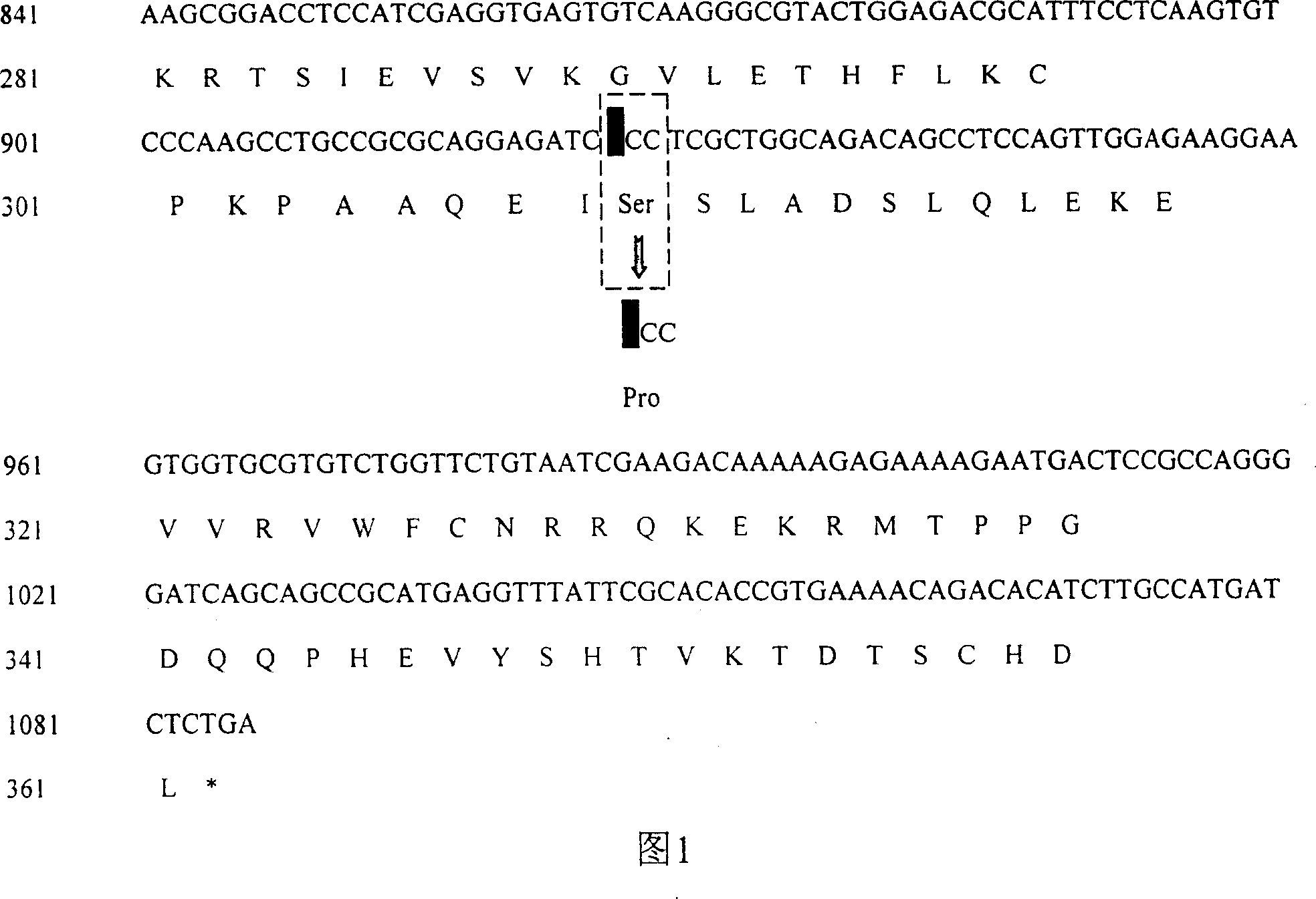
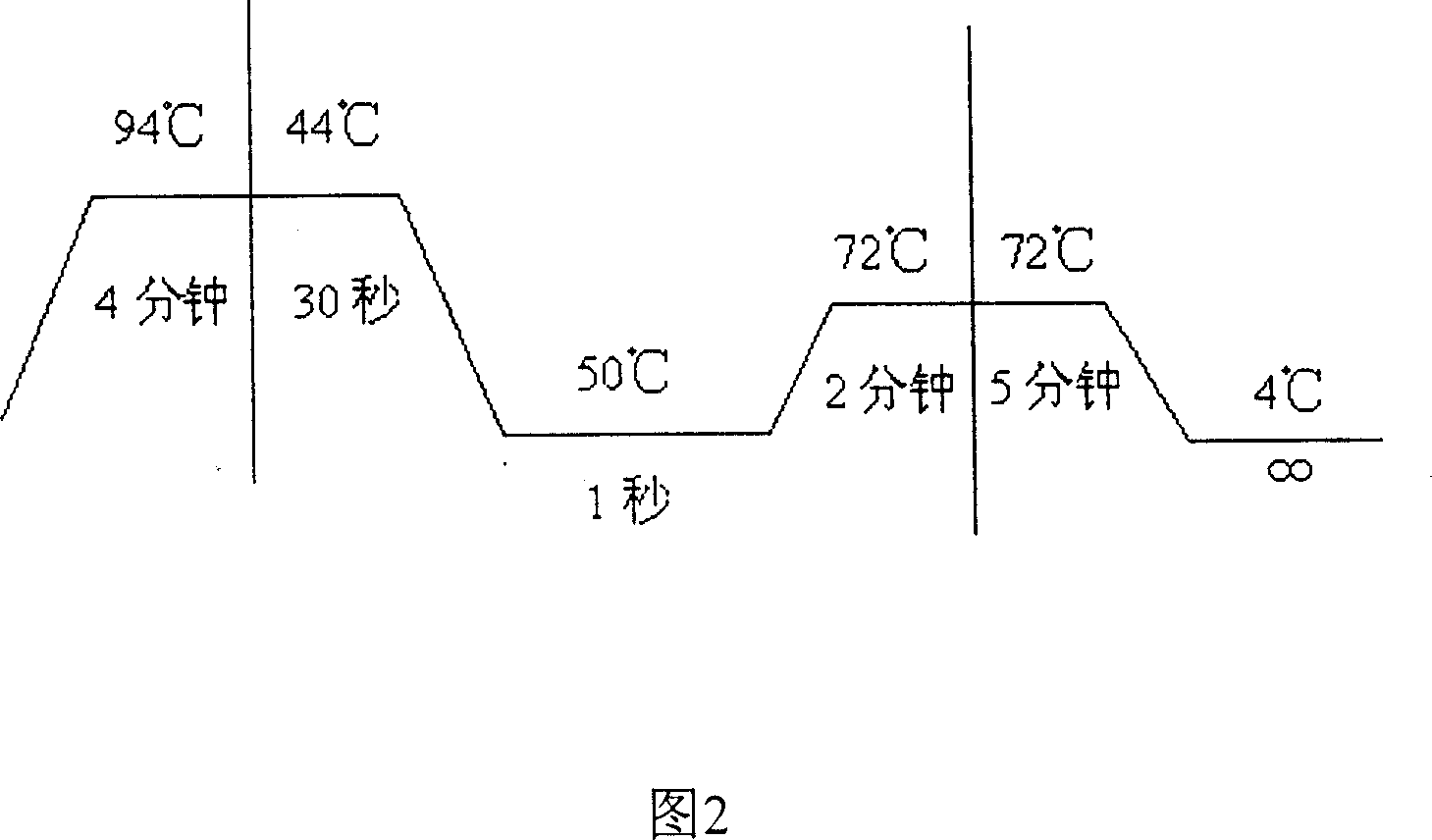
Deaf-related gene mutation and its detecting method
A gene and mutation site technology, applied in the field of kits for detecting POU3F4 mutant genes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] 1. Preparation of blood sample DNA of the subject to be tested
[0066] 1. Research object
[0067] A Chinese family with X-linked genetic congenital profound hearing loss 021 showed congenital profound hearing loss. Temporal bone CT examination showed that the internal auditory canal was enlarged, showing an X-linked recessive inheritance pattern. A total of 31 members of the 021 family were investigated, including 17 males and 14 females. Eight patients, all male, had the same audiological phenotype. The POU3F4 gene mutation was detected in the 31 family members according to the following method, and all 8 male patients were found to be hemizygous for the mutation, and 8 heterozygous carriers were detected among the females. No mutation was found in 15 family members. In addition, 110 normal controls with normal hearing and no genetic background of hearing loss were selected for POU3F4 gene mutation detection, and no mutation was found.
[0068] All participants w...
Embodiment 2
[0099] 1. Purification of PCR products——96-well plate method
[0100] 1. Add 50 μl sterile water to the 96-well plate containing the PCR product and mix well.
[0101] 2. Transfer it to the Millipore purification plate, put it on the vacuum pump for about 3 minutes, and see that there is no water in the purification plate.
