Methods and systems for performing thrombectomy procedures
a thrombosis and thrombosis technology, applied in the field of intralumenal therapy for the treatment of vascular disease states, can solve the problems of hemorrhagic stroke, reduced the number of devices used for some disease states, and symptomatic neurological deficits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
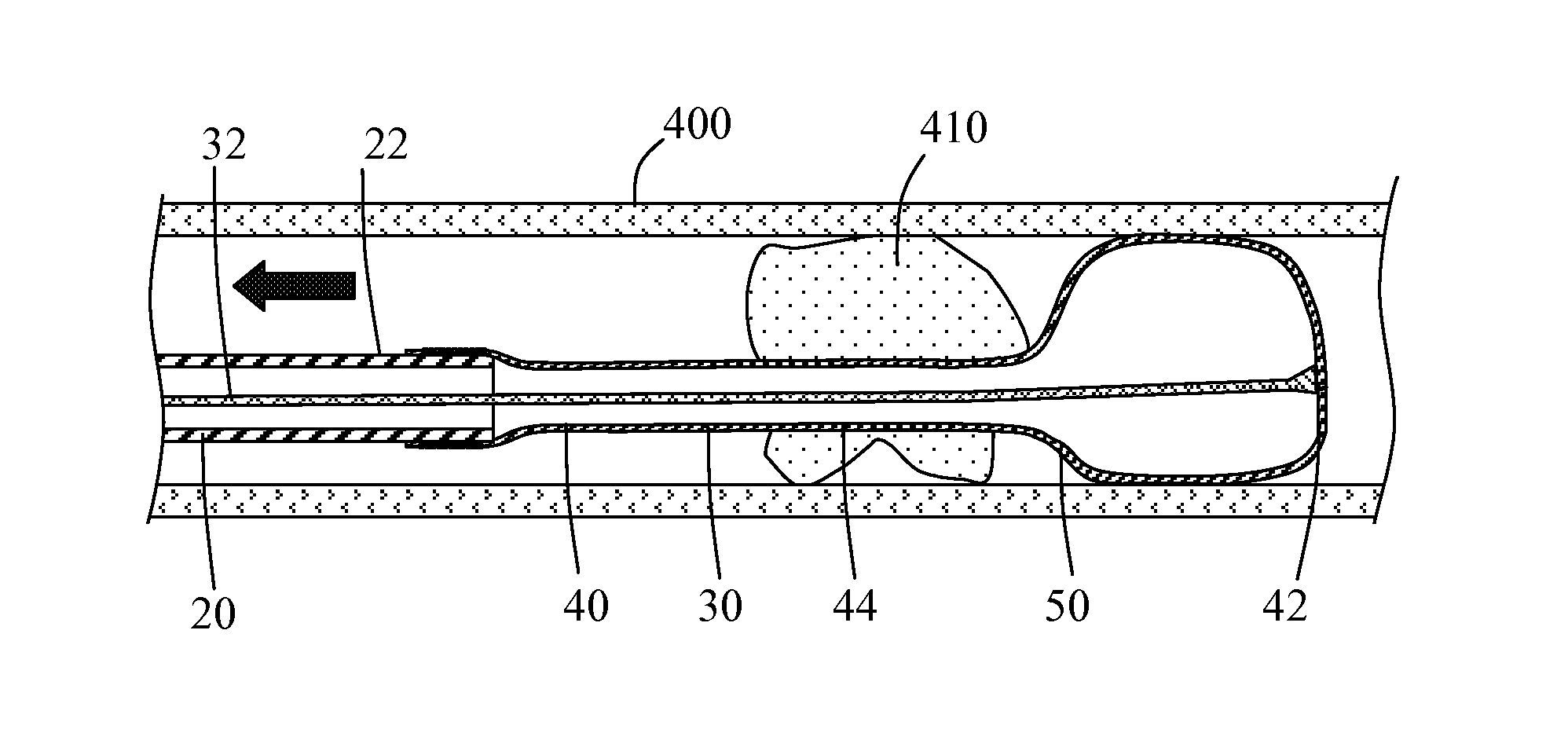
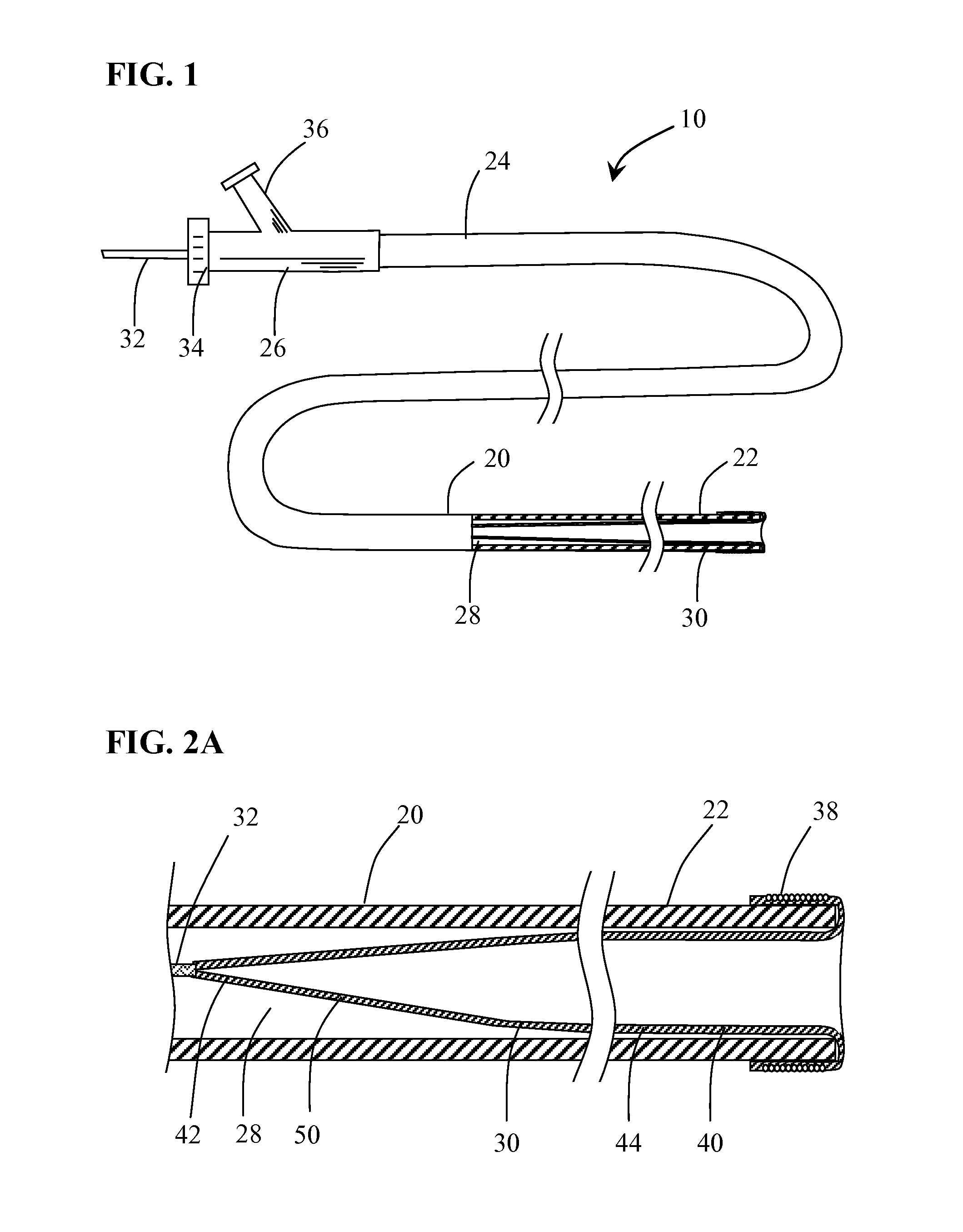
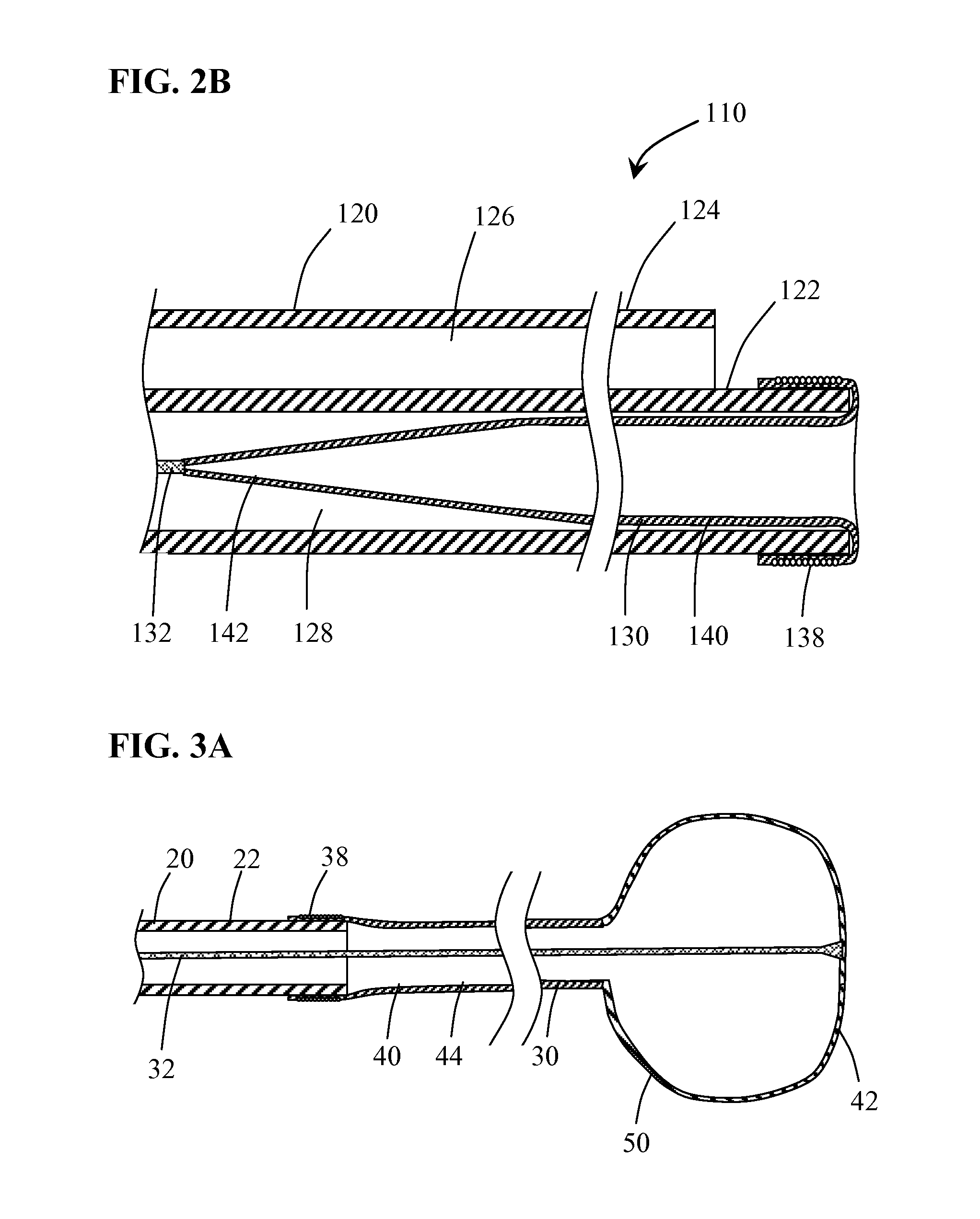
[0022]Methods and systems for capturing and removing an embolus or thrombus from an area of the body are herein described. While the terms “thrombectomy” and “thrombus” generally refer to removal of a specific type of embolus, the usage herein should be considered more broadly to include the removal additional types of emboli such as plaque, solid tissue fragments, clots and foreign objects that may block or restrict the normal flow of blood within the vasculature. FIG. 1 illustrates a thrombectomy system 10 according to an embodiment of the present invention. Thrombectomy system 10 includes an elongate catheter 20 having distal end 22, proximal end 24 including hub member 26 and lumen 28 extending therethrough. Coupled to distal end 22 of catheter 20 is balloon member 30. An elongate flexible tether member 32 coupled to balloon member 30 is slidably positioned within lumen 28 and extends through hub member 26. Balloon member 30 has a delivery configuration in which it is everted an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com