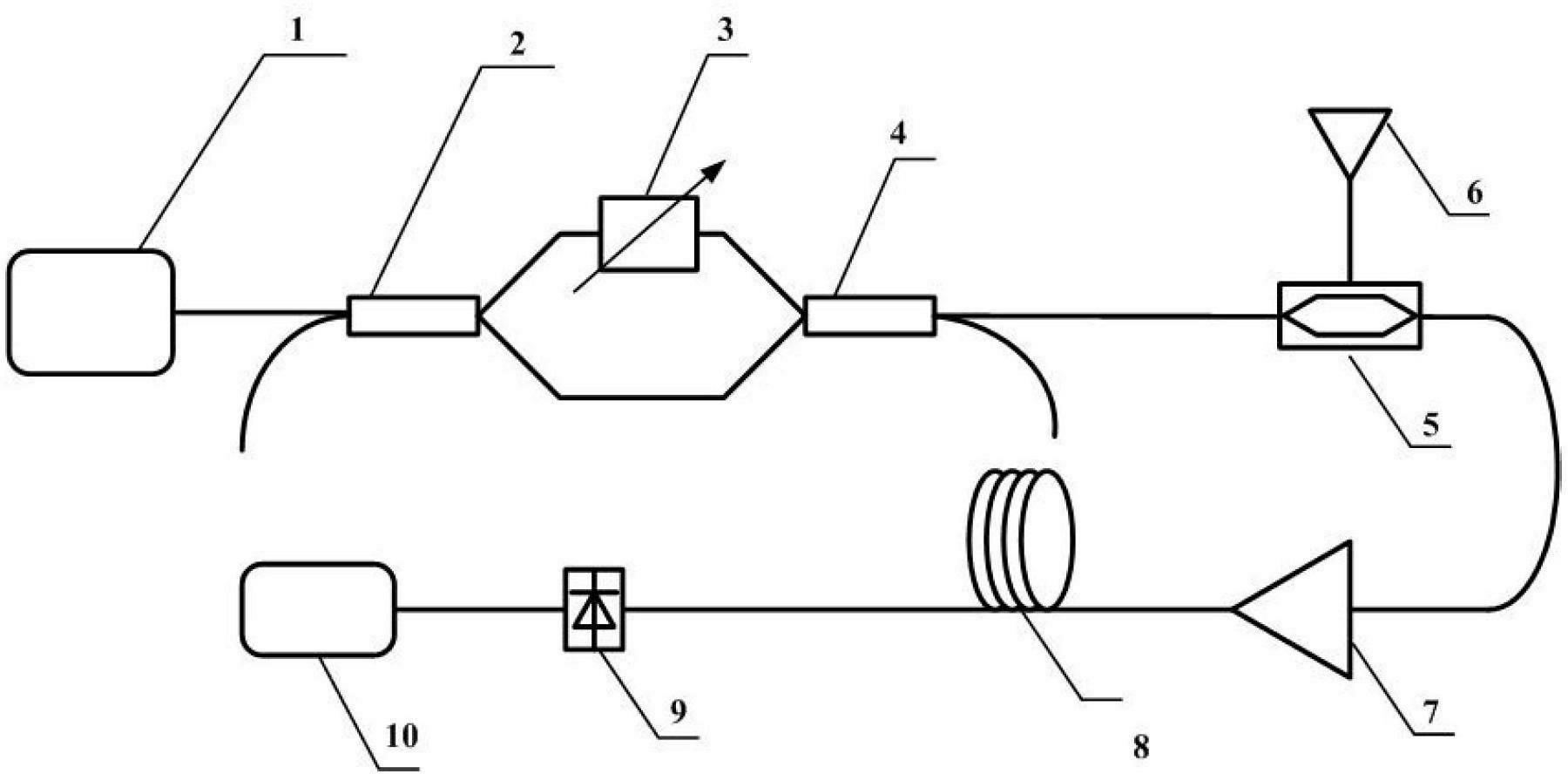
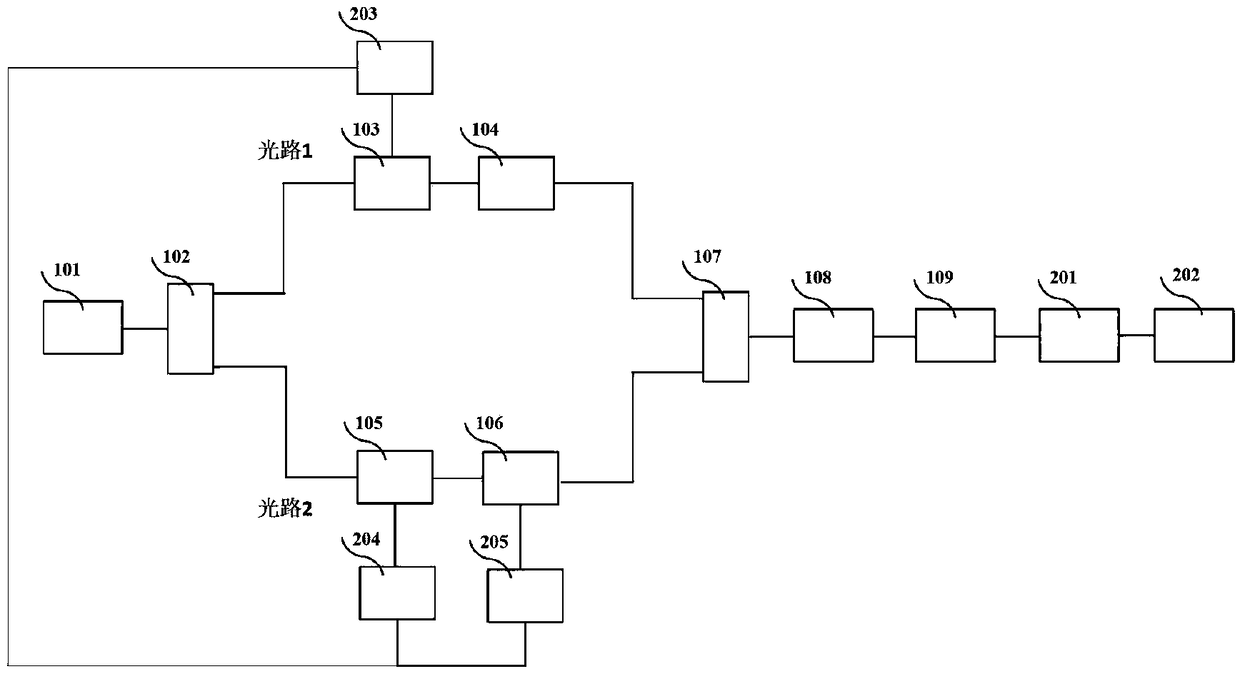
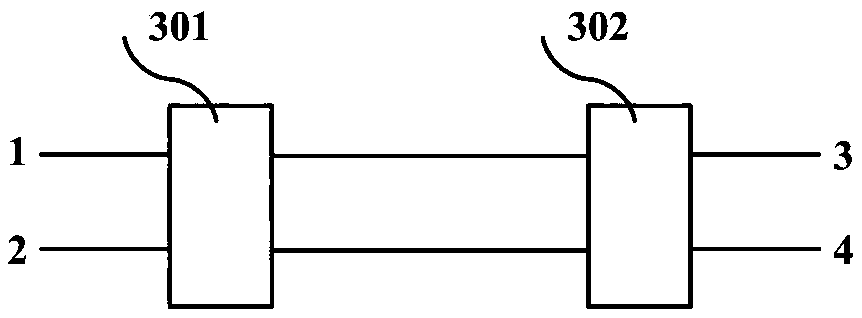
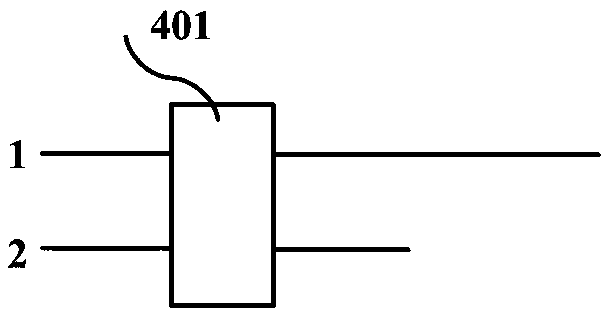
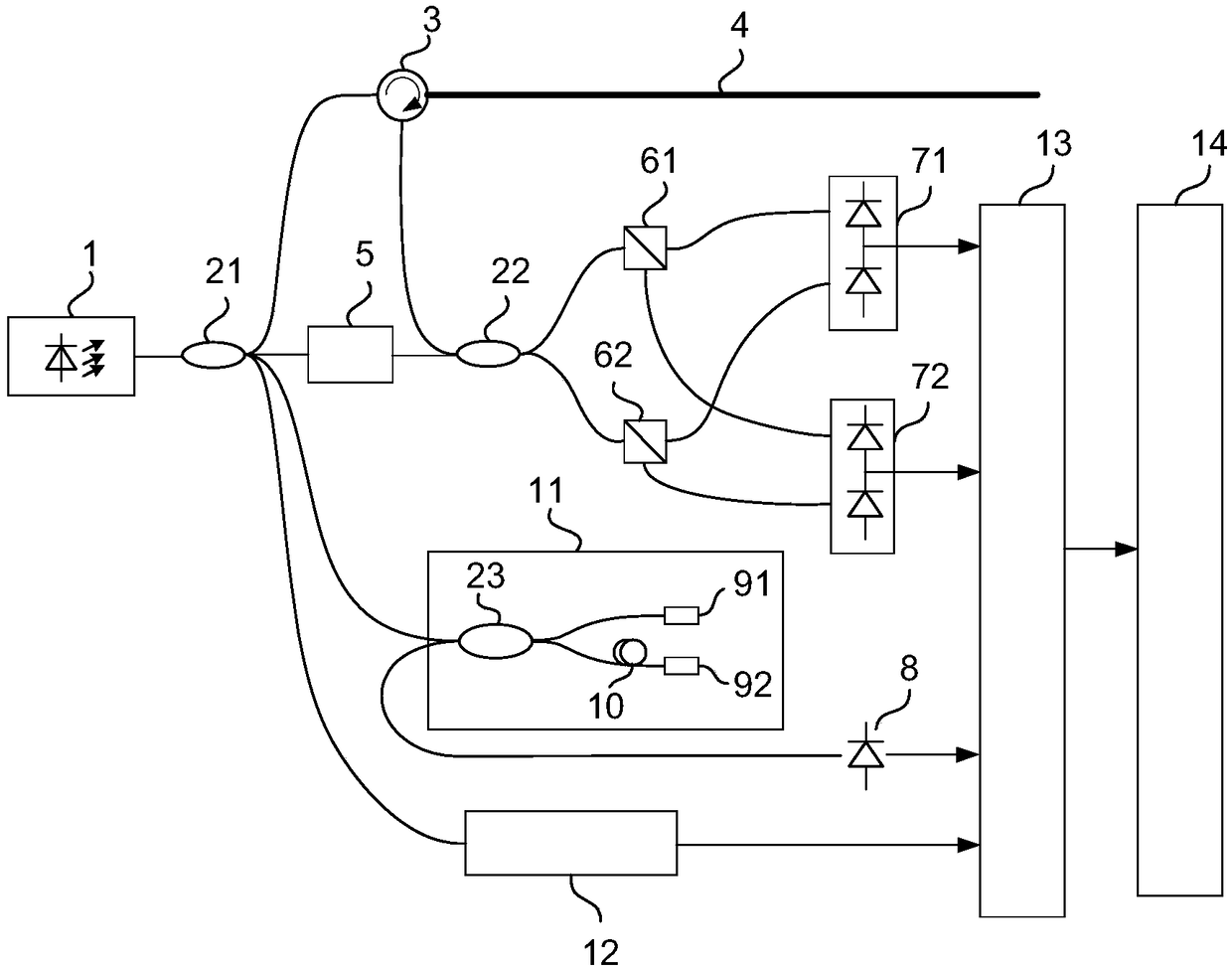
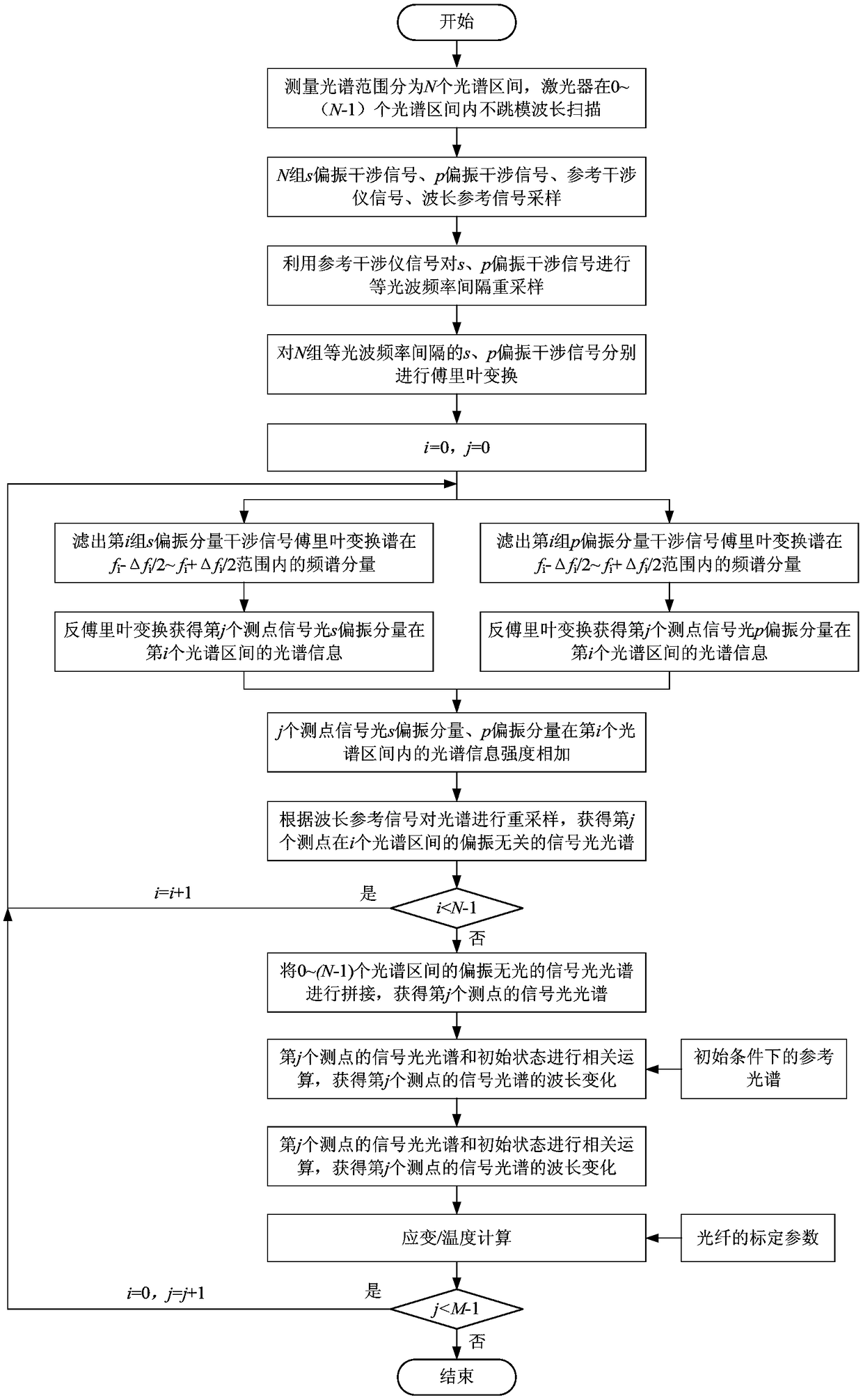
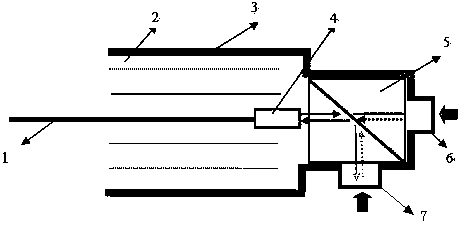
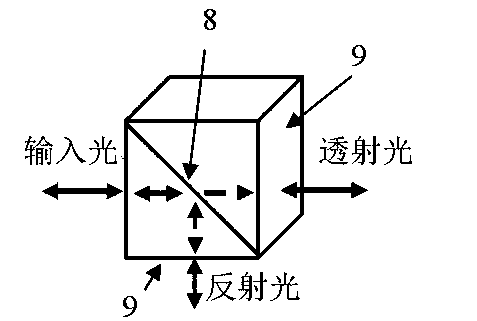
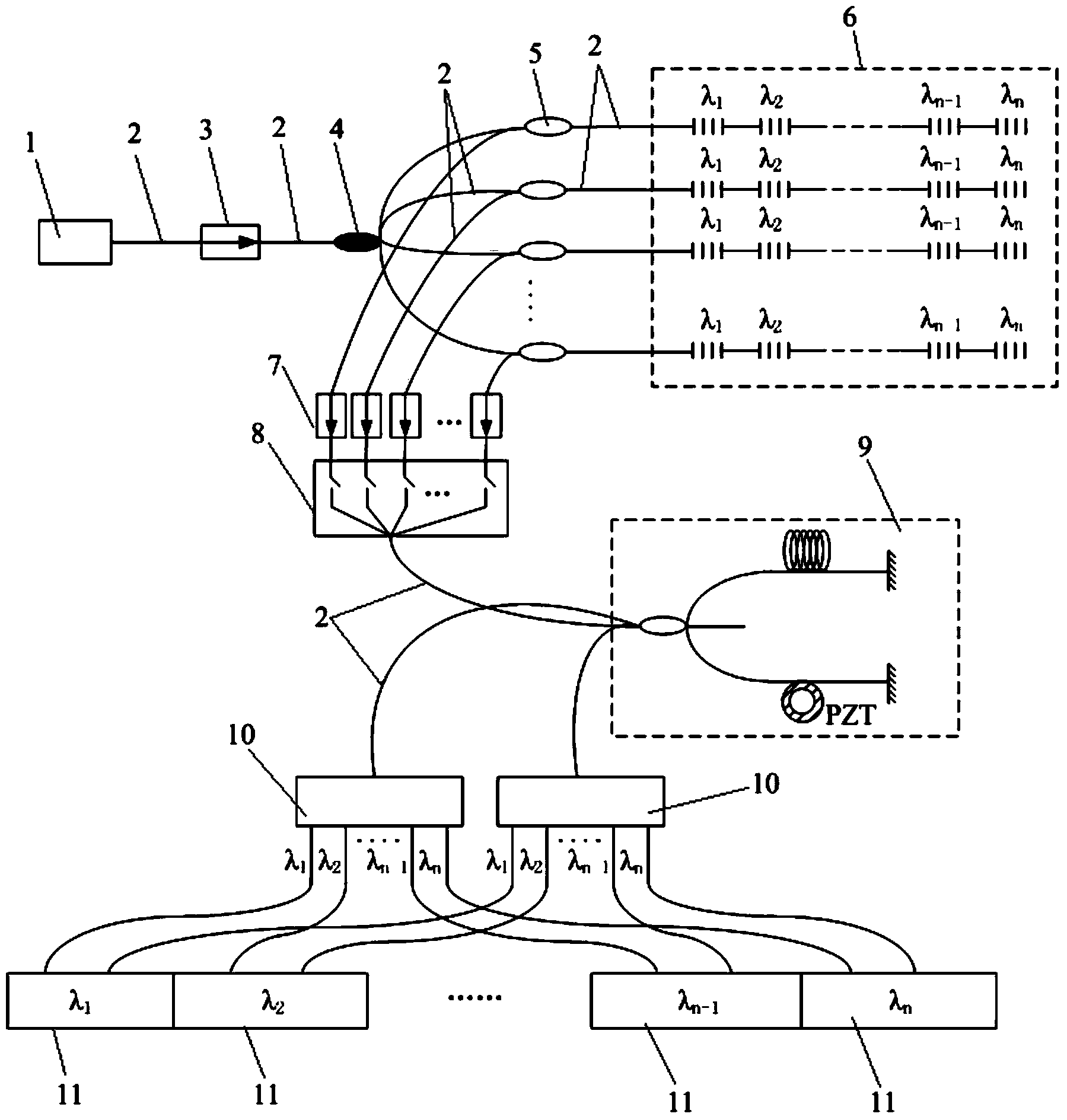
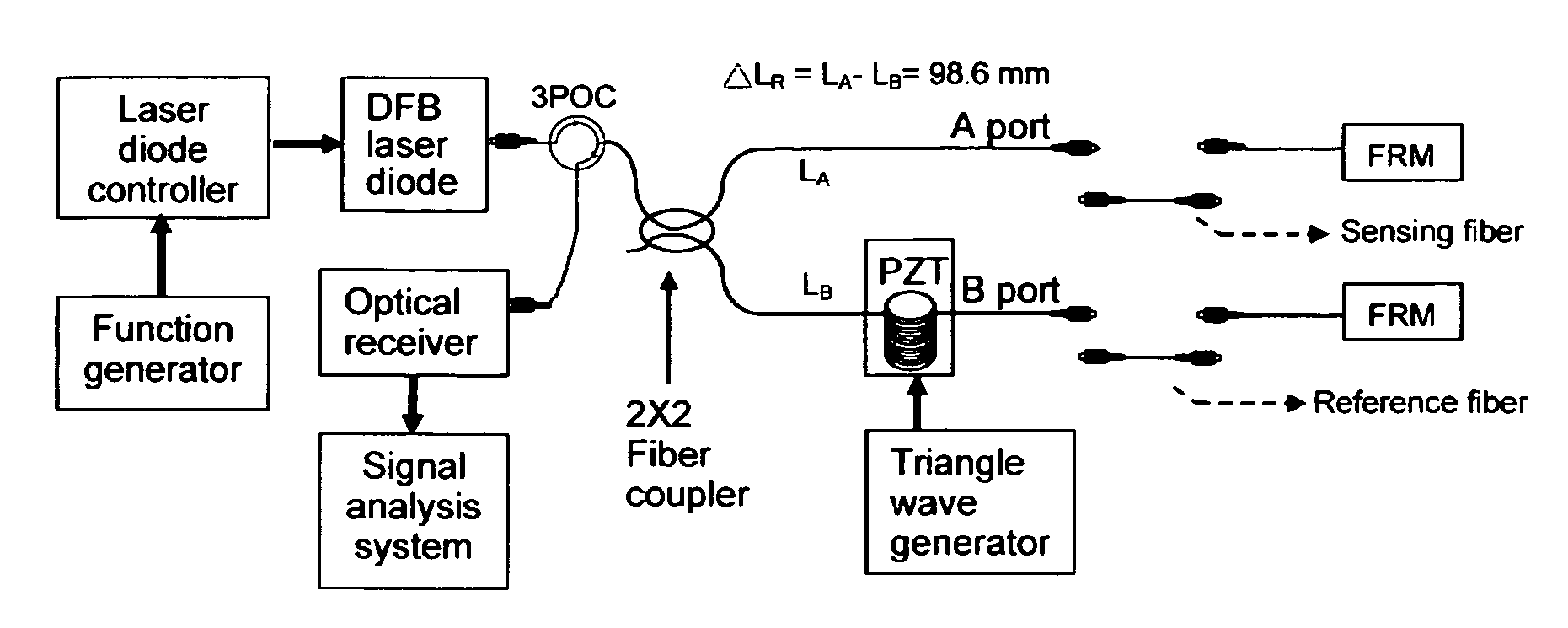
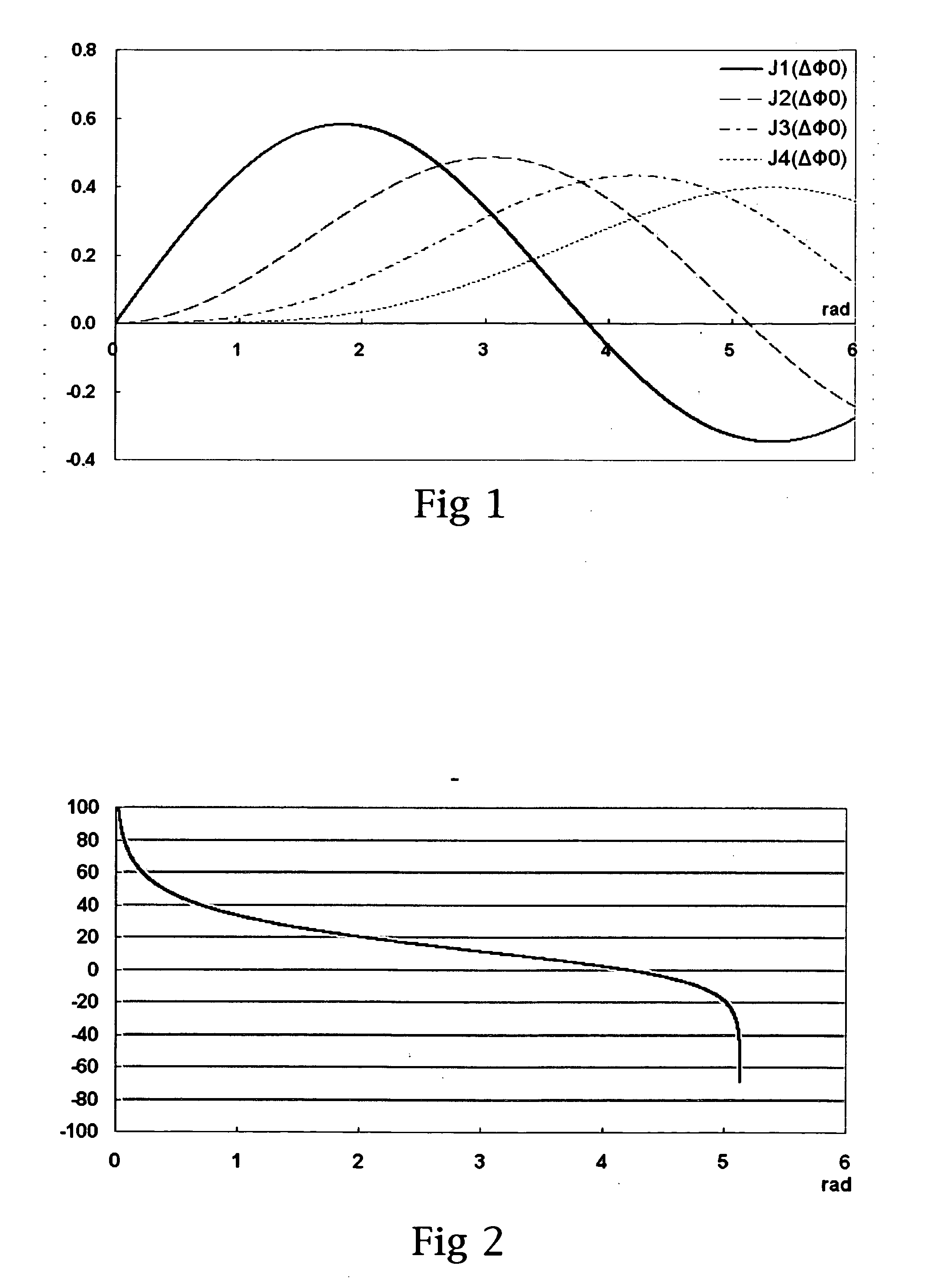
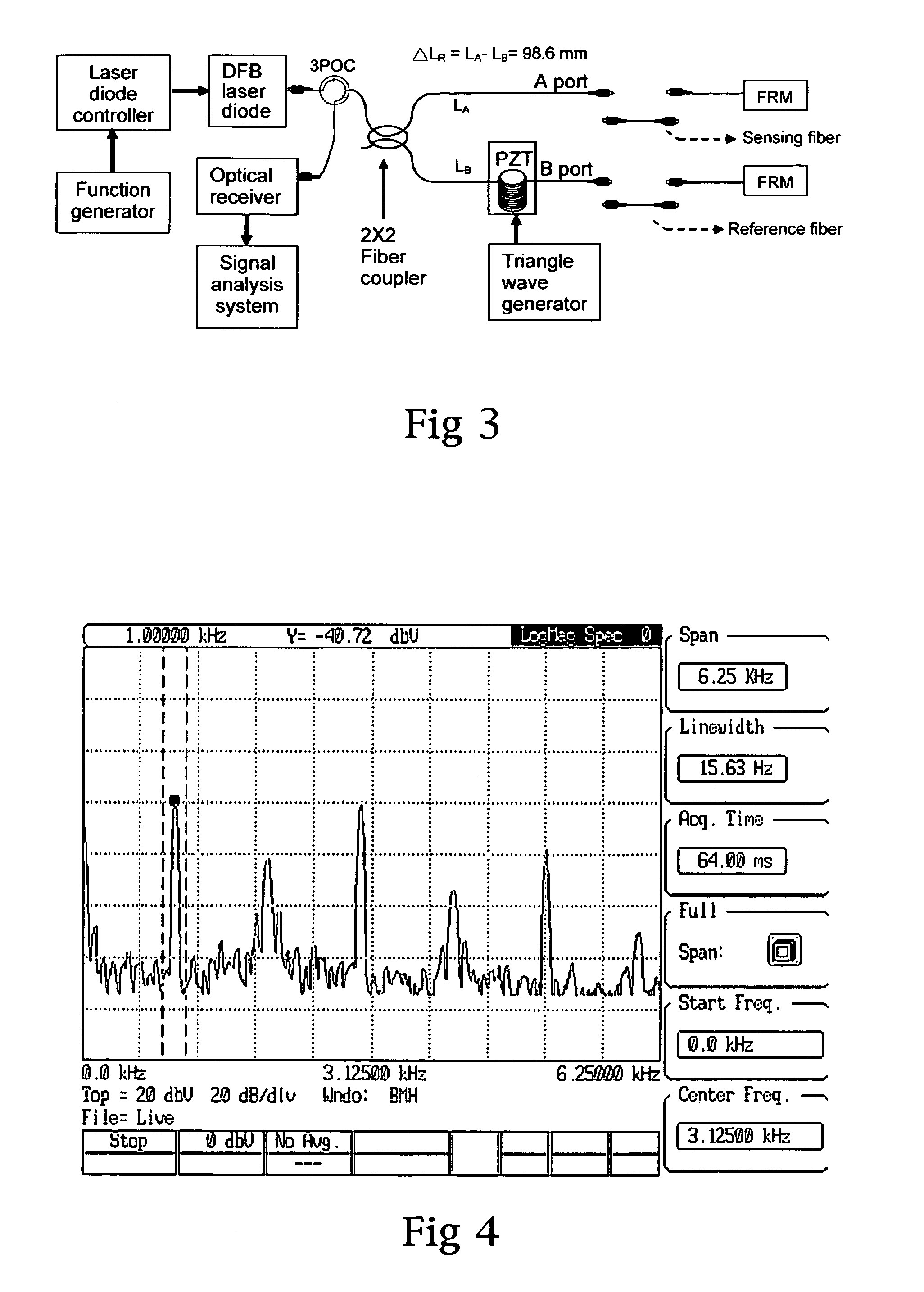
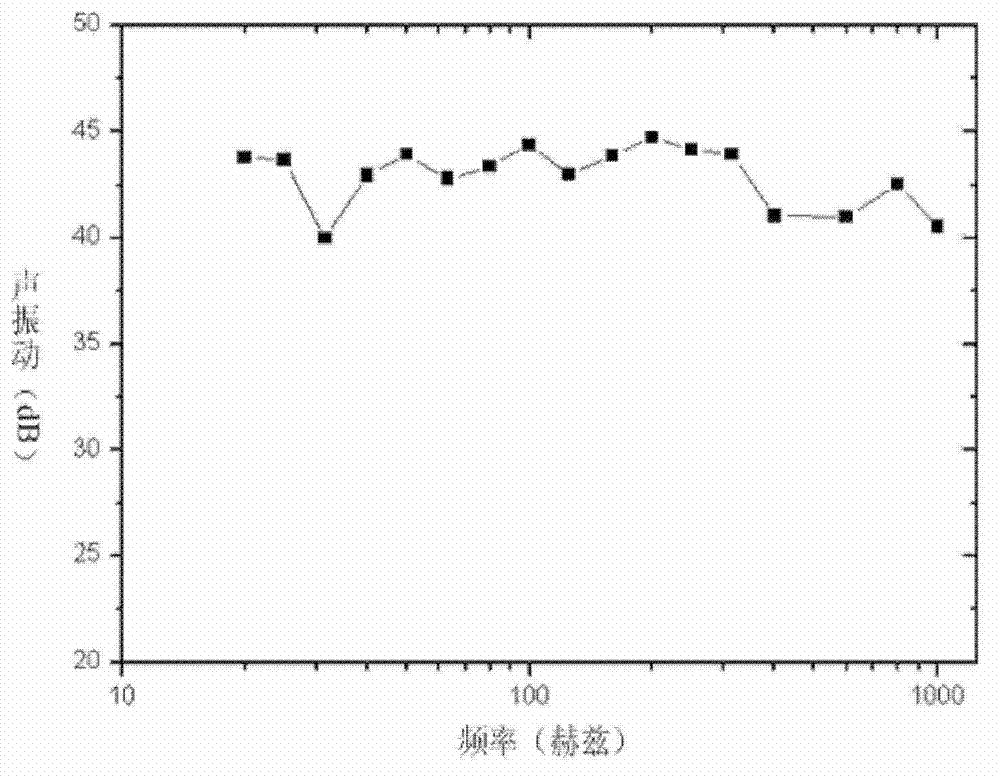
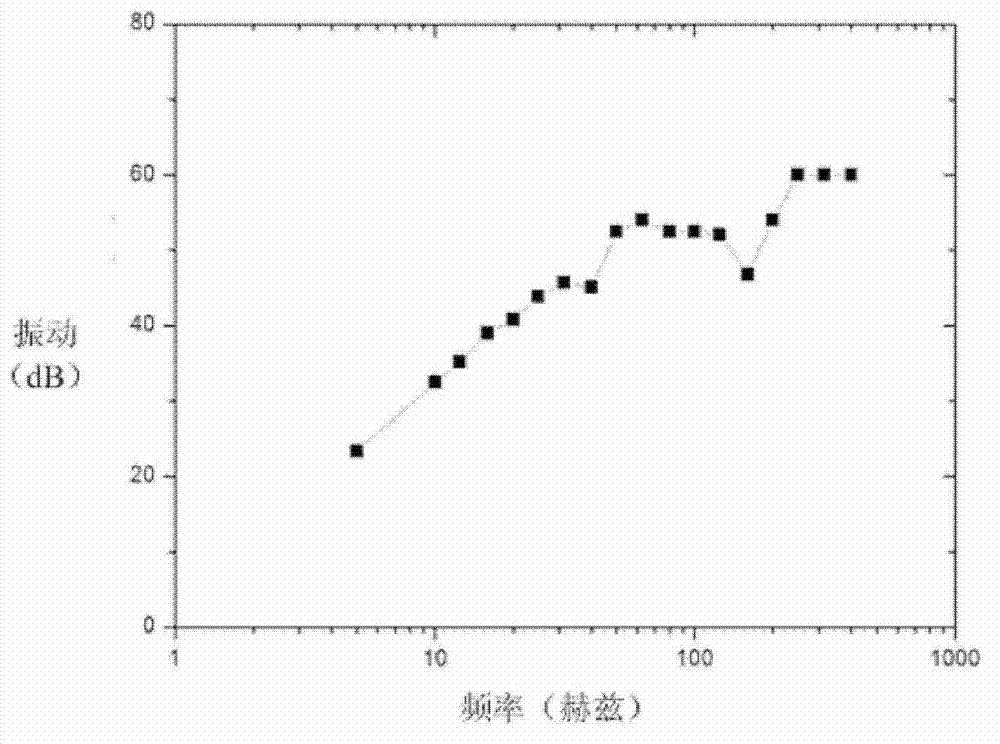
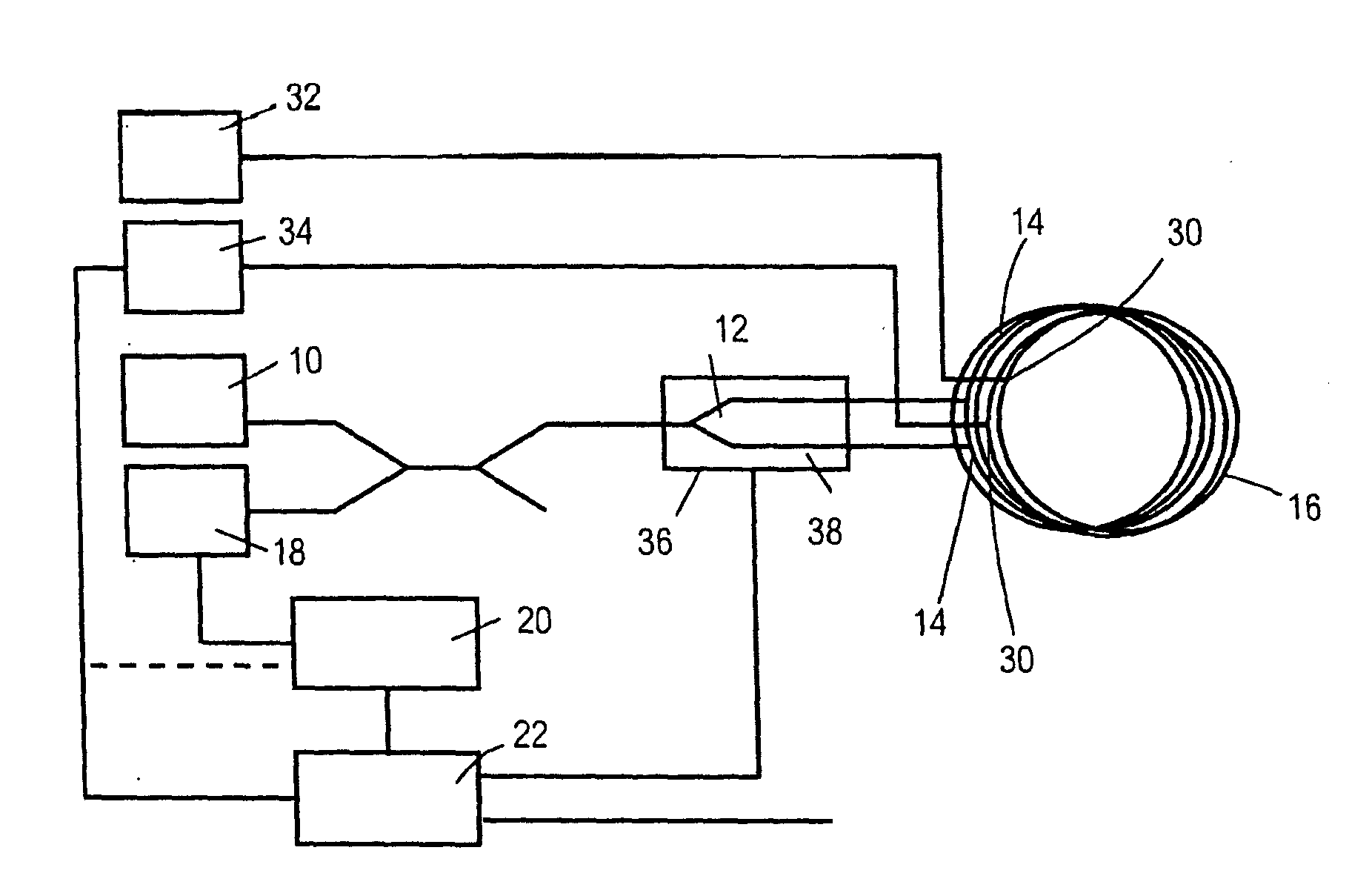
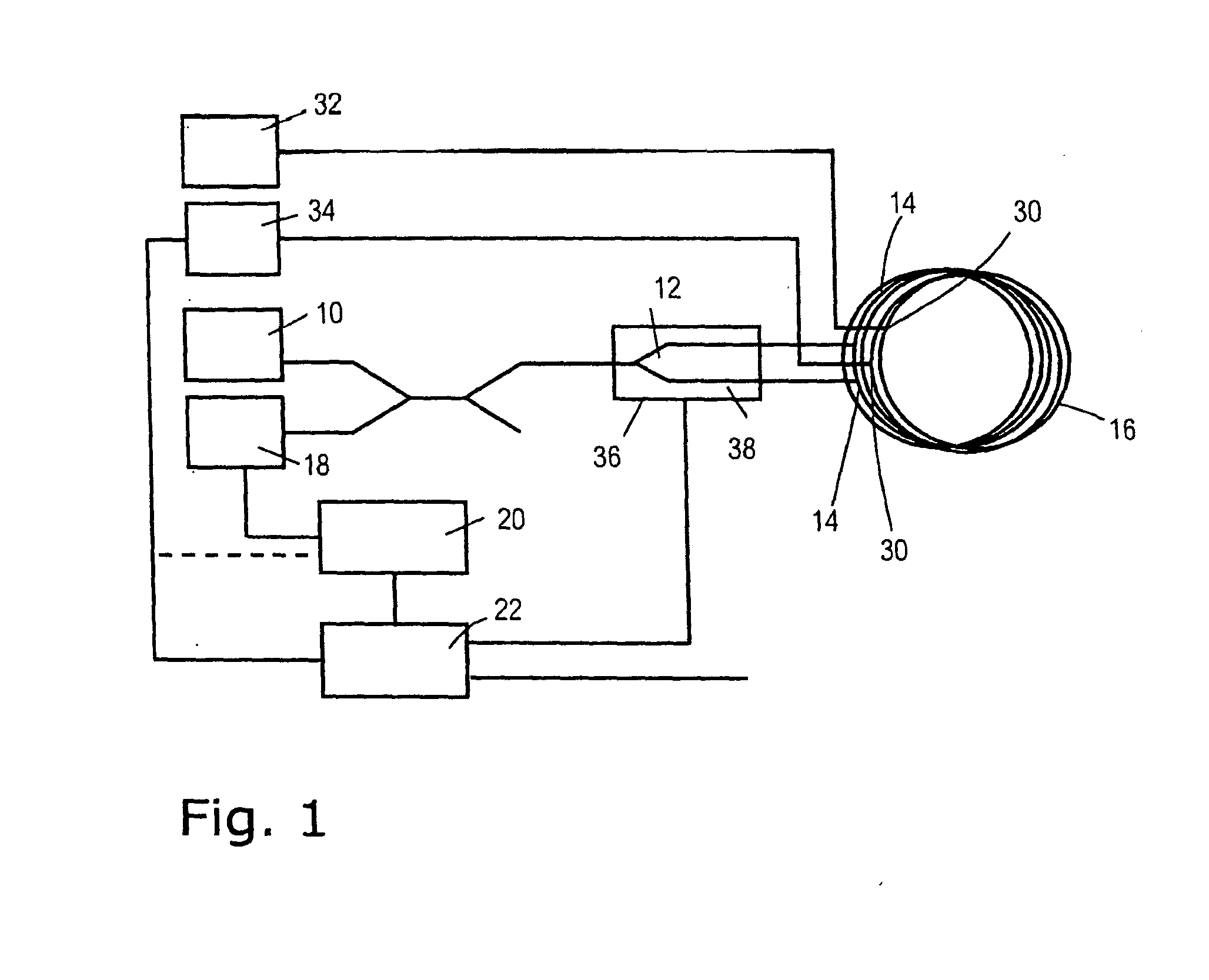
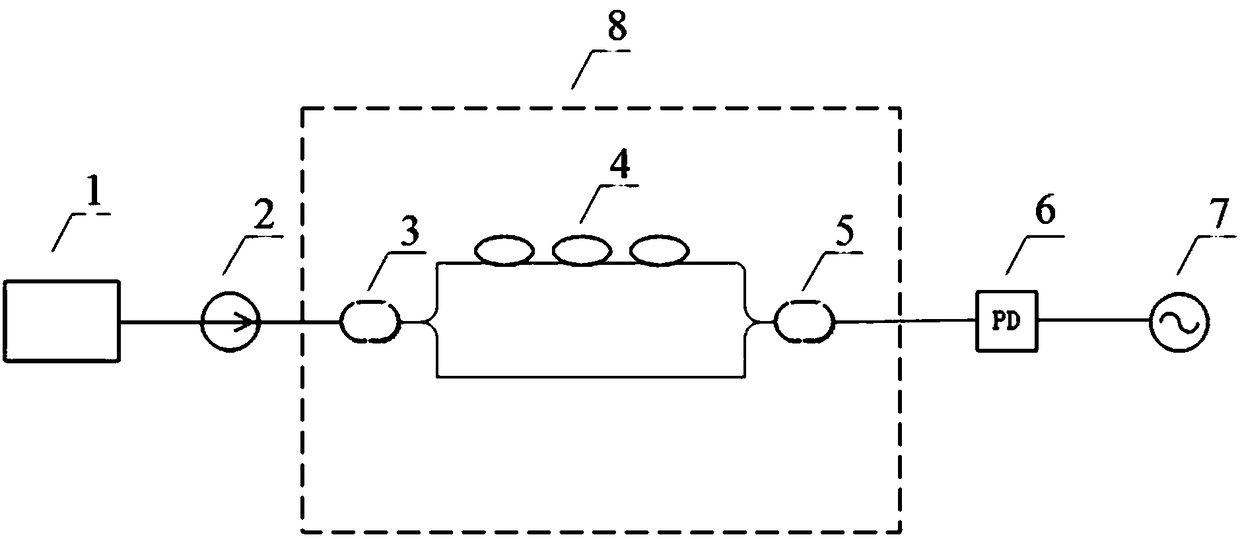
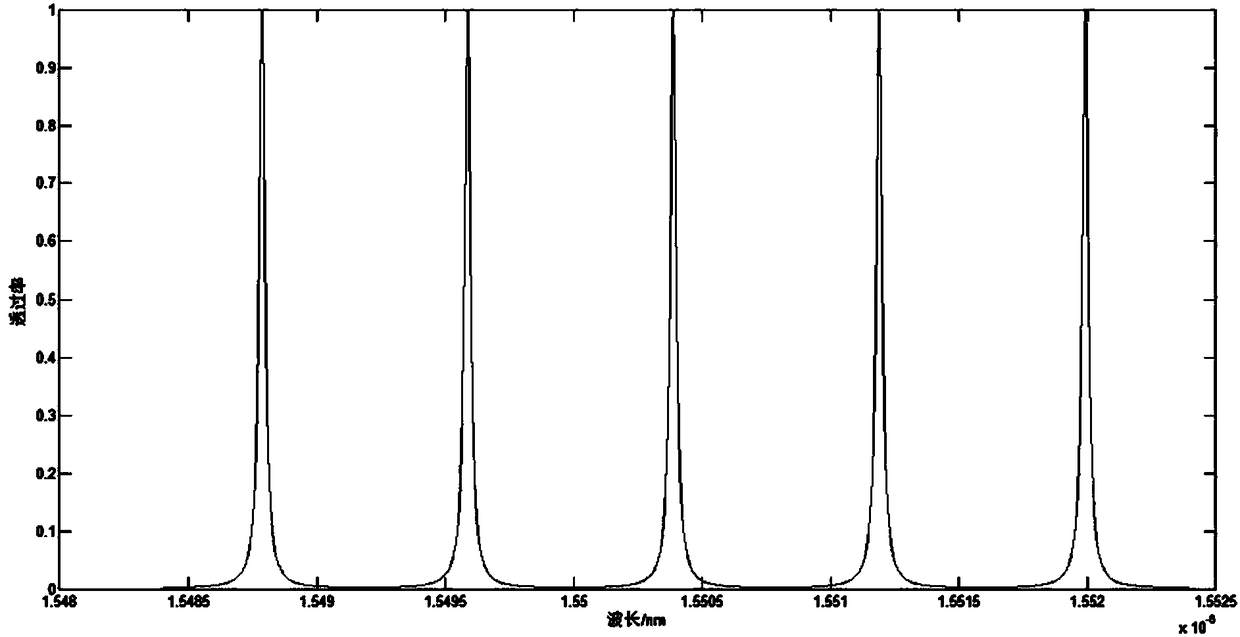
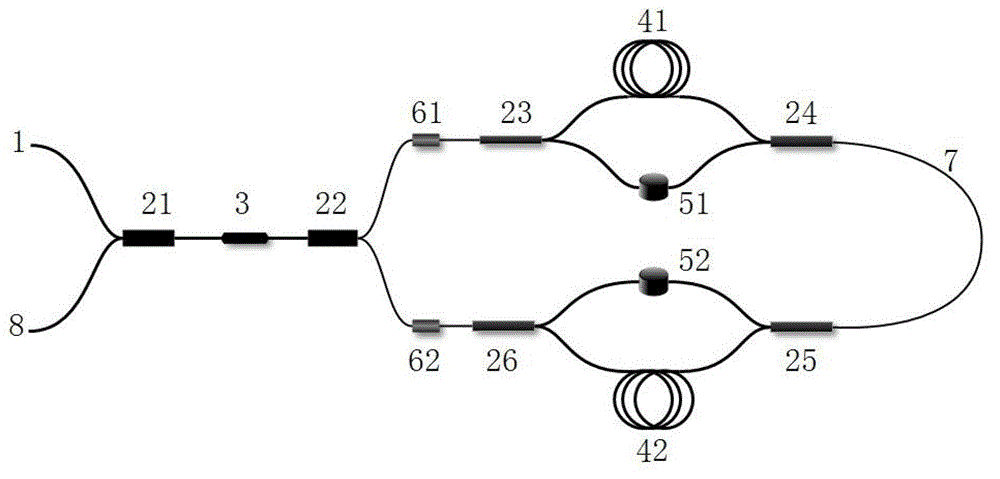
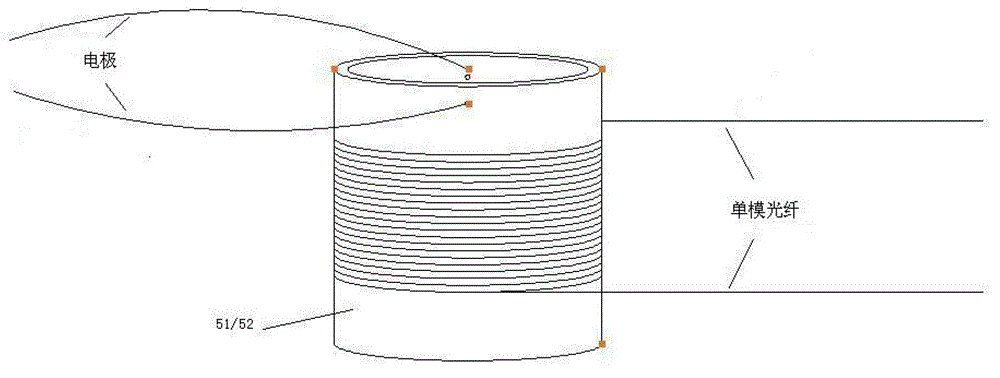
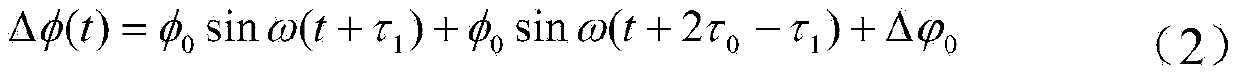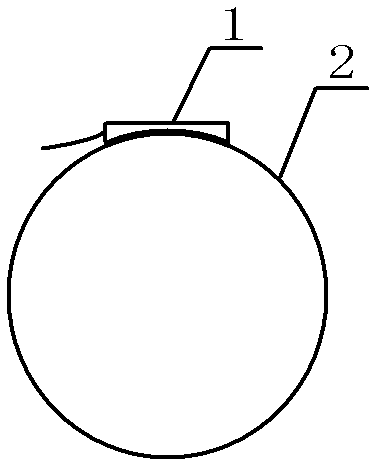Patents
Literature
71 results about "Fiber optic interferometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Non-contact micro-vibration measuring system based on non-equilibrium Michelson fiber-optic interferometer
InactiveCN102564564AHigh sensitivityLarge dynamic rangeSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansFiberCarrier signal
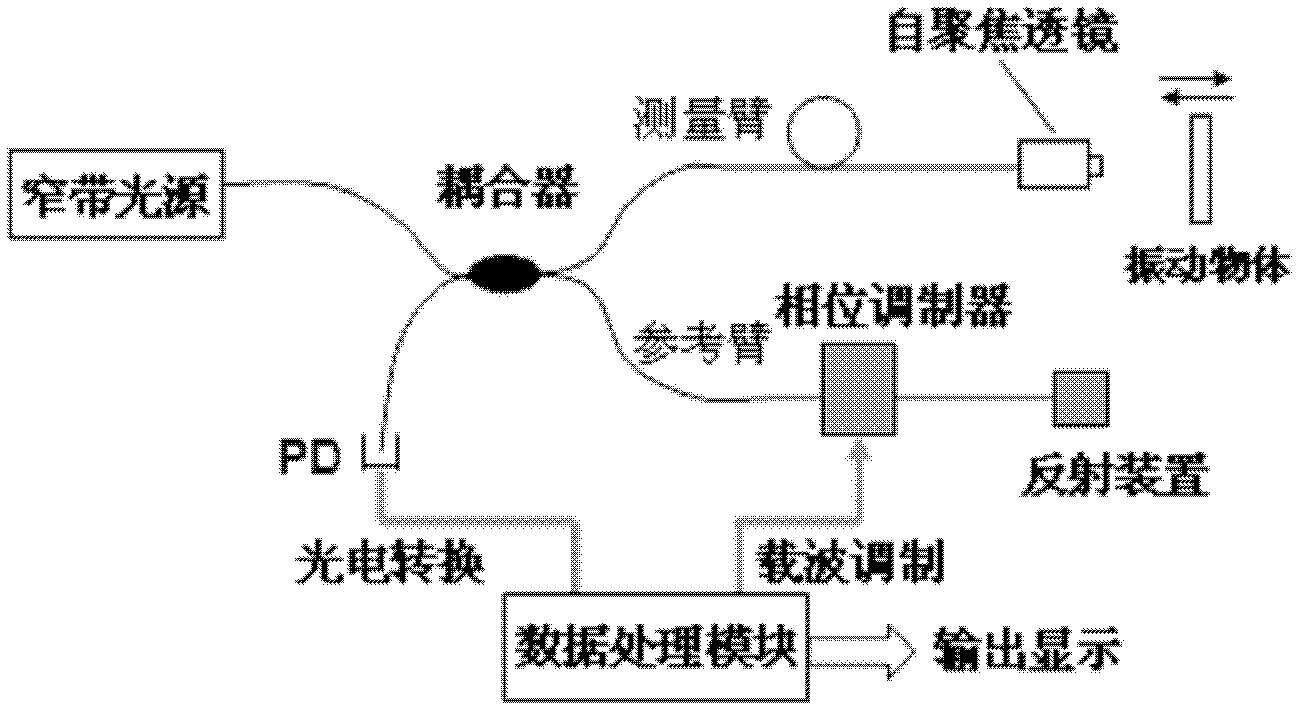
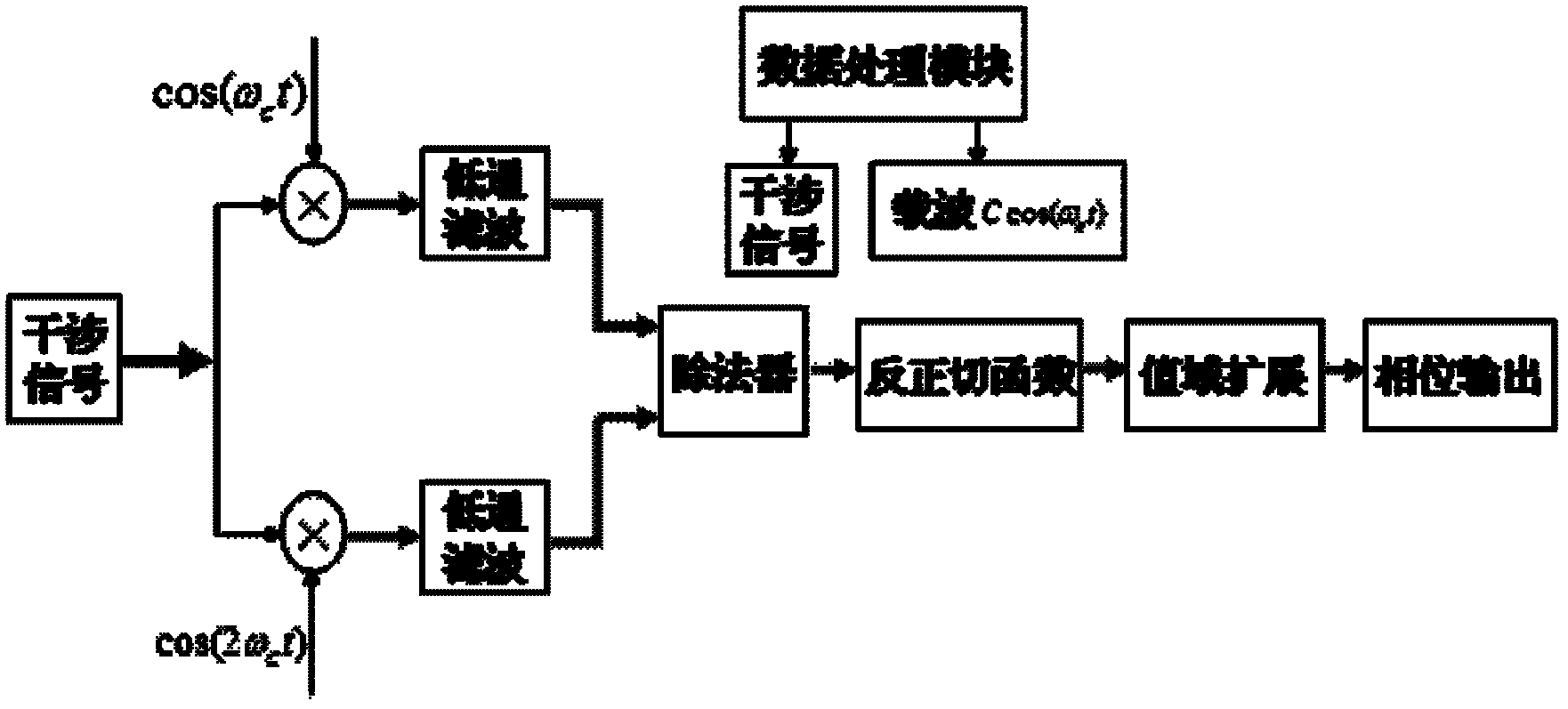
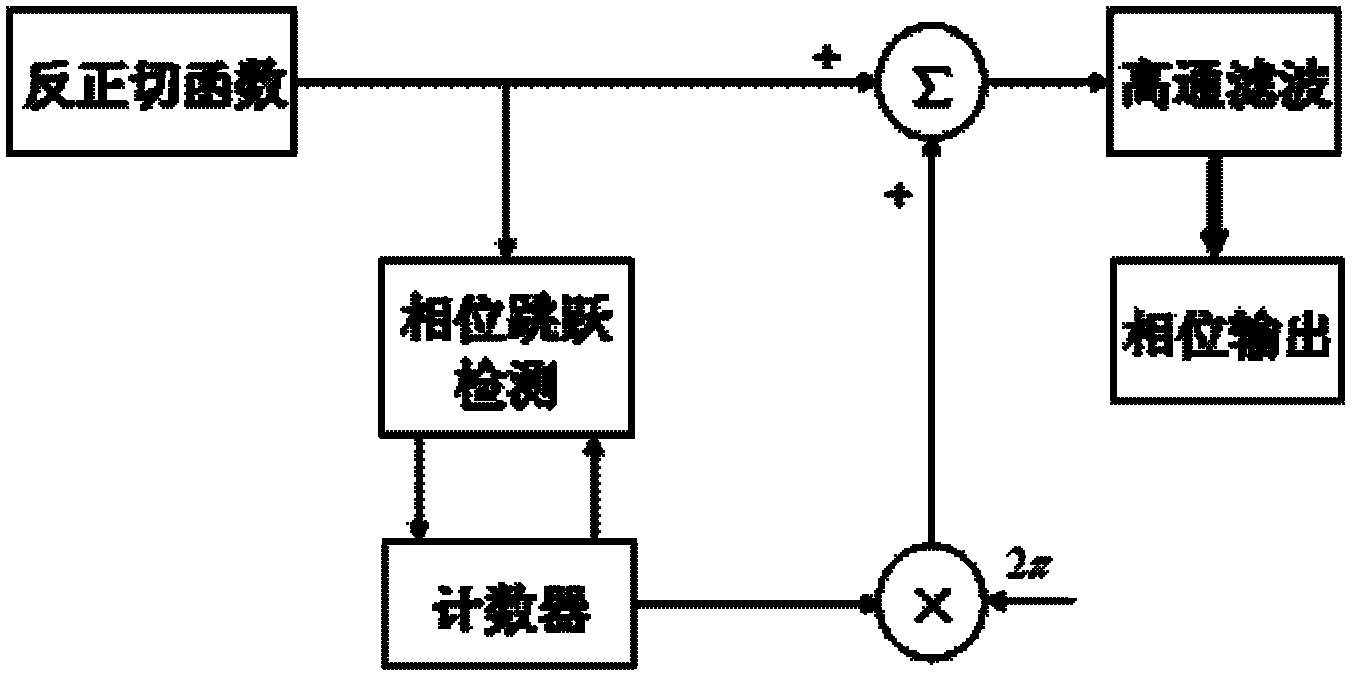
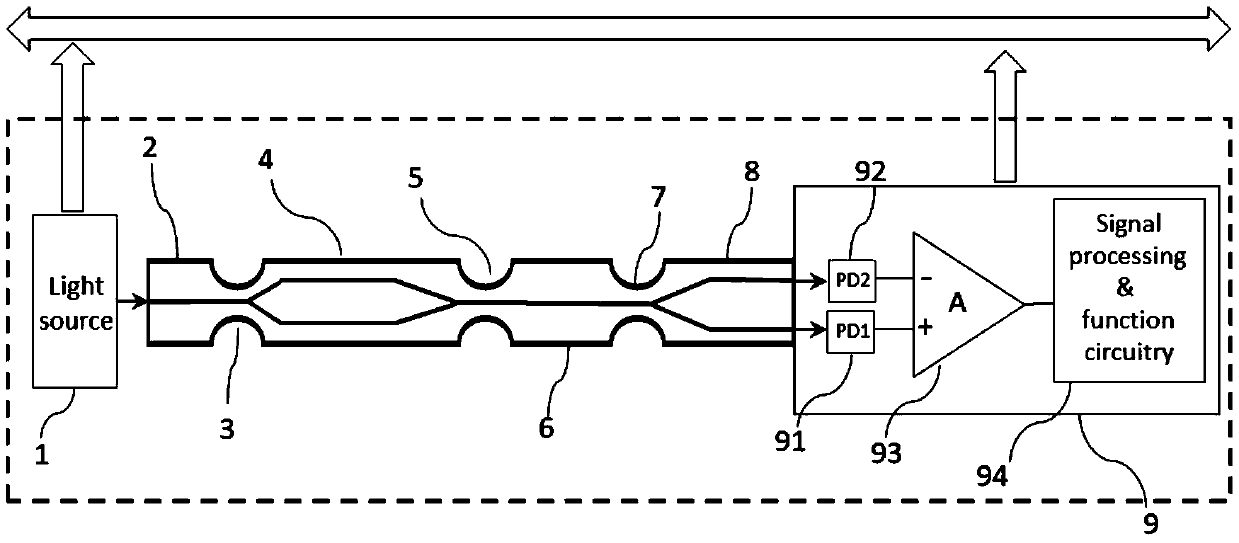
The invention discloses a non-contact micro-vibration measuring system based on a non-equilibrium Michelson fiber-optic interferometer, which belongs to the technical field of fiber-optic sensing. The non-contact micro-vibration measuring system is characterized in that lights pass through a narrow-band light source, a coupler and the non-equilibrium Michelson fiber-optic interferometer in sequence, wherein one path of the lights irradiates to the surface of an object vertically by an optical-fiber self-focusing lens, then returns and is coupled into optical fiber; the other path of the lights is returned by a reflecting device at the