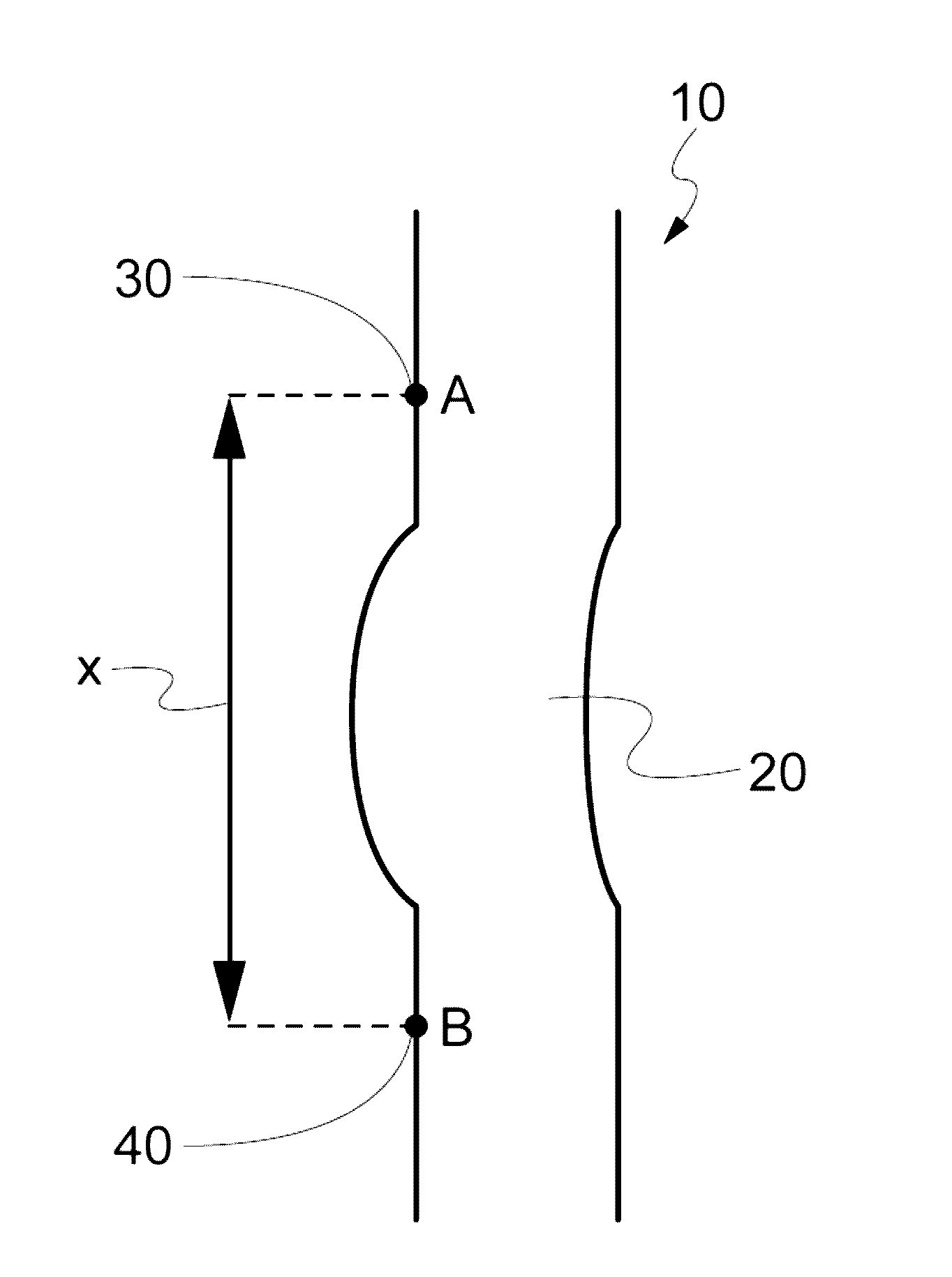
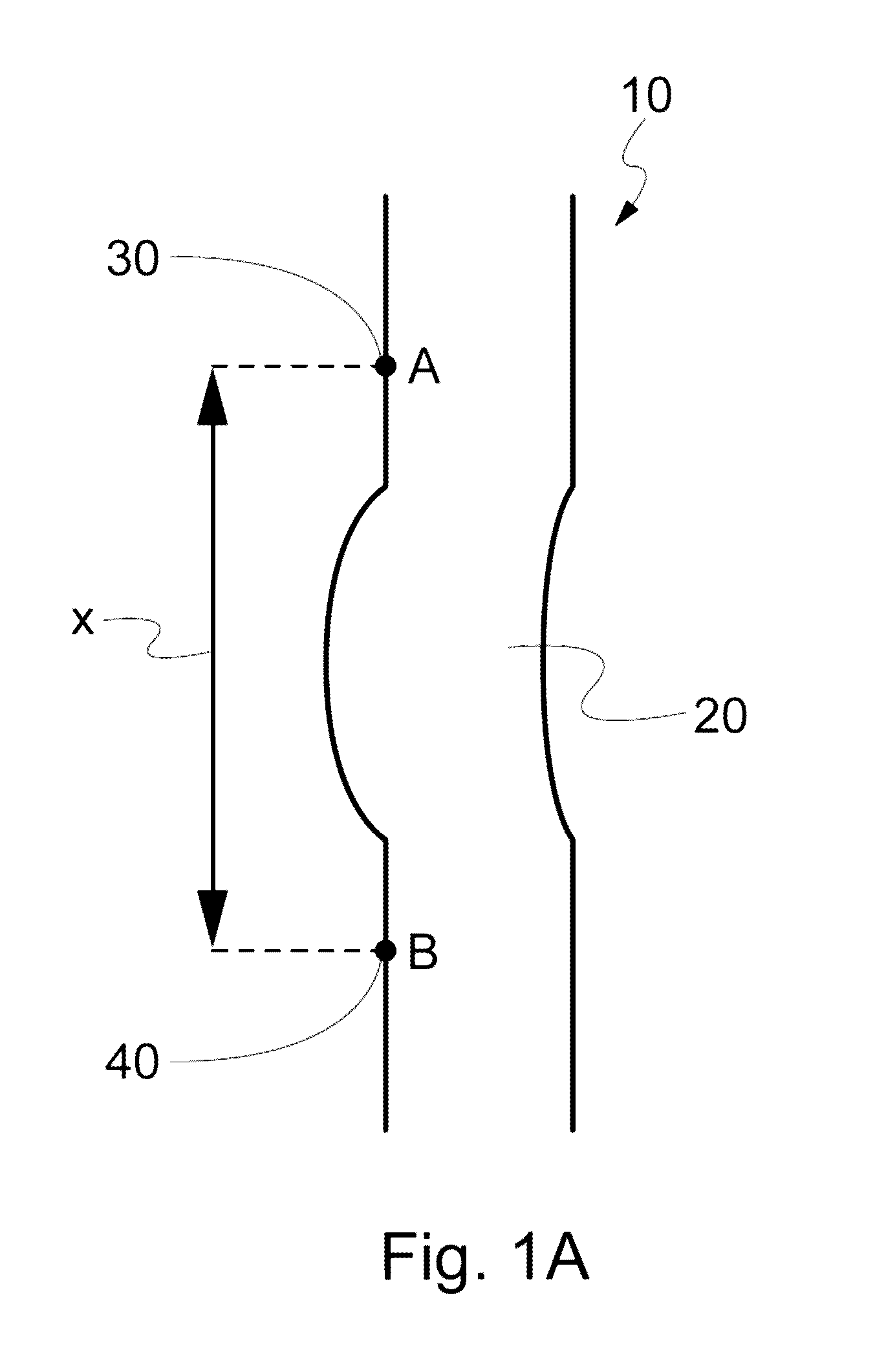
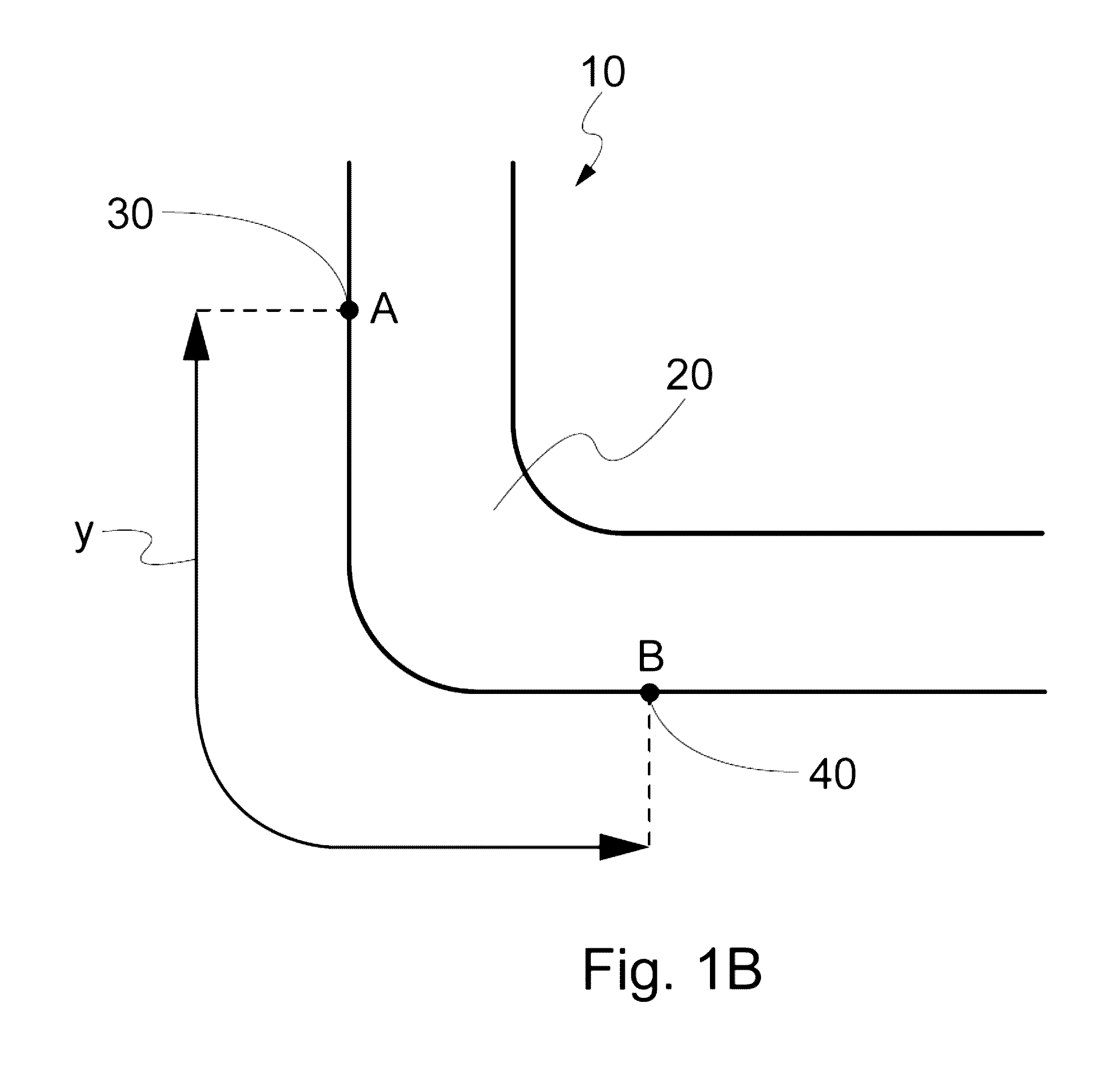
Elastic fabric and process of preparation
a technology of elastic fabric and process, applied in the field of stretchable fabrics, can solve the problems of insufficient comfort level, fabric drawbacks, and inability to stretch stretchable fabrics along the warp direction, and achieve the effects of avoiding tightness and discomfort, reducing the amount of stretch, and improving the holding power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0052]Reference now should be made to the drawings, in which the same reference numbers are used throughout the different figures to designate the same components.
[0053]It will be understood that, although the terms first, second, third, etc. may be used herein to describe various elements, these elements should not be limited by these terms.
[0054]These terms are only used to distinguish one element from another element. Thus, a first element discussed below could be termed a second element without departing from the teachings of the present disclosure.
[0055]The terminology used herein is for the purpose of describing particular embodiments only and is not intended to be limiting. As used herein, the singular forms “a”, “an”, and “the” are intended to include the plural forms as well, unless the context clearly indicates otherwise. It will be further understood that the terms “comprises” and / or “comprising” or “includes” and / or “including” when used in this specification, specify th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| elongation | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com