Modulation of breast cancer growth by modulation of xbp1 activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
The UPR is Activated in Human Breast Cancer Patients
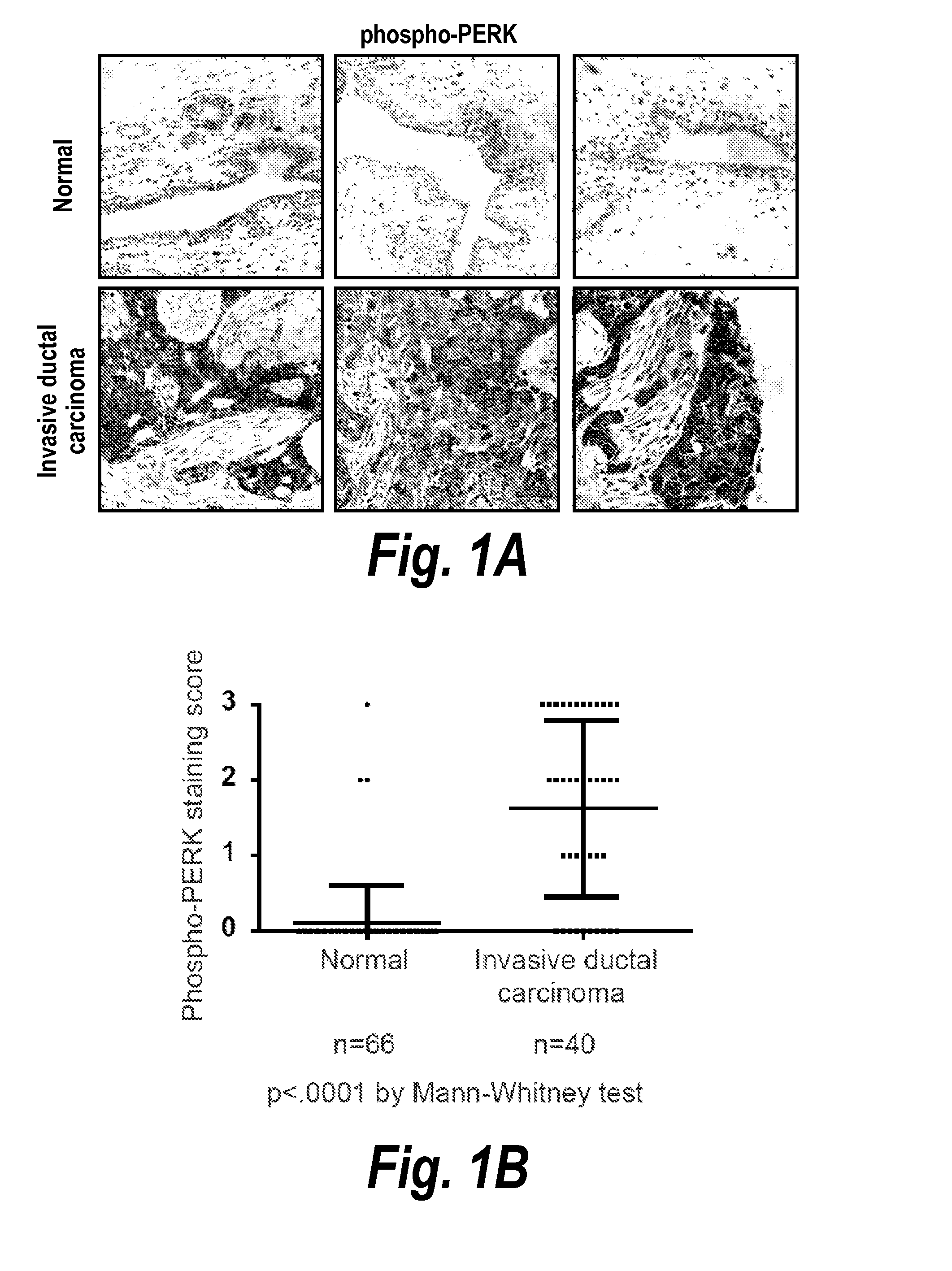
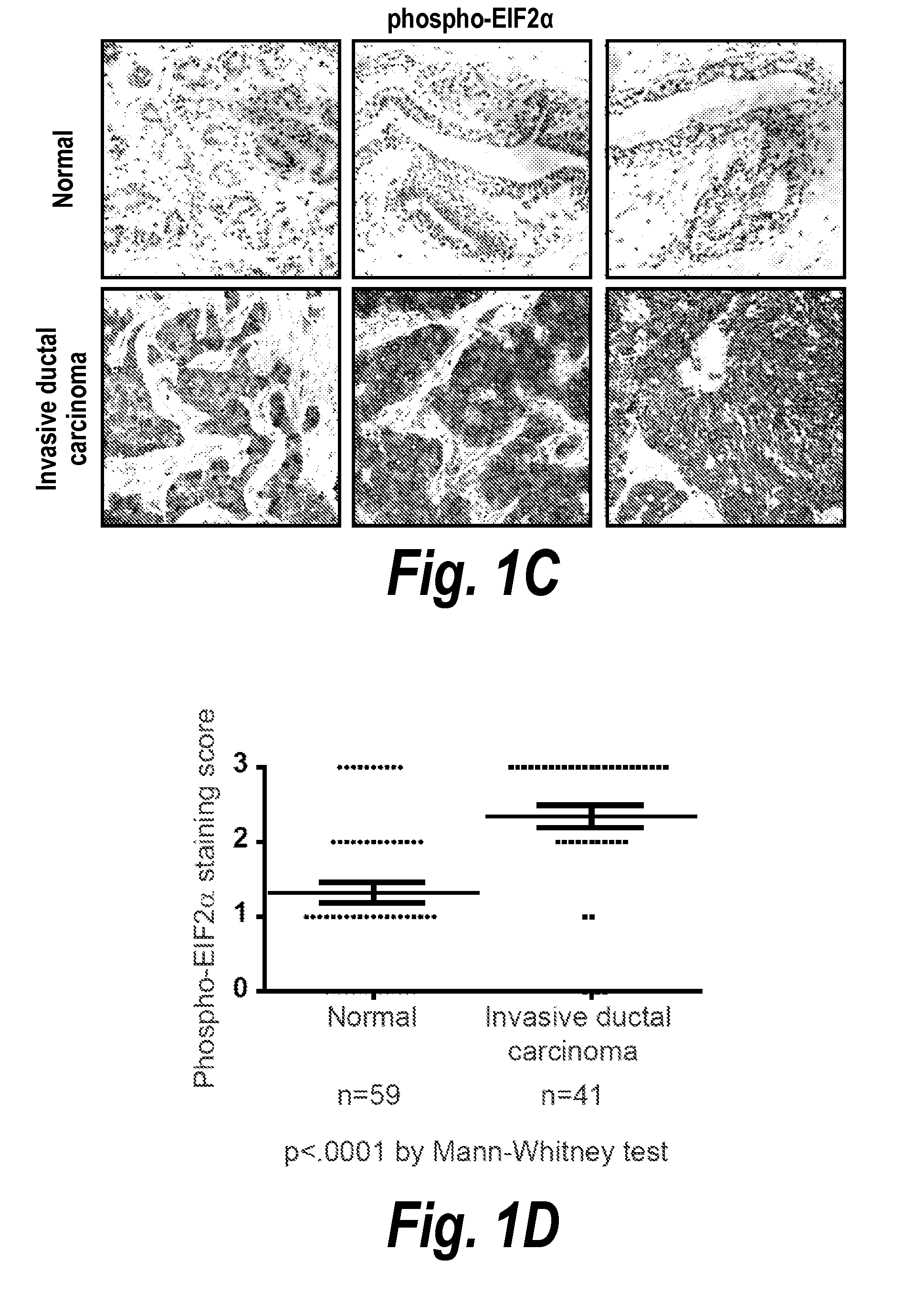
[0158]To determine whether the UPR is activated in breast cancer, we used immunohistochemistry (IHC) to examine the phosphorylation of PERK, a marker of UPR activation, in human primary breast tumor samples. By staining breast cancer tissue microarrays (TMA) containing 66 normal breast tissue samples and 40 tumor tissue samples, we found that PERK was preferentially phosphorylated in breast tumors, but not in normal breast tissue (FIG. 1A, 1B), suggesting that activation of the UPR occurs specifically in tumors. Next, the same TMA were stained with antibodies specifically recognizing phosphorylation of eukaryotic translational initiation factor 2α (eIF2α), another marker of UPR activation. Similarly, eIF2α was phosphorylated in malignant breast tumors but not normal breast tissue (FIG. 1C, 1D). Thus, the UPR is preferentially activated in breast tumors.
