Bi-component fiber for the production of spunbonded fabric
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
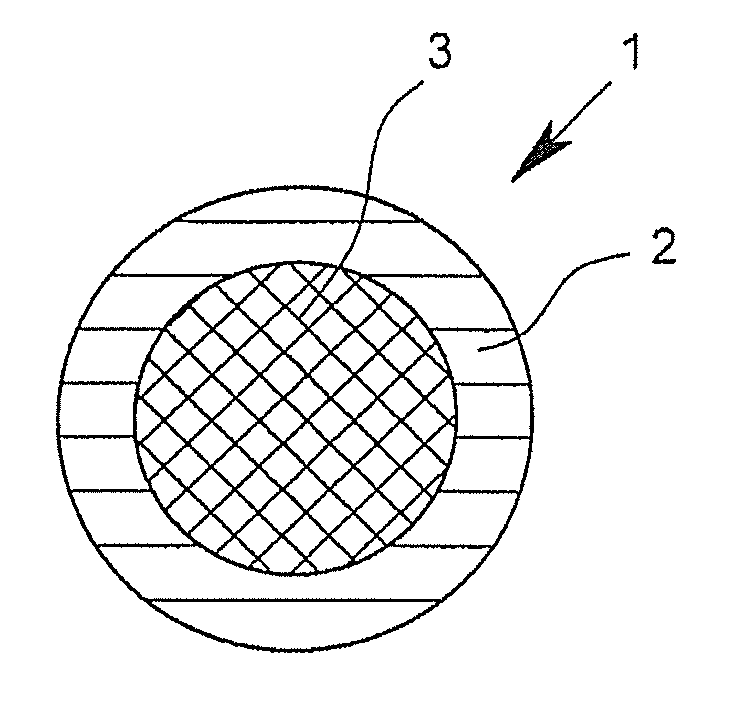
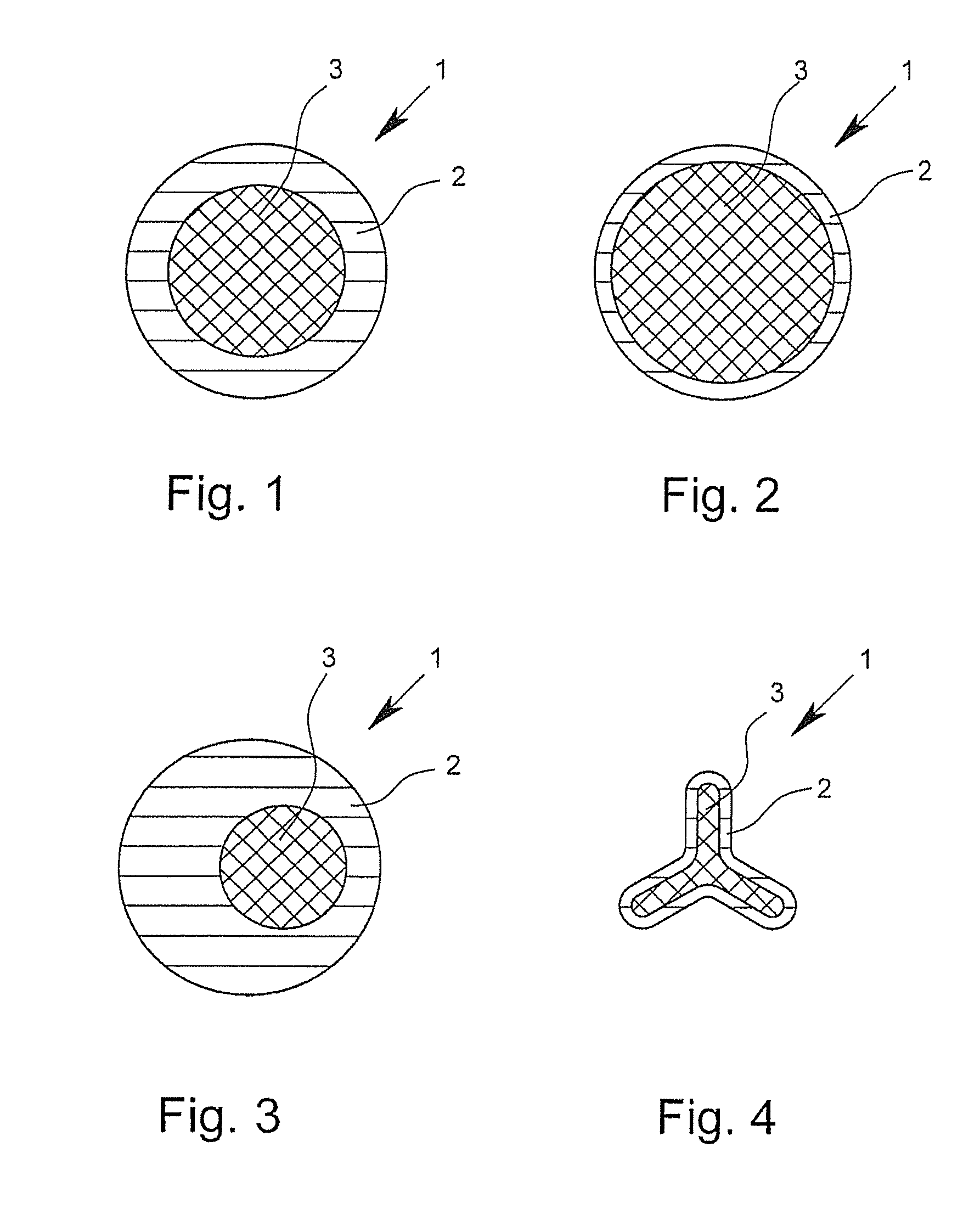
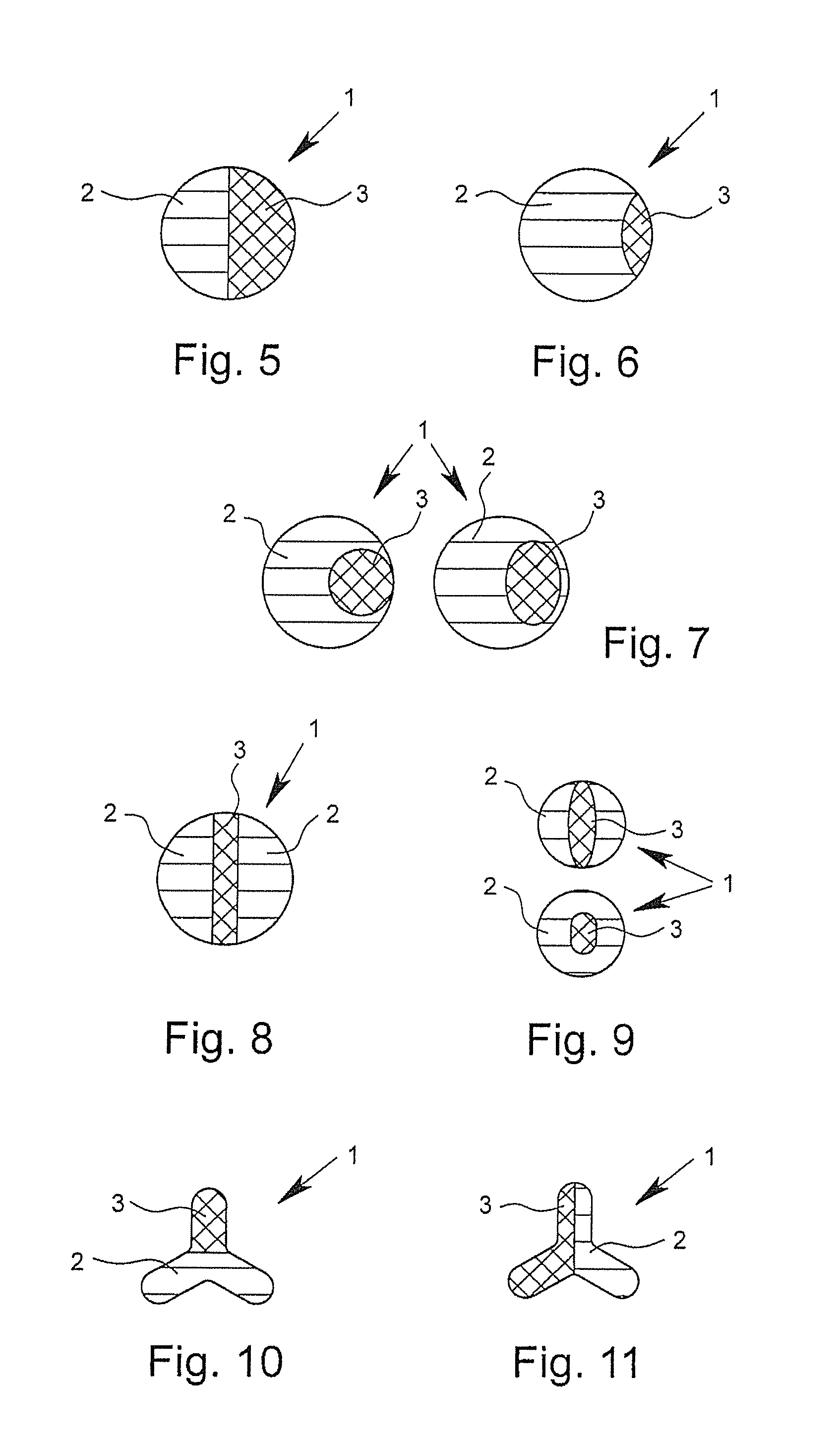
[0096]FIGS. 1 to 16 show cross-sectional views of bi-component fibers 1 according to the invention by way of example. The depicted bi-component fibers 1, in each case, have a first component 2 and a second component 3. In the core-sheath fibers depicted in FIGS. 1 and 4, in this case, the first component 2 surrounds the second component 3 and thus forms the outer surface of the fiber. In this case, the bi-component fibers 1 depicted in FIGS. 1 to 3 have an at least approximately circular or round geometry in cross-section. The bi-component fiber depicted in FIG. 4 shows, however, a trilobal cross-section. Such trilobal cross-sections, like other multilobal cross-sections as well, have the effect that the fiber has a larger outer surface in relation to its mass than is the case with fibers with a circular cross section. In the case of “core-sheath fibers,” in which the proportion of the components forming the sheath is very small, for example approximately 2%, but certainly even in “...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com