Method of fast imaging of nmr parameters with variably-accelerated sensitivity encoding
a sensitivity encoding and fast imaging technology, applied in the direction of nmr measurement, instruments, magnetic measurement, etc., can solve the problems of spatial image ‘unfolding’ artifacts that limit the acceleration factor that can be practically used, and the overall acquisition time is too long
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027]Some embodiments of the current invention are discussed in detail below. In describing embodiments, specific terminology is employed for the sake of clarity. However, the invention is not intended to be limited to the specific terminology so selected. A person skilled in the relevant art will recognize that other equivalent components can be employed and other methods developed without departing from the broad concepts of the current invention. All references cited anywhere in this specification, including the Background and Detailed Description sections, are incorporated by reference as if each had been individually incorporated.
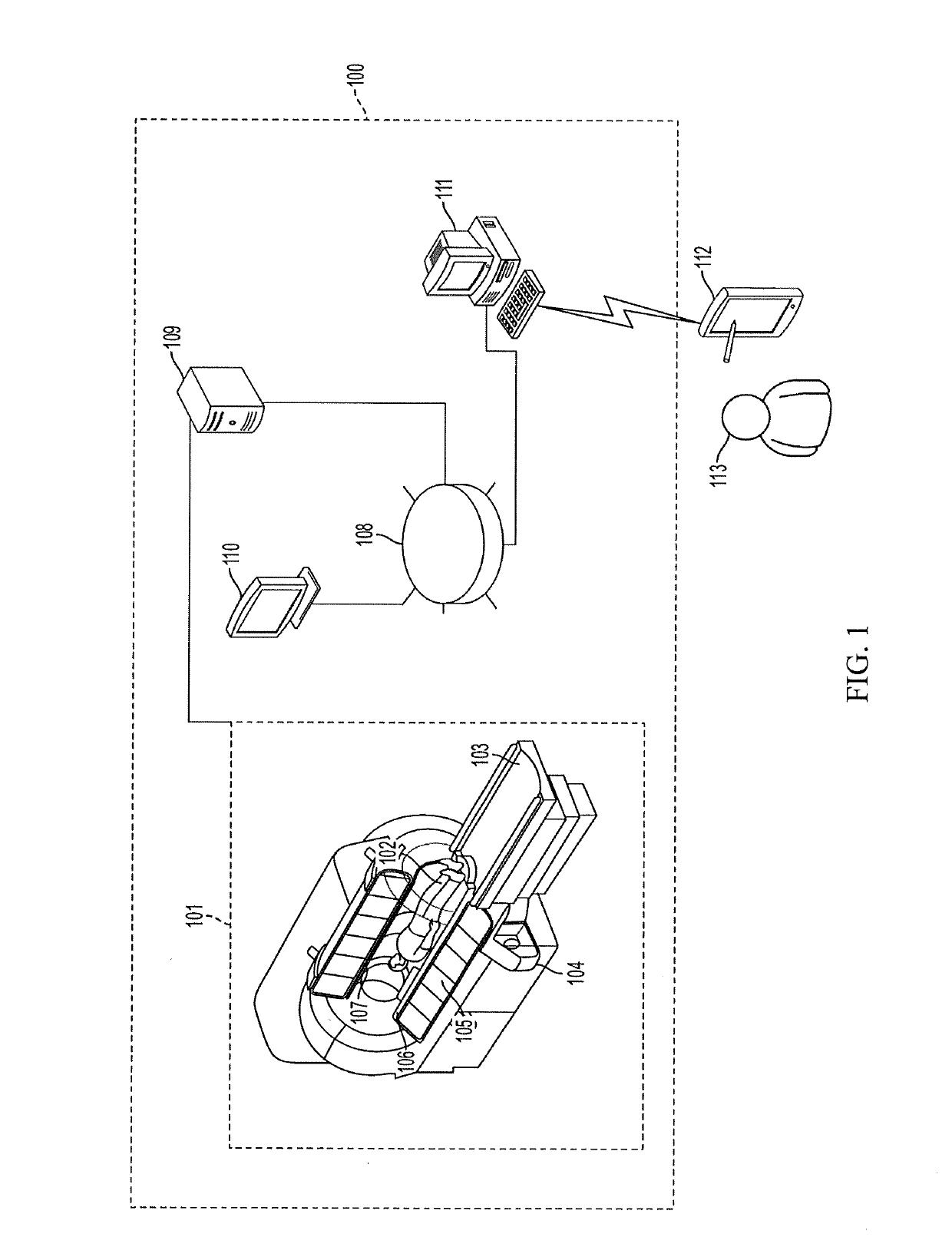
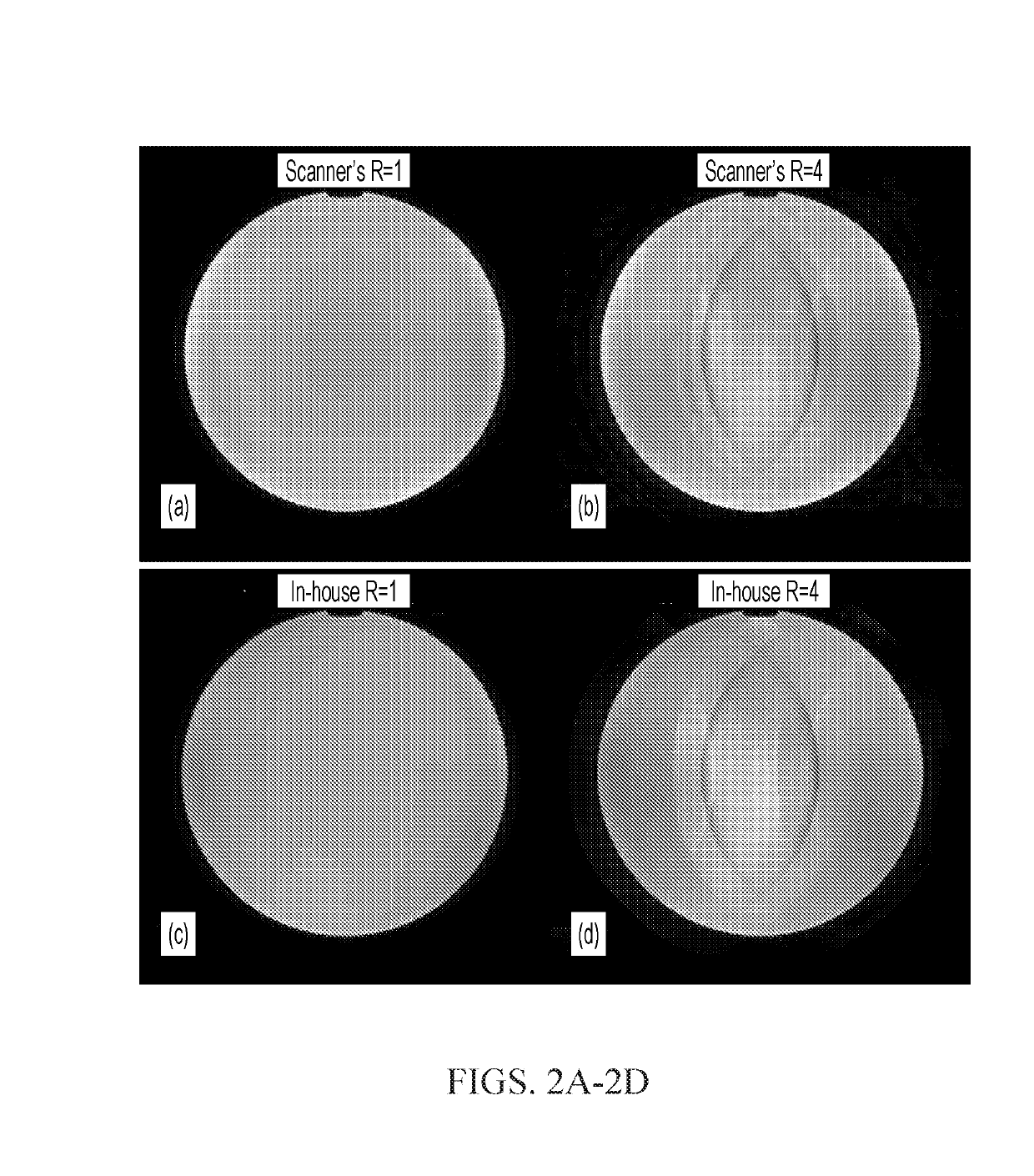
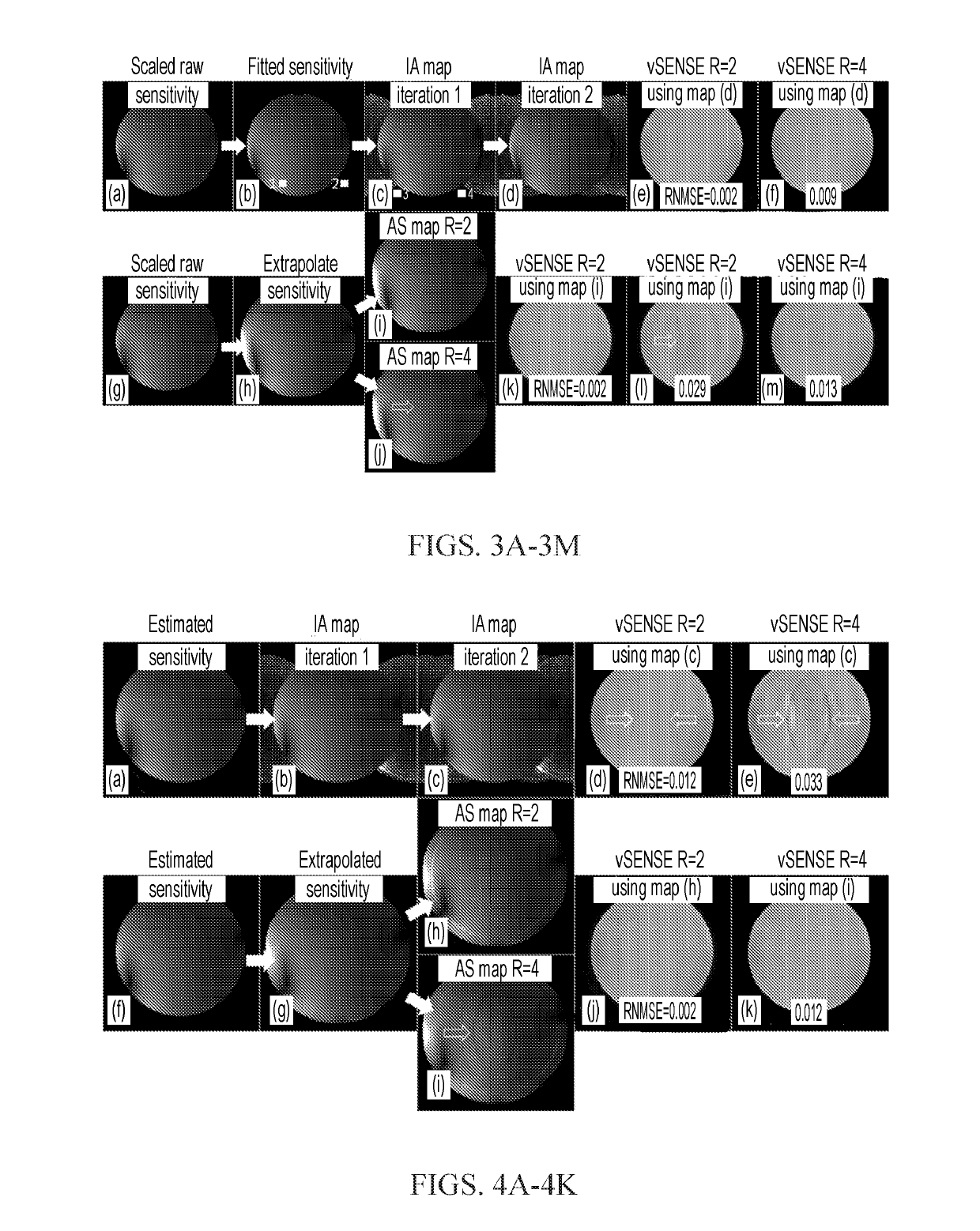
[0028]According to some embodiments of the invention, our new method, termed ‘variably-accelerated sensitivity encoding’ or ‘vSENSE,’ can be used to measure any or all of the above mentioned parameters in an image pixel-by-pixel or voxel-by-voxel manner as in a conventional MRI experiment, including but not limited to the following: nuclear spin densi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com