Two-freedom parallel-connecting mechanism with passive constrained branch
A passive constraint, degree of freedom technology, used in manipulators, manufacturing tools, program-controlled manipulators, etc., can solve problems such as poor lateral load bearing capacity and inability to meet dynamic stiffness requirements, and achieve improved lateral bearing capacity, bearing capacity/ The effect of the mechanism's high weight ratio and large working space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
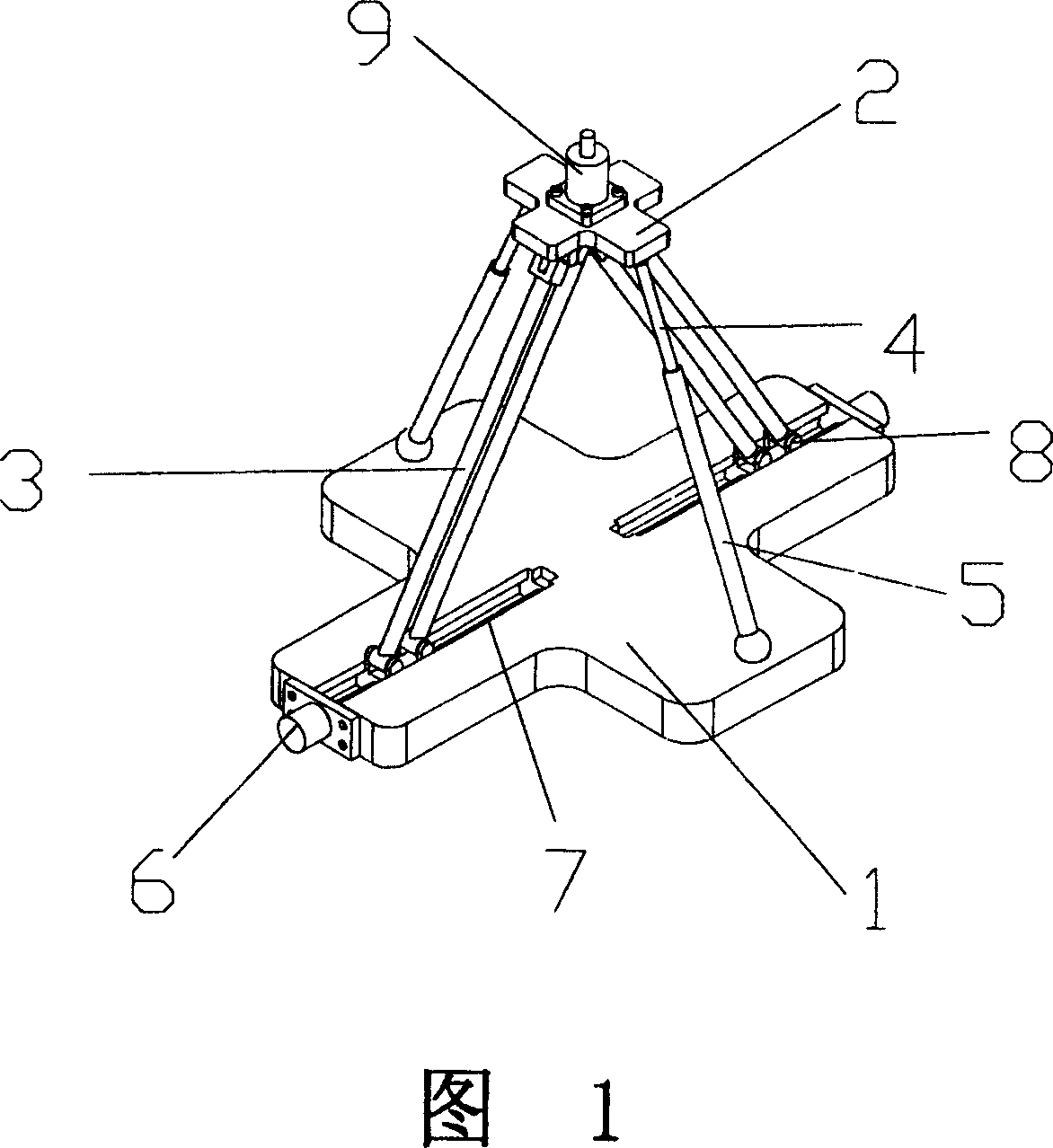
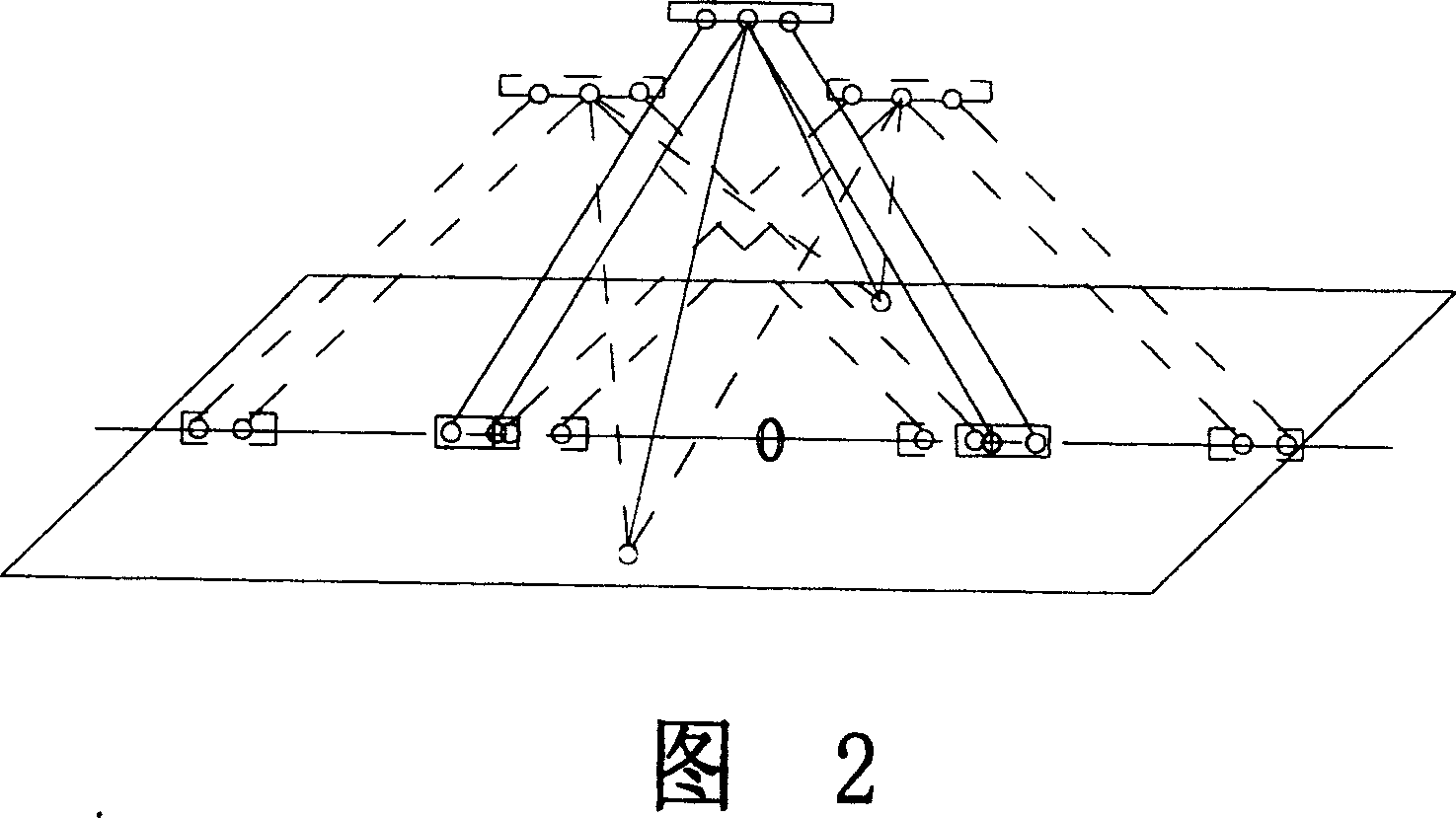
[0018] Referring to Figures 1 and 2, a two-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism with passive restraint branches includes a static platform 1 and a dynamic platform 2, the static platform 1 is parallel to the dynamic platform 2, the static platform 1 and the The moving platform 2 is connected by two sets of fixed-length active branches 3 and two scalable passive restraint branches. The plane where the two sets of active branches 3 are located is perpendicular to the plane where the two passive restraint branches are located. It is scattered from the moving platform 2 to the static platform 1. Two groups of active branches 3 are equal in length, and each group of active branches is made up of two fixed-length rods. The two passive restraints are also equal in length, and each passive restraint branch is composed of a telescopic rod 4 and a sleeve rod 5, and both of them adopt electromagnetic controllable damping rods, and electromagnetic controllable damping rods are installed i...
