Method for evaluating the allergen sensitivity of an individual
An allergen and sensitivity technology, applied in allergic diseases, material testing products, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as inability to measure interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[1162] The induction of immediate symptoms of type I allergy by allergen cross-linking of effector cells (mast cells and basophils) that bind IgE antibodies is a crucial event (Ka-wakami T, et al., Nat Rev Immunol (2002) 2:773-86). As described in the classic experiment of Prausnitz and Küstner (Prausnitz C, et al., Centralbe F Bact 1 Abt Orig (1921) 86:160-8), this event is dependent on three factors, namely, allergen-specific IgE antibodies, effector cells and allergens. Since the characterization of IgE antibodies and the development of diagnostic tests capable of accurately measuring the amount of allergen-specific IgE antibodies, certain tests have studied the level of allergen-specific serum IgE antibodies and the response of allergic patients to allergens. (Stenius B et al., Clin Allergy (1971) 1:37-55; Bryant DH et al., Clin Allergy (1975) 5:145-57; Pauli G et al., Clin Allergy (1977) 7:337 -46; Bousquet J et al Clin Allergy (1987) 17:529-36; Witteman AM et al J Alle...
Embodiment 2
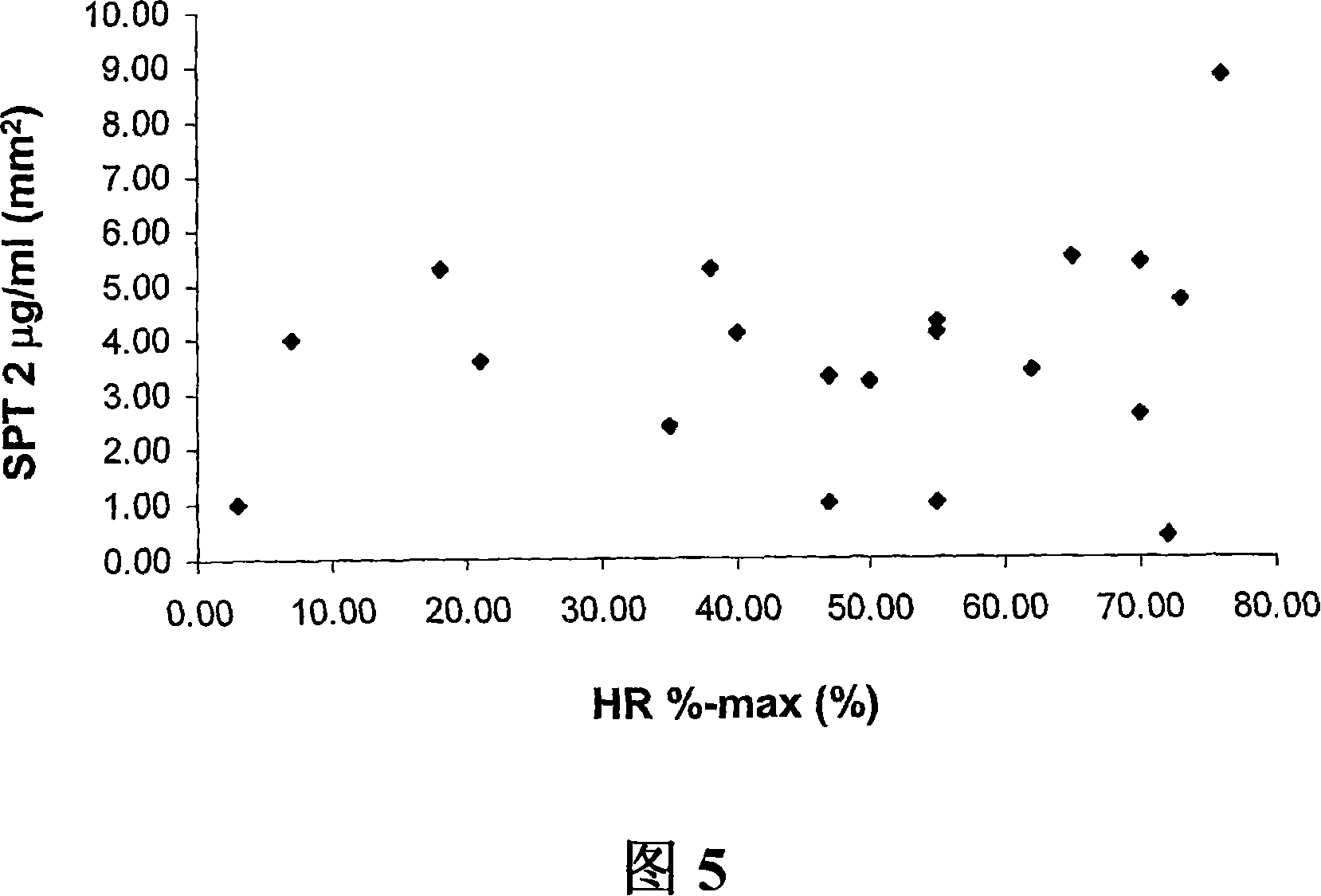
[1203] To determine the patient's sensitivity prior to treatment so that the correct dose can be administered, a whole blood basophil histamine release test is used. Patients with high sensitivity will receive smaller doses than patients with low sensitivity. Before treatment, dose-response curves were established using purified allergens. Simultaneously, cells are stimulated with anti-IgE to determine overall cellular sensitivity, which can affect sensitivity to allergens. The success of the treatment will usually be manageable after 4-8 weeks of treatment, after anti-allergen IgG antibodies become detectable. Because, blocking IgG antibodies may be responsible for the decreased sensitivity, it is useful to determine IgG levels for a given allergen. In addition, the dose response was again determined using purified allergen and anti-IgE. Doses giving maximal cell activation (ie maximal histamine release or CD203c upregulation) or doses determined to give some degree of act...