tail end of the optical fiber of a reference arm; the two paths of lights pass through the coupler, a photoelectric coupler (PD) and a data processing module; simultaneously, the data processing module generates carriers waves to control a phase modulator on an interference arm; and finally, a result is obtained by a phase demodulation technology of a phase generation carrier (PGC) based on calculation of arc tangent (ARCTAN). The non-contact micro-vibration measuring system has the beneficial effects that due to the adoption of the combination of the Michelson fiber-optic interferometer and the phase generation carriers based on calculation of the arc tangent, the flexibility is high, the response is good, no influence by factors of light intensity and visibility drifting is caused, and the online measurement on non-contact micro-vibration can be realized.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Single-response microwave photonic filter-based frequency measurement device and measurement method
ActiveCN102636694AMeasured forRealize detectionFrequency analysisMeasurement deviceFrequency measurements
The invention discloses a single-response microwave photonic filter-based frequency measurement device and a measurement method, and relates to a frequency measurement device and method. The frequency measurement device is provided with a broadband light source, a Mach-Zehnder fiber optic interferometer, an electro-optical modulator, an optical fiber amplifier, a microwave antenna, a dispersion optical fiber, a photo detector and an electrodynamic meter. A tunable single-response microwave photonic filter can be realized by using a structure based on combined Mach-Zehnder fiber optic interferometer spectral division and dispersion optical fiber; the transmission peak frequency position of the single-response microwave photonic filter is adjusted by scanning an adjustable delay line of the optical fiber; and the detection of the frequency of a measured microwave signal is realized by restoring measurement of electric