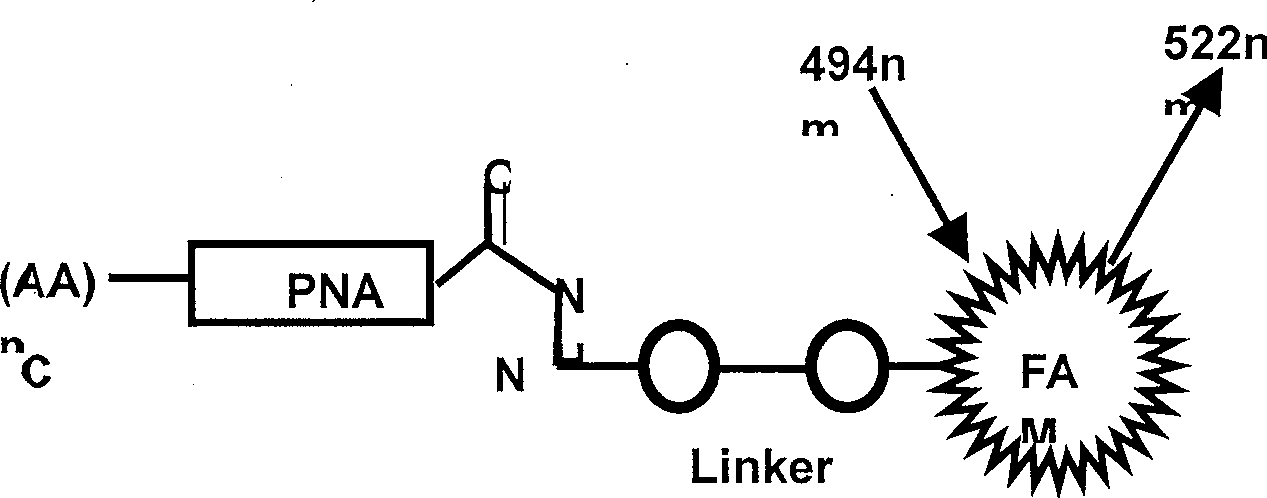
PNA probe for detecting red tide organism Takayama pulchellum and its uses
A technology of Gymnodinium and peptide nucleic acid, which is applied to the application field of low-abundance single target red tide algae cells, and can solve the problems such as the use of PNA probes that are not seen.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
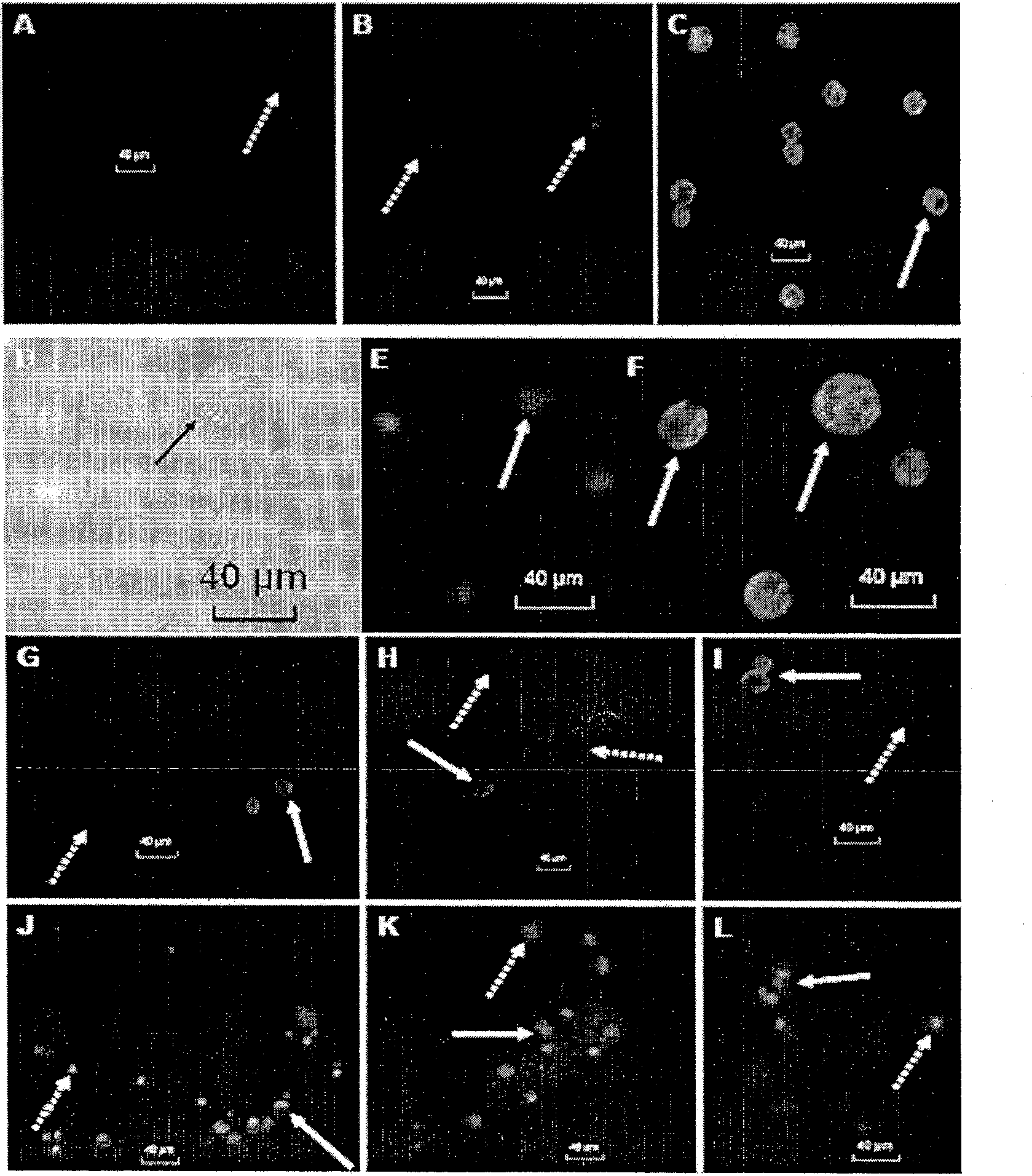
[0047] Example 1: Whole cell fluorescence in situ hybridization detection of T. pulchellum pure algal cells and other algae for cross experiments.
[0048] 1. Sources and culture methods of all testing materials:
[0049] On-site sample collection method: collect 5-10L seawater with a water collector, filter and concentrate with 10μm sieve, reduce the water volume to 100-200mL, measure the volume, and add 1 / 10 volume of paraformaldehyde ( 10%), the final concentration was 1%, and counted by microscopy. Use a capillary glass tube or a 10 μl micropipette to separate live cells from freshly collected unfixed samples to pick out multiple single cells of the target algae under a stereo microscope (according to the situation, pre-filter with sieve or add f / 2 medium pre-culture), placed in a multi-well cell culture plate, observed under microscope and added to f / 2 medium for culture. cultured in culture flasks. The algae that have been separated and can grow normally are filtered...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Example 2: Comparison of hybridization effects between PNA probes and DNA probes.
[0059] 1. Testing materials:
[0060] The names and sources of the algal cell strains used in the experiment are shown in Table 3. For the cultivation method, see item 1 of Example 1 for details.
[0061] 2. Detection method:
[0062] See item 2 of Example 1 for details. The quantitative analysis of the fluorescence signal intensity of in situ hybridization of DNA and PNA probes was performed using the Simple PCI professional image analysis software system of C-image Company.
