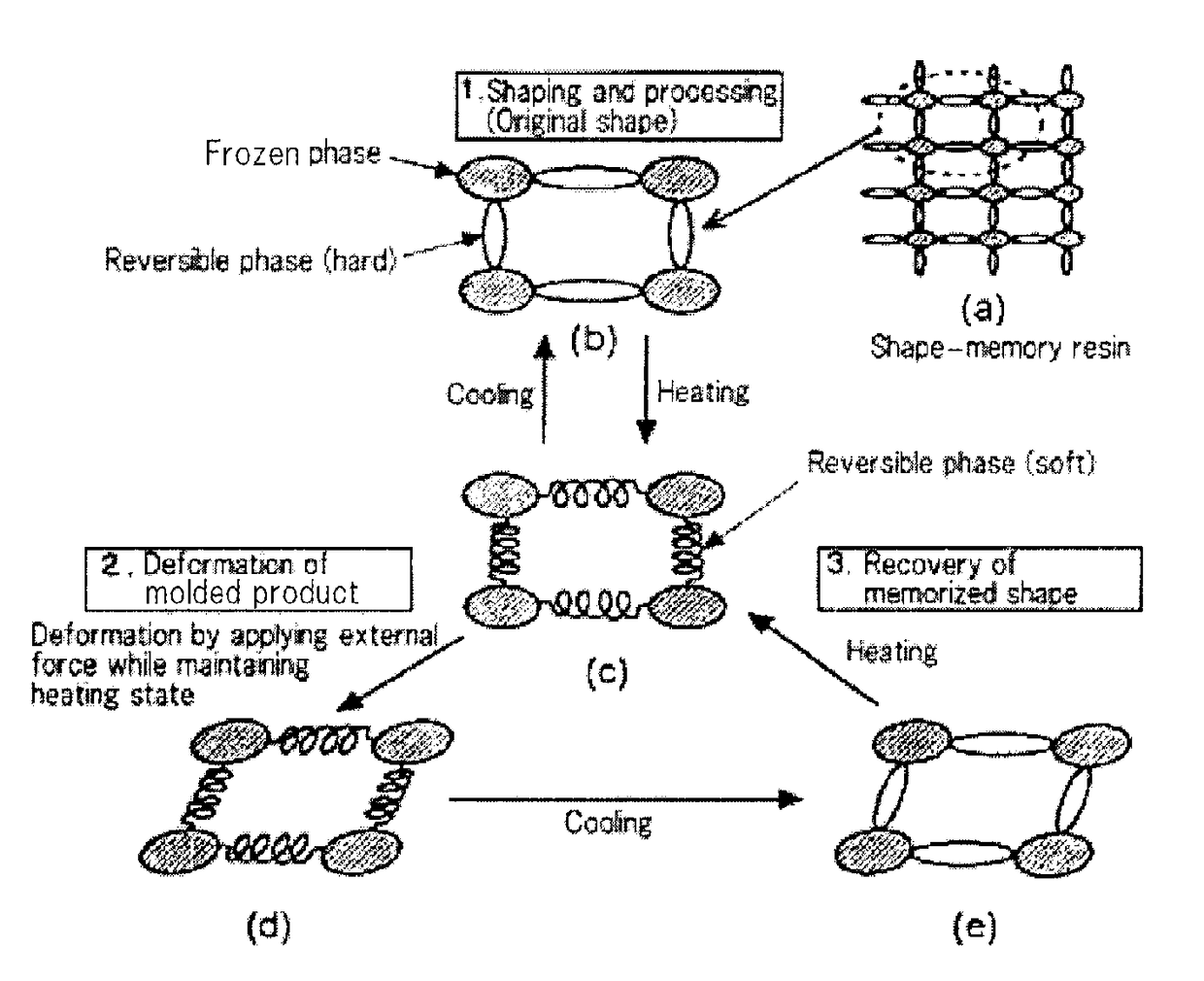
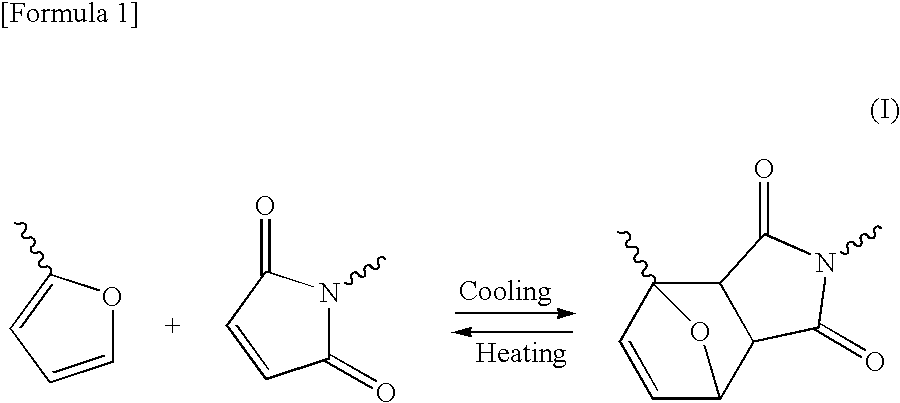
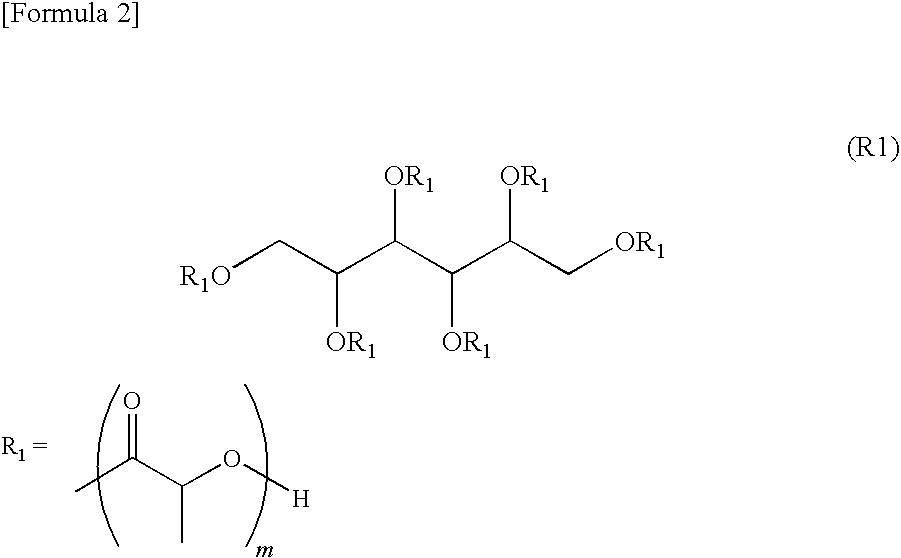
Shape-memory resin, molded product composed of the resin, and method of using the molded product
a technology of shape memory and resin, which is applied in the field of shape memory resin, molded product composed of resin, and method of using molded product, can solve the problems of no mechanical properties, polylactic acid has not yet become widespread, and polylactic acid is more expensive than petroleum-based resins, etc., and achieves excellent shape memory properties, high mechanical strength, and high toughness.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Synthesis of Terminal Hydroxy Polylactic Acid
[0070]2220 g of polylactic acid (Terramac; manufactured by Unitika Ltd.) and 76.8 g of sorbitol were melted and mixed at 210° C. for 12 hours to carry out a transesterification, so as to obtain an ester compound. A solution obtained by dissolving this ester compound in 5 L of chloroform was poured into an excessive amount of methanol, and it was reprecipitated, so as to obtain terminal hydroxy polylactic acid [R1]. Its number average molecular weight was 7300, and its Tg was 46.8° C.
[0071]
[Synthesis of Flexible Polymer (Terminal Hydroxy Polybutylene Succinate (PBS))]
[0072]117 g of succinic anhydride and 128 g of 1,4-butanediol were heated at 190° C. for 4 hours, and they were then further heated under a reduced pressure for 2 hours, to carry out a dehydration condensation reaction, thereby obtaining an ester compound. A solution obtained by dissolving this ester compound in 200 mL of chloroform was poured into an excessive amount of metha...
example 2
[0080]As a flexible polymer, polybutylene succinate [R3] (Bionore: manufactured by Showa Highpolymer Co., Ltd.) (number average molecular weight=21300; Tg=−32° C.) was used.
[0081]
