Light-emitting device and illuminating device
A technology for light-emitting devices and light-emitting elements, which is applied to electrical components, electric solid-state devices, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of low on-axis luminosity, large emission angle, increased light loss, etc., and achieves improved emission light intensity and light extraction efficiency. High, the effect of suppressing color variation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
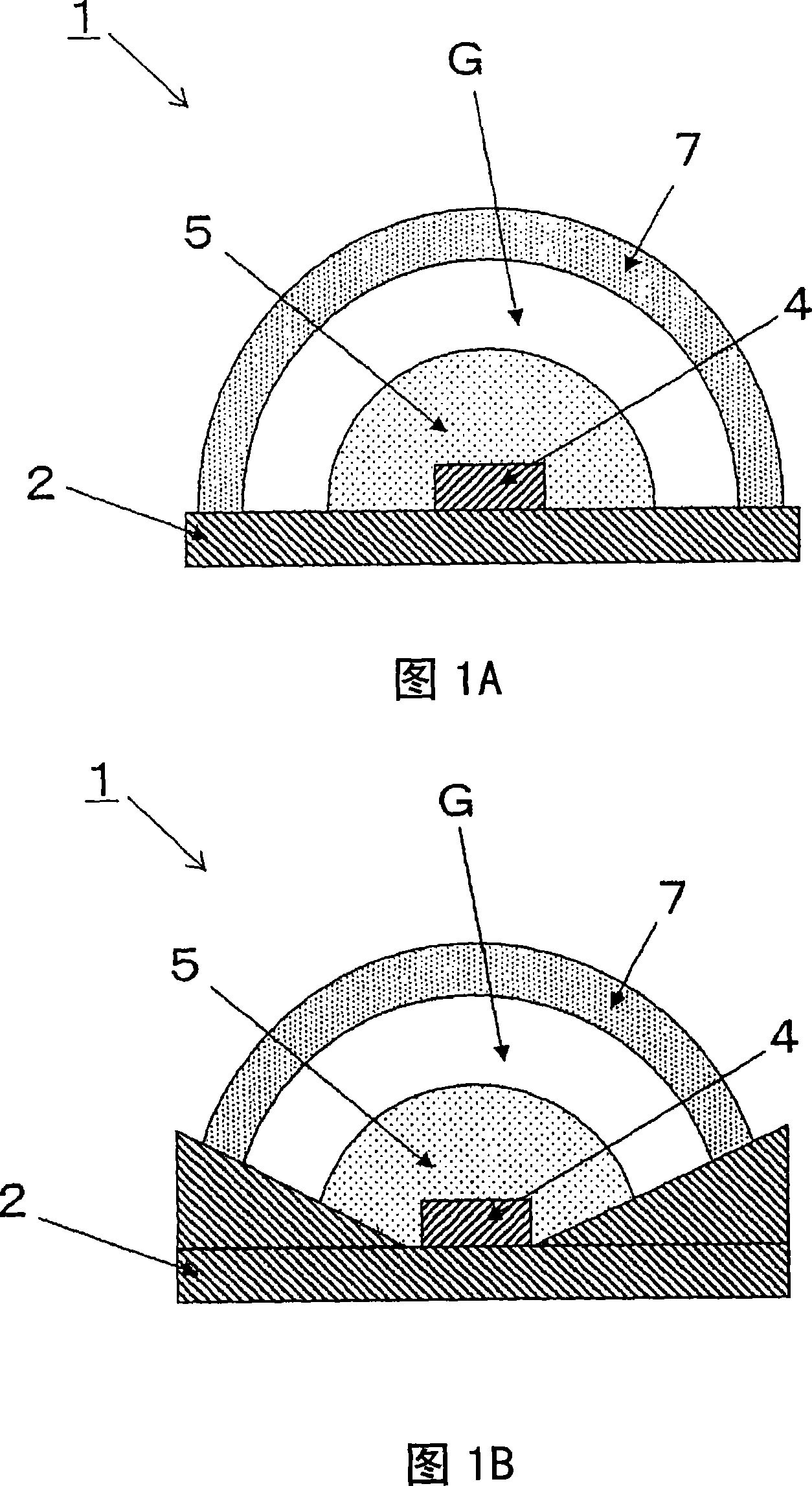
[0069] 1A and 1B are cross-sectional views showing the first embodiment of the present invention. First, as shown in FIG. 1A, the light-emitting device 1 is composed of a base 2, a light-emitting element 4, a first light-transmitting portion 5, a second light-transmitting portion 7, a third light-transmitting portion G, and the like.
[0070] On the base 2, a wiring conductor for supplying current to the light-emitting element 4 is formed extending from the upper surface to the lower surface or the side surface.
[0071] The light emitting element 4 is mounted on the upper surface of the base 2 so as to be electrically connected to the wiring conductor of the base 2.
[0072] The first light-transmitting portion 5 is formed of a light-transmitting material, and covers the light-emitting element 4.
[0073] The second translucent portion 7 is formed of a translucent material containing a phosphor that converts the wavelength of light emitted by the light-emitting element 4, and is ...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0089]Fig. 2 is a cross-sectional view showing a second embodiment of the present invention. The light-emitting device 1 is composed of a base 2, a housing 3, a light-emitting element 4, a first light-transmitting portion 5, a second light-transmitting portion 7, a third light-transmitting portion G, and the like.