[0063] 3. Results:
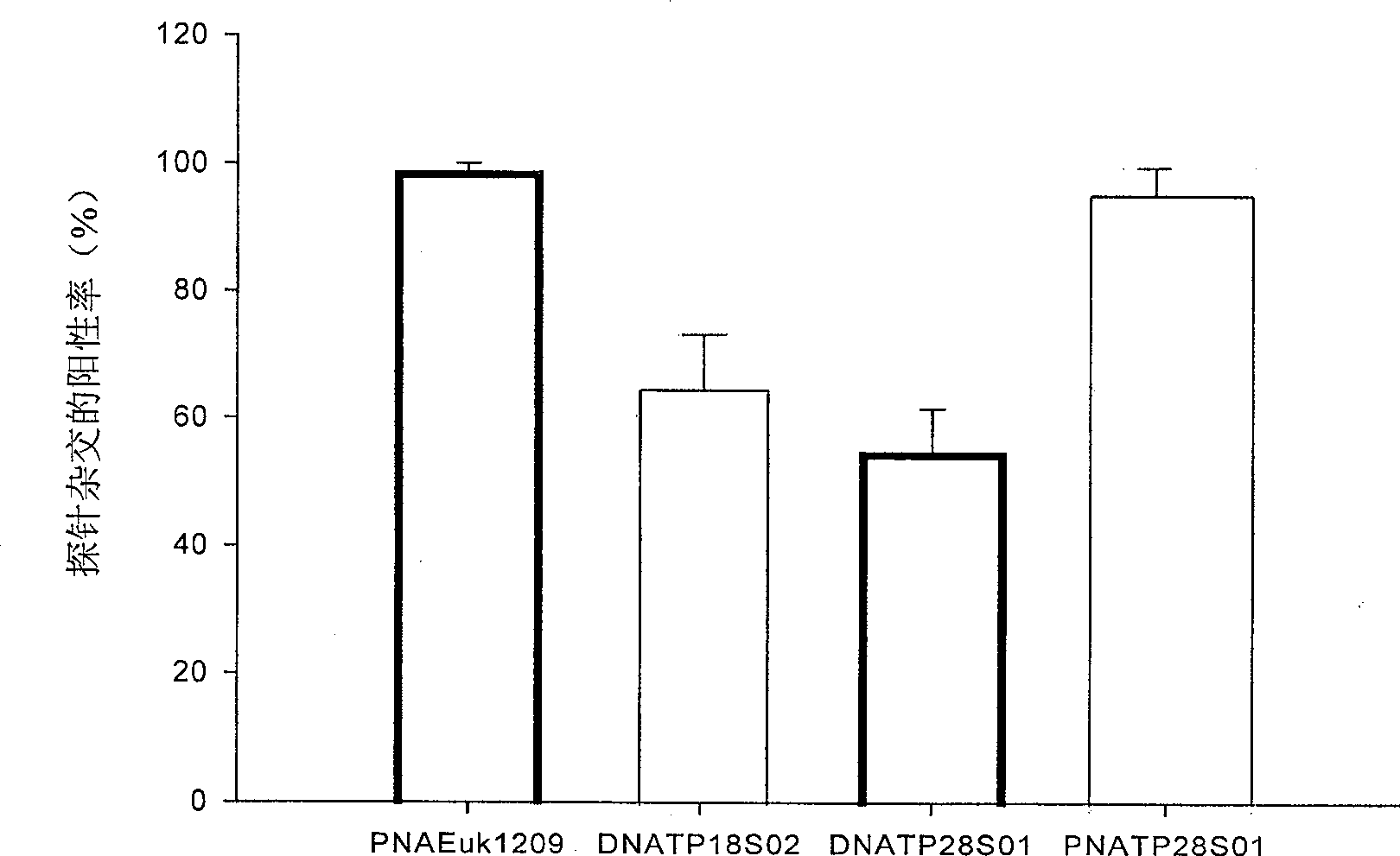
[0064] Under the same probe concentration, comparing the hybridization efficiency and fluorescence intensity after hybridization of the DNA probe DNATP18S02 with the highest hybridization rate and the DNA probe DNATP18S02 with a similar sequence to the PNA probe, it was found that under the same hybridization conditions, the PNA The hybridization rate (95%) of the probe was significantly h...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Example 3: Whole-cell fluorescent hybridization detection of mixed algal species samples with fluorescently labeled PNA probes.
[0069] 1. Testing materials:
[0070] The names and sources of the algal cell strains used in the experiment are shown in Table 3. For the cultivation method of algae, refer to the first clause of embodiment 1.
[0071] 2. Detection method:
[0072] For details, see Article 2 of Example 1.
[0073] 3. Results:
[0074] Mixed samples I (Mixed samples I) are composed of Heterophyta akashiwo, Stigneria conicerii, Dunaliella salina, Chrysopsis zhanjiangensis, Sclerostenella mesospergiae and Thalassiosira wischii. Mixed samples II (Mixed samples II) consisted of Prorodinium minutiae, Alexandrium minutis, Prorocentrum donghaiense, Karenia mikii and Gymnodinium brevis. In the two mixed samples, about 1 / 5 of the mixed volume of the target algae cell culture liquid was added and mixed with natural seawater to simulate the sample characteristics o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com