Method for improving zero bias temperature sensitivity of optical fiber gyroscope
A temperature sensitivity, fiber optic gyroscope technology, applied in Sagnac effect gyroscopes and other directions, can solve the problems of high power consumption, unapplied, complex structure, etc., to eliminate the zero offset change and improve the temperature sensitivity performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and embodiment the present invention will be further described:
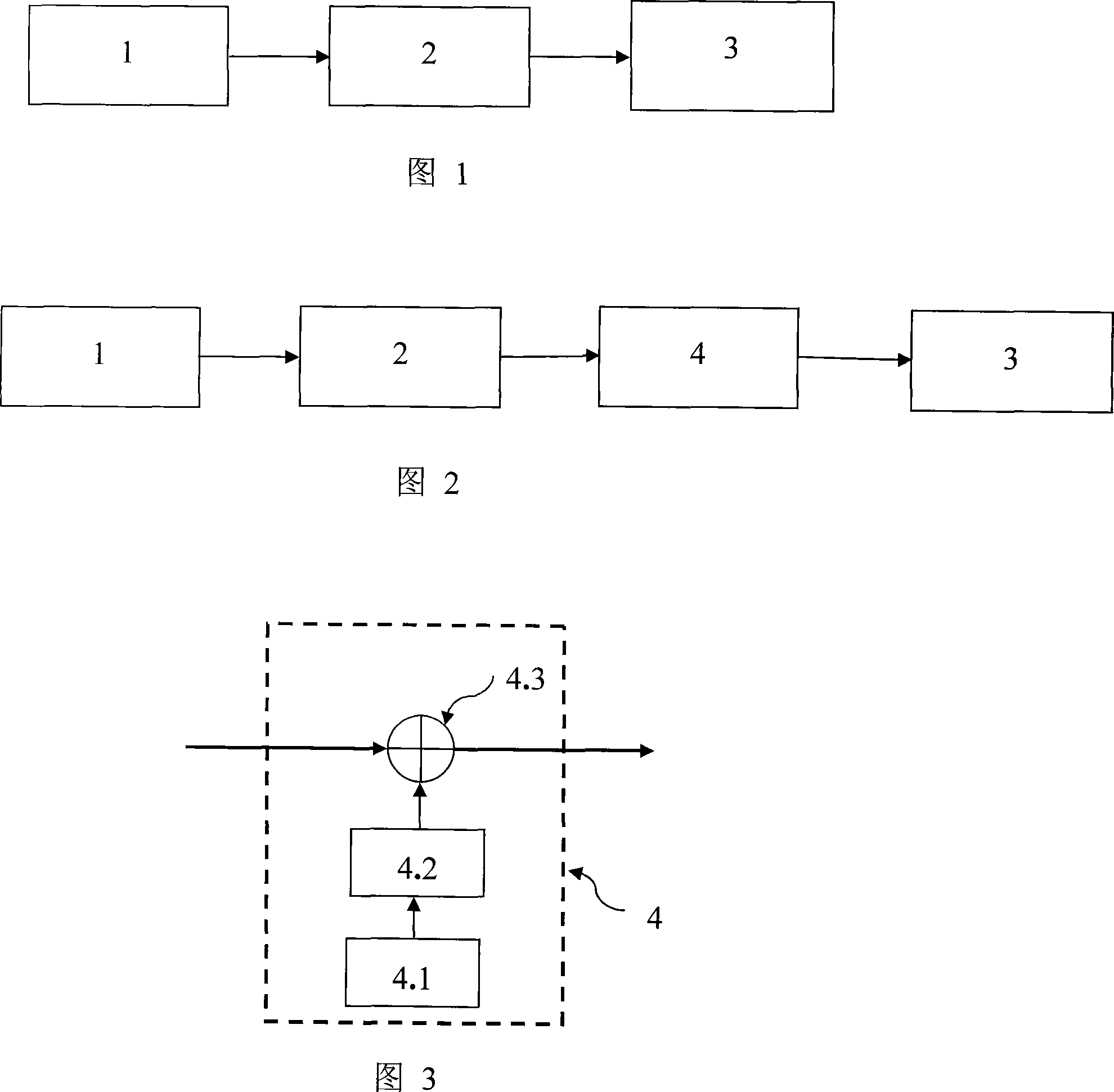
[0031] Figure 1 shows the signal processing structure of the fiber optic gyroscope without a compensator, which includes three parts: sampling channel 1, central processing unit 2 and communication interface 3, where sampling channel 1 realizes the conversion of the optical signal from the optical fiber gyroscope optical system into The electrical signal is sent to the central processing unit 2, and the central processing unit 2 performs demodulation, filtering and other calculations after receiving the signal from the sampling channel 1 to obtain the speed of the system where the fiber optic gyroscope is located, and sends the speed to the communication interface 3, through Communication interface 3 is uploaded to the host computer.
[0032] Figure 2 shows the structure of the fiber optic gyroscope signal processing part after adding the compensator, which i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com