[0102] 3. Add 50 μl of deionized water to the purification plate again, and continue to filter until there is no water in the purification plate.
[0103] 4. Remove the purification plate from the vacuum pump, add 20 μl of deionized water to the plate, let it rest for 15 minutes, shake it for another 15 minutes, and then suck it into a new 96-well plate.
[0104] 5. Store in a -20°C refrigerator.
[0105] 2. Quantification by electrophoresis
[0106] 1. Sample preparation
[0107] Take a 96-well spotting plate, add 6 μl of sample buffer to each well, remove the PCR product (2 μl) from each well of the cavity plate containing the PCR product, transfer t...
Embodiment 3
[0120] 1. Purity and dosage requirements of PCR product DNA template
[0121] DNA purity: OD 260 / OD 280 = 1.6 to 2.0.
[0122] DNA concentration: PCR product 10ng / μl.
[0123] DNA consumption:
[0124] PCR product
[0125] 100-200bp 1-3ng
[0126] 200-500bp 3-10ng
[0127] 500-1000bp 5-20ng
[0128] 1000-2000bp 10-40ng
[0129] >2000bp 40-100ng
[0130] 2. Sequencing reaction
[0131] 1. The reagents required for the sequencing reaction should be freshly prepared, and the reagents that need to be sterilized by autoclaving must be sterilized before use. The equipment required for the sequencing reaction (such as 384-well plates, tips, etc.) should also be clean and sterile.
[0132] 2. In order to ensure the freshness of sequencing samples and reaction reagents, it should be operated on ice when adding samples.
[0133] 3. The current reaction system is 5 μl, and the amount of various reagents added is shown in Tabl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com