signal power through the photo detector. The microwave electronic filter has an incoherent filter structure; and meanwhile, the detection of a multi-frequency microwave signal is realized through quick length scanning of the adjustable delay line. Remote high-frequency microwave signal frequency measurement of electromagnetic interference can be realized.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Device for measuring arm length difference of fiber optic interferometer
PendingCN108827601AImprove stabilityHigh measurement accuracyTesting optical propertiesTesting fibre optics/optical waveguide devicesFiber couplerPolarization-maintaining optical fiber
The invention relates to a device for measuring the arm length difference of a fiber optic interferometer, and mainly solves a problem that a measurement system employing an optical interference method is not high in stability and is low in measurement precision. The device provided by the invention comprises a narrow linewidth laser, a polarization-maintaining fiber coupler, a phase modulator, apolarization state controller, an acousto-optic frequency shifter, a fiber coupler, a to-be-tested fiber optic interferometer, a photoelectric detector, a frequency spectrograph, a signal processing and display module and a microwave signal generator. The device carries out the interference in microwave domain through a double optical frequency comb, and measures an interference signal by using the frequency spectrograph. The device can obtain the arm length difference of the to-be-tested fiber optic interferometer by the bandwidth of the interference signal in one cycle, and can achieve the measurement of the precision changes through changing the frequency interval of the optical frequency comb, thereby improving the measurement accuracy and the stability of the system, and ironing out the defect that a method employing optical interference cannot achieve the measurement of the arm length difference. The device is simple in workflow is simple and is high in generalizability.