[0090] On the base 2, a wiring conductor for supplying current to the light emitting element 4 is arranged from the upper surface to the lower surface or to the side surface.
[0091] The light emitting element 4 is mounted on the upper surface of the base 2 so as to be electrically connected to the wiring conductor of the base 2.
[0092] The casing 3 is fixed on the base 2 and has an inner surface inclined upward in a manner of surrounding the light emitting element 4. It is preferable that the inner surface of the housing 3 has light reflectivity from the viewpoint of light use efficiency.
[0093] The first light-transmitting portion 5 is formed of a light-transmit...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
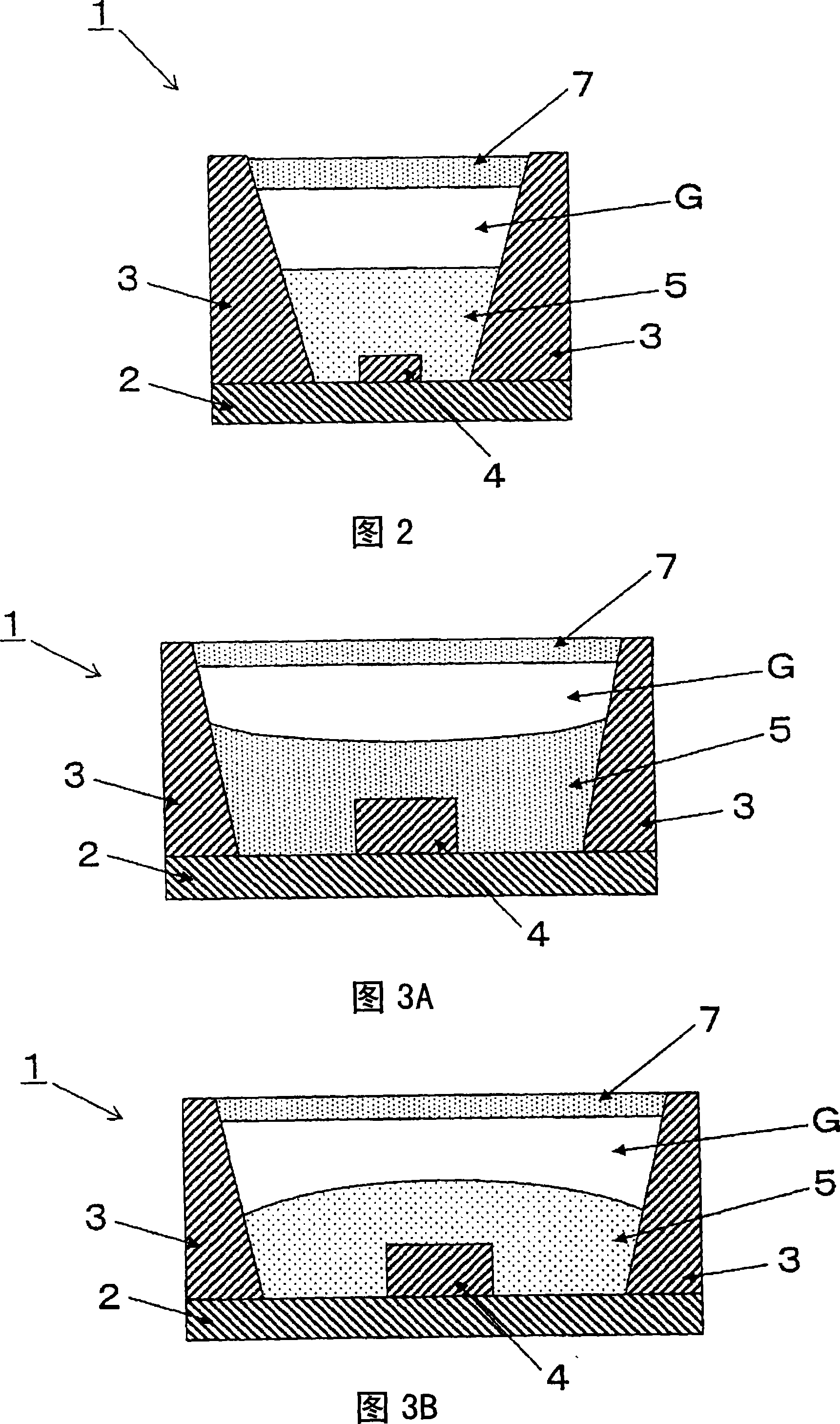
[0106] 3A and 3B are cross-sectional views showing a third embodiment of the present invention. First, as shown in FIG. 3A, the light-emitting device 1 is composed of a base 2, a housing 3, a light-emitting element 4, a first light-transmitting portion 5, a second light-transmitting portion 7, a third light-transmitting portion G, and the like.
[0107] On the base 2, a wiring conductor for supplying current to the light emitting element is formed extending from the upper surface to the lower surface.
[0108] The light emitting element 4 is mounted on the upper surface of the base 2 so as to be electrically connected to the wiring conductor of the base 2.
[0109] The housing 3 is fixed on the base 2 and has an inner surface inclined upward so as to surround the light emitting element 4. It is preferable that the inner surface of the housing 3 has light reflectivity from the viewpoint of light use efficiency.
[0110] The first light-transmitting portion 5 is formed of a light-tr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com