Anti-allergen antibodies
a technology of anti-allergen antibodies and antibodies, which is applied in the field of anti-allergen antibodies, can solve the problems of severe systemic reactions, large emergency visits, hospital admissions, and deaths each year, and achieve the effects of reducing and increasing the number of hospital admissions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
of Peanut-Secific Antibodies by ELISA Assay
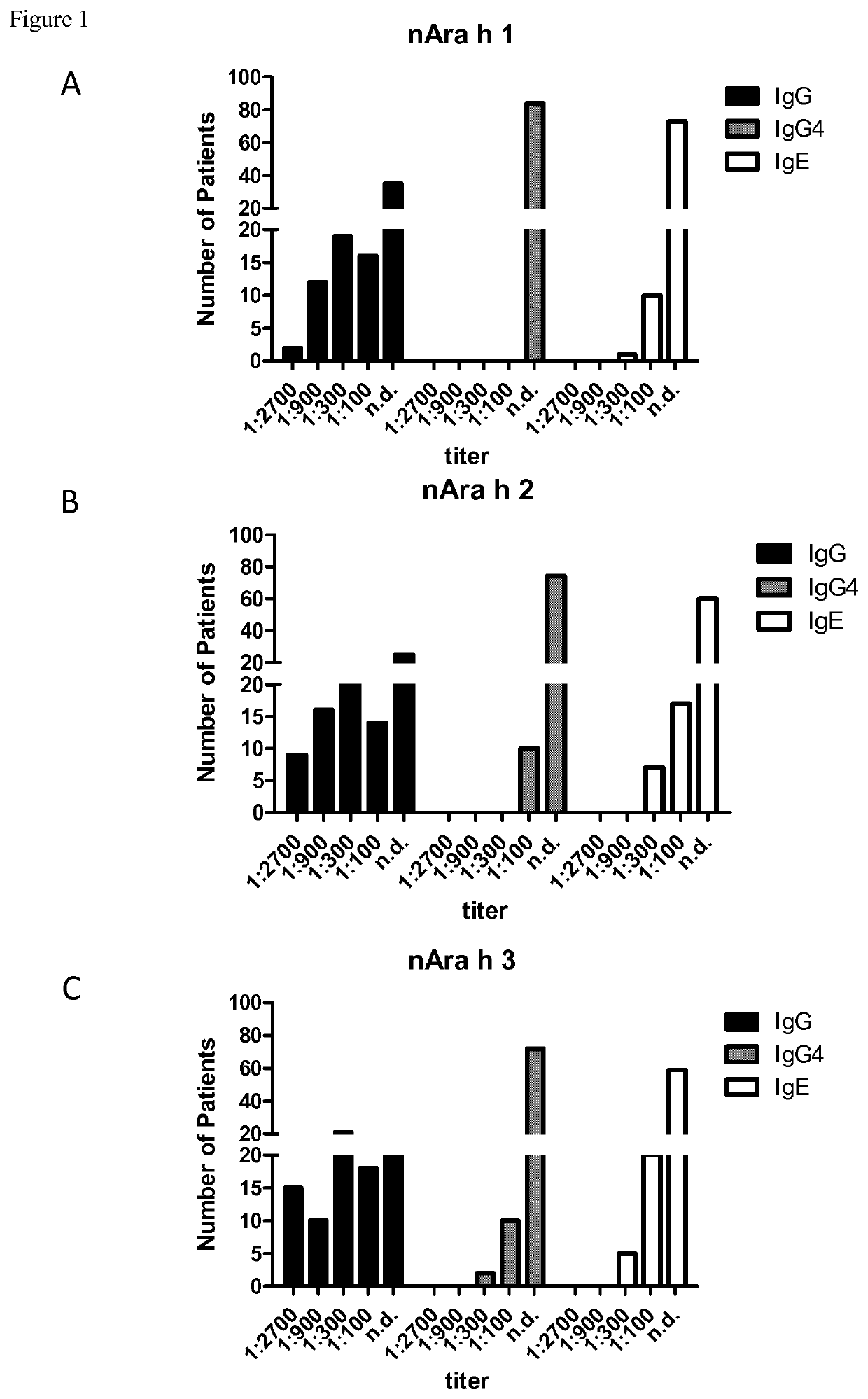
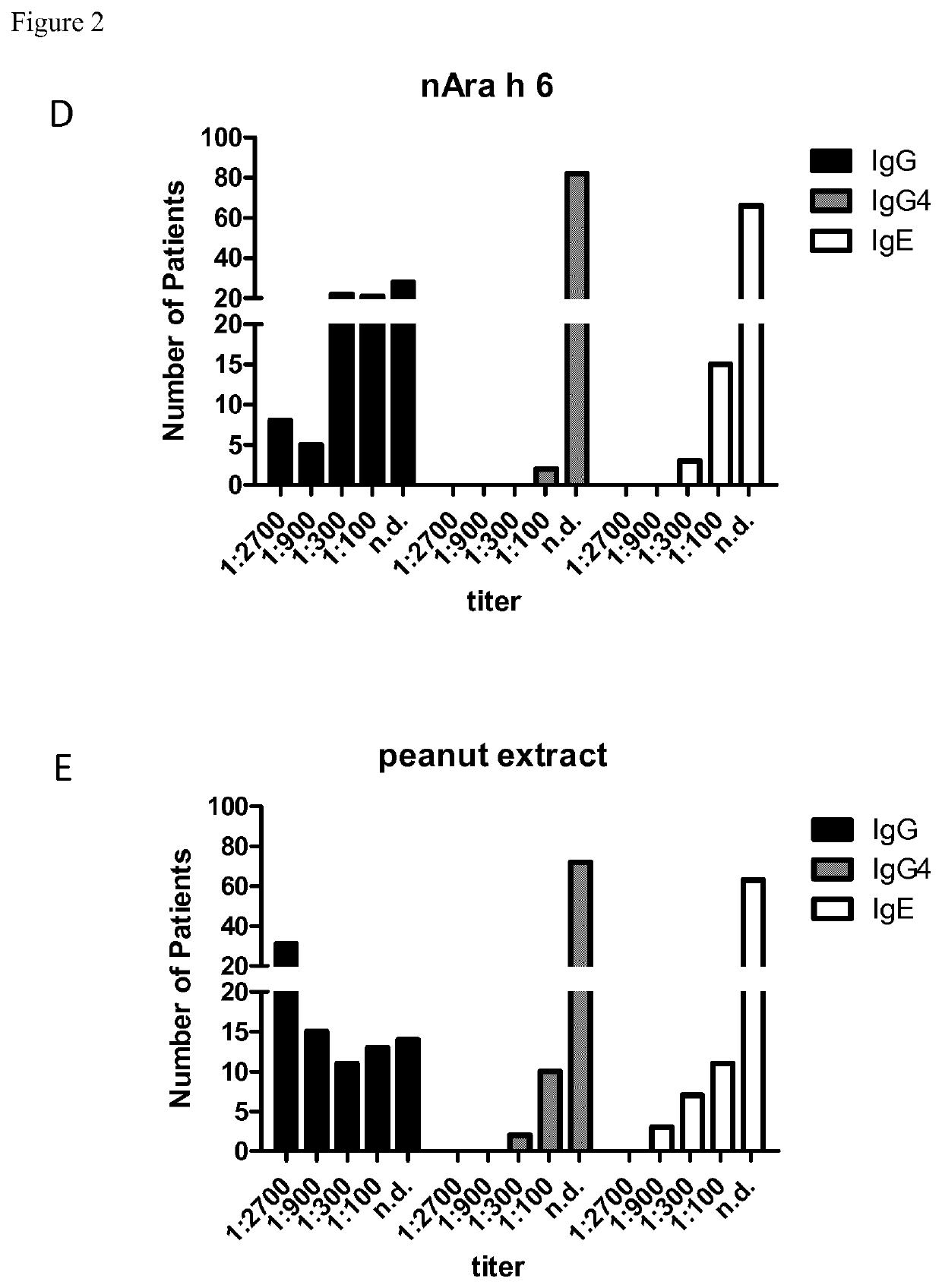
[0245]Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was used to evaluate allergen reactivity in the sera of allergic patients. Allergens (Ara h 2, Ara h 1, Ara h 3, Ara h 6, peanut extract) were coated on plates and anti-peanut antibody levels in sera from allergic patients were detected using HRP-conjugated anti-human antibody. Altogether, sera from 84 allergic patients, were used in the assays. The following protocol describes the experimental procedures for the detection of anti-allergen antibodies by ELISA assay. Allergic patients have shown seroreactivity against several Ara h peanut allergens, implicating the suitability of these antibodies against allergic response induced by several peanut allergens.