Owner:苏州维创度信息科技有限公司
Improved phase generated carrier (PGC) demodulation method
ActiveCN105157733AImprove phase resolutionLarge dynamic rangeConverting sensor output opticallyCarrier signalFiber optic interferometer
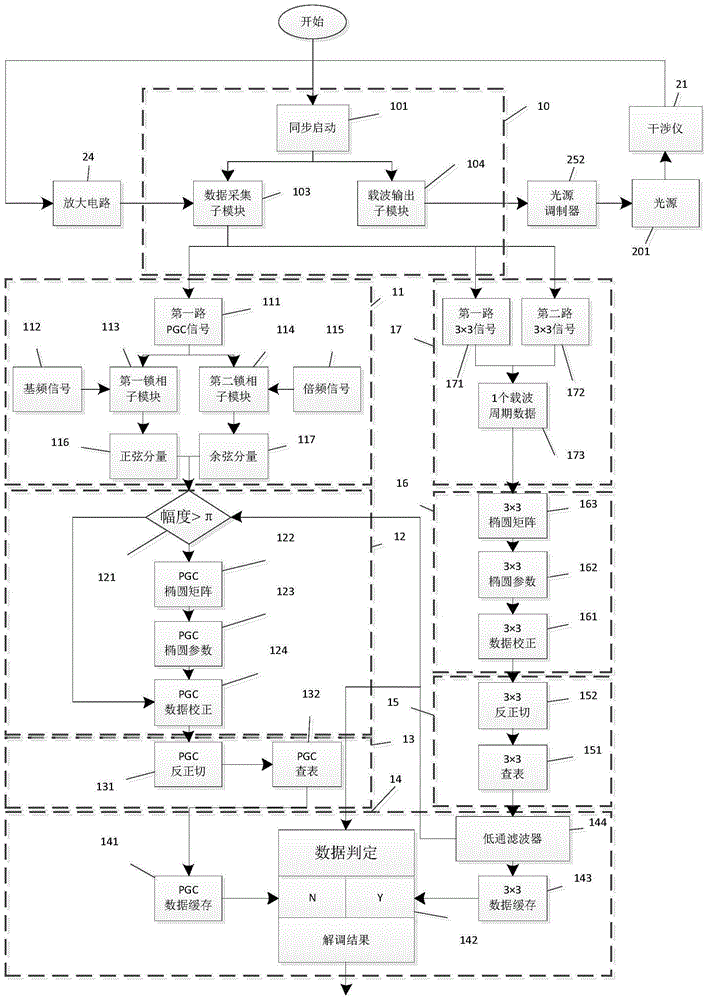
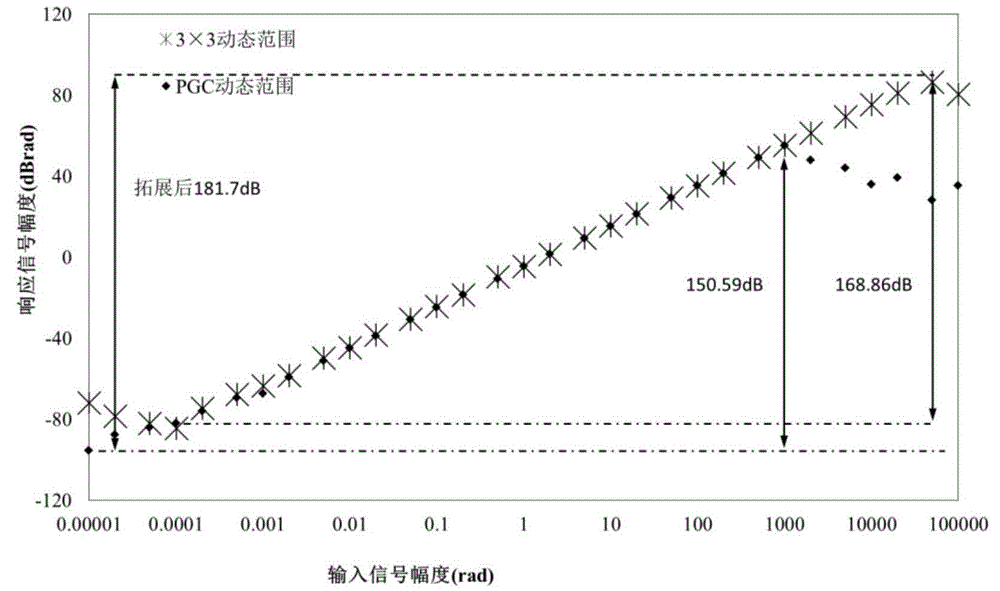
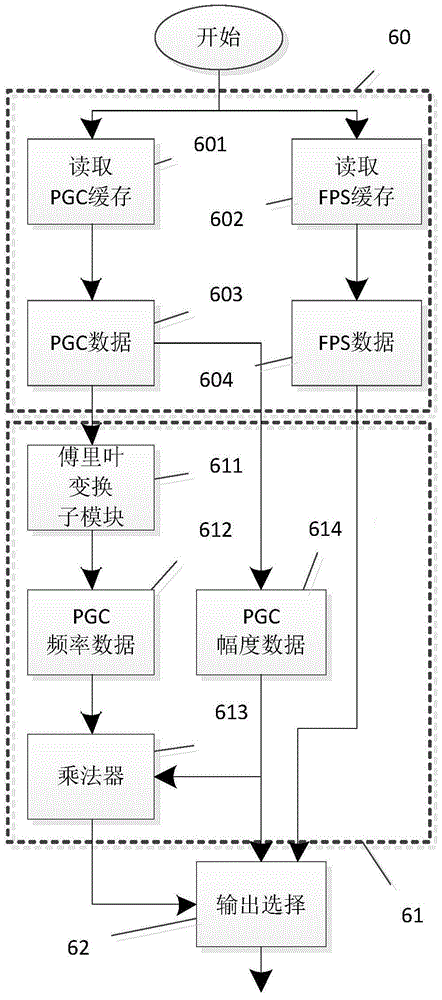
The invention belongs to the field of fiber-optic interferometer measurement, and more particularly relates to an improved phase generated carrier (PGC) demodulation method. The improved phase generated carrier (PGC) demodulation method comprises the steps of using a first path of fixed phase FPS signals and a second path of FPS signals that are outputted by a 3x3 coupler at the rear end of an interferometer for FPS algorithm phase demodulation; and using a phase generated carrier algorithm for demodulating a first path of PGC signals and finally performing reasonable integration of the demodulation results of the two algorithms. The invention combines the fixed phase method based on the 3x3 coupler with the PGC algorithm, and uses the PGC algorithm for demodulating low-frequency small signals and the FPS algorithm for outputting high-frequency large signals, so as to improve the phase resolution of the system and enlarge the dynamic range while an original sampling rate is maintained, thereby finally increasing the phase resolution and dynamic range and eliminating associated amplitude modulation influence under a constant sampling rate.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Adhesive-assembled fiber-optic interferometer
InactiveUS20060233484A1Limiting amount of adhesiveSlow curingInterferometersSpectrum generation using multiple reflectionAdhesiveEngineering
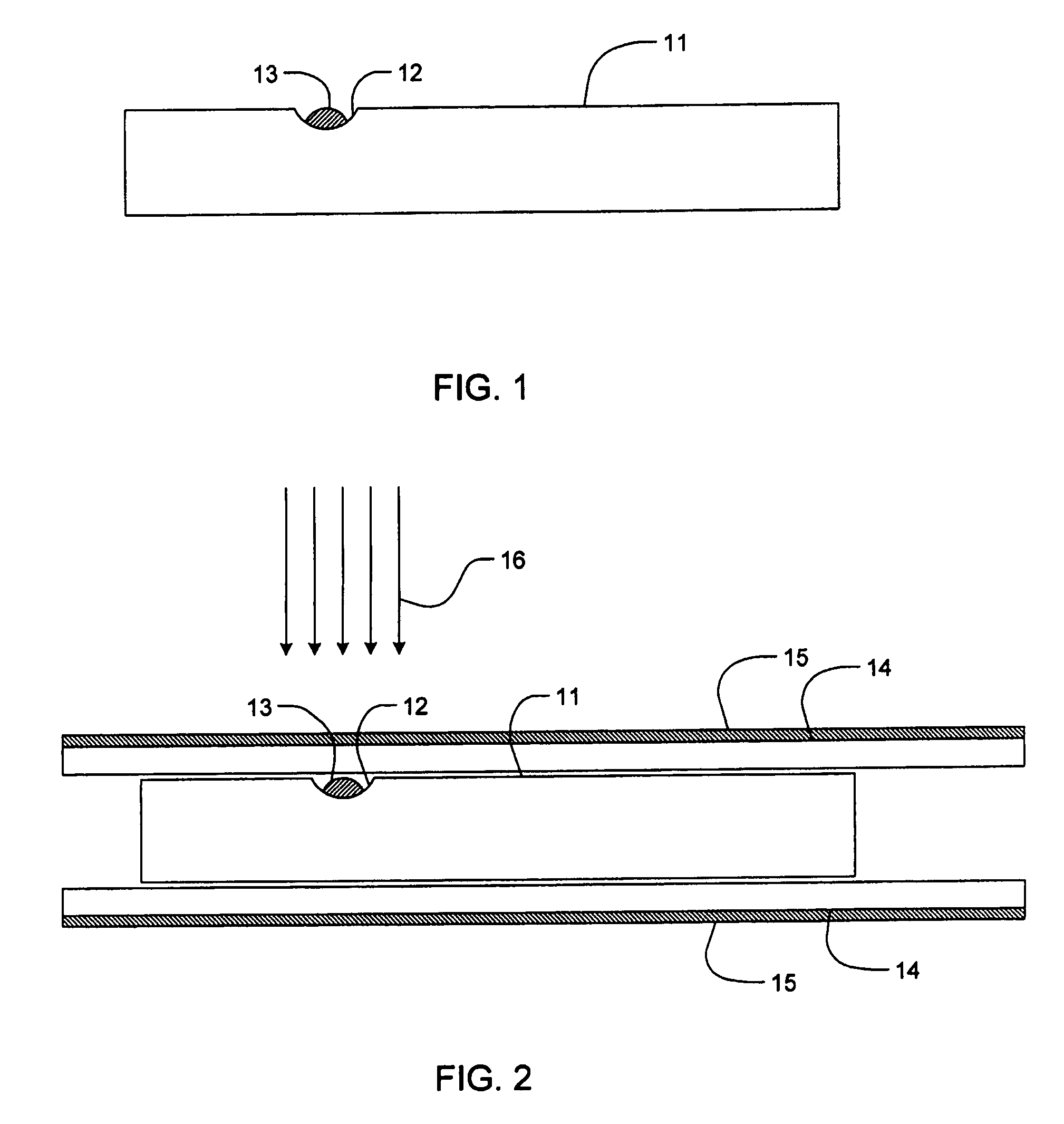
A method to assemble optical fiber devices and a fiber optic sensor is provided. It features a small adhesive joint between the fiber and a capillary tube by means of a small recess carved on the side of the fiber. This recess acts as a reservoir for the adhesive during the insertion of the fiber inside the tube. Then, the tube is heated so that the adhesive swells out of the recess to make the joint between the tube and the fiber. This method is used to assemble a fiber optic Fabry-Perot interferometer. This interferometer can be used as a sensor for the measurement of a number of physical parameters.
Owner:OPSENS
Real-time closed-loop measuring and tracking method of half-wave voltage of integrated electro-optical phase modulator
InactiveCN101881669AMeet the test requirements for measurement accuracyNot affected by driftOptical measurementsCurrent/voltage measurementMeasurement deviceClosed loop
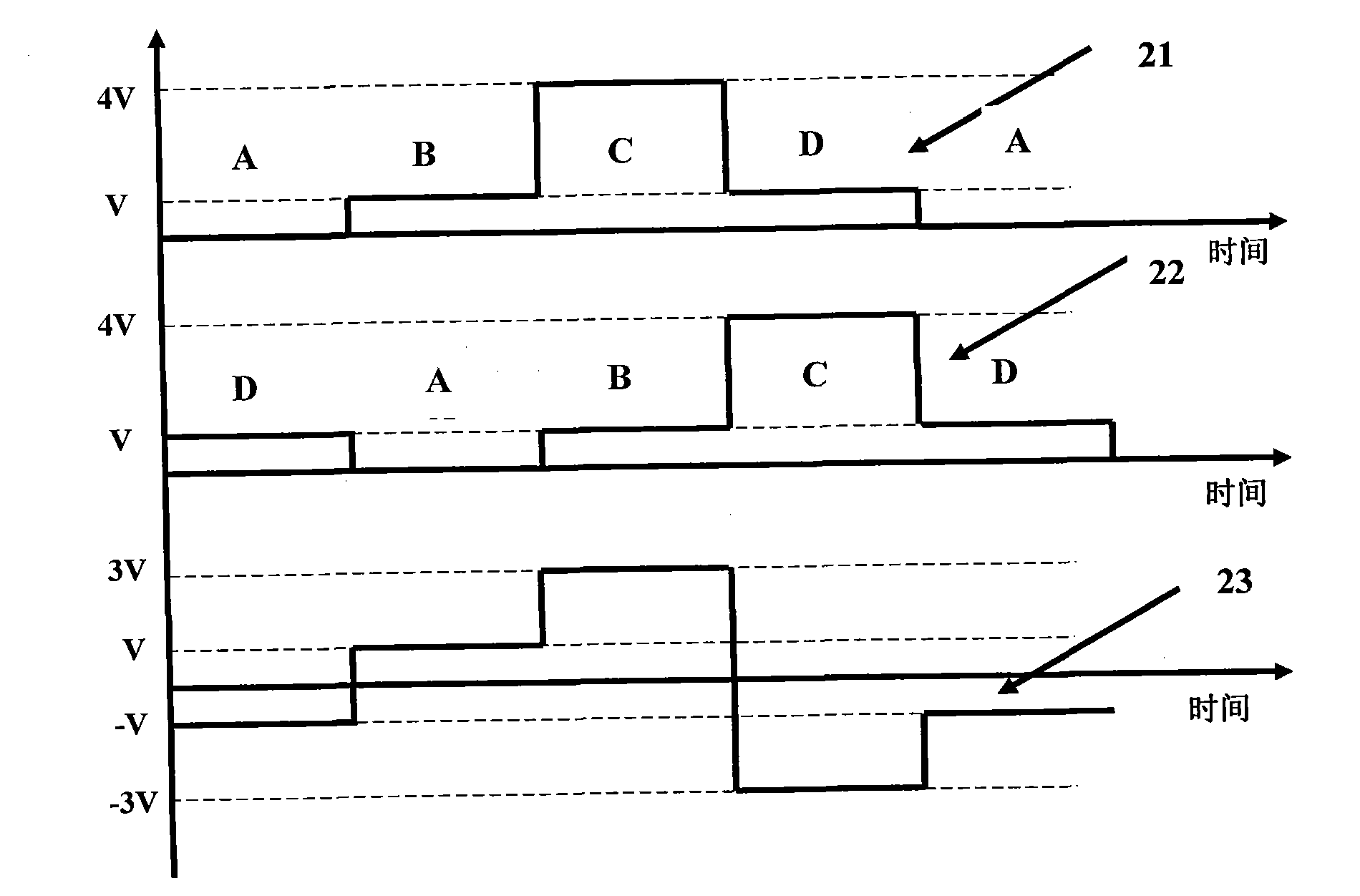
The invention discloses a real-time closed-loop measuring and tracking method of the half-wave voltage of an integrated electro-optical phase modulator. One Sagnac fiber optic interferometer is used as a measuring device, and the phase of the fiber optic interferometer is modulated by the measured integrated electro-optical phase modulator. An adopted phase modulating signal comprises four modulation steps A, B, C and D, the duration time of each modulation step equals to the transition time of the Sagnac fiber optic interferometer, the modulation voltage signals of the four modulation steps are respectively 0, V, 4V and V, and the magnitude of V is adjustable. The interferometer output signals corresponding to the phases B and C are measured by using a sampling circuit, the magnitude of V is adjusted according to an established policy until the measurement precision is met, and thus, the real-time closed-loop measurement and tracking to the half-wave voltage can be realized. The method has the characteristic of real-time measurement due to the adoption of closed-loop measurement, the method can be used for tracking the half-wave voltage, and the precision and the reliability of measurement are high and can not be influenced by the drift of the sampling circuit.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
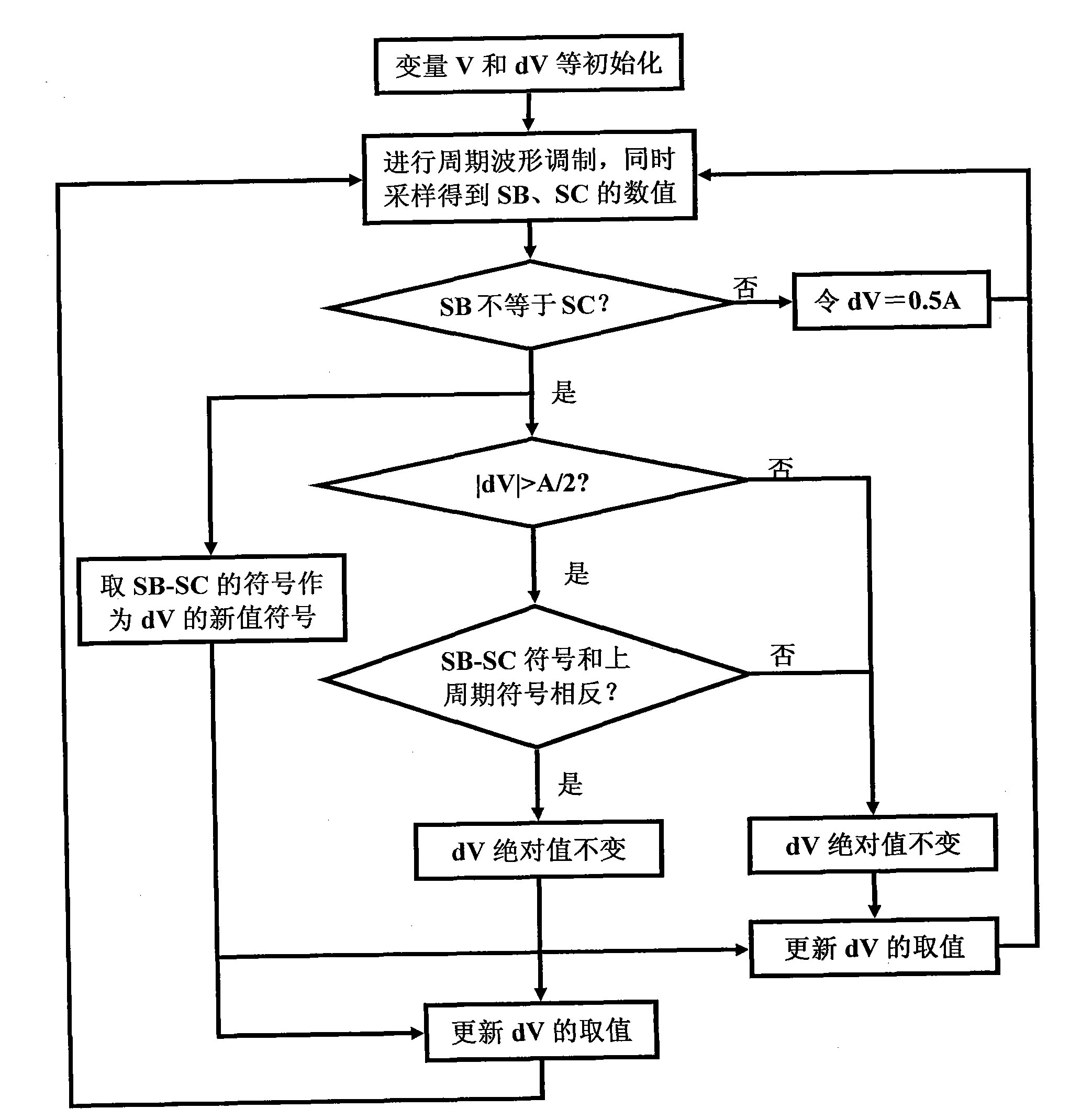
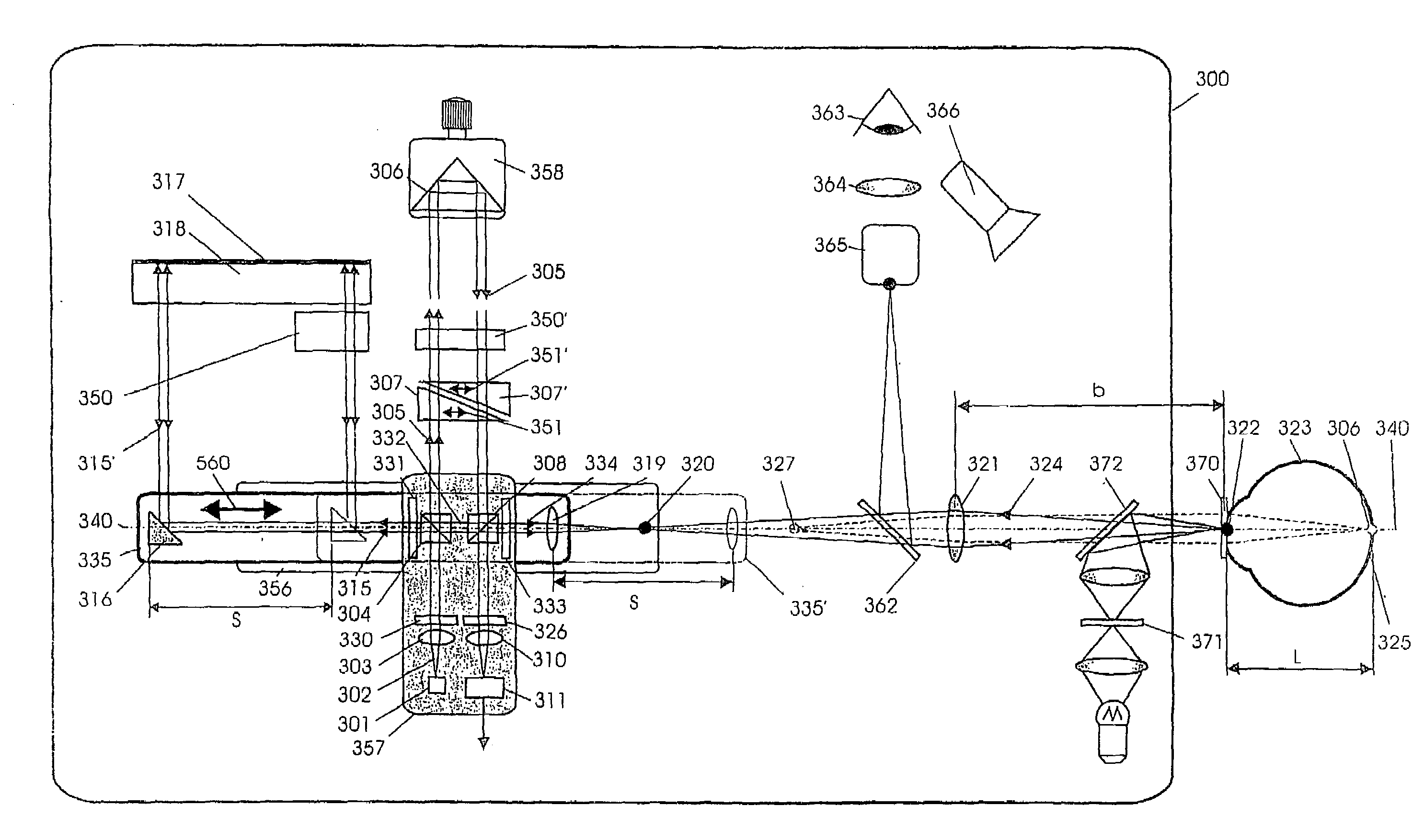
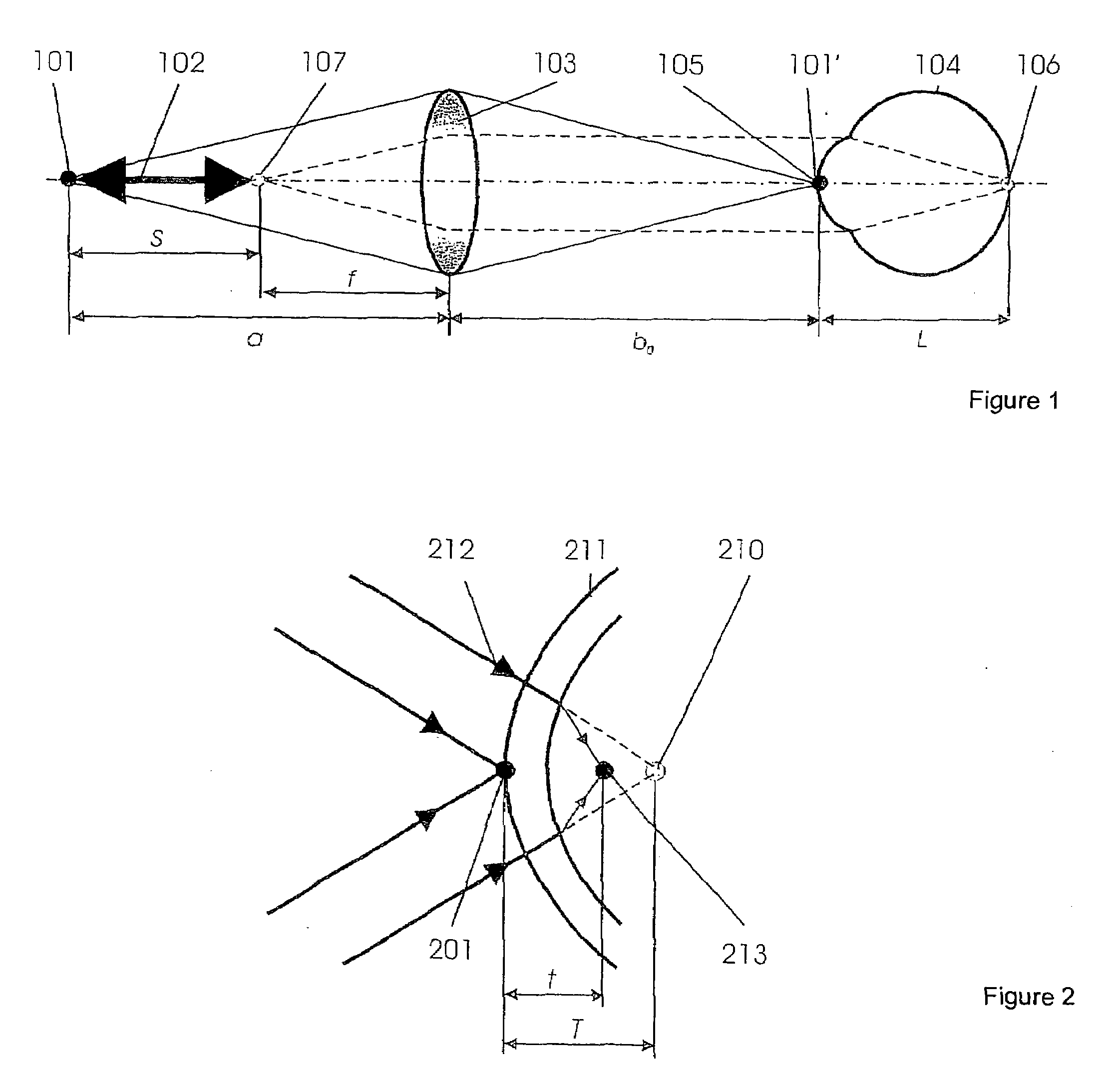
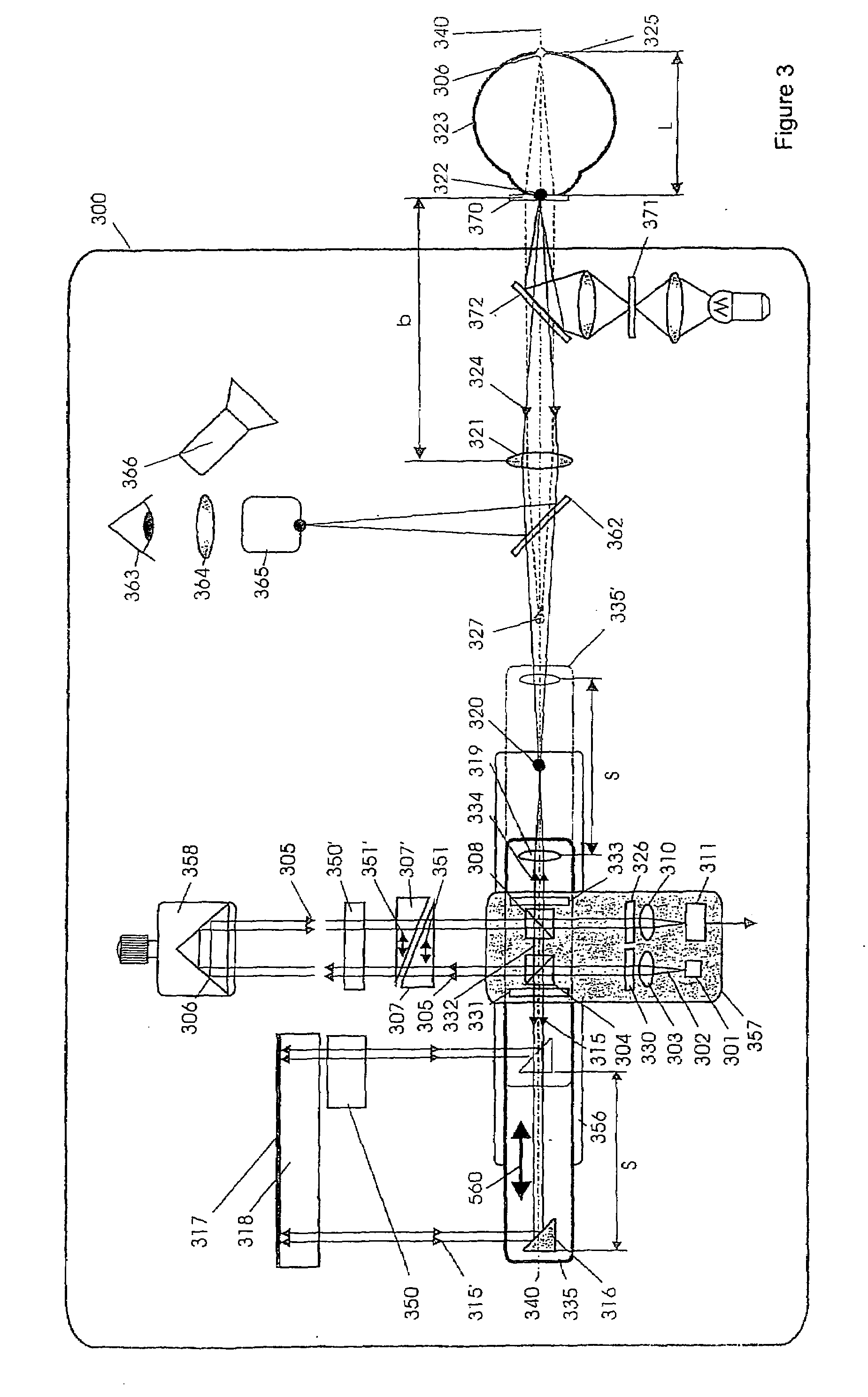
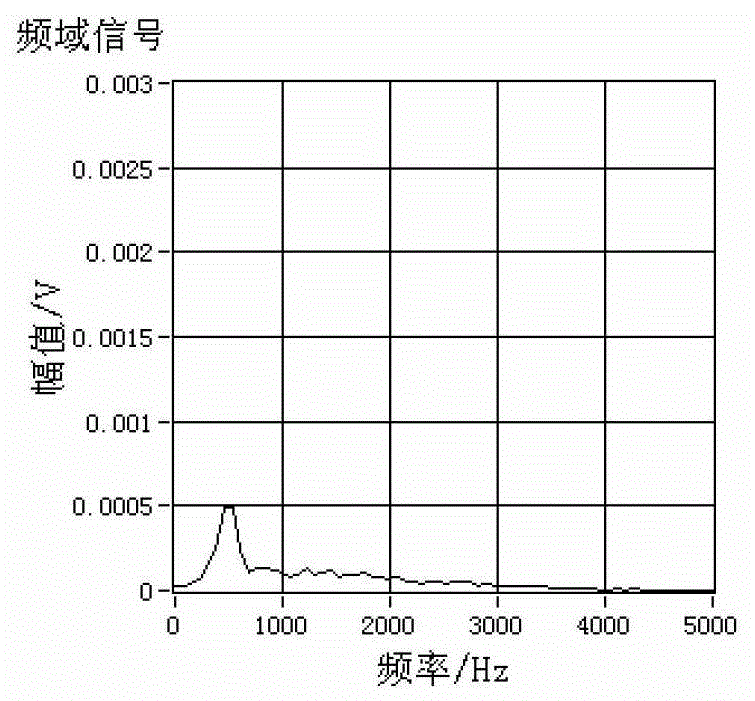
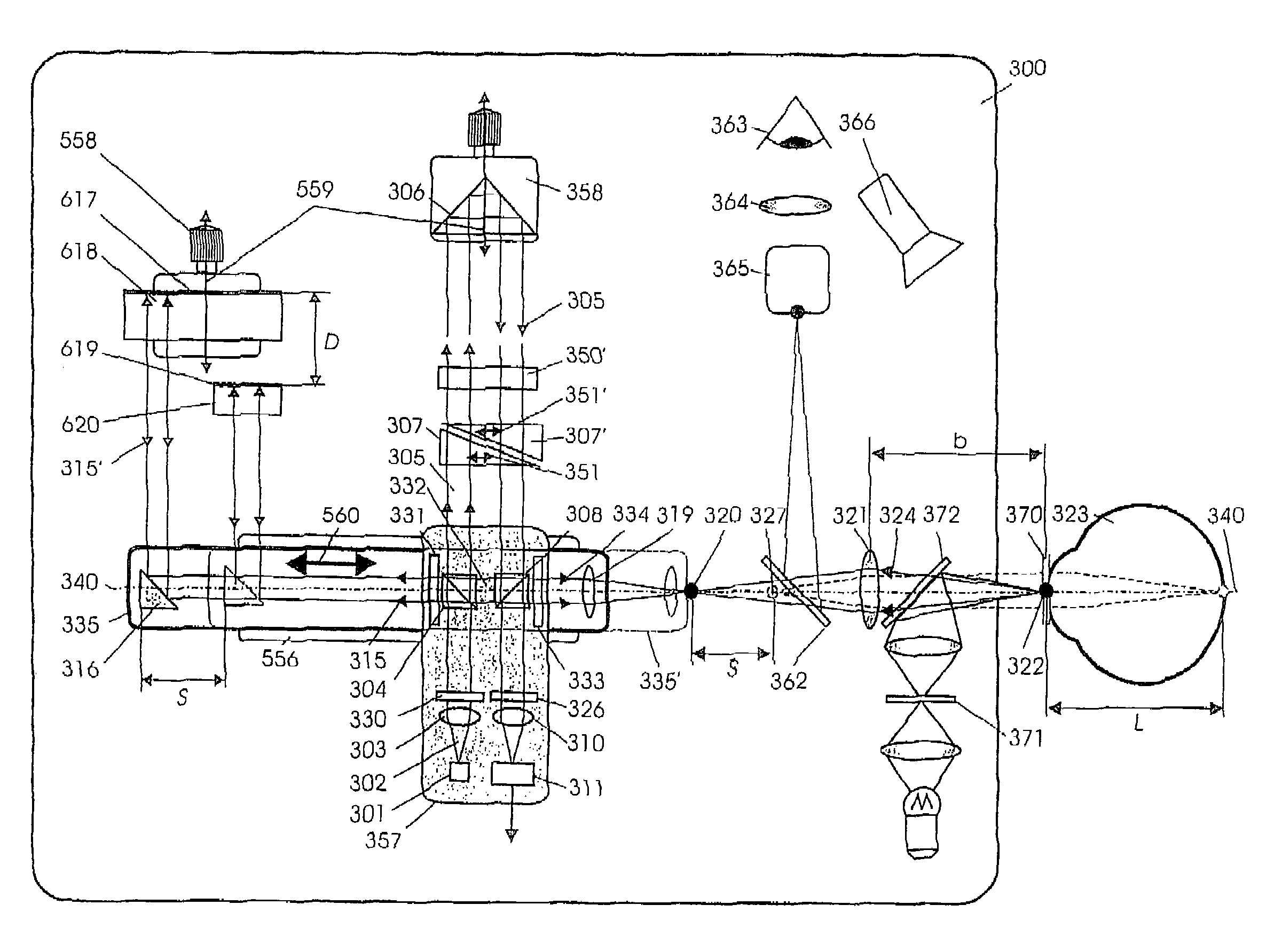
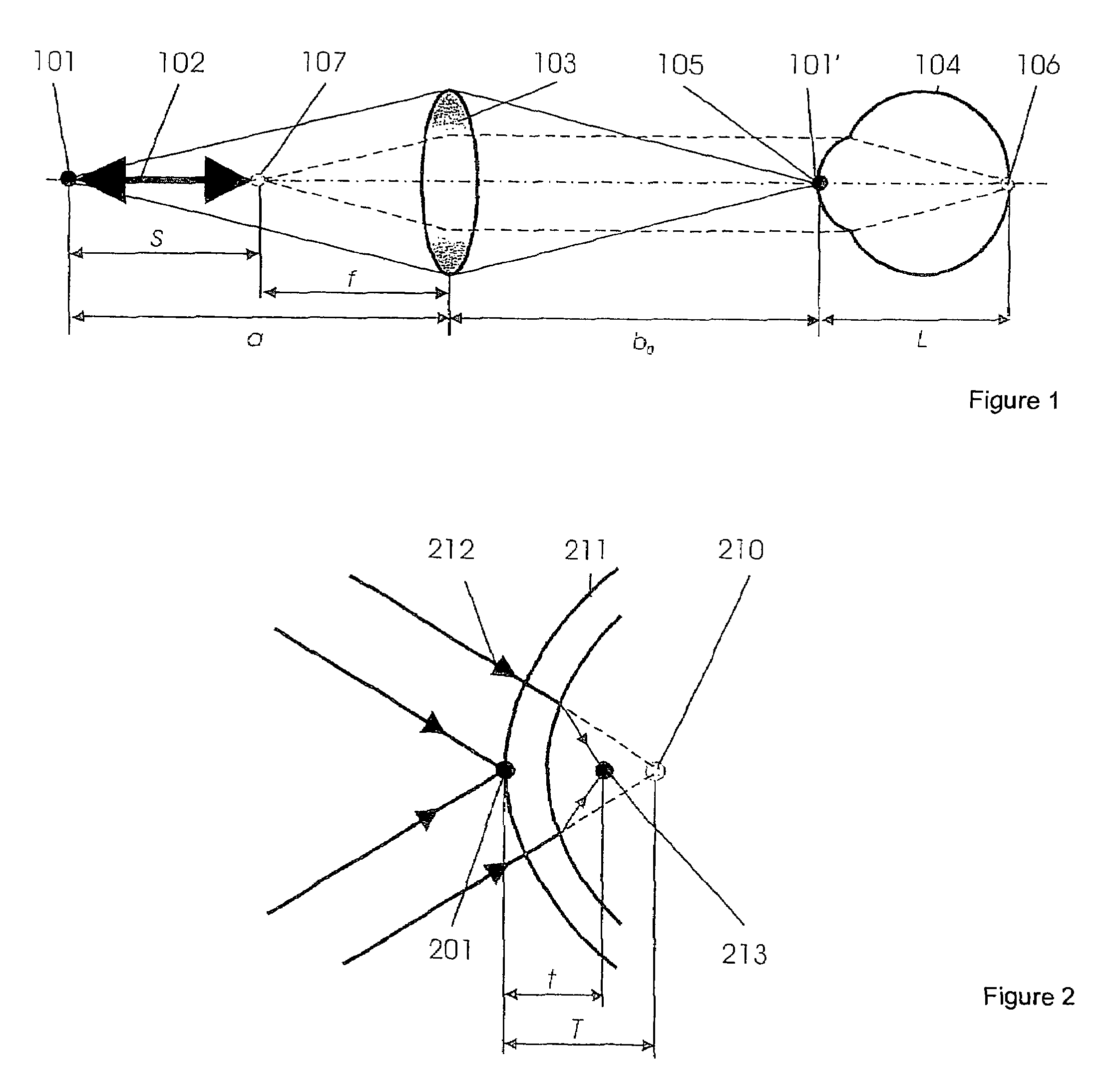
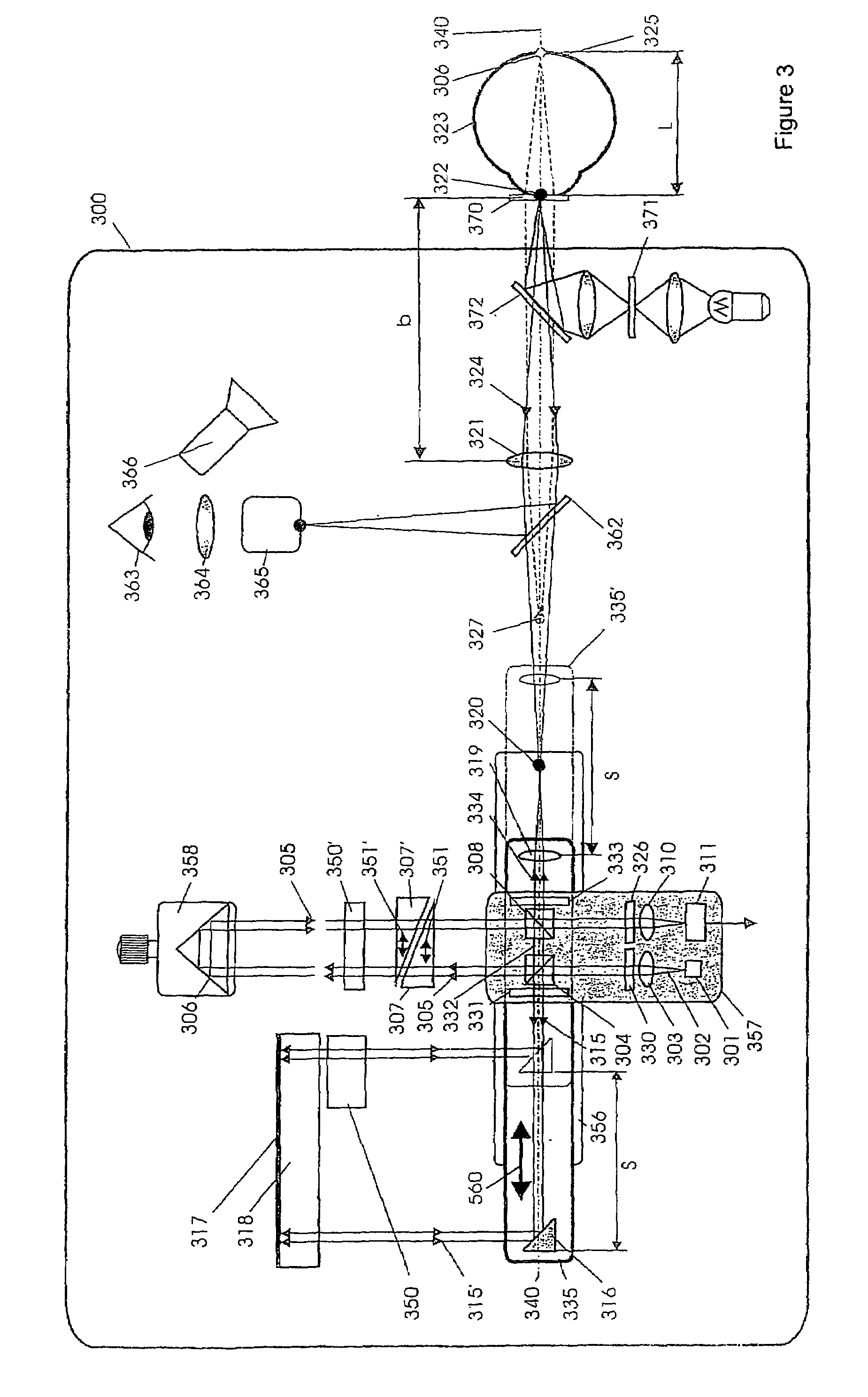
Short-Coherence Interferometeric Measurement of Length on the Eye
Two problems arise when measuring length at the eye by short-coherence interferometry. First, the measurement focus and coherence window usually do not coincide. Second, the scanning process along the eye axis is time-consuming. Both result in poor signal quality and inaccurate measurements. The present application is directed to a short-coherence interferometer in which a right-angle mirror and focusing optics jointly carry out a periodic back-and-forth movement in such a way that the measurement beam focus which is generated by the focusing optics and imaged on the eye by relay optics is moved synchronously with the coherence window from the cornea along the optic axis of the eye to the fovea centralis. Further, different path lengths are generated in the measurement beam path and reference beam path by means of a plurality of reflectors, so that the scanning process is limited to distances which are smaller than the optical length of the eye. The present invention is advantageously implemented using on a fiber-optic interferometer. According to the invention, the reference interferometer arm and measurement interferometer arm are combined with the arms of a fiber-optic interferometer.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Spectrum splicing optical frequency domain reflection-type distributed fiber sensor and signal demodulation method
ActiveCN109186644AReduced requirement for non-mode-hopping spectral rangeLow cost designConverting sensor output opticallyPhotovoltaic detectorsMiniaturization
