Method for operating a rotational-speed-variable refrigerant compressor
a technology of rotational speed and variable temperature, which is applied in the field of method for operating a refrigerant compressor, can solve the problems of increasing the energy consumption the evaporator unavoidably heating the refrigerant, and the inability of the electronic control device of the refrigerant compressor to react to any special operating state, etc., to achieve the effect of preventing overheating and being easy to adap
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
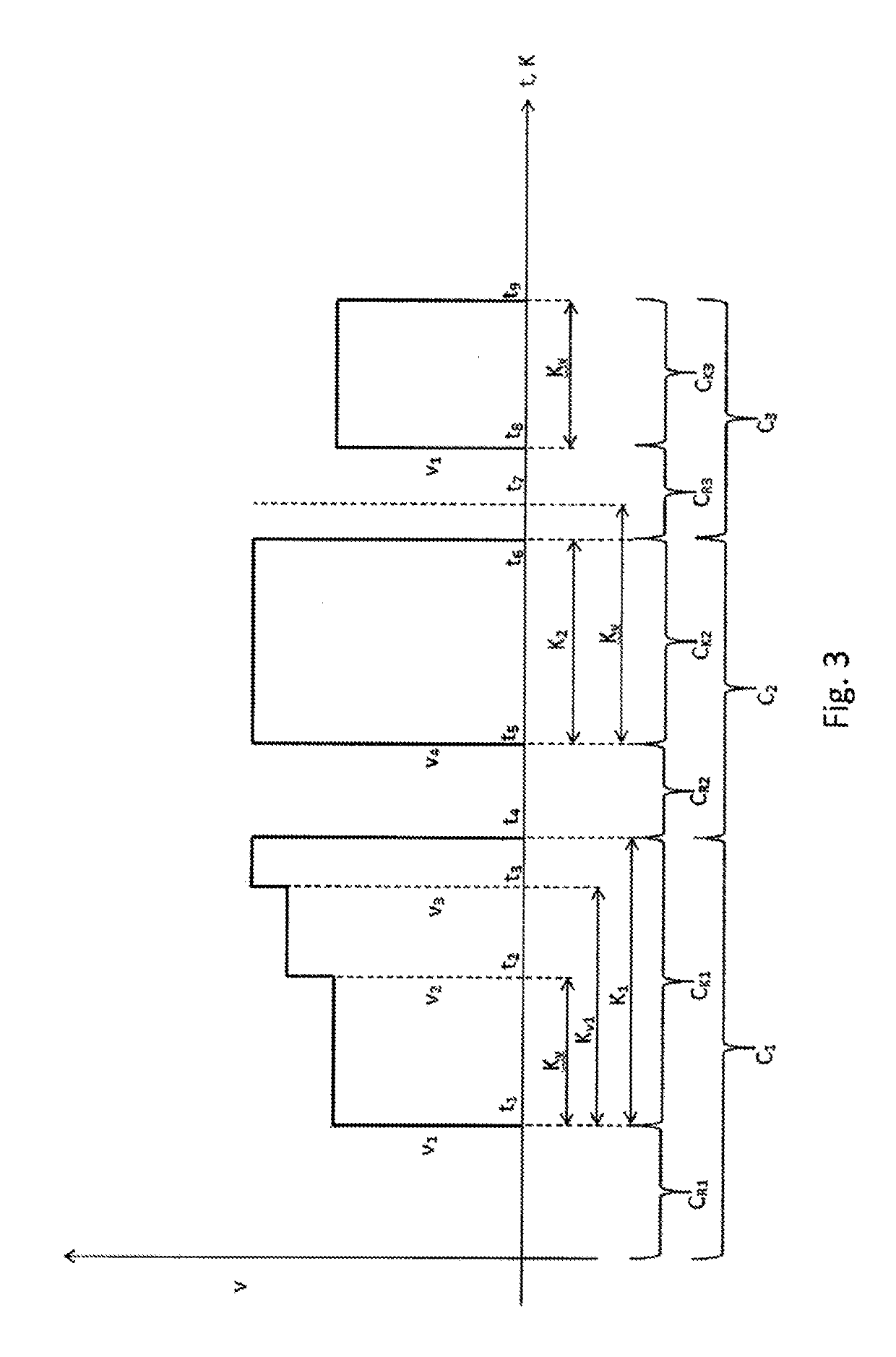
[0097]FIG. 5 shows a schematic representation of the rotary speed behavior after a defrost operation according the method according to the invention;
second embodiment
[0098]FIG. 6 shows a schematic representation of the rotary speed behavior after a defrost operation according to the method according to the invention;
third embodiment
[0099]FIG. 7 shows a schematic representation of the rotary speed behavior after a power outage according to the method according to the invention.
