Centralized heat capacity matrix method of finite element solving rolling process temperature field
A rolling process and heat capacity matrix technology, applied in the field of rolling, can solve problems such as affecting calculation stability and accuracy, time and space oscillation, and less than ideal effects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
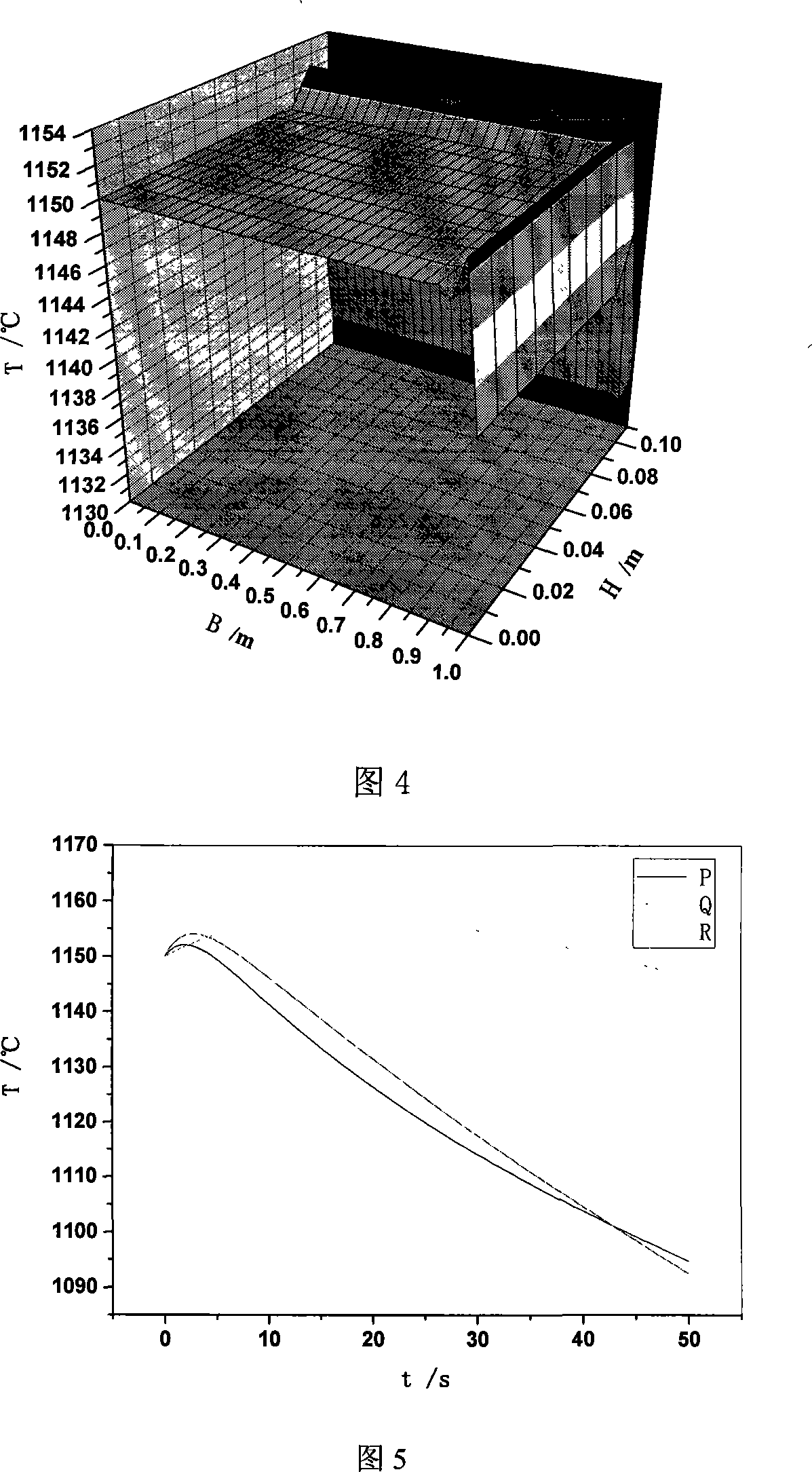
[0078] The calculation of the two-dimensional transient temperature field of the cross section in the process of air cooling after the plate comes out of the heating furnace is taken as an example to illustrate.
[0079] (1) Calculation conditions
[0080] Steel plate width B=2.0m, thickness H=0.22m, density ρ=7800.0kg / m3, specific heat c=670.0J / (kg.K), thermal conductivity k=30.0W / (m.K), and air The heat transfer coefficient is regarded as a function of temperature, the initial temperature of the steel plate is uniformly distributed (T0=1150°C), and the ambient temperature T∞=25°C.
[0081] (2) Finite element mesh
[0082] Assuming that the rolled piece is symmetrical, take a quarter of the section as the research object, take its symmetry center as the origin coordinates, use quadrilateral isoparametric elements, the number of elements in the width direction is m=30, and the number of elements in the thickness direction is n=10. The element division is shown in Figure 3 sh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com