Embodiment 2
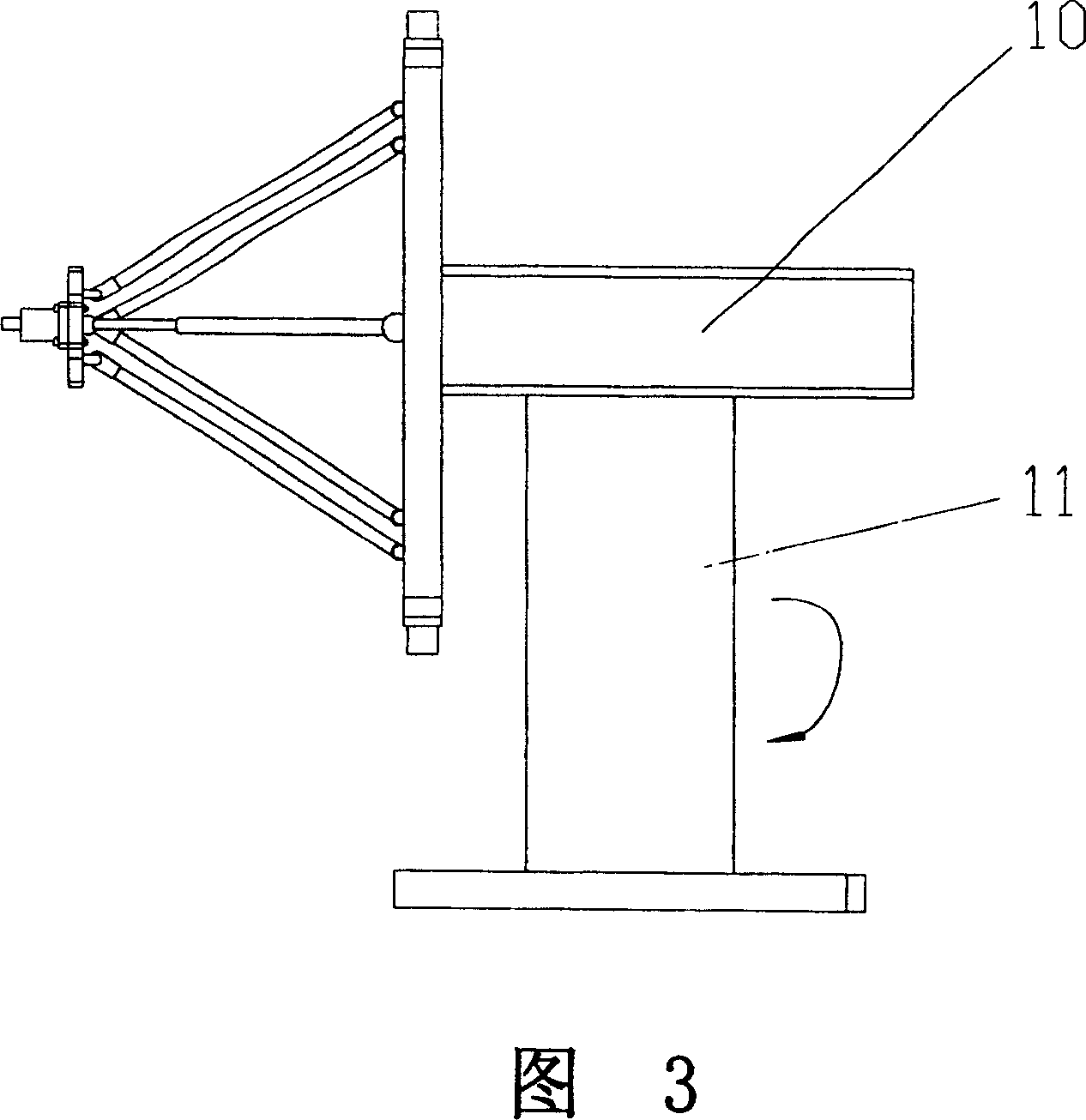
[0022] Referring to Figure 3, the two-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism with passive restraint branches described in Embodiment 1 is applied to a hybrid robot:
[0023] The two-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism with passive restraint branches described in Embodiment 1 is used as a module and placed on the connecting frame 10 and the rotating platform 11 . The rotary platform 11 can have various forms, such as: the rotary platform moves along the vertical direction, adjusts the working height of the two-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism, or the rotary platform rotates around the axis of its own column.
Embodiment 3
[0025] Referring to Figure 4, the two-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism with passive constraint branches described in Embodiment 1 is applied to a hybrid robot:
[0026] The two-degree-of-freedom parallel mechanism with passive restraint branches described in Embodiment 1 is fixed on the vertical sliding table 12, and the vertical sliding table 12 moves in the horizontal direction to expand the working range, and overcome the parallel problem by rationally planning the moving path of the vertical sliding table 12. There are disadvantages such as small working space and limited posture of the mechanism.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com