3-d femur orthopedic drill guide
a drill guide and femur technology, applied in bone drill guides, medical science, surgery, etc., can solve the problems of femoral condyle cartilage damage, lateral/collateral ligament damage, and the correct three-dimensional (3-d) directional direction of the planar guide, so as to improve the function of the drill guid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
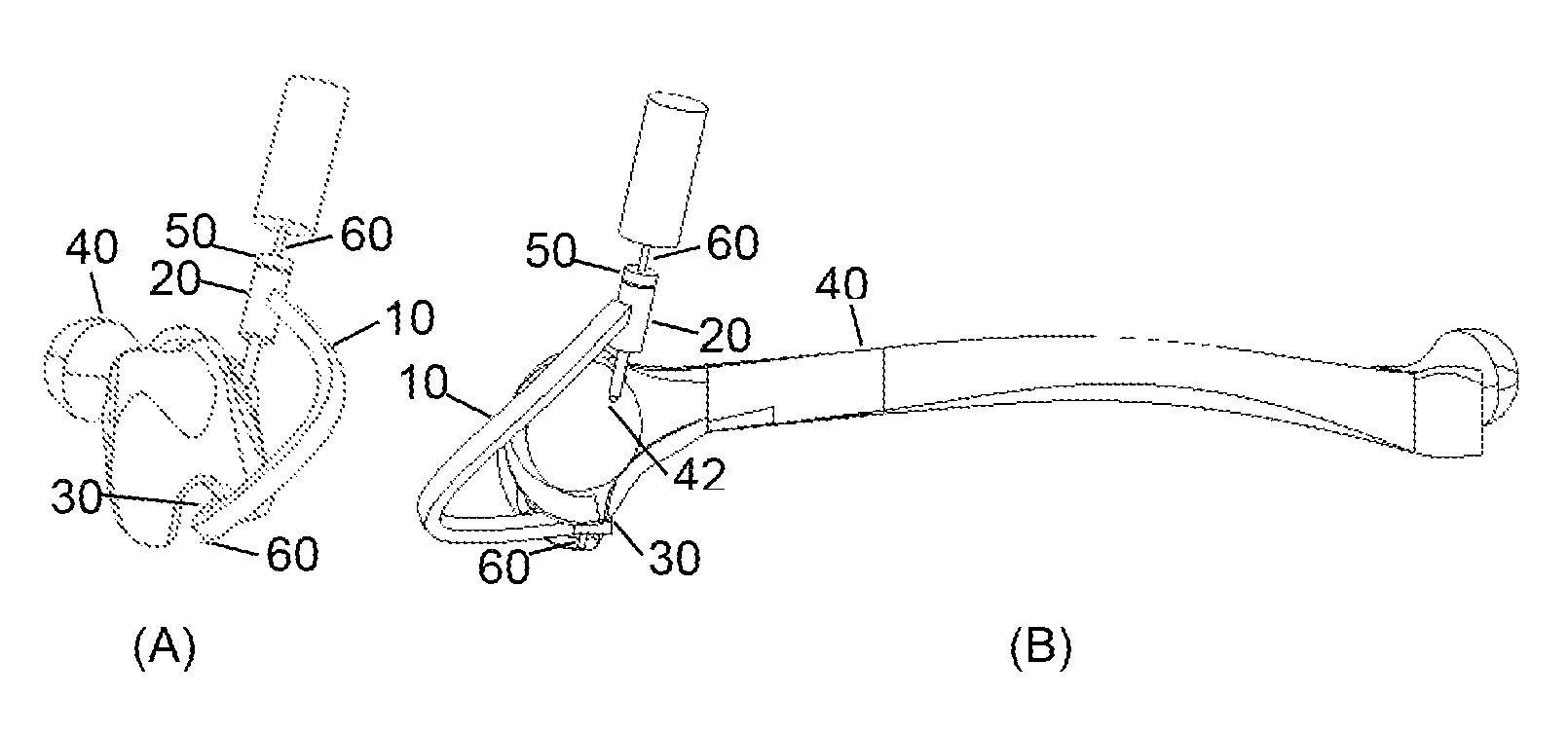
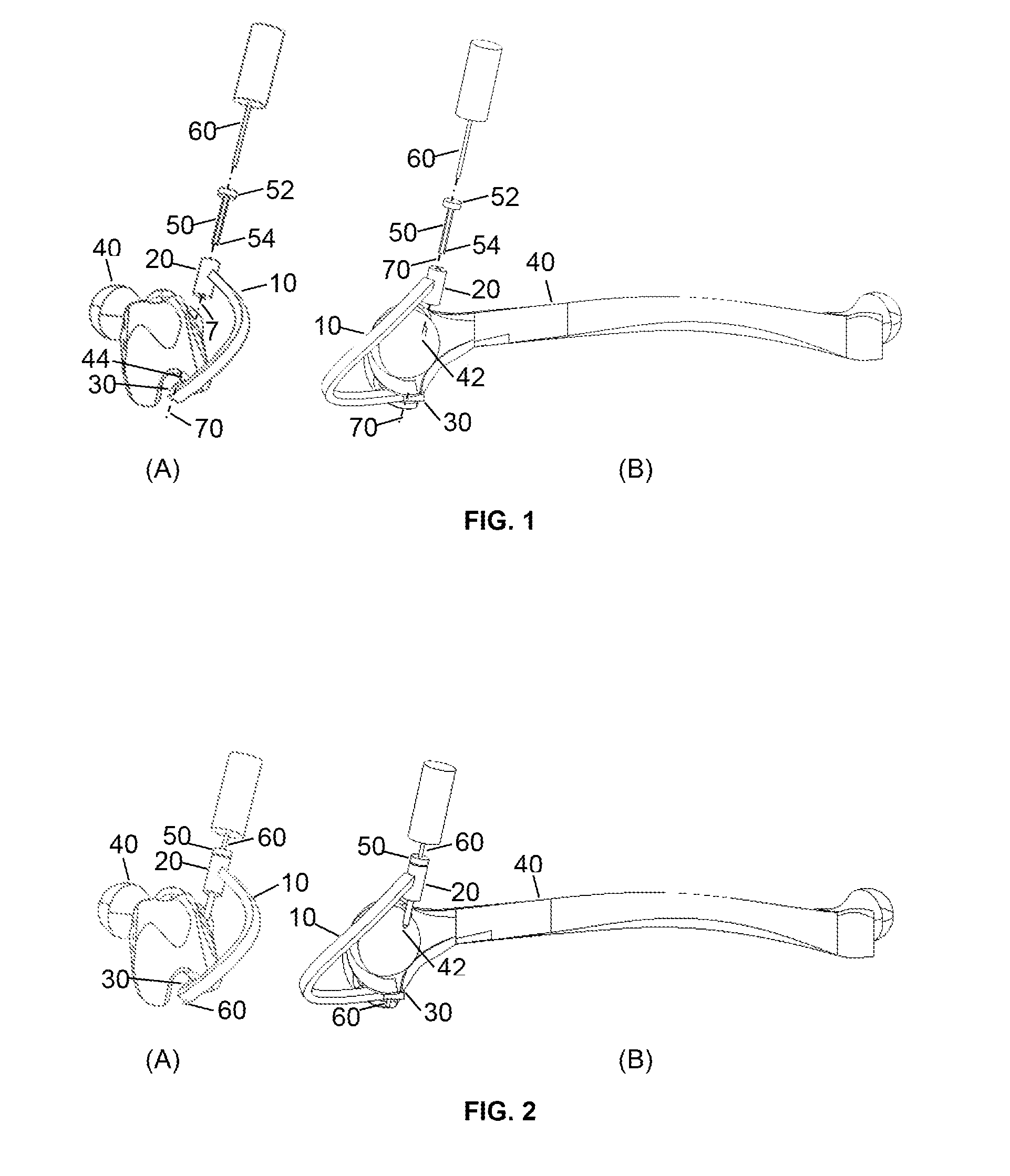
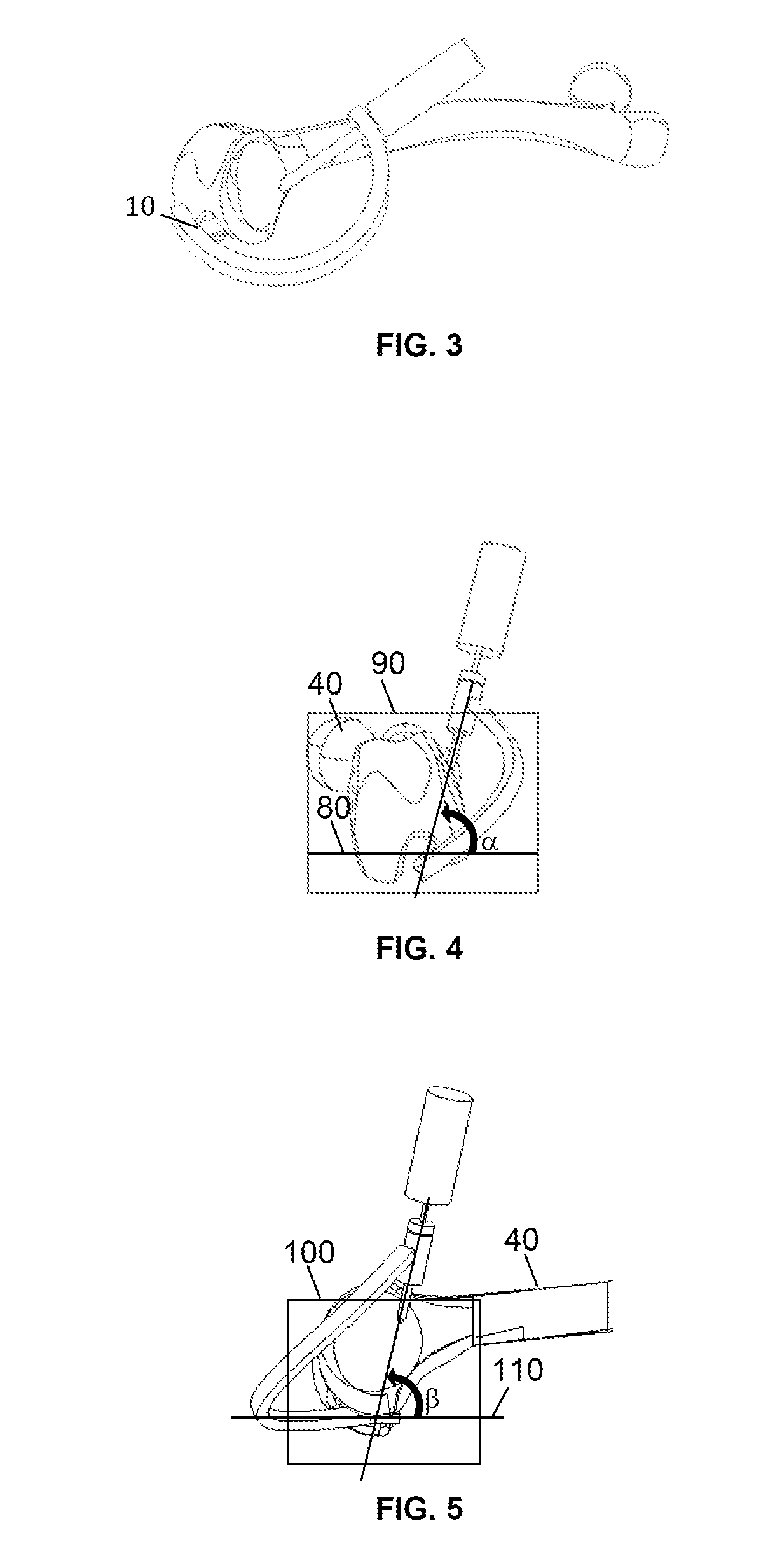
[0018]To drill a femoral through hole, a three dimensional orthopedic drill guide device is used. The three dimensional orthopedic drill guide device (FIG. 1 and FIG. 2) is comprised of an arm (10), a hollow sleeve (20), a removable hollow bullet-shaped pilot (50), and a support base (30). The arm (10) has two ends where the first end is attached to the hollow sleeve (20). The second end of the arm (10) is attached to the support base (30). The arm (10) function is to connect the hollow sleeve (20) and support base (30). The arm (10) shape avoids the contact with the patella and the thigh when the orthopedic drill guide device is installed in the femur (40). The offset distance of the arm (10) is between 20 mm or larger moving away from the knee in the inferior direction to avoid contact with the patella, and a distance between 20 mm or larger in the lateral direction to avoid contact with the thigh. The arm (30) also serves as a means for the surgeon to grasp, position, and maneuve...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com