Fault detection in rotor driven equipment using rotational invariant transform of sub-sampled 3-axis vibrational data
a technology of vibrational data and rotor drive, which is applied in the direction of machine parts testing, structural/machine measurement, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as controlling sampling errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
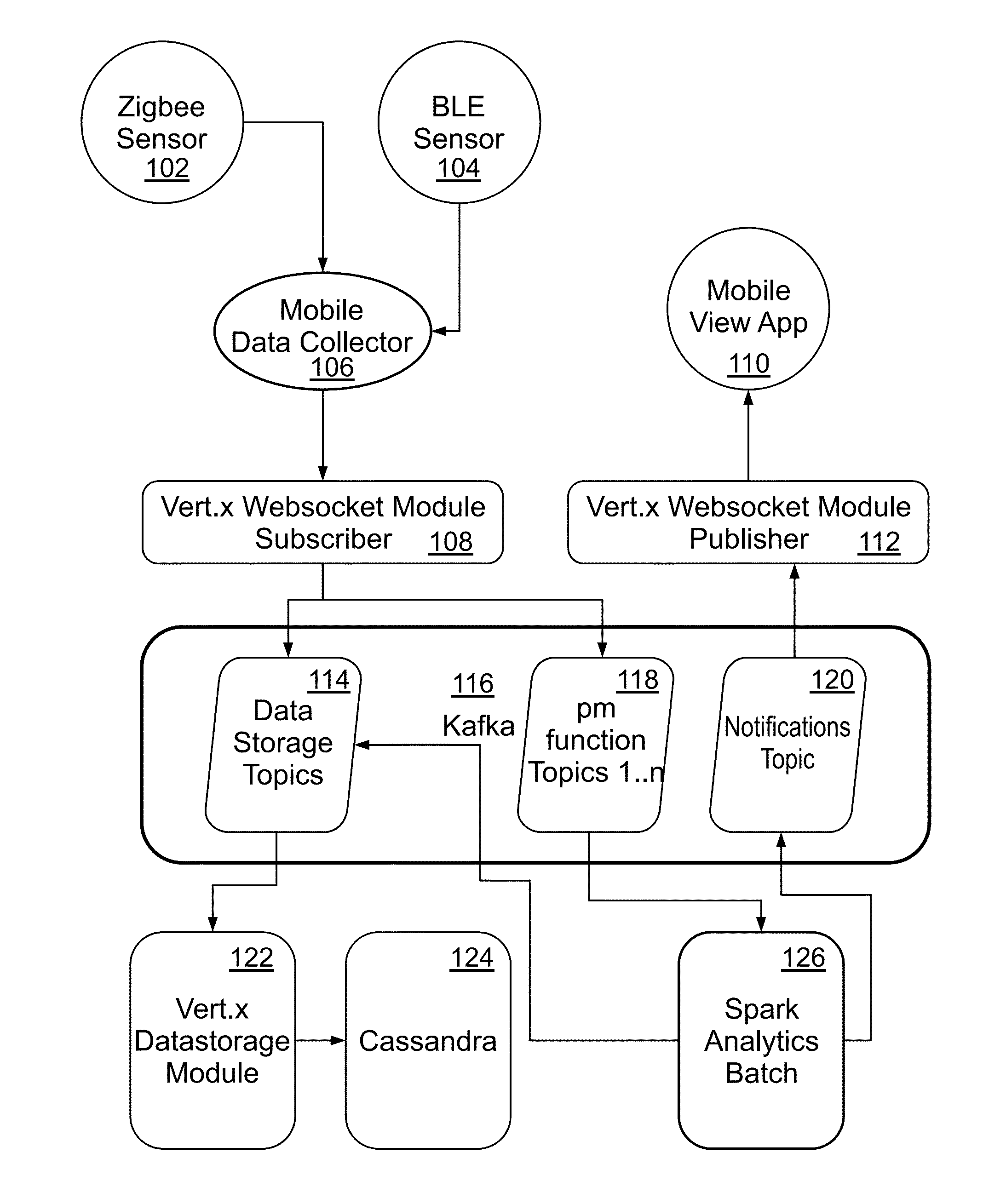
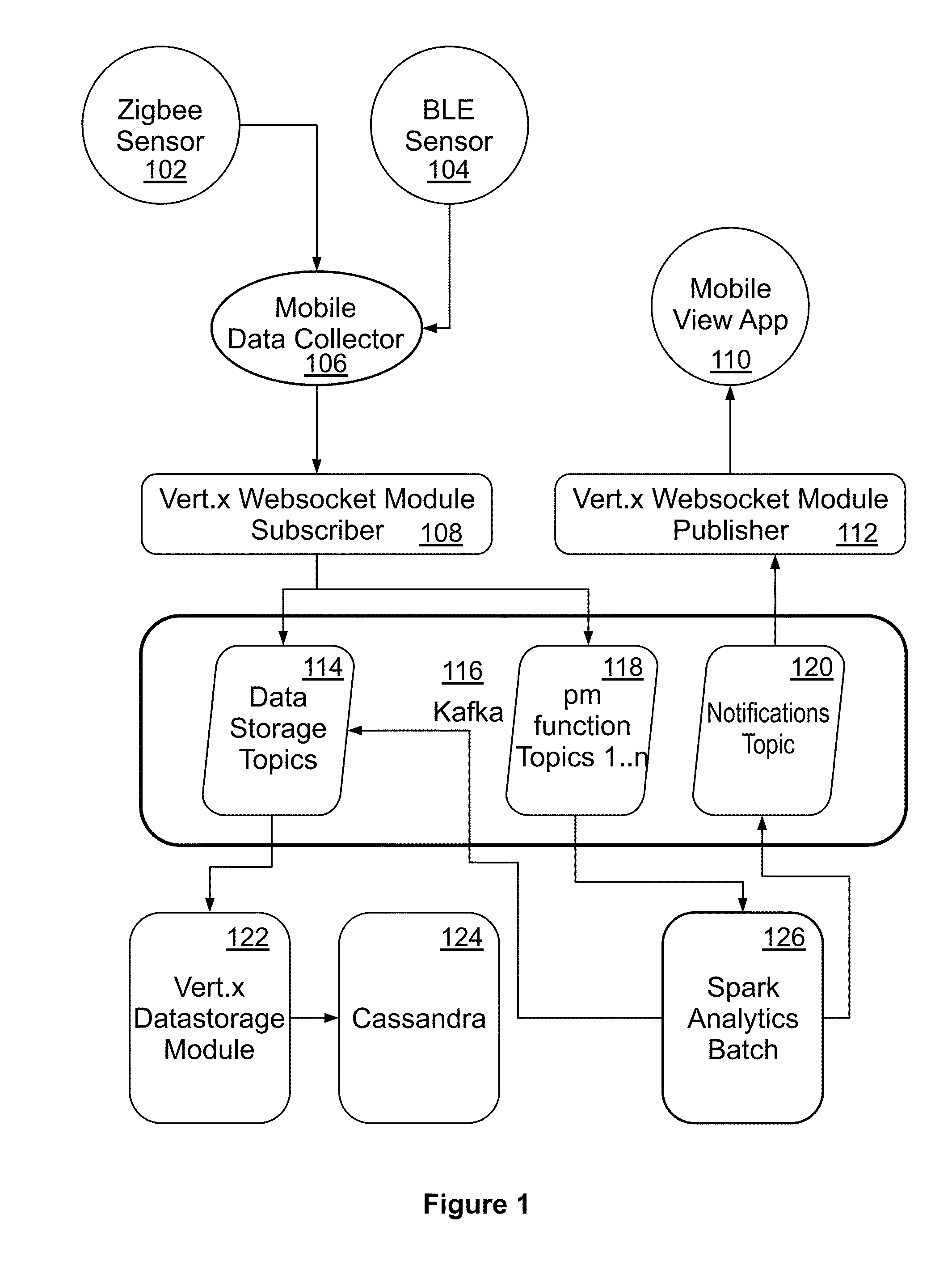
[0030]Example embodiments as described below may be used to provide a method, an apparatus and / or a system for fault detection in rotor driven equipment through big data analytics. Although the present embodiments have been described with reference to specific example embodiments, it will be evident that various modifications and changes may be made to these embodiments without departing from the broader spirit and scope of the various embodiments.
[0031]In one or more embodiments, vibrations of a fault free rotor in time domain may be represented by
x_j(t)=Σi=1∞αi*sin(i*Ω*t)|j=1,2,2
Ω is fundamental frequency and i, j, and k are three Cartesian vectors. In vibration analysis of a rotor, revolution per second of rotor may be multiplied by 2π.
[0032]Fundamental harmonics and other harmonics generated by a rotor may depend on the rotor's speed. Rotation speed of the rotor may commonly vary between 200-3000 RPM (Revolutions Per Minute). With such rotation speeds, the fundamental harmonics ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com