example 2
XBP1 is Required for Transformation of Immortalized Mammary Epithelial Cells
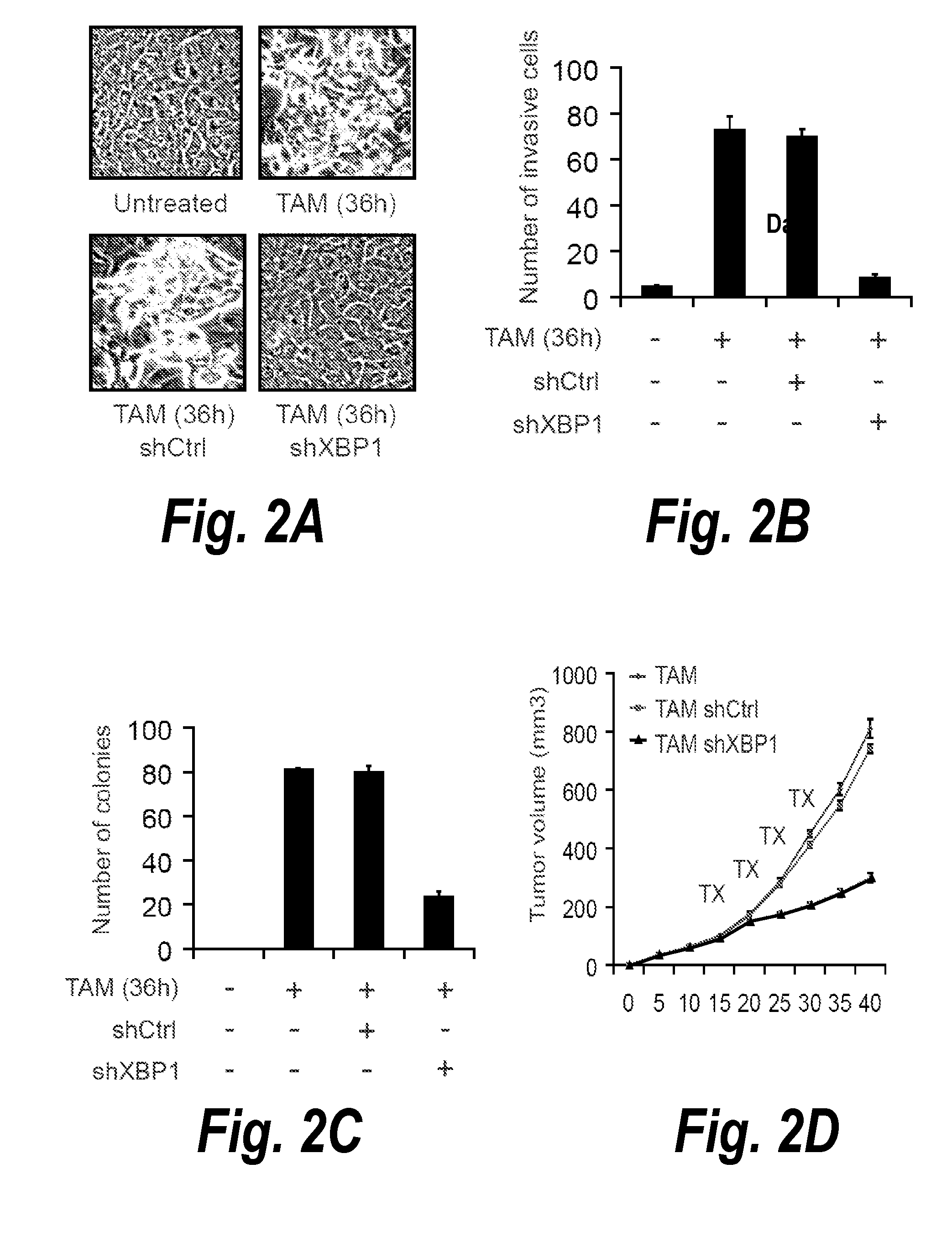
[0159]The IRE1-XBP1 axis of the UPR shows robust conservation from yeast to metazoans, including humans. To investigate the role of XBP1 in cellular transformation, we used MCF10A immortalized mammary epithelial cells that express ER-Src, a fusion of the Src kinase oncoprotein (v-Src) and the ligand binding domain of the estrogen receptor. Treatment of these cells with tamoxifen (TAM) for 36 hr results in neoplastic transformation, including the ability to form colonies in soft agar, increased motility and invasive ability, and tumor formation upon injection into nude mice (Iliopoulos, D., et al. 2009. Cell 139, 693-706). Knockdown of XBP1 expression with a highly effective shRNA (Figure S1) blocked the neoplastic transformation of MCF10A ER-Src cells (FIG. 2A). Furthermore, XBP1 silencing reduced the invasiveness and the ability of MCF10A ER-Src cells to form colonies in soft agar and tumors in immunodefici...
example 3
XBP1 Inhibition Blocks Breast Cancer Cell Growth and Invasiveness Both Ex Vivo and In Vivo; XBP1 Silencing Blocks Triple Negative Breast Cancer Progression
[0160]To further characterize the function of XBP1 in breast cancer, we first determined the activation status of XBP1 in different breast cancer cell lines. Breast cancers can be classified as luminal or basal-like, depending on their expression of different cytokeratins (Perou, C. M., et al. 2000. Nature 406, 747-752; Vargo-Gogola, T., et al. 2007. Cancer 7, 659-672). Unexpectedly, XBP1 was preferentially spliced and activated in basal-like breast cancer cells (FIG. 3A), which harbor a transcriptome similar to that of triple negative breast cancer (TNBC), a subtype of breast cancer that is extremely aggressive and difficult to target due to the lack of expression of the estrogen (ER), progesterone (PR) and human epidermal growth factor 2 (HER2) receptors (Foulkes, W. D., et al. 2010. N Engl J Med 363, 1938-1948). In particular, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Therapeutic | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com