[0082][R1] and [R3] were melted and mixed (170° C.) at the composition ratio shown in Table 2, and lysine triisocyanate used as a linker was then added to the mixture. The linker was added thereto, such that the amounts of terminal hydroxy groups in [R1] and [R3] could be equimolar to the amounts of isocyanate groups in the linker. Thereafter, the mixture was subjected to compression molding at 170° C. for 2 hours, so as to obtain a polylactic acid cross-linked product. The results obtained by evaluating the flexural strength, elongation at break, Tg, and shape-memory property of the obtained polylactic acid cross-linked product are shown in Table 3.
[0083]
TABLE 3Composition (wt %)Amount of linker addedPhysical properties of cross-linked PLAPLA(mg / polymer 1 g)BendingElongation(TerminalFlexible polymerLinkers...
example 3
Synthesis of Maleimide Group-Containing Polylactic Acid
[0084]25.0 g of β-alanine, 28.9 g of maleic anhydride, and 100 mL of THF were stirred in a nitrogen atmosphere at a room temperature for 24 hours. Thereafter, a solid was filtrated to obtain maleamide propionic acid [R4] (yield: 96%). Subsequently, 22.1 g of [R4], 6.11 g of orthophosphoric acid, 0.0937 g of BHT, 100 mL of xylene, 300 mL of toluene, and 20 mL of dioxane were each weighed, and they were then refluxed in a three-necked flask for 3 hours. The reaction temperature was 116° C. Thereafter, the reaction solution was cooled to a room temperature, and the solvent was then distilled away under a reduced pressure. The obtained solid was dissolved in chloroform. Thereafter, the chloroform was distilled away from this solution under a reduced pressure, and the solid was then recrystallized from diethyl ether, so as to obtain maleimide carboxylic acid [R5].
[0085]
[0086]6.25 g of [R5] was dissolved in 90 mL of chloroform, and th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| elongation at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tg | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com