WAYS OF IMPLEMENTING THE INVENTION
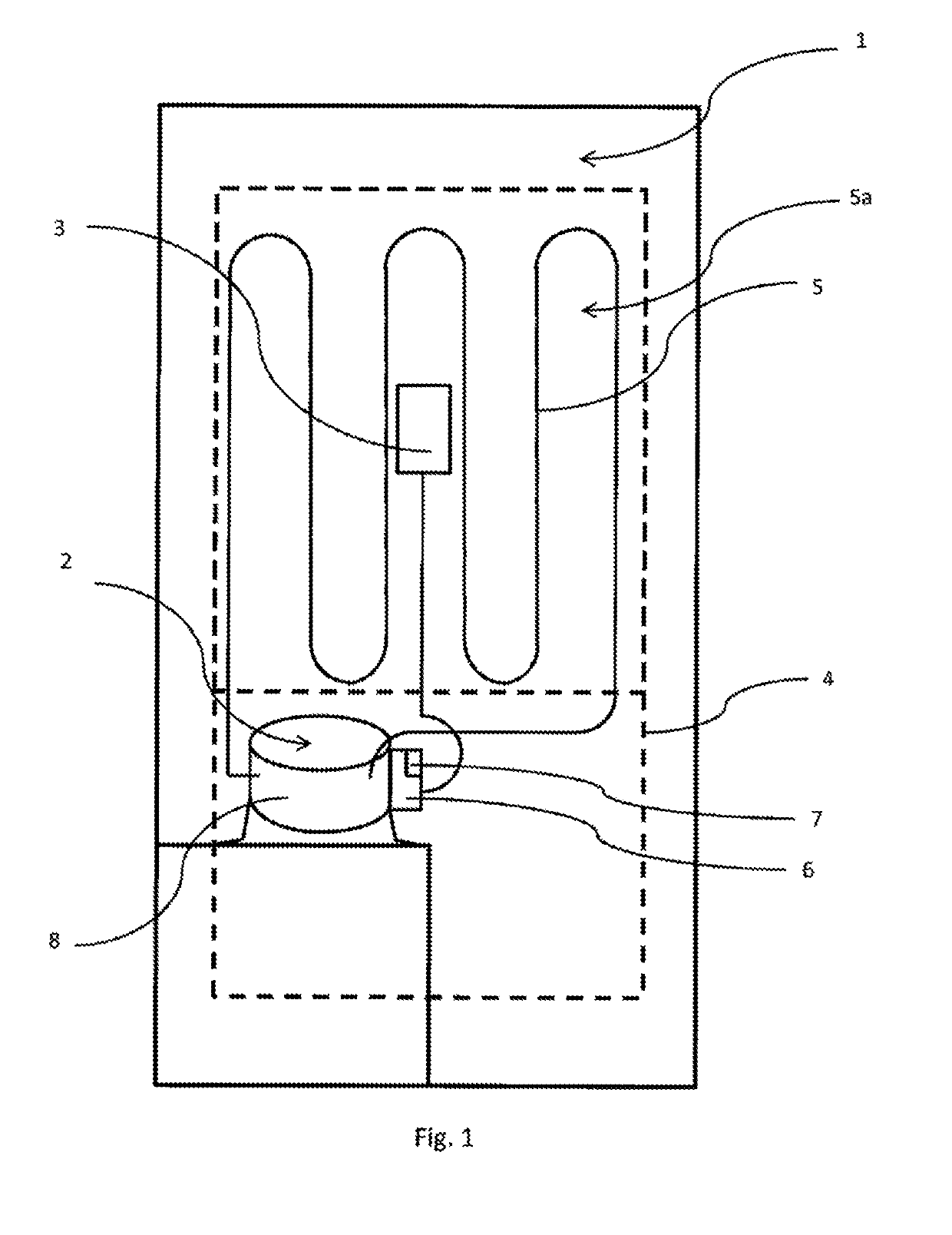
[0100]FIG. 1 shows a simple refrigeration system 1 with a variable-speed refrigerant compressor 2, a refrigerant line 5, and an evaporator 5a. Refrigerant compressor 2, refrigerant line 5, and evaporator 5a form a closed refrigerant system in which refrigerant circulates during the operation, thus during a cooling cycle CK of the refrigerant compressor 2. The refrigeration system 1 has a cooled volume 4, wherein heat can be removed or cooling output delivered by the evaporator 5a by evaporating the refrigerant in evaporator 5a.
