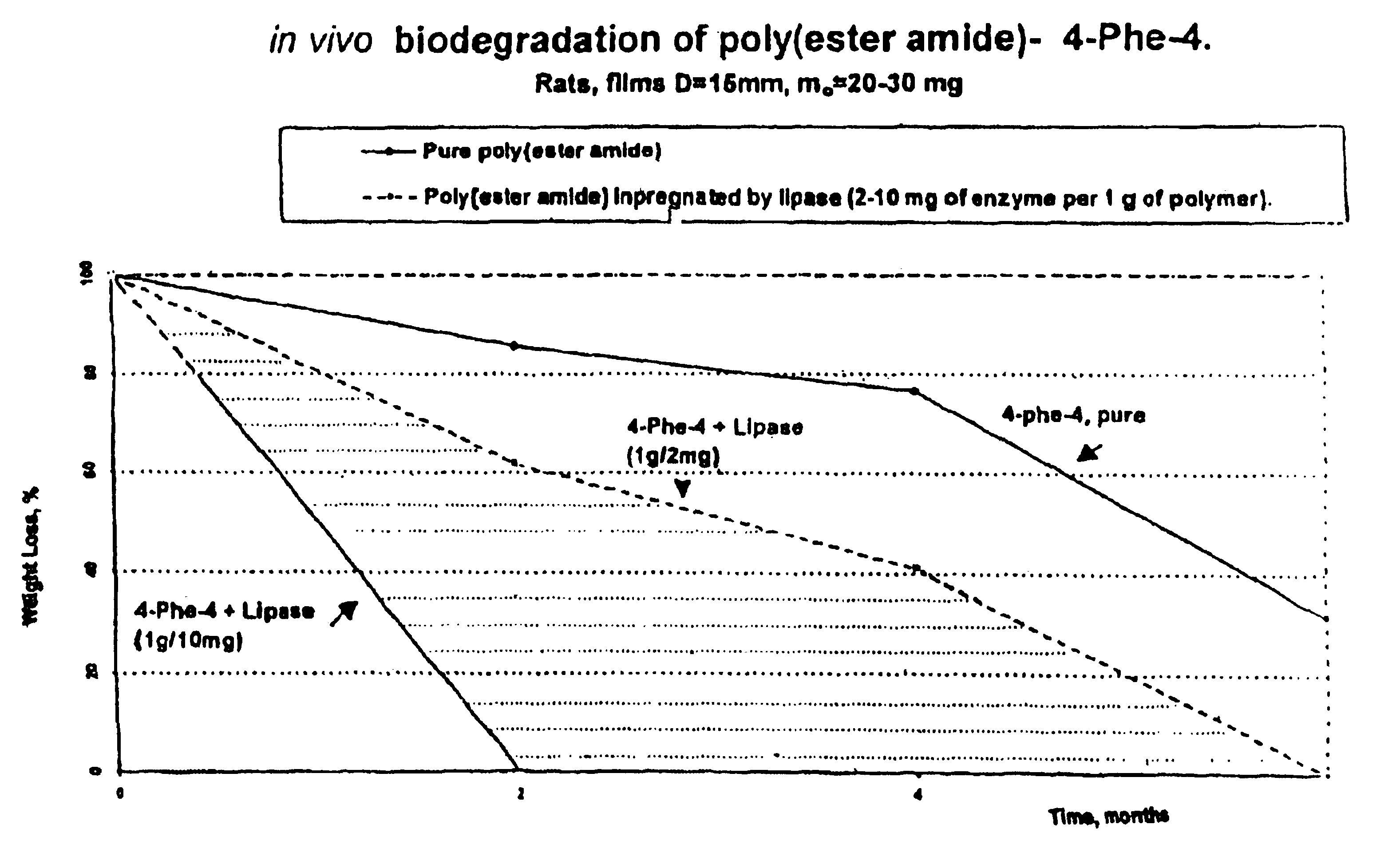
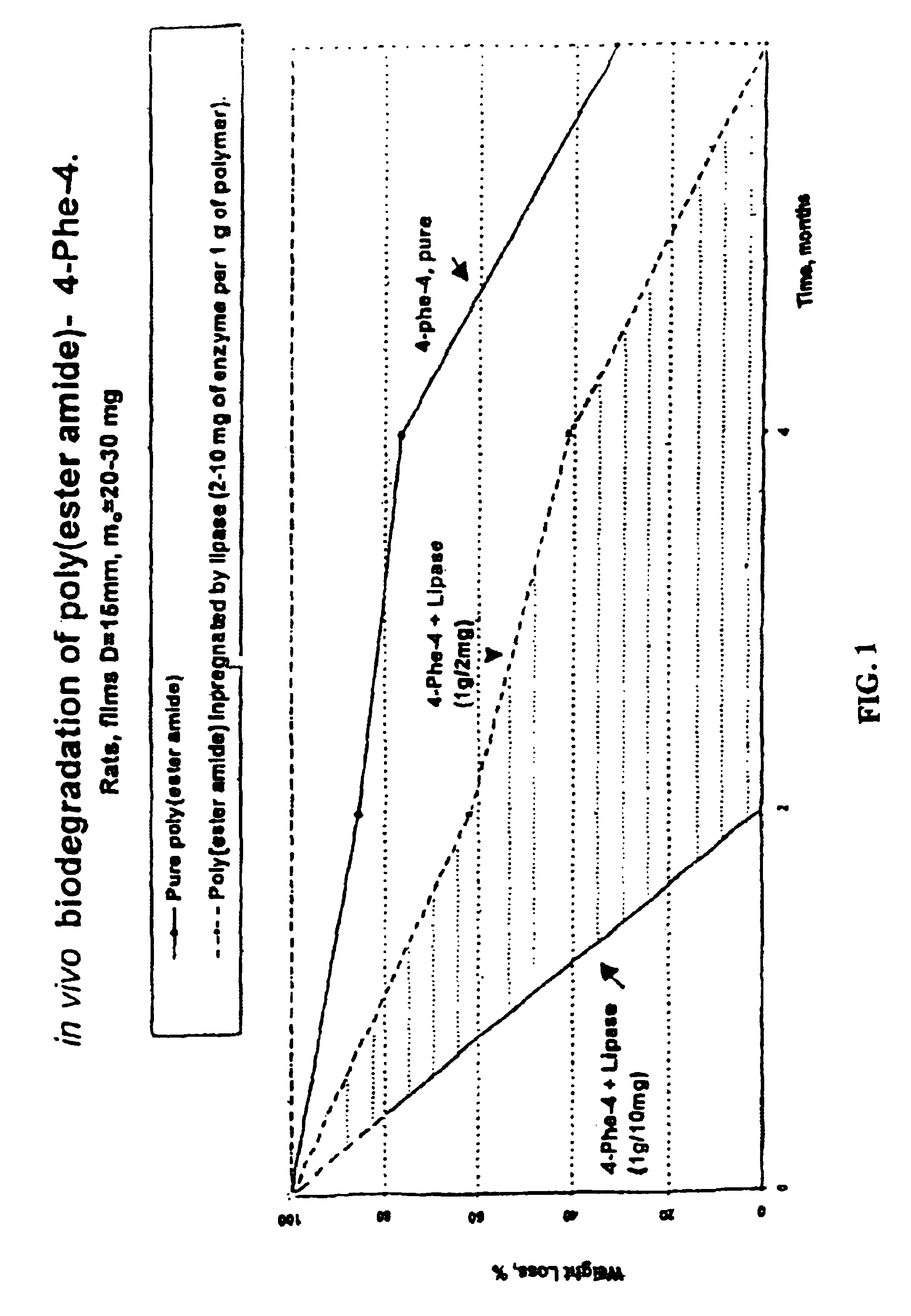
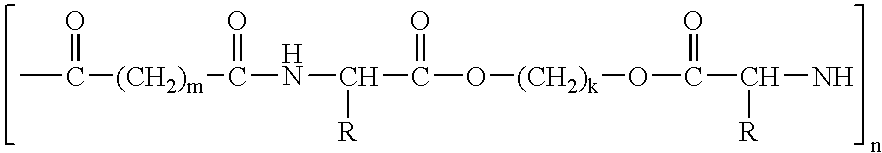
Polymer blends as biodegradable matrices for preparing biocomposites
a polymer blend and biodegradable technology, applied in the field of polymer matrices, can solve the problems of poor film-forming properties, less useful aromatic diols (e.g. bis-phenols) for these purposes, and less useful aromatic diacids (like phthalic acids, etc.) for these purposes, and achieves high enzyme-catalyzed biodegradation rates and high plasticity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0058]A complex of polyvalent bacteriophages directed toward Staphylococcus species, Streptococcus species, E. coli, Proteus species, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa with a titer of 2×106-2×107 plaque-forming units, was prepared and used as bioactive substance for this study. Bacteriophage were prepared as a lyophilized dry powder as follows: bacteriophages suspended in an aqueous sucrose-gelatin mixture were lyophilized, resulting in a dry mass that was ground into fine powder. In this process, 50 mg of dry preparation corresponds to 1 ml of liquid bacteriophage with a titer of 2×106-2×107. None of the individual components of bioactive composites (polymer, organic solvent, alpha-chymotrypsin, lipase) affected bacteriophages activity—100% of starting activity was retained in all cases.
[0059]A bioactive film was prepared as follows: A fine suspension of dry bacteriophage in a polymer solution with an appropriate solvent was cast on a glass surface and dried to constant weight. A composit...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com