Embodiment 3
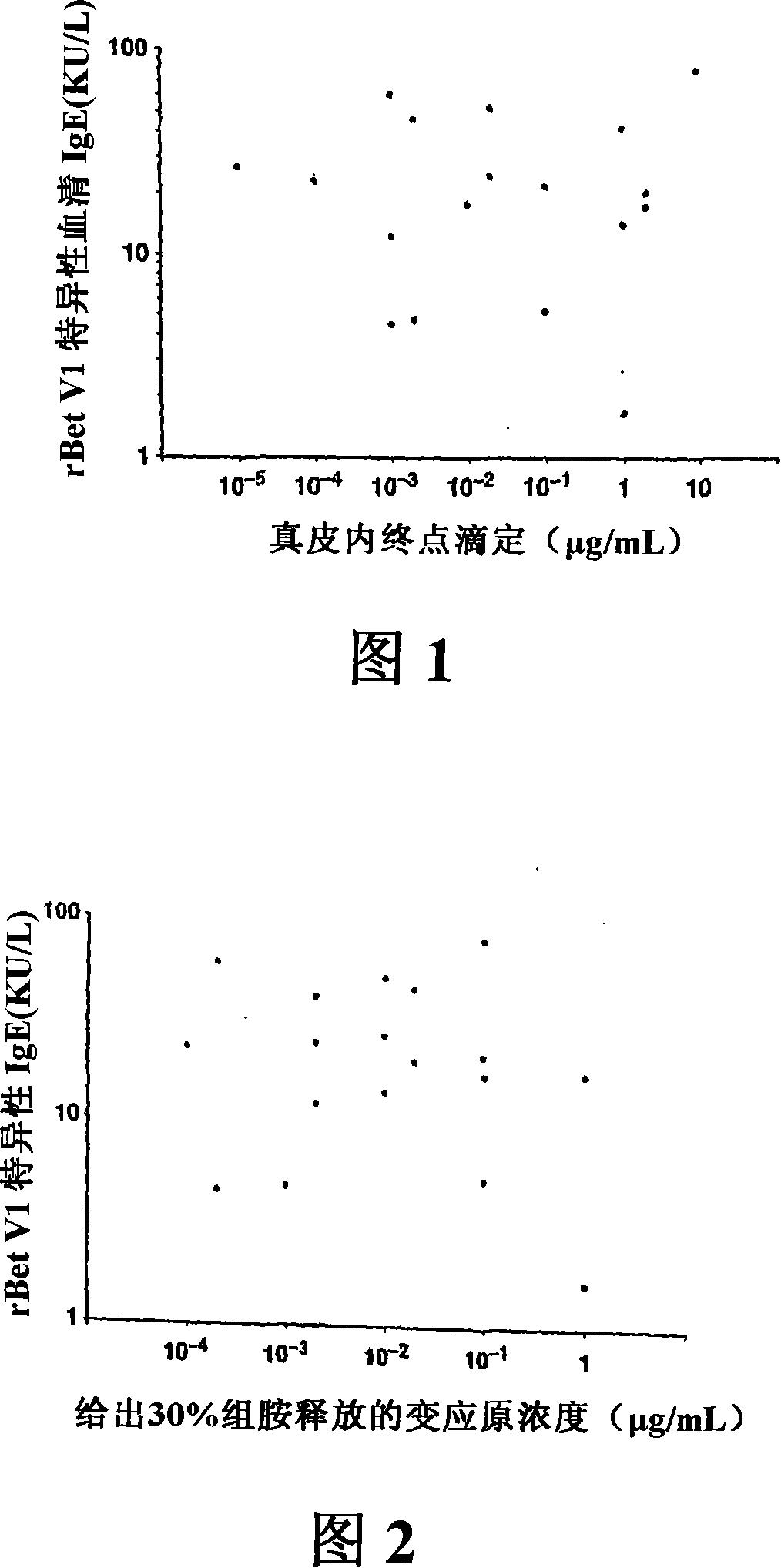
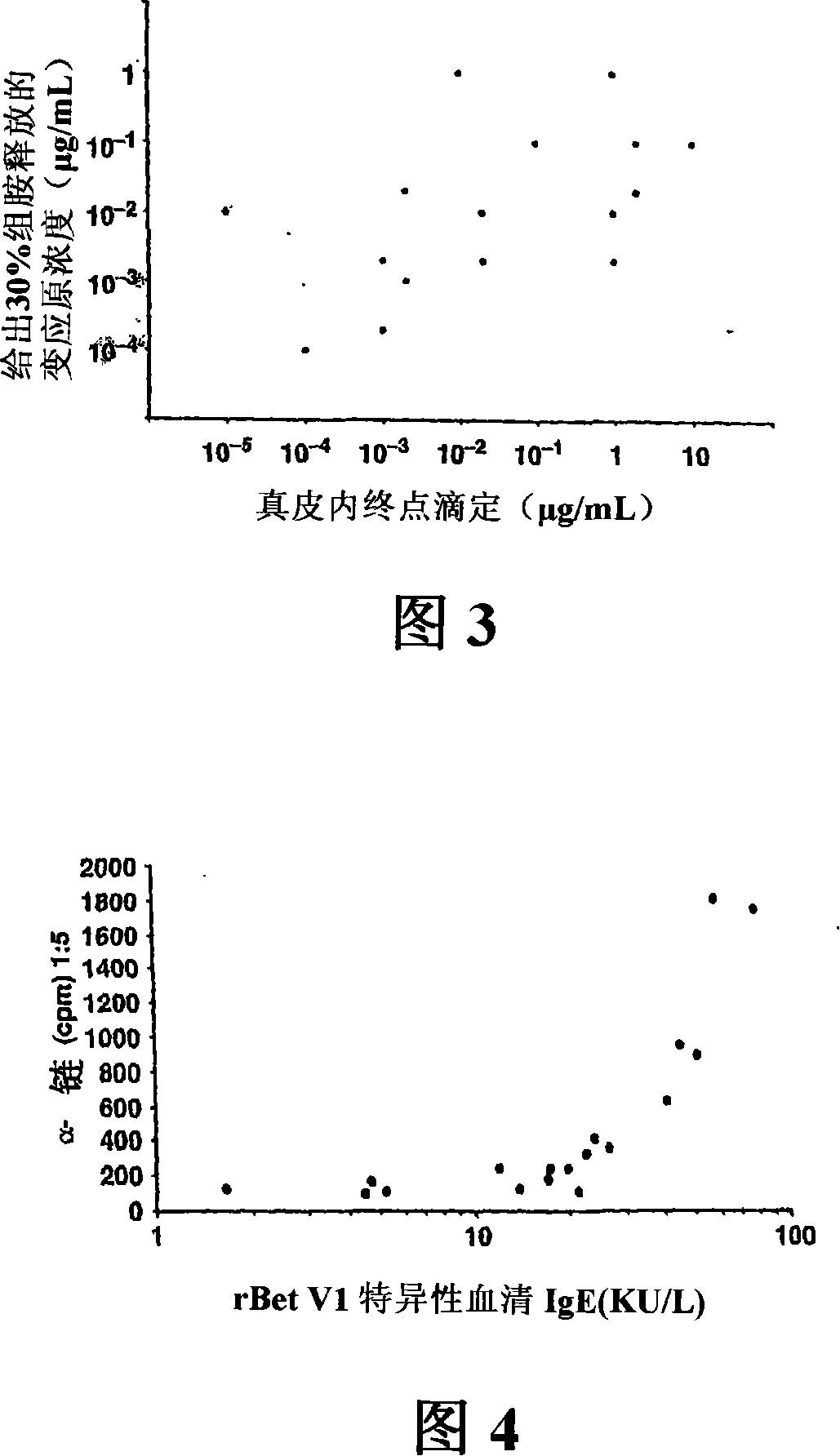
[1205] As described (Stahl-Skov et al. 1977. J Exp Immunol 27:432-439), no relationship between histamine release data and skin sensitivity was found when the basophil histamine release assay was performed with washed granulocyte preparations. relevance.
[1206] Histamine release can be performed using basophils from allergic patients. They were concentrated by dextran deposition, separated, washed, resuspended in histamine release buffer, and exposed to different concentrations of recombinant Bet in 96-well titer plates (TPP, Trasadingen, Switzerland) at 37°C. v1(10 -5 , 10 -4 ,, 10 -3 , 10 -2 , 10 -1 , 1 μg / ml) or anti-IgE mAbE-124-2-8 (1 μg / ml) for 30 minutes. After culturing, the cells were separated by centrifugation. The cell-free supernatant was recovered and analyzed for histamine content by using a commercial radioimmunoassay (Immunotech, Marseille, France). Histamine release was expressed as a percentage of total histamine measured in cell lysates (Valent et...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com