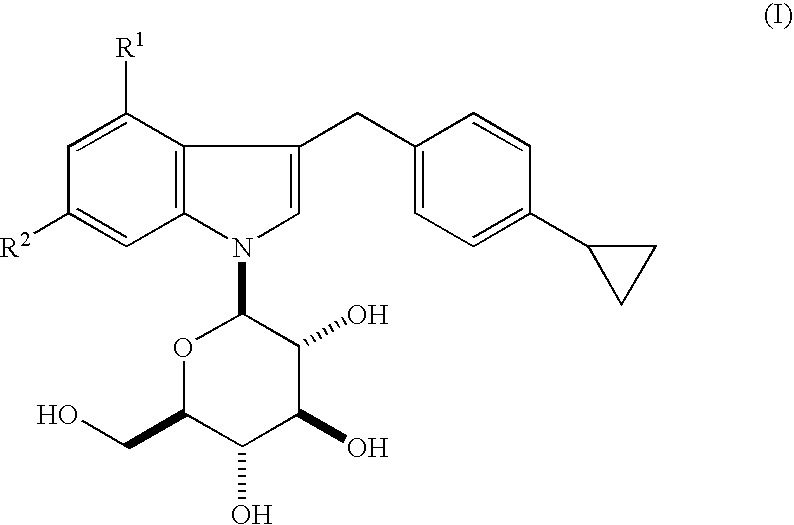
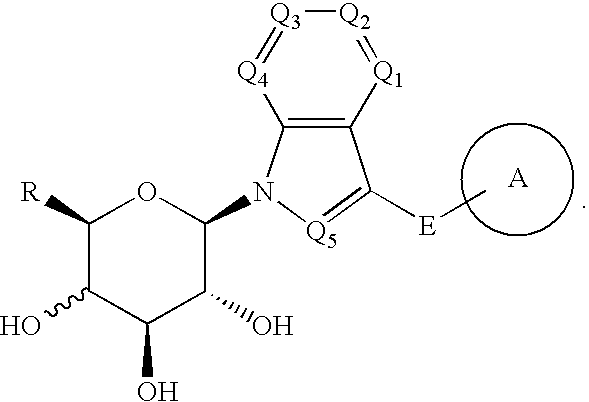
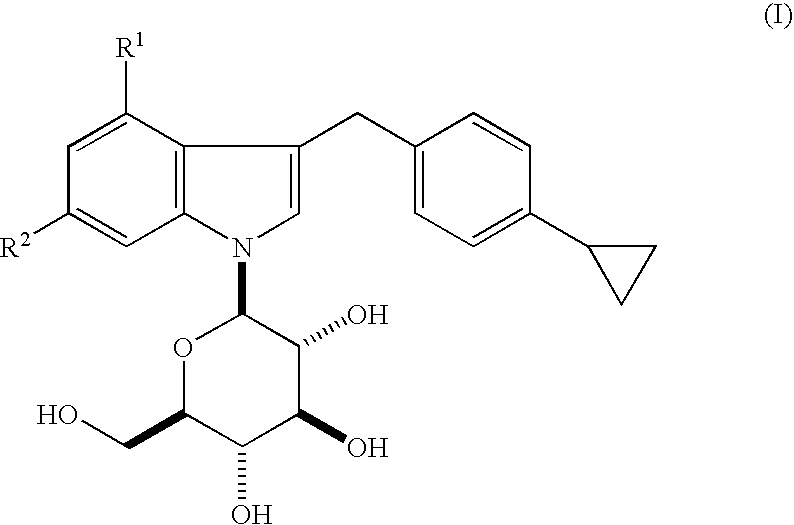
Indole derivatives
a technology of indole and derivatives, applied in the field of indole derivatives, can solve the problems of significant hypoglycemia, edema and heart failure, anti-diabetic agents have various side effects, etc., and achieve favorable characteristics in side effects and/or commercial viability, excellent blood glucose lowering effect, and the effect of excellent
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
3-(4-Cyclopropylphenylmethyl)-4-fluoro-1-(β-D-gluco-pyranosyl)indole
[0106]
(1) A mixture of 4-fluoroindoline (185 mg) and D-glucose (267 mg) in H2O (0.74 ml)-ethyl alcohol (9 ml) was refluxed under argon atmosphere for 24 hours. The solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure to give crude 4-fluoro-1-(β-D-glucopyranosyl)indoline, which was used in the subsequent step without further purification.
(2) The above compound was suspended in chloroform (8 ml), and thereto were added successively pyridine (0.873 ml), acetic anhydride (1.02 ml) and 4-(dimethylamino)pyridine (a catalytic amount). After being stirred at room temperature for 21 hours, the reaction solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure. The residue was dissolved in ethyl acetate, and the solution was washed with a 10% aqueous copper (II) sulfate solution twice and a saturated aqueous sodium hydrogen carbonate solution, and dried over magnesium sulfate. The insoluble materials were filtered off, and the filtrate was evap...
example 2
4-Chloro-3-(4-cyclopropylphenyl-methyl)-1-(β-D-glucopyranosyl)indole
[0107]
(1) A mixture of 4-chloroindoline (2.88 g) and D-glucose (3.38 g) in ethyl alcohol (150 ml)-H2O (10 ml) was refluxed under argon atmosphere overnight. The solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure and the residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (chloroform:methanol=100:0-88:12) to give 4-chloro-1-(β-D-glucopyranosyl)indoline (3.35 g) as a colorless foam. APCI-Mass m / Z 316 / 318 (M+H). 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ 2.87-3.02 (m, 2H), 3.07-3.12 (m, 1H), 3.20-3.32 (m, 2H), 3.38-3.47 (m, 2H), 3.51-3.60 (m, 2H), 3.68-3.73 (m, 1H), 4.34-4.37 (m, 1H), 4.63 (d, J=8.3-Hz, 1H), 4.93 (d, J=5.1 Hz, 1H), 5.03 (d, J=4.0 Hz, 1H), 5.06 (d, J=4.5 Hz, 1H), 6.53 (d, J=8.0 Hz, 1H), 6.60 (d, J=8.0 Hz, 1H), 6.99 (t, J=7.9 Hz, 1H).
(2) The above compound (3.3 g) was dissolved in 1,4-dioxane (150 ml), and thereto was added 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone (2.85 g). The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 12 ho...
example 3
3-(4-Cyclopropylphenylmethyl)-4,6-difluoro-1-(β-D-gluco-pyranosyl) indole
[0108]
[0109]The titled compound was obtained as colorless foam in a manner similar to Example 1 from 4,6-difluoroindoline. APCI-Mass m / Z 463 (M+NH4). 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) δ 0.58-0.62 (m, 2H), 0.88-0.91 (m, 2H), 1.82-1.88 (m, 1H), 3.20-3.50 (m, 4H), 3.59-3.70 (m, 2H), 3.99 (s, 2H), 4.54 (t, J=5.7 Hz, 1H), 5.10 (d, J=5.3 Hz, 1H), 5.19 (d, J=5.0 Hz, 1H), 5.22 (d, J=5.8 Hz, 1H), 5.35 (d, J=9.0 Hz, 1H), 6.78 (t, J=9.6 Hz, 1H), 6.96 (d, J=8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.11 (d, J=8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.22 (s, 1H), 7.30 (dd, J=10.0, 1.7 Hz, 1H).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com