Method for identifying risks as a result of stray currents
a technology of stray currents and risks, applied in the field of identifying risks as a result of stray currents, can solve the problems of stray currents flowing to the ground and to the structures at risk, corrosion of these structures, and electrical damage to the insulation between the rails and ground in one direction, so as to achieve easy evaluation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
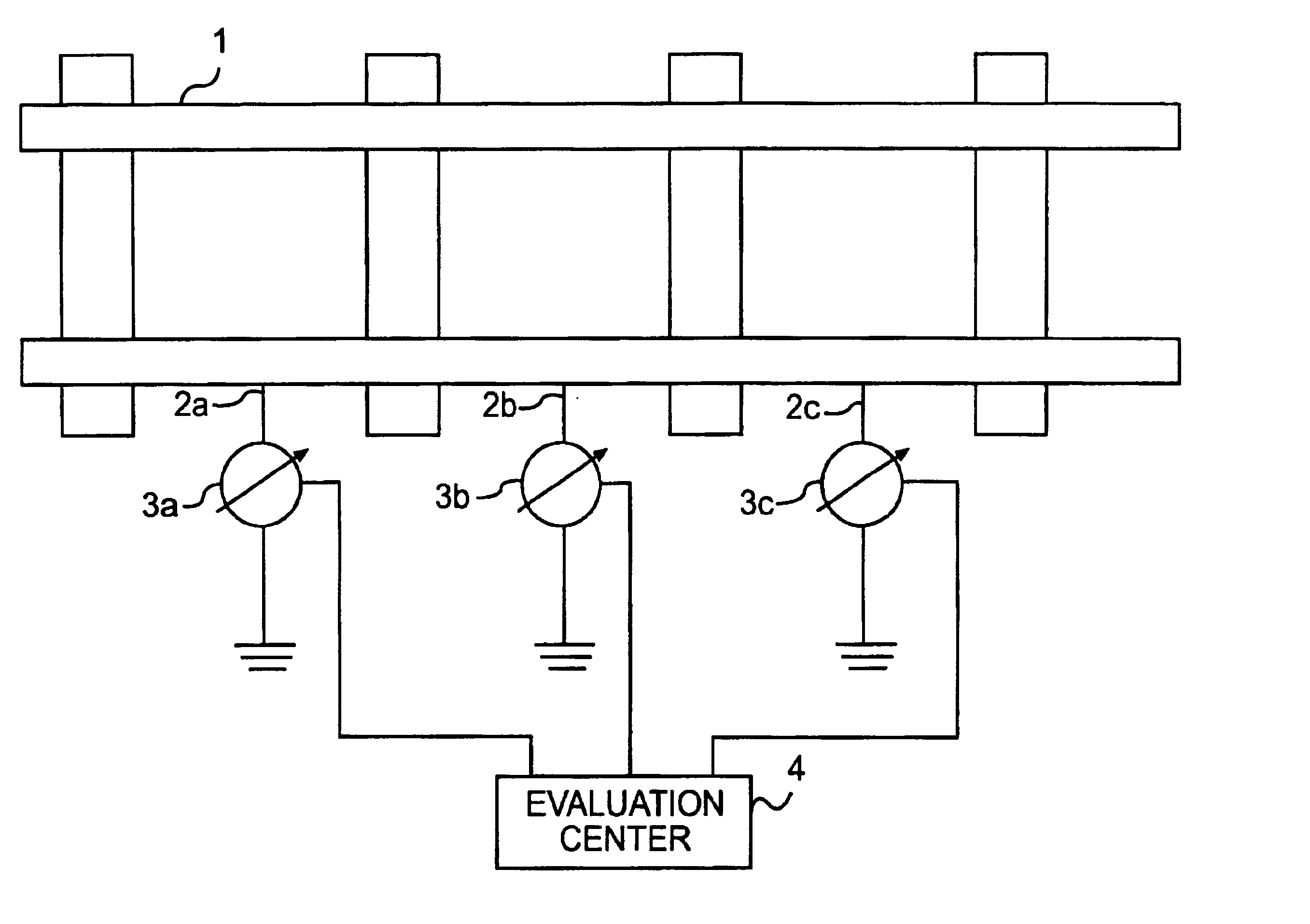
[0011]In accordance with a first embodiment, in which the voltage between the rail 1 and the ground is measured and an increased risk as a result of stray currents is indicated if there is a discrepancy from a voltage reference value, an object may be achieved by virtue of the voltage being measured at a plurality of measurement points 2a, 2b, 2c along the track and by virtue of the measurements being transmitted to an evaluation center 4 where they are evaluated centrally.
[0012]An advantage attained is that a plurality of simple voltage measurements suffice in order to obtain a reliable statement about the risk. These voltage measurements can be ascertained at a plurality of measurement points 2a, 2b, 2c using simple voltage measuring instruments 3a, 3b, 3c and are easy to evaluate in an evaluation unit 4. This involves a comparison with reference values.
second embodiment
[0013]In accordance with a second embodiment, an object may be achieved by virtue of activating a short-circuiter connecting a parallel path to the rail 1 for returning the traction current, by virtue of the current level in the parallel path being measured, and by virtue of an increased risk as a result of stray currents being indicated if there is a discrepancy from a current-level reference value.
[0014]Such a parallel path is a continuous tunnel reinforcement, for example. The parallel path is connected when required using a short-circuiter.
[0015]The second embodiment of the method in accordance with the invention involves the insight that current-level measurement in the parallel path can indicate damage to the insulation between the rail 1 and ground. This is because damage to this insulation reduces the electrical resistance of the rail 1 with respect to ground. Thus, a larger current is drained at that point. Since the electrical resistance of the parallel path remains the sa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com