[0246]ELISA for the Detection of Peanut-Specific Antibodies
[0247]96 well microplates (Costar®, Corning Incorporated, Corning, N.Y., USA) were coated with peanut allergens either extracted and purified from peanuts or recombinantly expressed....
example 2
A Determination of the Antibodies of the Present Invention
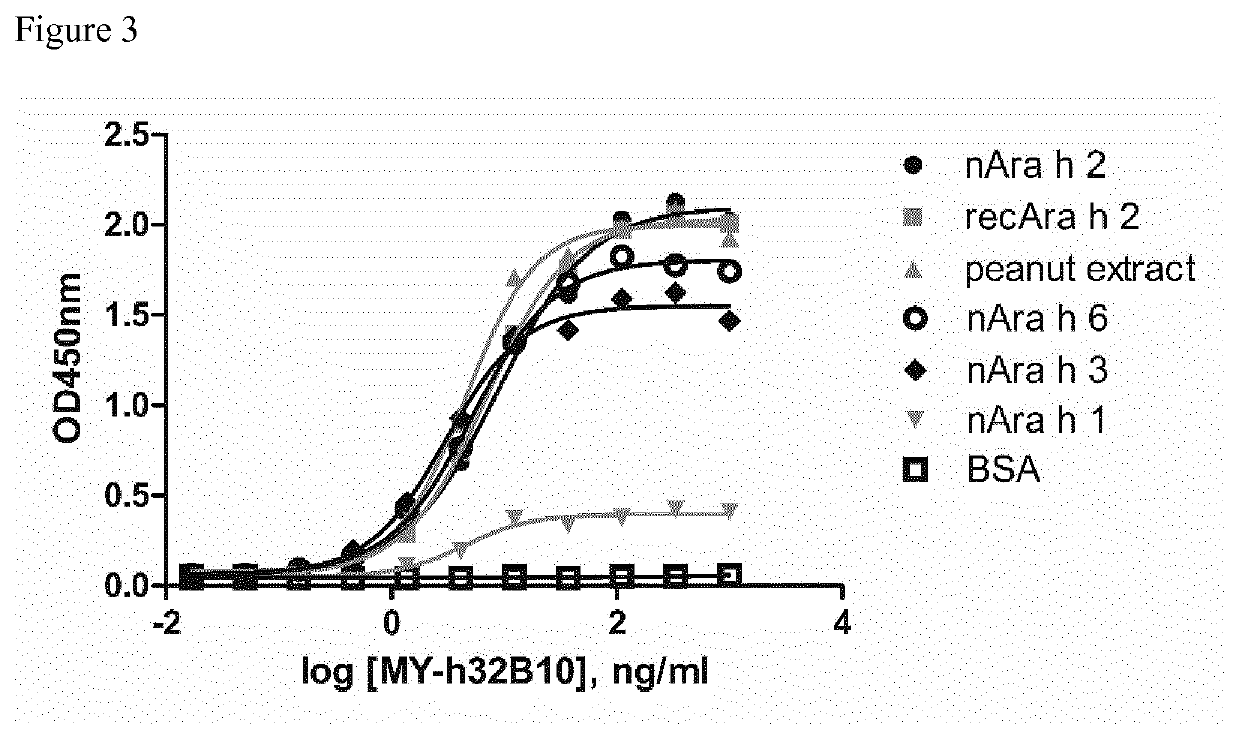
[0248]EC50 binding of exemplary anti-peanut antibodies of the present invention to peanut allergens or peanut extract, was determined by ELISA. Serial dilutions of MAbs (from 1000 ng / ml down to 0.0169 ng / ml) were incubated for 2 hours with antigen-coated plates (coating overnight at 4° C. or 1 h at 37° C. with 1 μg / ml antigen in PBS, followed by wash out and blocking with 2% BSA in PBS). The plates were subsequently washed and binding of MAbs was detected with anti-human HRP-conjugated Fc-gamma-specific secondary antibody (Jackson ImmunoResearch, West Grove, Pa., USA). Concentrations of MAb resulting in half of maximal binding to respective antigens (EC50, ng / ml) were calculated using GraphPad Prism 5 software on sigmoidal dose-response curves (variable slope, 4 parameters) obtained by plotting the log of the concentration versus OD450 nm measurements; for the results see FIG. 3 and table 2.
TABLE 2EC50 ELISA determination of ...
example 3
petition with Human-Mouse Chimeric Constructs of Anti-Peanut Antibodies
[0249]As first step of mapping, differential binding of anti-peanut MAbs of the present invention to distinct antigen binding sites was examined to determine the number of different binding sites. For this purpose, MAbs were expressed either with human (hMAb) or mouse (hmMab) Fc and cross-competition experiments were carried out by coating antigen on plates and by detecting binding of human Mabs in the presence of titrated amount of hmMabs. Detection of hMAbs bound to the ligand was performed by a HRP conjugated secondary antibody directed against the Fc portion of the primary antibody (Jackson ImmunoResearch, West Grove, Pa., USA). As may be seen from Table 3, exemplary anti-peanut allergens antibodies 37D5 and 12G10 of the present invention compete each other for binding of Ara h 2 but not with antibodies 4B2 and 32B10, indicating that 12G10 and 37D5 bind other sites of Ara h 2 than 4B2 and 32B10.
TABLE 3The dif...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com