The present invention discloses a spectrum splicing optical frequency domain reflection-type distributed fiber sensor and a signal demodulation method. The spectrum splicing optical frequency domain reflection-type distributed fiber sensor comprises a narrow linewidth scanning laser, a first optical fiber coupler, an optical circulator, a sensing optical fiber, a polarization control unit, a second optical fiber coupler, a first polarization beam splitter, a second polarization beam splitter, a first balance photoelectric detector, a second balance photoelectric detector, a third optical fibercoupler, a first Faraday rotation reflector, a second Faraday rotation reflector, a reference fiber optic interferometer, a photoelectric detector and a signal collection processing unit. Through spectrum splicing, it is avoided that a laser with a broadband spectrum range and without mode jump is employed to reduce the cost; the laser package and control are simplified to facilitate miniaturization design; and the requirements for the environment temperature and the vibration condition are reduced to facilitate project promotion application.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF AEROSPACE CONTROL DEVICES
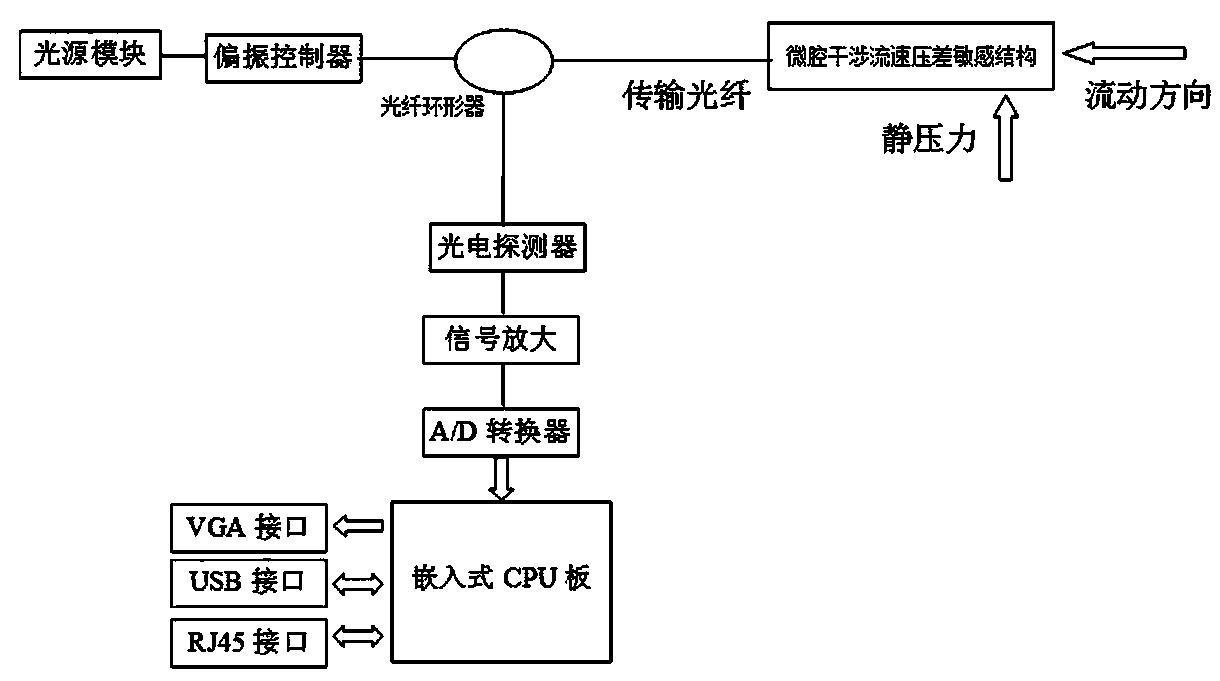
Micro-cavity interference flow velocity differential-pressure-sensitive structure and flow velocity and quantity sensor with micro-cavity interference fiber
InactiveCN103697954AHigh sensitivityAchieving Vibration Disturbance ErrorVolume/mass flow measurementFluid speed measurementDifferential pressureClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a micro-cavity interference flow velocity differential-pressure-sensitive structure and a flow velocity and quantity sensor with a micro-cavity interference fiber. By the aid of the micro-cavity interference flow velocity differential-pressure-sensitive structure and the flow velocity and quantity sensor, problems of extremely long interference light paths, severe polarization signal fading and temperature drifting of signals and influence on the measurement precision of existing fiber-optic interferometers can be solved. The micro-cavity interference flow velocity differential-pressure-sensitive structure comprises a transmission fiber, a shell, a fiber collimator and a light beam splitting cube; the fiber collimator and the light beam splitting cube are arranged in the shell; the light beam splitting cube is connected with a first pressure-sensitive membrane and a second pressure-sensitive membrane which are sleeved on the shell, the first pressure-sensitive membrane is used for sensing the static pressure of liquid, and the second pressure-sensitive membrane is used for sensing the flow velocity pressure of the liquid; light-wave signals in the transmission fiber are collimated by the fiber collimator and are outputted to the light beam splitting cube, and interference light-wave signals which are reflected by the first pressure-sensitive membrane and the second pressure-sensitive membrane are coupled by the fiber collimator and are inputted into the transmission fiber; light outputted by the fiber collimator is split into two beams by the light beam splitting cube, and light reflected by the first pressure-sensitive membrane is interfered with and light reflected by the second pressure-sensitive membrane by the aid of the light beam splitting cube, so that the interference light-wave signals with flow velocity differential pressure information can be generated.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Quantum optical fiber interferometer
ActiveCN106225666AHighly integratedReduce volumeUsing optical meansFiber optic interferometerElectro-optic modulator
The invention discloses a quantum optical fiber interferometer comprising a quantum compression light source, an electro-optic modulator, a first optical fiber splitter, a first optical fiber phase shifter, a second optical fiber phase shifter, a second optical fiber splitter and a balance detector. The defects that the existing interferometer system is limited by the classic shot noise limit can be overcome, and the system can perform low frequency phase measurement by using a high frequency compression source.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Optical fiber laser sensor time division and wavelength division combined multiplexing method
ActiveCN103954307AGuaranteed continuous pumpingReduce the difficulty of timing controlActive medium shape and constructionConverting sensor output opticallyLaser sensorTime-division multiplexing
The invention discloses an optical fiber laser sensor time division and wavelength division combined multiplexing method. The method comprises the steps that (1) intensity modulation is conducted on output light of an optical fiber laser through an optical switch so as to generate a narrow-pulse optical signal with the high extinction ratio to achieve channel selection, and a time division multiplexing structure is built; (2) an optical fiber laser sensor linear wavelength division multiplexing array is built in each time division multiplexing channel so as to achieve optical fiber laser sensor time division and wavelength division combined multiplexing; (3) displacement information of each laser wavelength in the selected channel is converted into interferometer output phase changes through the same non-equilibrium fiber optic interferometer; (4) interference information with different wavelengths is separated into n signal demodulator circuits, and a sensing signal which corresponds to the time division channel, has the corresponding wavelength and is at the position of the optical fiber laser sensor is demodulated. According to the optical fiber laser sensor time division and wavelength division combined multiplexing method, the multiplexing number of the optical fiber laser sensor array is improved to the greater degree, and the whole optical fiber laser sensing system is thinner, lighter and more reliable.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
For path imbalance measurement of the two arms fiber optic interferometer
InactiveUS20100171960A1Accurate measurementReduce errorsUsing optical meansFourth harmonicCarrier signal
Path imbalance measurement of the two arms fiber optic interferometer includes employing a current carrier signal to modulate the semiconductor laser light source of the interferometer to let it output interference signals to generate a carrier phase signal through path imbalance of the interferometer. Then, the interference signals are expanded to be the harmonic components of carrier phase signal frequency by Bessel function. Subsequently, we use the specific relation between the second and the fourth harmonic components of the interference signals to develop the theory of path imbalance measurement. The method mentioned above can measure a few decimeters of path imbalance and its accuracy can reach to a millimeter.