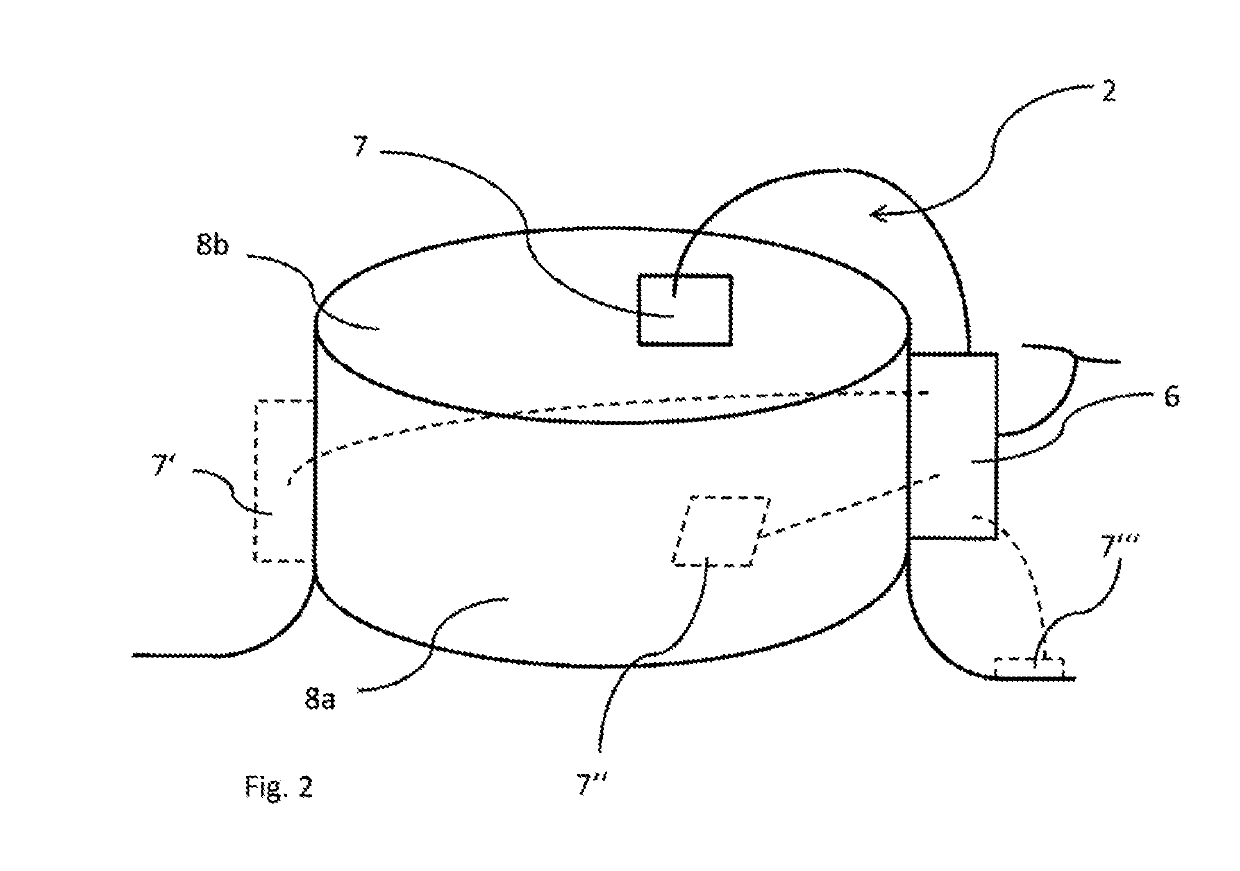
[0101]The individual components of the refrigerant compressor 2, thus at least one piston-cylinder unit in which the refrigerant is cyclically compressed and an electric drive unit, via which the piston-cylinder unit can be driven, are disposed within a housing 8 of the refrigerant...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com