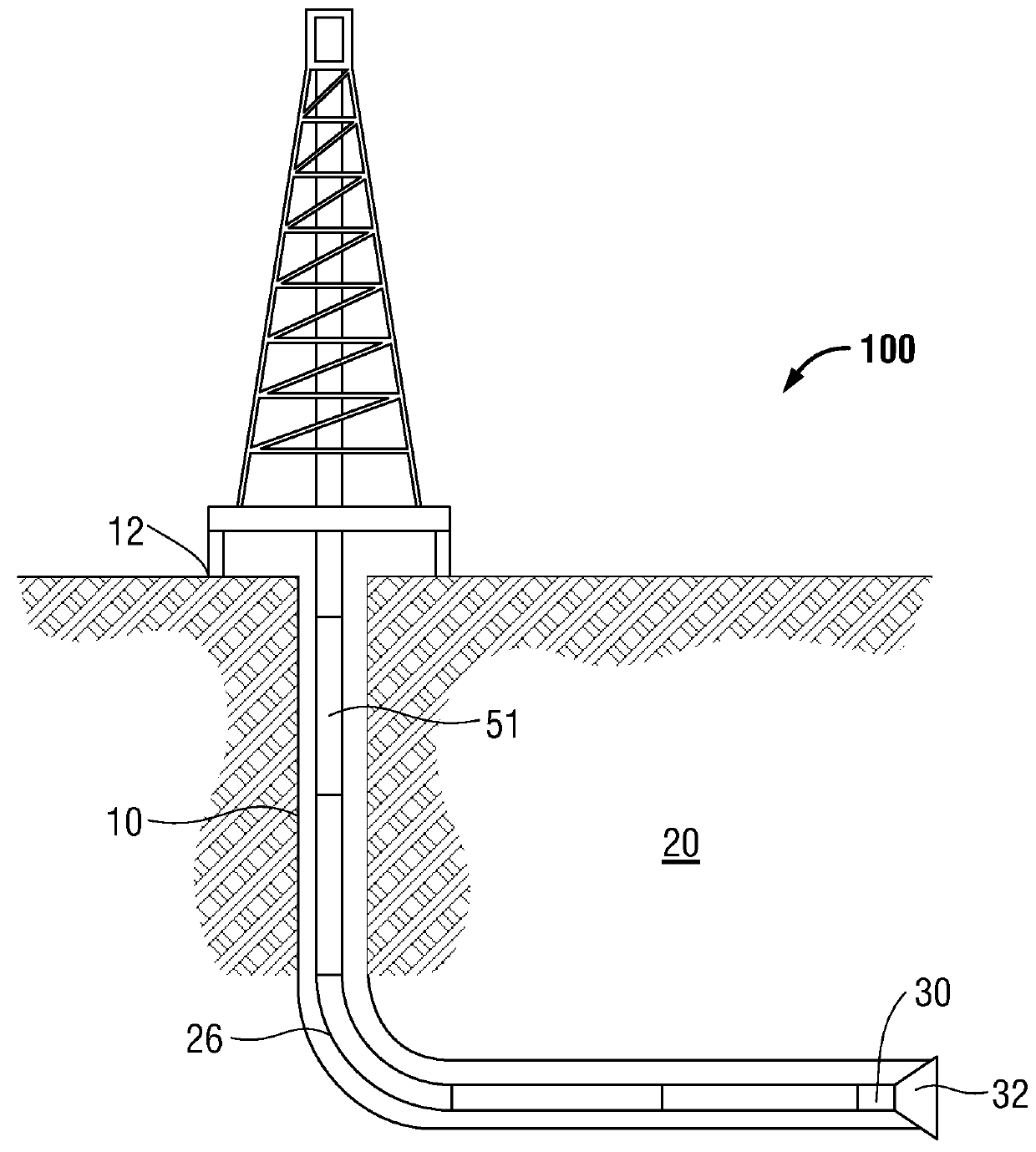
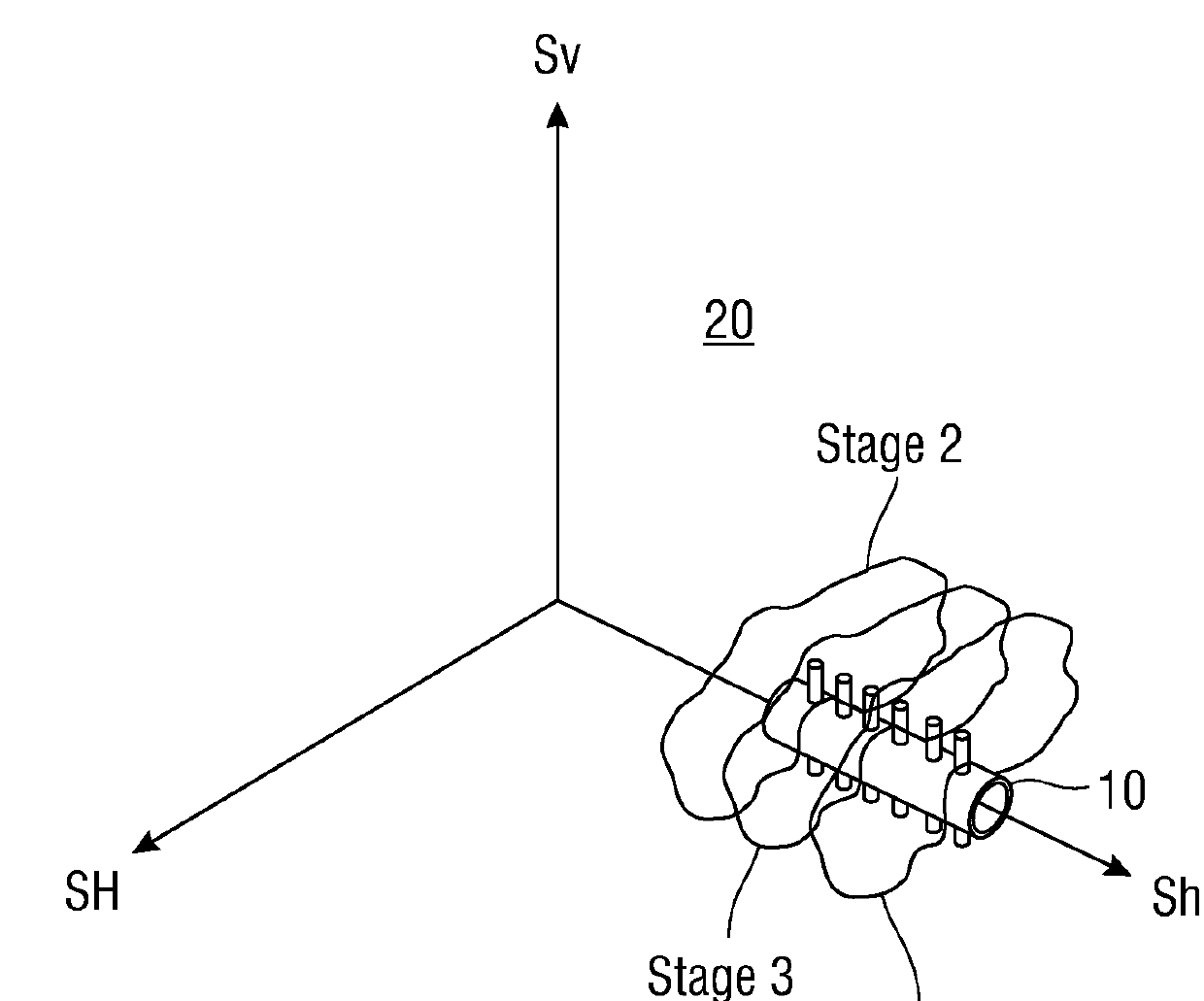
Shale geomechanics for multi-stage hydraulic fracturing optimization in resource shale and tight plays
a technology of hydraulic fracturing optimization and resource shale, applied in the direction of fluid removal, instruments, borehole/well accessories, etc., can solve the problems of tight plays, inability to meet the needs of large-scale production,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0011]As an initial matter, it will be appreciated that the development of an actual, real commercial application incorporating aspects of the disclosed embodiments will require many implementation-specific decisions to achieve the developer's ultimate goal for the commercial embodiment. Such implementation-specific decisions may include, and likely are not limited to, compliance with system-related, business-related, government-related and other constraints, which may vary by specific implementation, location and from time to time. While a developer's efforts might be complex and time-consuming in an absolute sense, such efforts would nevertheless be a routine undertaking for those of skill in this art having the benefits of this disclosure. It also should be understood that the embodiments disclosed and taught herein are susceptible to numerous and various modifications and alternative forms. Thus, the use of a singular term, such as, but not limited to, “a” and the like, is not i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com