Owner:NXTAR FIBER OPTIC SECURITY
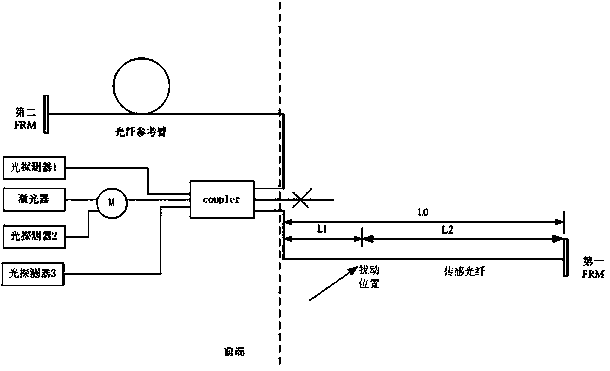
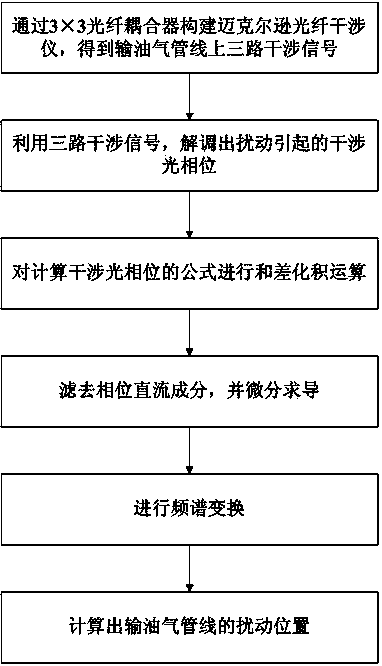
Distributed fiber-optic sensing based oil-gas pipeline safety monitoring system and method
ActiveCN104197206AAvoid cumbersome and expensiveAvoid the dilemmaPipeline systemsFiberPhase difference
The invention discloses a distributed fiber-optic sensing based oil-gas pipeline safety monitoring system and method. The method includes the steps of 1, establishing a Michelson fiber-optic interferometer with a 3*3 fiber-optic coupler to obtain three interference signals of an oil-gas pipeline, with each two of the interference signals, having a fixed phase difference 2Pi / 3; 2, demodulating the interference signals to obtain an interference optical phase Delta Phi(5t) caused by disturbance; 3, subjecting a formula of the interference optical phase Delta Phi(5t) to a sum-difference to product operation; 4, filtering a phase direct-current component and performing derivation by differentiation; 5, performing spectrum transformation; 6, calculating a disturbance position L2 of the oil-gas pipeline. The distributed fiber-optic sensing based oil-gas pipeline safety monitoring system and method has the advantages that complex and expensive hardware equipment is omitted, the diploma of sensitivity and trapped wave point aliasing in the white light interferometer positioning technology is also avoided, insertion loss is low, the system and the method are applicable to safety warning for long-distance wide-range oil and gas pipelines, an available monitoring range is up to 150km, and the system and the method have a promising application prospect.
Owner:SUZHOU GUANGLAN INFORMATION TECH
Interferometric sensor based on microstructured optical fiber selectively filled with functional materials
InactiveCN102818583AImplementation is flexibleImprove sensor sensitivityCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideResponse sensitivityPhotonic bandgap
The invention discloses an interferometric sensor based on a microstructured optical fiber selectively filled with functional materials. A birefringent microstructured optical fiber selectively filled with functional materials is used as a sensing head, and the functional materials are selectively filled into two adjacent air vent holes in the periphery of a fiber core of a refractive index guiding microstructured optical fiber in which triangular lattice air vent holes are distributed, so that birefringent fiber with a transmission mechanism of mixing refractive index and photonic band gap is realized. As null characteristic that group birefringence of the birefringent fiber is at a specific wavelength is utilized, and a transmission spectrum of a Sagnac fiber optic interferometer comprising the birefringent fiber presents a spectral characteristic different from that of a common interferometer, the interferometric sensor has superhigh response sensitivity to outside parameters. The interferometric sensor based on the microstructured optical fiber selectively filled with the functional materials has the advantages of flexibility in realizing manner and high sensing sensitivity and capability of being widely applied in high sensitivity sensing measurement of parameters such as temperature, refractive index and the like as well as manufacturing fields of optical elements such as photoswitches, tunable filters and the like.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Temperature insensitive low coherence based optical metrology for nondestructive characterization of physical characteristics of materials
This invention is a device for measuring of absolute distances by means of low coherence optical interferometry. The proposed apparatus eliminates thermal of the conventional fiber optic interferometers caused by variation of the refractive index of the optical fiber material to change of the temperature.
Owner:APPLEJACK 199
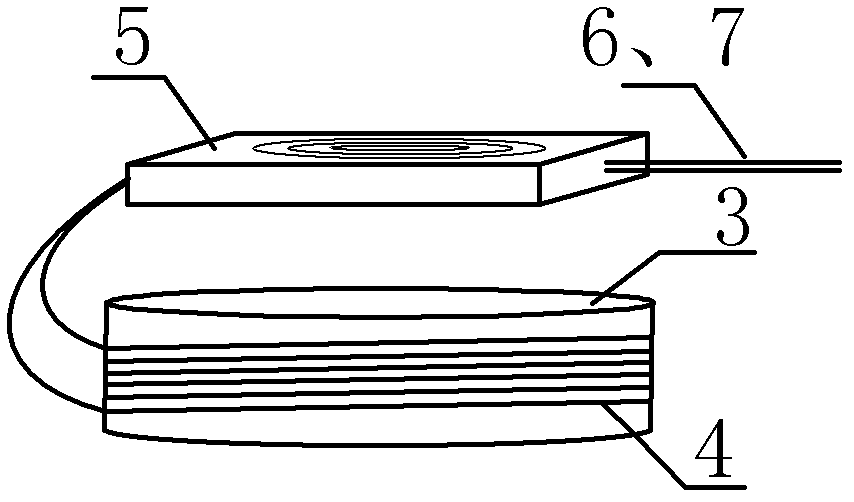
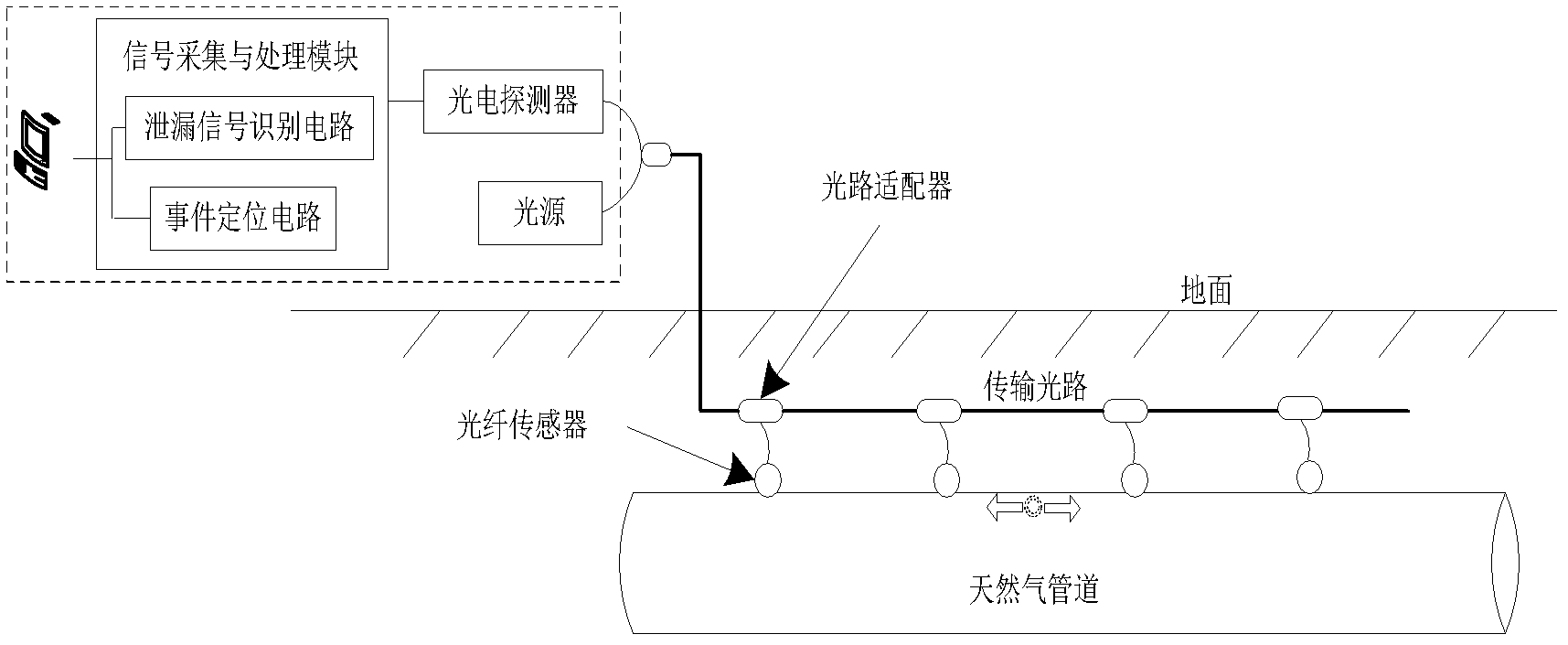
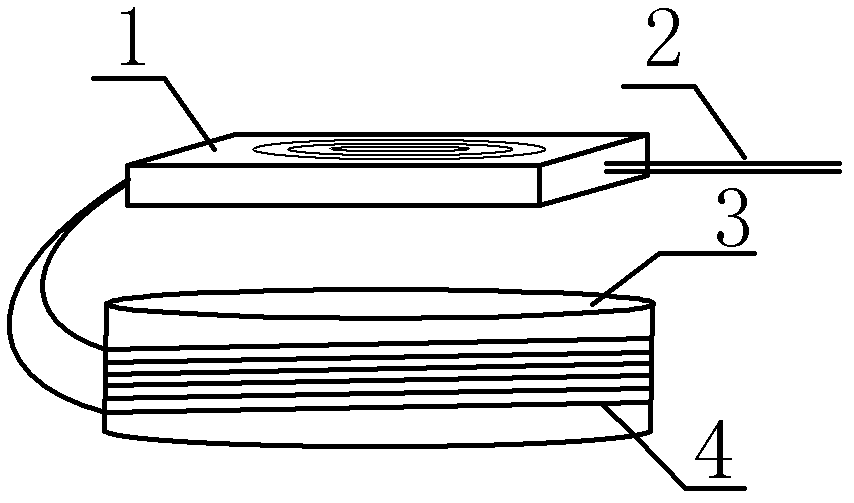
Optical fiber sensor for detecting natural gas pipeline leakage
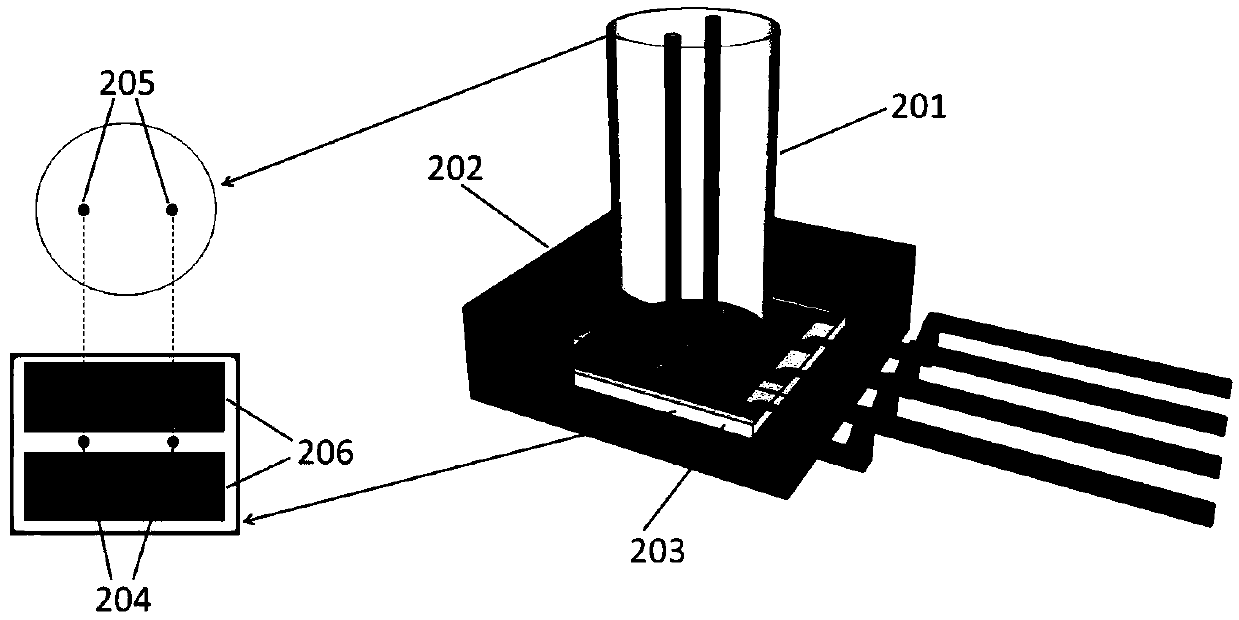
InactiveCN102997052AAdjustable detection sensitivityGood noise isolationPipeline systemsEngineeringFiber optic interferometer
The invention relates to an optical fiber sensor which is suitable for a natural gas pipeline leakage detection system. The optical fiber sensor consists of an elastic cylinder (3), a fiber optic interferometer (4) and a tail fiber disk fiber box (5), wherein interference arms of the fiber optic interferometer are uniformly and orderly wound on the periphery of the elastic cylinder (3); an optical fiber and the elastic cylinder are tightly bonded together by using a bonding agent; the fiber optic interferometer left after winding and relevant devices of the fiber optic interferometer are orderly wound in the tail fiber disk fiber box (5); the tail fiber disk fiber box (1) is fixed on the top of the elastic cylinder (3) by using a bonding agent; the elastic cylinder (3) is a steel short cylinder of which the bottom is inwardly depressed and the radian is consistent with that of the outer surface of a pipeline; and during installation of the sensor, the inwardly-depressed end of the elastic cylinder (3) is bonded on the surface of a natural gas pipeline by using a bonding agent. A front end probe with high positioning accuracy and high sensitivity is provided for a quasi-distributed natural gas pipeline leakage detection system.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
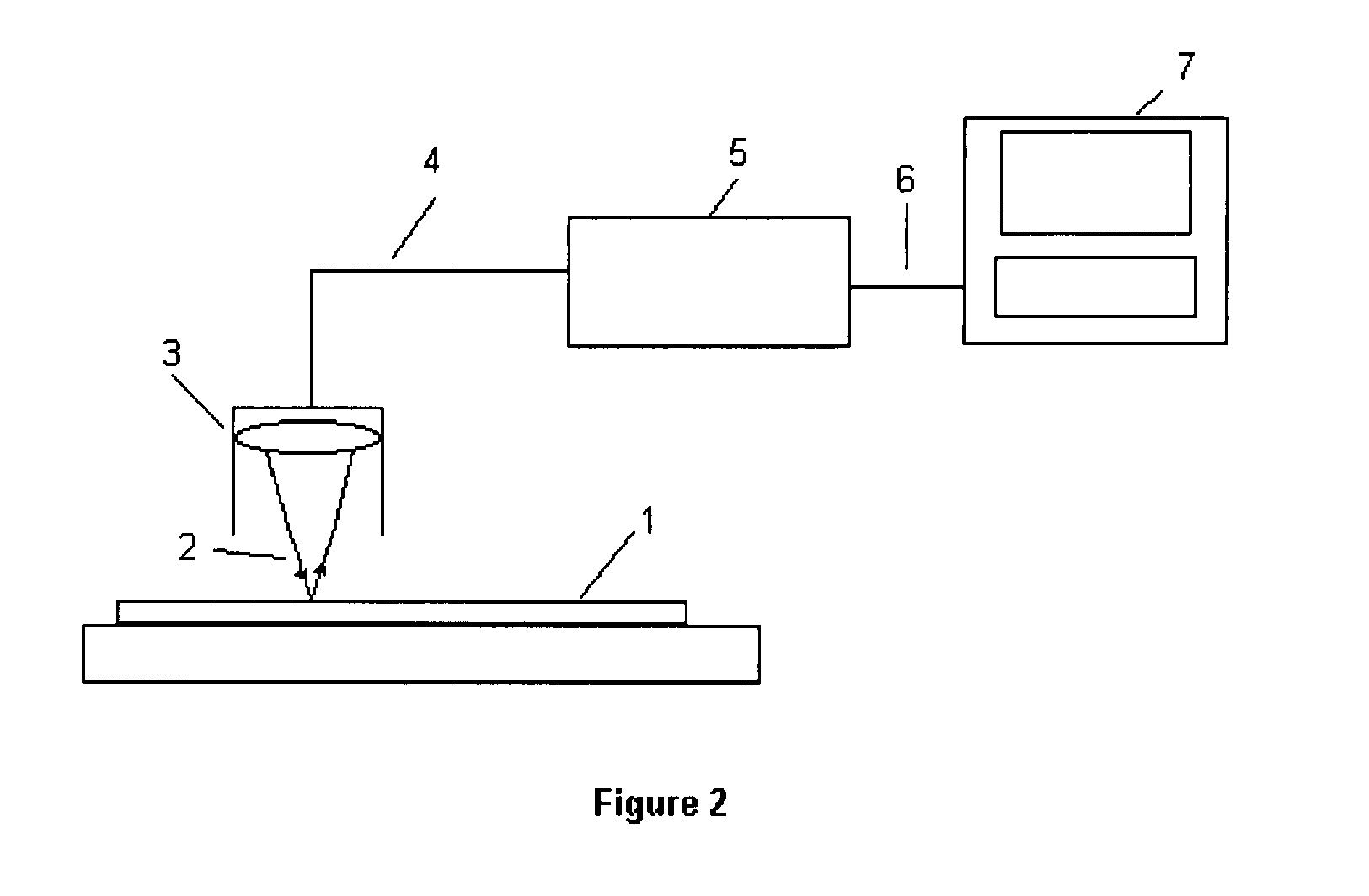
Integrated interference type micro-displacement optical fiber sensor, calibration device thereof and calibration method thereof
ActiveCN105737741AAchieve integrationSolve the problem of micro-displacement detectionUsing optical meansFast measurementData acquisition
The invention discloses an integrated interference type micro-displacement optical fiber sensor, a calibration device thereof and a calibration method for the same. The integrated interference type micro-displacement optical fiber sensor comprises an optical fiber collimator, a super small optical fiber lens, an optical fiber interference module, an indication laser device, a broadband laser device, a data collection card and a computer. The calibration device of the integrated interference type micro-displacement optical fiber sensor comprises an object reflector, a fixed platform, and a five-dimension regulation table with threads. The calibration method of the integrated interference type micro-displacement optical fiber sensor comprises steps of enabling the output terminal of the super small optical fiber lens to directly face the object reflector, moving the five-dimension regulation table with threads through an axis, and obtaining a function relation between the voltage of outputting the interference intensity and the micro-displacement, wherein the function relation is the calibration function of the integrated interference type micro-displacement optical fiber sensor. The calibration method disclosed by the invention can be used for the micro-displacement calibration which is high in accuracy and fast in measurement.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
System for comprehensively measuring multiple parameters of fiber optic interferometer
InactiveCN103759924AEasy to measureEliminate jumpingTesting optical propertiesRayleigh scatteringCarrier signal
Disclosed is a system for comprehensively measuring multiple parameters of a fiber optic interferometer. The system comprises a semiconductor laser unit with tunable narrow linewidth, an opto-isolator, the interferometer, a carrier wave circuit, a photoelectric detector, a data acquisition card and a data-processing machine, wherein the semiconductor laser unit is used for providing transmission signal light, the input end of the opto-isolator is connected with the output end of the semiconductor laser unit with the tunable narrow linewidth, a port 1 of the interferometer is connected with the output end of the opto-isolator, the interferometer is used for reducing the influence of rayleigh scattering light on the laser unit so as to protect the laser unit to work stably for a long time, the output end of the carrier wave circuit is connected with a port 3 of the interferometer, the carrier wave circuit is used for providing the interferometer with PZT modulating signals, the input end of the photoelectric detector is connected with a port 2 of the interferometer, the input end of the data acquisition card is connected with the output end of the photoelectric detector, the data acquisition card is used for converting received optical signals into electric signals, the input end of the data-processing machine is connected with the output end of the data acquisition card, and the data-processing machine is used for processing digital signals collected by the data acquisition card and giving out parameter values through nonlinearity minimum least squares and fitting by using visibility, modulation amplitude and initial phase difference as undetermined parameters.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bio-directional common optical path distributed fiber optic interferometer
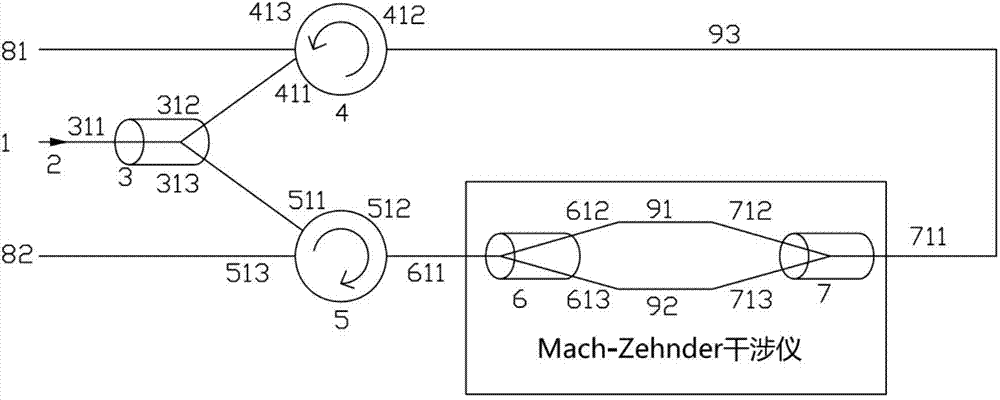
InactiveCN104729548AImplement distributed detectionReduce occupancyConverting sensor output opticallyFiberMach–Zehnder interferometer
The invention discloses a bio-directional common optical path distributed fiber optic interferometer. The bio-directional common optical path distributed fiber optic interferometer comprises a fiber optic isolator, a first fiber optic optical splitter, a Mach-Zehnder interferometer composed of a same second fiber optic optical splitter and a third fiber optic optical splitter, a first fiber optic circulator and a second fiber optic circulator; light enters the first fiber optic optical splitter after passing through the fiber optic isolator, the light is divided into two paths of the light with the same light intensity, one path of the light enters the second fiber optic optical splitter after passing through the first fiber optic circulator, the other path of the light enters the third fiber optic optical splitter after passing through the second fiber optic circulator, the light in the positive and the light in the negative directions are connected directly through a straight-through arm, one path of interference signals output by the third fiber optic optical splitter enters a first receiving end after passing through the first fiber optic circulator, the other path of the interference signals output by the third fiber optic optical splitter enters a second receiving end after passing through the second fiber optic circulator, and the waveforms of the two paths of the interference signals are consistent. The bio-directional common optical path distributed fiber optic interferometer has the advantages that the number of occupied cores of fiber optic in communication optical cables is reduced, and the signal intensity of the optical signals received by the receiving ends is increased greatly.
