Semiconductor device
a technology of semiconductor devices and solder joints, applied in semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state device details, electrical devices, etc., can solve problems such as cracks at the boundary of sealing resin and solder, and achieve the effect of preventing cracks
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
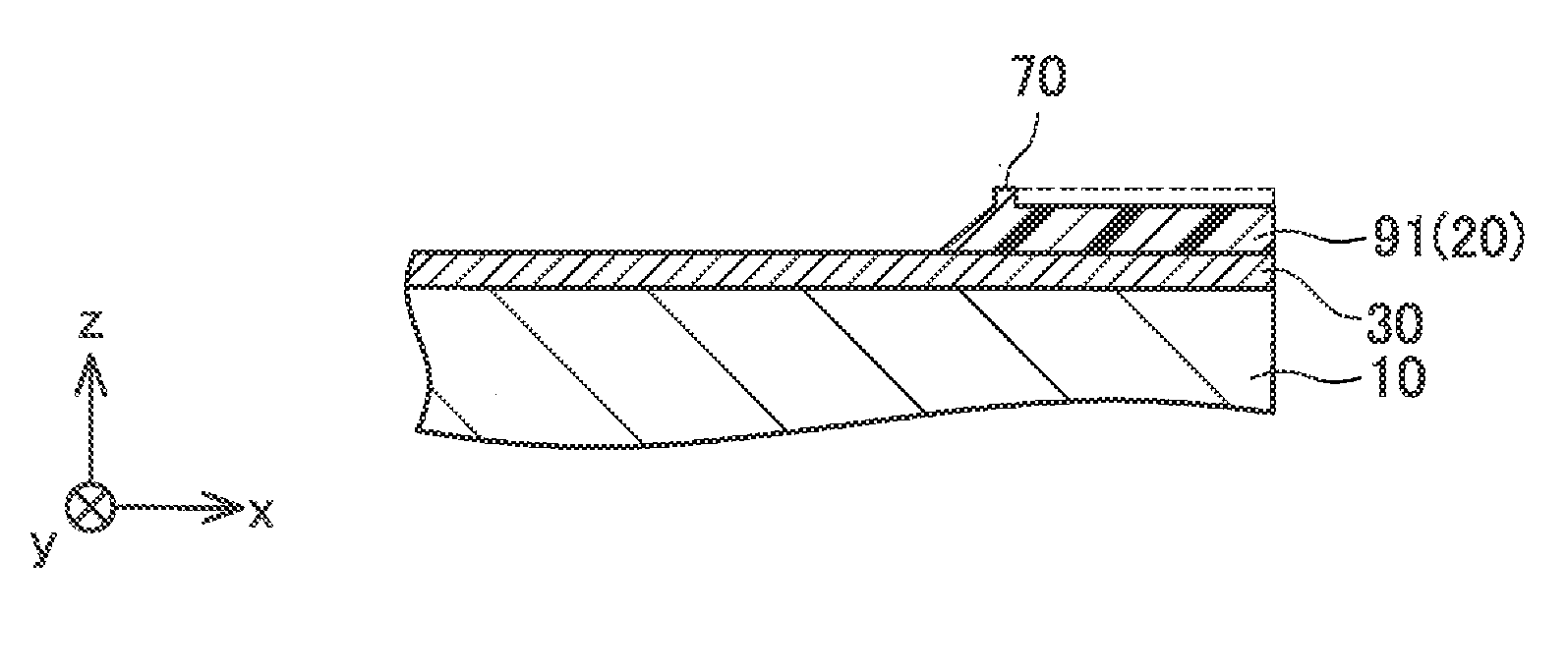
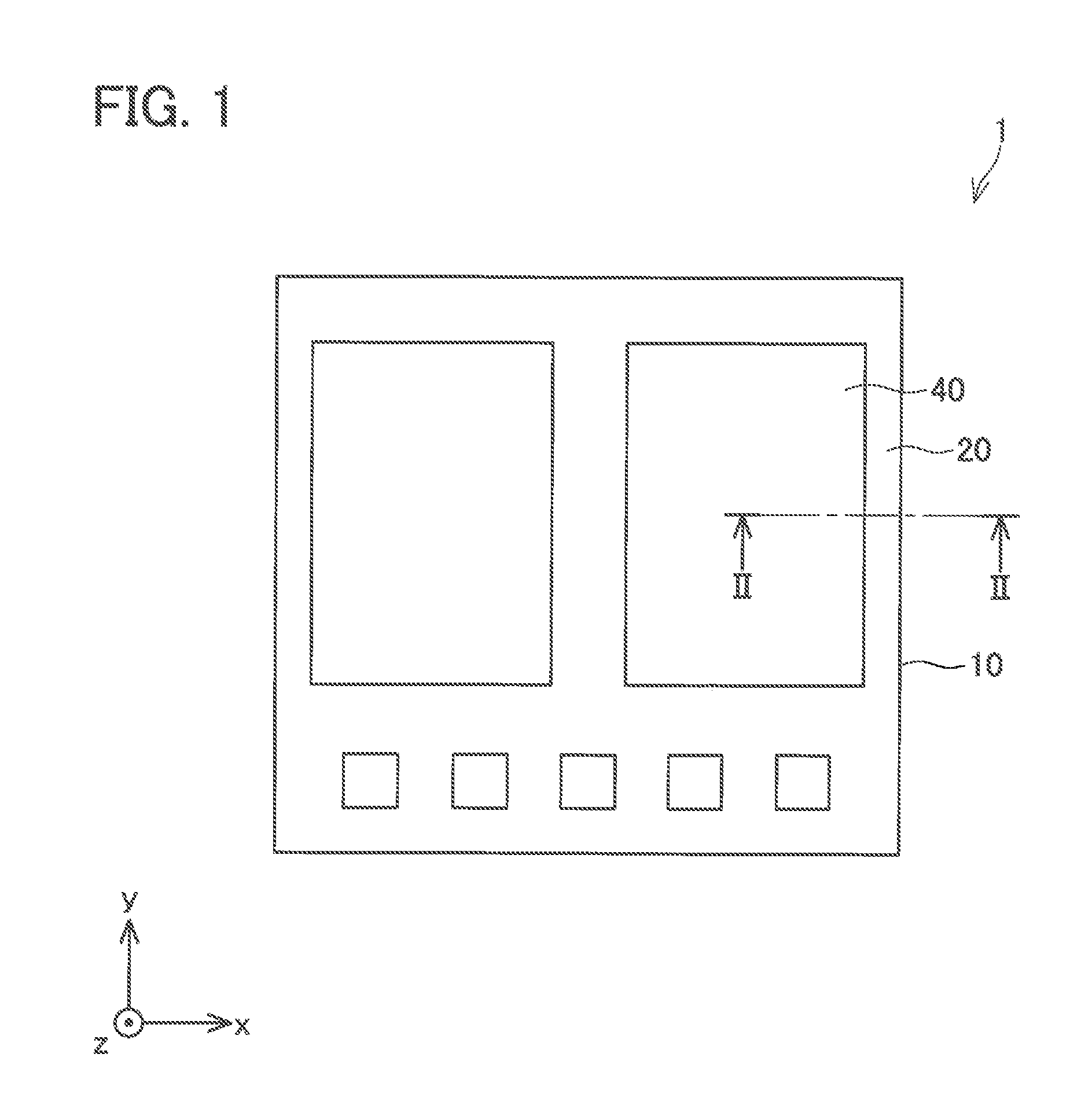
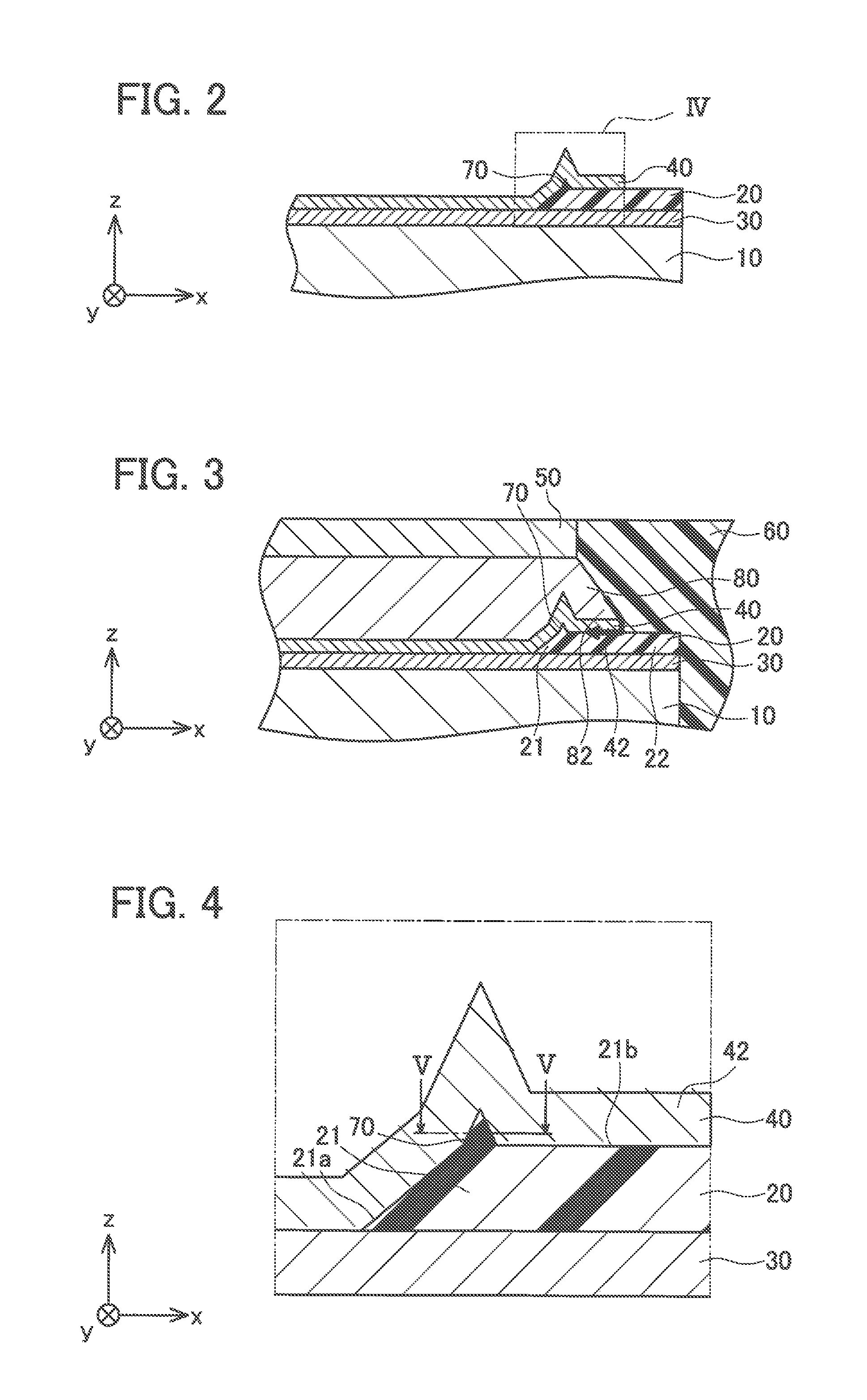
[0021]An embodiment will be described below with reference to the attached drawings. As illustrated in FIG. 1 and FIG. 2, a semiconductor device 1 includes a semiconductor substrate 10, an electrode 30 formed on a surface of the semiconductor substrate 10, an insulation film 20 formed on a surface of the electrode 30, and a metal film 40 formed on t he surface of the electrode 30 and a surface of the insulation film 20. As illustrated in FIG. 3, the semiconductor device 1 further includes a lead frame 50 joined to the metal film 40 by solder 80 and sealing resin 60 sealing an entire structure. In FIG. 1 and FIG. 2, the solder 80, the lead frame 50, and the sealing resin 60 are omitted.
[0022]The semiconductor substrate 10 is made of silicon (Si). As other examples, the semiconductor substrate 10 may be made of silicon carbide (SiC), gallium nitride (GaN), and the like. A semiconductor element (not shown) is formed within the semiconductor substrate 10. An insulated gate bipolar trans...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| stress | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thermal expansion coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com