be reduced in a concentration-dependent manner (FIG. 2, B). Concentrations of more than 0.5 μM niclosamide reduced the endogenous S100A4 mRNA amount to less than 50% of the solvent-treated control (control vs niclosamide, 1 μM mean 47.4%, 95% Cl 39.3% to 55.4%; P<0.01, 1.5 μM mean 39.2%, 95% Cl 11.4% to 89.7%; P<0.01, 2 μM mean 39.1, 95% Cl 18.3% to 59.9%, P<0.01, 2.5 μM mean 36.7%, 95% Cl 18.6% to 54.8%; P<0.001). Similar effects were observed at the S100A4 protein...
example 3
Effect of Niclosamide on S100A4-Induced Cell Migration and Invasion
[0088]S100A4 is a main regulator of cell motility (25). Thus, the effect of niclosamide on S100A4-induced cell migration in HCT116-vector and HCT116-S100A4 cells was analyzed. The number of migrated cells was inhibited in HCT116-vector cells in the presence of niclosamide (control vs niclosamide, mean 100.0% vs 43.0%, mean difference 57.0%, 95% Cl 40.3% to 73.7%, P<0.0001) (FIG. 3, A). In contrast, migration rates of HCT116-S100A4 cells showed no reduction upon niclosamide treatment (control vs niclosamide, mean 145.0% vs 117.0%, mean difference 28%, 95% Cl −7.8% to 63.9%, statistically not significant).
[0089]The invasion rates of HCT116-vector and HCT116-S100A4 cells were also determined, since S100A4 is well known to stimulate cell invasion (11). The number of invaded cells was decreased in niclosamide-treated HCT116-vector cells (control vs niclosamide, mean 100% vs 30.1%, mean difference 69.9%, 95% Cl 10.9% to 12...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com