Owner:浙江诺可电子科技发展有限公司
Feedback locking structure capable of simultaneously realizing laser frequency stabilization and noise suppression
InactiveCN110890689ASuppress signal noiseFrequency stabilityLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersFrequency stabilizationLine width
The invention relates to the technical field of lasers, and discloses a feedback locking structure capable of simultaneously realizing laser frequency stabilization and noise suppression. On one hand,an atomic saturation absorption light path and a servo circuit for the feedback control of a laser piezoelectric ceramic control end are adopted in a first feedback locking loop, so that the laser frequency of the laser can be locked on a spectral line of the atomic saturation absorption spectrum, and the purpose of frequency stabilization is achieved; on the other hand, an optical fiber interferometer and a servo circuit for the feedback control of a laser current modulation end are adopted in a second feedback locking loop, so that the signal noise of the laser can be effectively suppressed, the purpose of noise suppression is achieved. Meanwhile, compared with an existing laser line width suppression scheme, an optical structure is greatly simplified, the overall size is reduced, the precise matching of a light path and a space mode of a reference cavity is not needed, and the implementation difficulty is reduced. In addition, the feedback locking structure also has the advantagesof easiness in integration, no need of free space optical path adjustment, low environmental parameter sensitivity and the like.
Owner:CHENGDUSCEON ELECTRONICS
Shock isolation and sound isolation package structure of fiber optic interferometer
InactiveCN102901521AGood shock isolationEnsure consistencySpecial purpose recording/indication apparatusIsolation effectEngineering
The invention discloses a shock isolation and sound isolation package structure of a fiber optic interferometer. The shock isolation and sound isolation package structure comprises a lower structure, a middle structure, an upper structure and a sound isolation device, wherein the middle structure is circular and is fixedly arranged on the lower structure; the upper structure is fixedly arranged on the middle structure and comprises an upper fixed flat plate and four elastic bands; four stand columns are uniformly assembled on the upper fixed flat plate; a fixed pulley is assembled on one side of the upper end of each stand column; one ends of the four elastic bands are fixed with the upper fixed flat plate; the four elastic bands are bridged over the fixed pulleys on the stand columns respectively; and the sound isolation device is suspended at the other ends of the four elastic bands on the upper structure. The shock isolation level is gradually changed from vibration frequency of 1 Hz to 1KHz, the shock isolation effect is not less than 20 dB, and the sound isolation level is from 10 Hz to 1 KHz, so that the sound isolation effect of not less than 40 dB is realized, thereby meeting the working requirement under severe environments.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
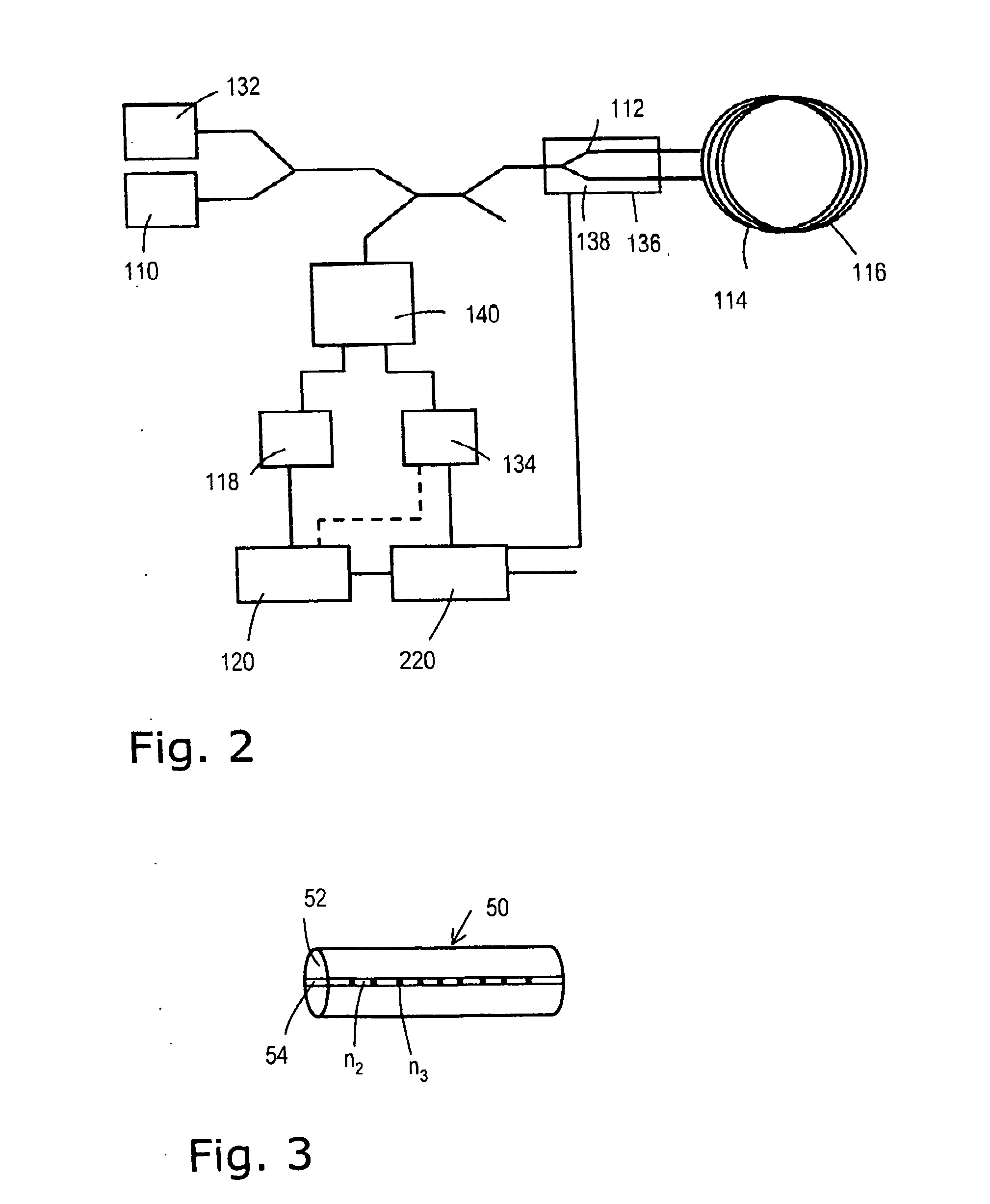
Fiber optic interferometer and method for determining physical state parameters in the interior of a fiber coil of a fiber optic interferometer
InactiveUS20110149293A1Sagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsState parameterLight beam
A fiber-optic interferometer comprising an optical fiber wound to form a fiber coil into which two partial light beams of a first light source can be coupled. The Bragg structure is integrated into the fiber coil. Said Bragg structure comprises an optical fiber having a periodically varying refractive index. In a method for determining physical state parameters in the interior of a fiber coil of a fiber optic interferometer information about physical state parameters in the interior of the fiber coil is obtained on the basis of the reflection wavelength of a Bragg structure comprising an optical fiber having a periodically varying refractive index is integrated into the fiber coil.
Owner:NORSROP GRUMAN LITEF GMBKH
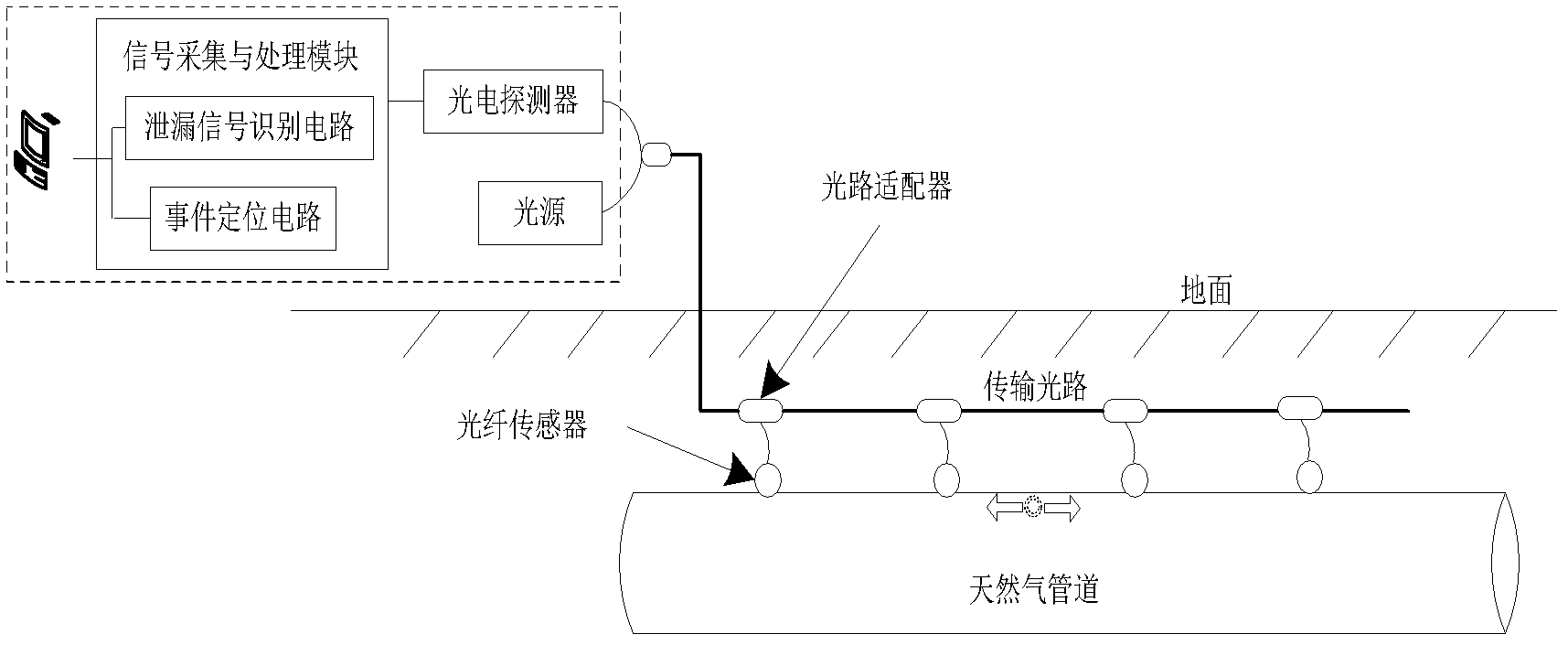
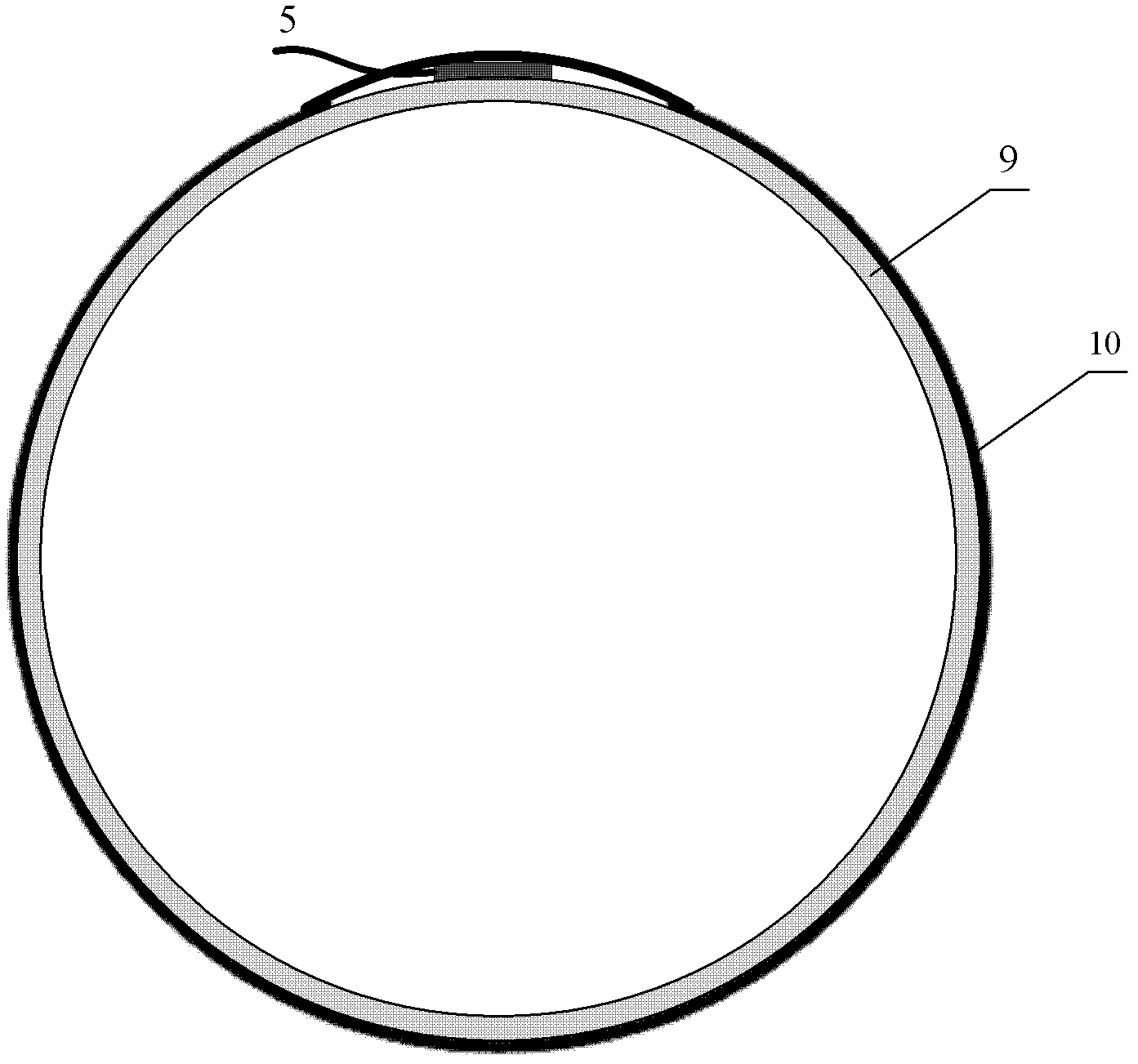
Method for installing optical fiber sensor for natural gas pipeline leakage optical fiber monitoring system
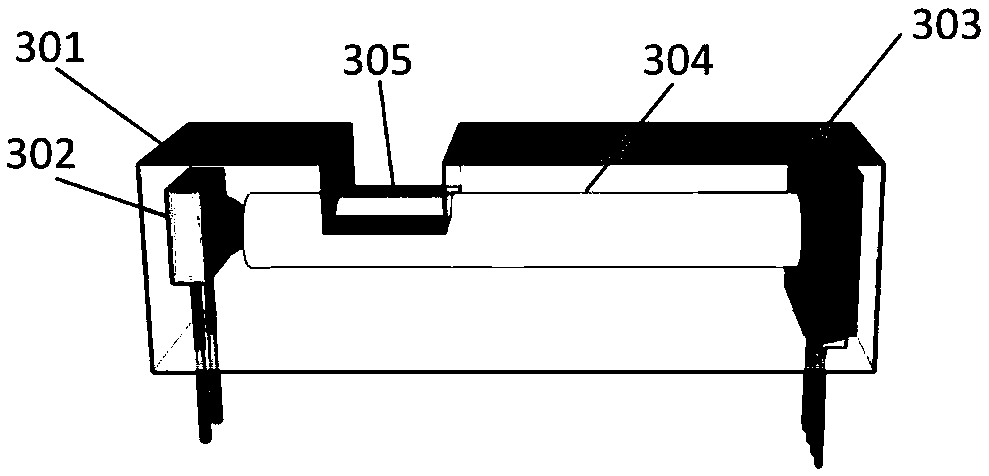
InactiveCN102997049AHigh detection sensitivityHigh sensitivityPipeline systemsMonitoring systemEngineering
The invention discloses a method for installing an optical fiber sensor for a natural gas pipeline leakage optical fiber monitoring system. The optical fiber sensor for detecting radial vibration of the pipeline consists of an elastic cylinder (3), a fiber optic interferometer (4) and a tail fiber disk fiber box (1); interference arms of the fiber optic interferometer are uniformly and orderly wound on the periphery of the elastic cylinder (3); an optical fiber and the elastic cylinder (3) are bonded together by using a bonding agent; the fiber optic interferometer left after winding and relevant devices of the fiber optic interferometer are orderly wound in the tail fiber disk fiber box (1); the tail fiber disk fiber box (1) is fixed on the top of the elastic cylinder (3) by using a bonding agent; and the inner depressed end of the elastic cylinder (3) is bonded on the outer surface of a natural gas pipeline by using a bonding agent, and subjected to corresponding pipeline anti-corrosion treatment, so that the entire sensor and an anti-corrosion layer on the surface of the pipeline are butted seamlessly. Due to the adoption of method, the sensitivity of an optical fiber sensing unit probe can be effectively controlled, and good insulating and shielding effects are achieved on signal interference except natural gas leakage.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Detection system for single frequency laser mode hopping
InactiveCN108155540AObserve changes in real timeGet the frequency shift size directlySemiconductor lasersOptical apparatus testingPhotovoltaic detectorsFiber optic interferometer
The invention relates to a detection system for single frequency laser mode hopping. The detection system comprises an opto-isolator, a fiber optic interferometer, a photoelectric detector and an oscilloscope, the fiber optic interferometer comprises a first coupler, a second coupler, a transmission fiber and a delay optical fiber, an input end of the first coupler is connected with a single frequency laser through optical fibers, and an output end of the second coupler is connected with the photoelectric detector through optical fiber; the transmission optical fiber and the delay optical fiber are in parallel between the first coupler and the second coupler, so that the output light of the single frequency laser causes interference; the oscilloscope is connected with the photoelectric detector. The detection system for single frequency laser mode hopping can be detected in real time, low in cost and easy to implement.
Owner:CANALASER TECH
Double-Sagnac pipeline safety monitoring system
ActiveCN102913761AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImprove real-time performancePipeline systemsSound sourcesData signal
The invention provides a double-Sagnac annular fiber optic interferometer sensor and belongs to the technical field of an optical sensor. According to the double-Sagnac annular fiber optic interferometer sensor, an optical fiber which is paved along a pipeline is used as a sensing optical fiber; when destructive disturbance happens closely to the pipeline, a vibration sound source is generated on the ground surface; a soil layer is used as a propagation medium to cause a partial vibration effect on the optical fiber in a cable; the vibration can modulate an optical signal transmitted in the optical fiber and a terminal of the cable utilizes a light signal receiving device to obtain a needed result; and data signal analysis treatment and safety evaluation are carried out. The optical fiber is paved along the pipeline and is located below the pipeline; a rubber layer is arranged at the outer part to protect; and an excitation end and a receiving end are connected in a serial connection manner to be used for exciting and receiving signals. According to the double-Sagnac annular fiber optic interferometer sensor, the phenomena that other methods cannot carry out in-time monitoring on possible destructive behaviors and cannot carry out in-time positioning on a damaged or disturbed place can be solved, so that the monitoring time, the monitoring range and the judging precision are effectively improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Short-coherence interferometric measurement of length on the eye
Two problems arise when measuring length at the eye by short-coherence interferometry. First, the measurement focus and coherence window usually do not coincide. Second, the scanning process along the eye axis is time-consumin g. Both result in poor signal quality and inaccurate measurements. The present application is directed to a short-coherence interferometer in which a right-angle mirror and focusing optics jointly carry out a periodic back-and-forth movement in such a way that the measurement beam focus which is generated by the focusing optics and imaged on the eye by relay optics is moved synchronously with the coherence window from the cornea along the optic axis of the eye to the fovea centralis. Further, different path lengths are generated in the measurement beam path and reference beam path by means of a plurality of reflectors, so that the scanning process is limited to distances which are smaller than the optical length of the eye. The present invention is advantageously implemented using on a fiber-optic interferometer. According to the invention, the reference interferometer arm and measurement interferometer arm are combined with the arms of a fiber-optic interferometer.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Highly integrated fiber optic interferometer
InactiveCN109579886AHigh sensitivityHigh speedConverting sensor output opticallyDual coreThe Internet
The invention provides a highly integrated fiber optic interferometer. The highly integrated fiber optic interferometer consists of a light source, a single-mode single-core input fiber, a first split-light cone coupling region, a single-mode dual-core sensing fiber, a combined light cone coupling region, a single-mode single-core transmission fiber, a second split-light cone coupling region, anda single-mode dual-core output fiber, and a photo-detecting chip. The highly integrated fiber optic interferometer uses a photo-detecting chip designed in an integrated circuit process that matches the position and shape of the output fiber core to perform collection, photoelectric conversion, and process on the output of the interference light. The highly integrated fiber optic interferometer greatly increases the integration of the overall system, reduces the size of the interferometer system, reduces the complexity of the system, and increases the reliability. The highly integrated fiber optic interferometer can be used for accurate measurement and real-time monitoring of various physical quantities such as temperature, pressure, and magnetic force, and can be widely used as a sensor node in the sensor network and the Internet of Things system.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Self-evaluation device and method of fiber optic interferometer for noise testing
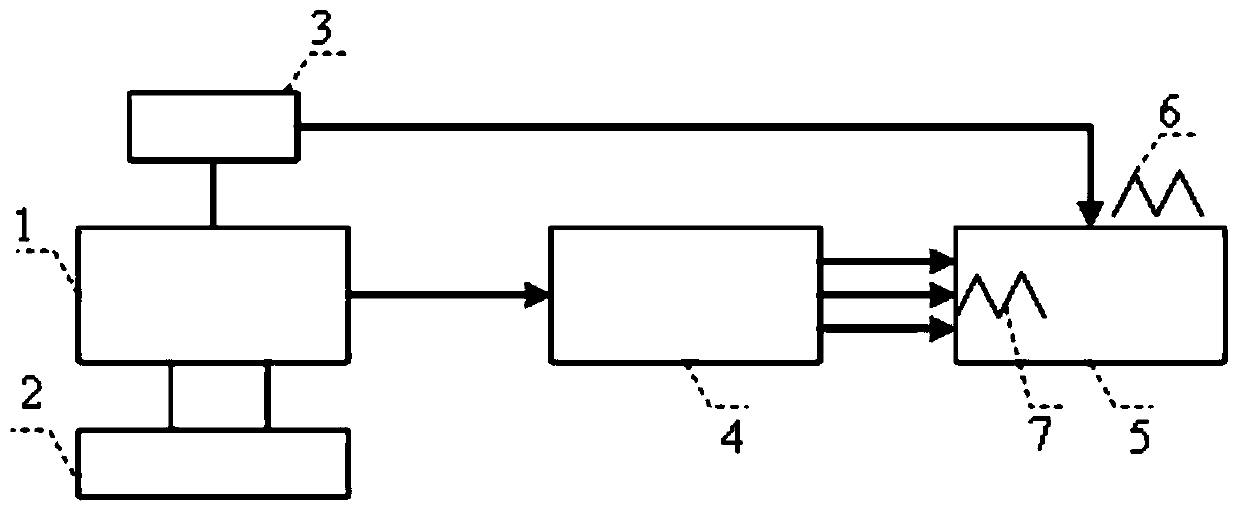
InactiveCN109932163AImprove robustnessLow costLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersPhase differenceData acquisition
The invention discloses a self-evaluation device of a fiber optic interferometer for noise testing. The self-evaluation device comprises an internal modulation semiconductor DFB laser, a laser drivingtemperature control circuit board, a modulation signal generation template, a 120-degree phase difference fiber optic interferometer, and a data acquisition and processing module. The internal modulation semiconductor DFB laser comprises a driving current input terminal, a temperature control voltage input terminal, a modulation signal input terminal and a light output terminal. The laser drivingtemperature control circuit board outputs a driving current and a temperature control voltage to the driving current input terminal and the temperature control voltage input terminal of the internalmodulation semiconductor DFB laser. The modulation signal generation module generates two pieces of identical modulation information, wherein the first piece of modulation information is input into the modulation signal input terminal of the internal modulation semiconductor DFB laser, and the second piece of modulation information is input into the data acquisition and processing module. The self-evaluation device is used for evaluating the phase demodulation correctness of the fiber optic interferometer for noise testing, and can easily make a correct judgment on a test result.
Owner:南京聚科光电技术有限公司
Optical fiber interferometer with relaxed loop tolerance and QKD system using the same
ActiveUS7254295B2Wheel based transmissionFrictional rollers based transmissionCost effectivenessTime delays
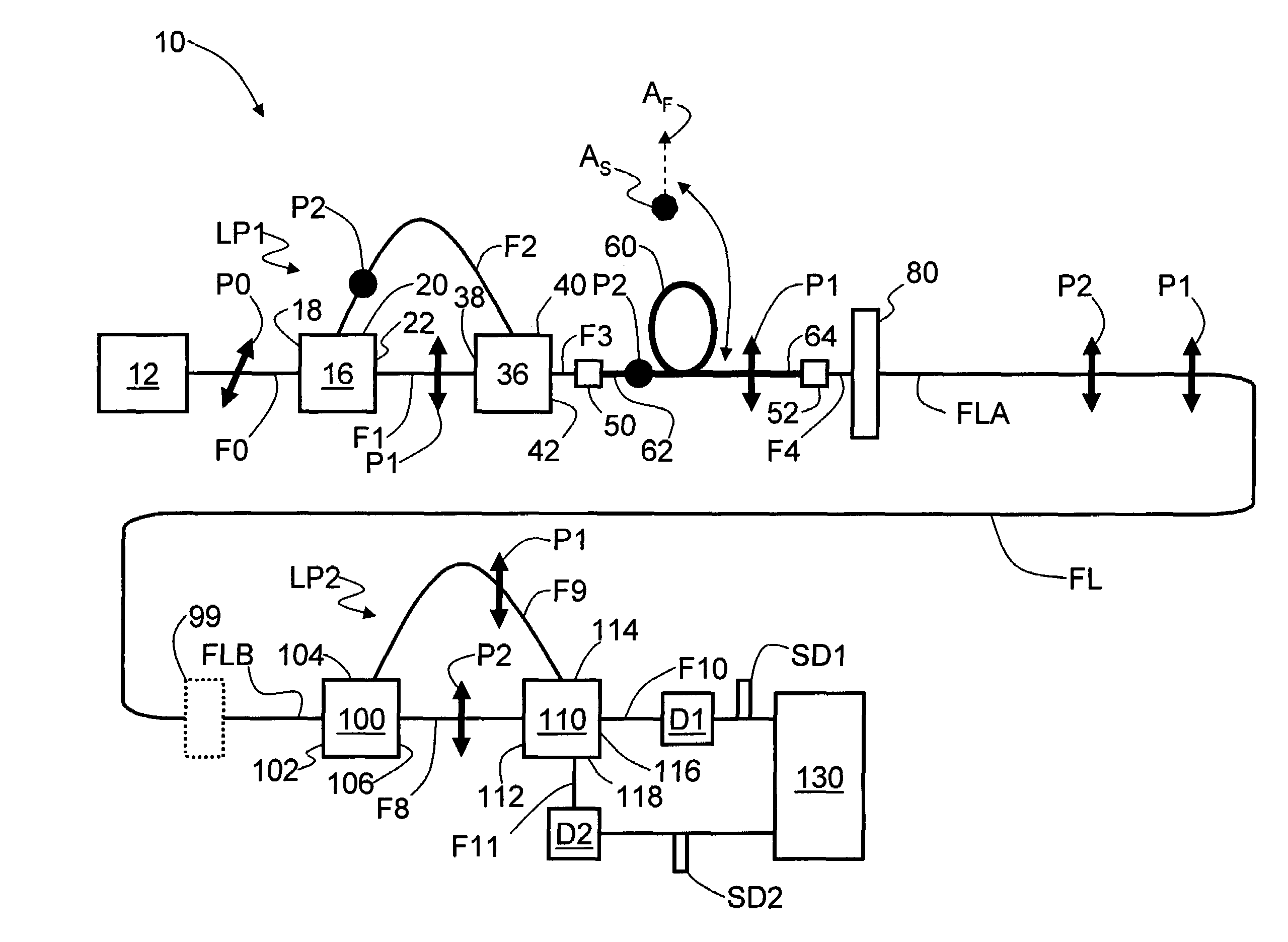
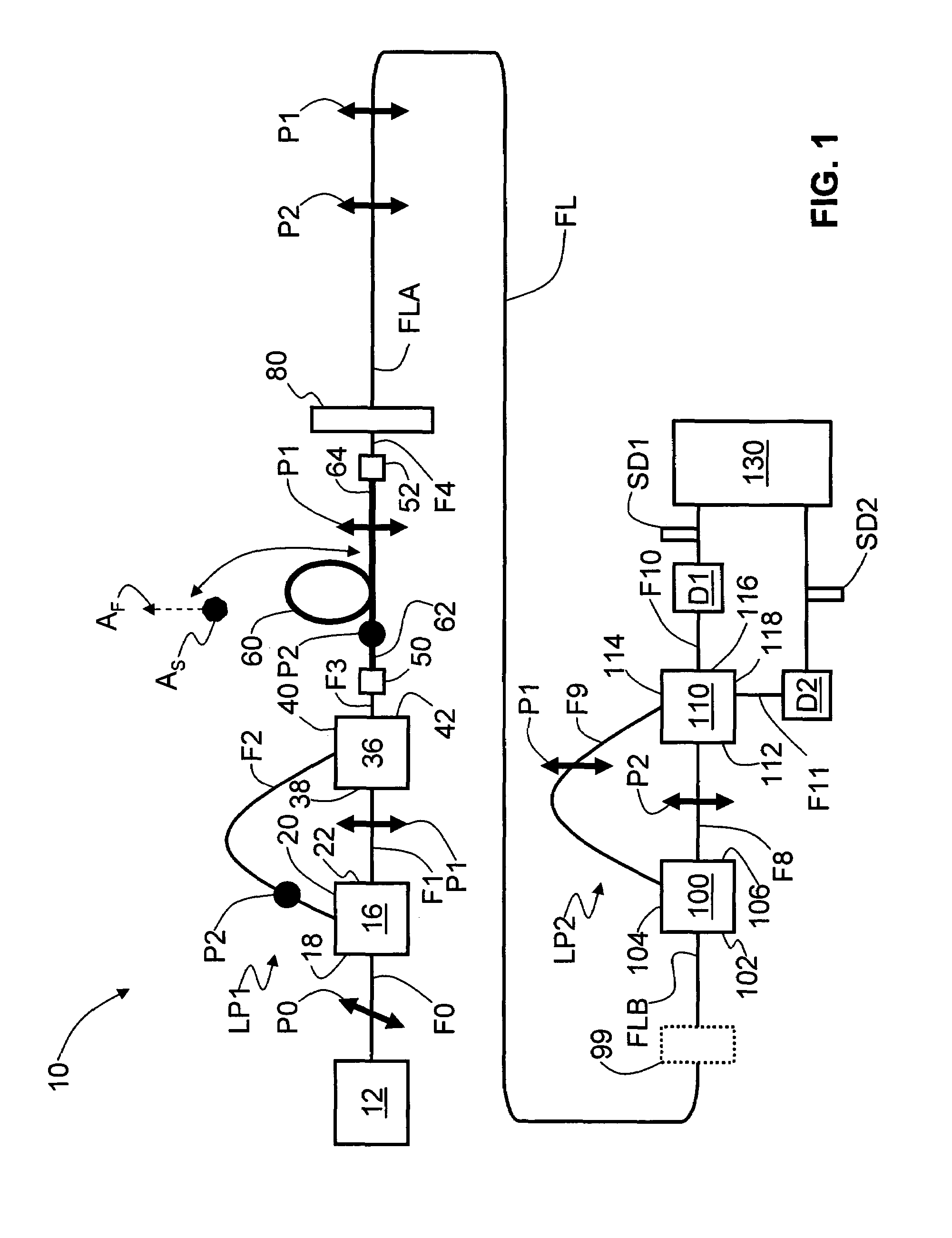
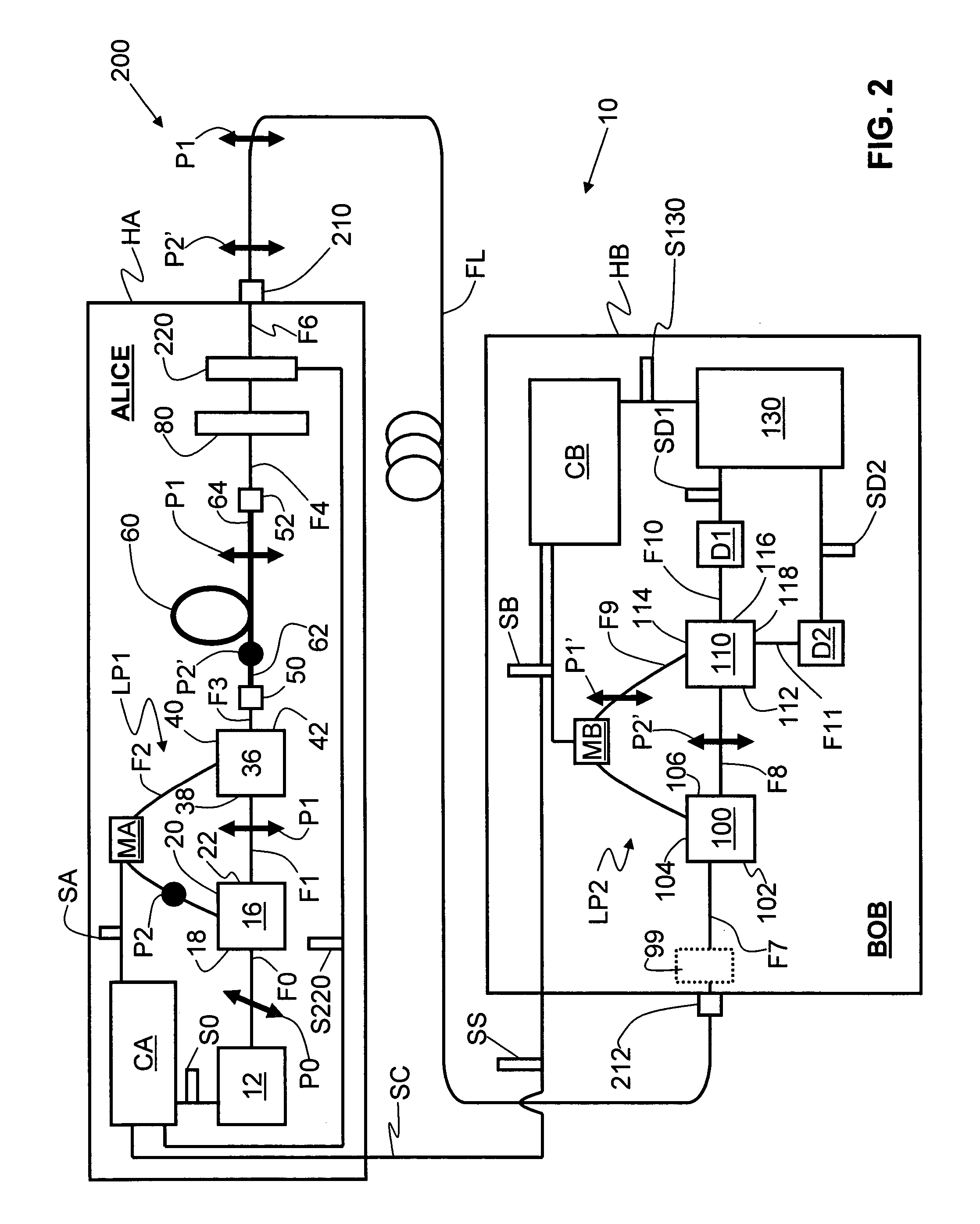
An optical fiber interferometer (10) with relaxed loop tolerance, and a quantum key distribution (QKD) system (200) using same is disclosed. The interferometer includes two optical fiber loops (LP1 and LP2). The loops have an optical path length (OPL) difference between them. A polarization-maintaining (PM) optical fiber section (60) of length (L60) and having fast and slow optical axes (AF and AS) optically couples the two loops. The length and fast-slow axis orientation is selected to introduce a time delay (ΔT1-2) between orthogonally polarized optical pulses traveling therethrough that compensates for the OPL difference. This allows for drastically relaxed tolerances when making the loops, leading to easier and more cost-effective manufacturing of the interferometer as well as related devices such as a optical-fiber-based QKD system.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
Method for calculating occurrence positions of pre-warning events in external safety pre-warning and positioning system of photoelectric composite cables
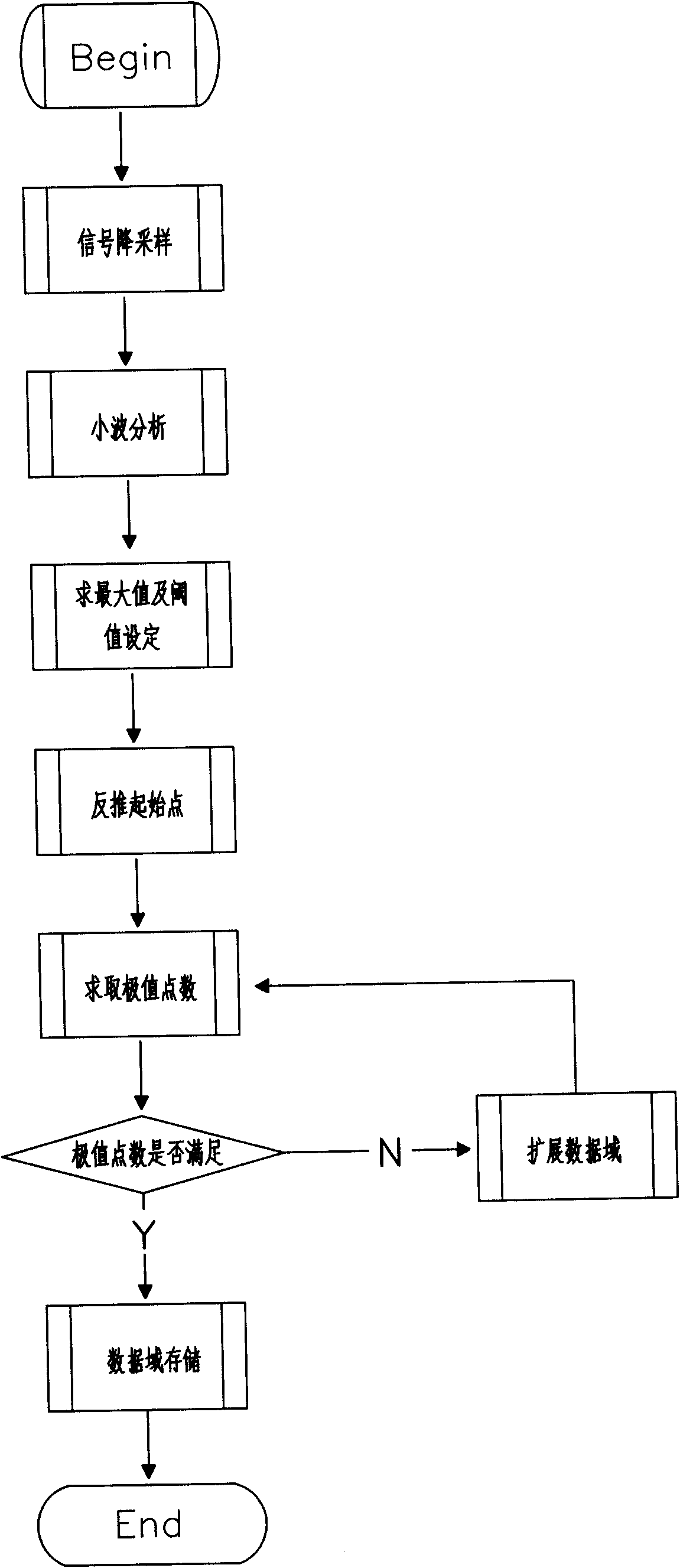
ActiveCN101626271ARealize accurate position judgmentRealize accurate judgmentLine-transmission monitoring/testingElectromagnetic transmissionData fieldTwo step
The invention discloses a method for calculating occurrence positions of pre-warning events in an external safety pre-warning and positioning system of photoelectric composite cables, which comprises the following two steps: step one, selecting a typical data field, and then calculating the occurrence positions of the events; and step two, performing a wavelet generalized mutual correlation positioning method. Through the two steps of calculations, the external safety pre-warning and positioning system of the photoelectric composite cables detects position information of the pre-warning events. The method for calculating the occurrence positions of the pre-warning events in the external safety pre-warning and positioning system of the photoelectric composite cables saves the investigationtime of event precaution and provides time allowance for the precautionary measures of the events so that correlative personnel can get to the site from nearby and the use efficiency of the personnelis improved; and the method provides a fact basis for the detection of data stealing events from the technical aspects. The implementation process of the method needs no constructions on the prior fiber network but only needs to mount a bidirectional common-path distributed fiber optic interferometer at two ends of a node of a communication optical fiber to achieve the designed functions of the system, thus the method not only is suitable for terrestrial environments but also is suitable for underwater environments, is simple to use, and has wide suitable environments.
Owner:浙江诺可电子科技发展有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com