Two-dimensional transversal zeeman double-frequency laser linearity/coaxiality measuring device
A coaxiality measurement, Zeeman dual-frequency technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, optical devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of inability to guarantee the consistency of angle rotation, inability to measure at the same time, and errors, etc., to shorten the measurement time, The effect of simple structure and small deviation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0043] The present invention will be further described below with reference to the accompanying drawings and in conjunction with the embodiments.
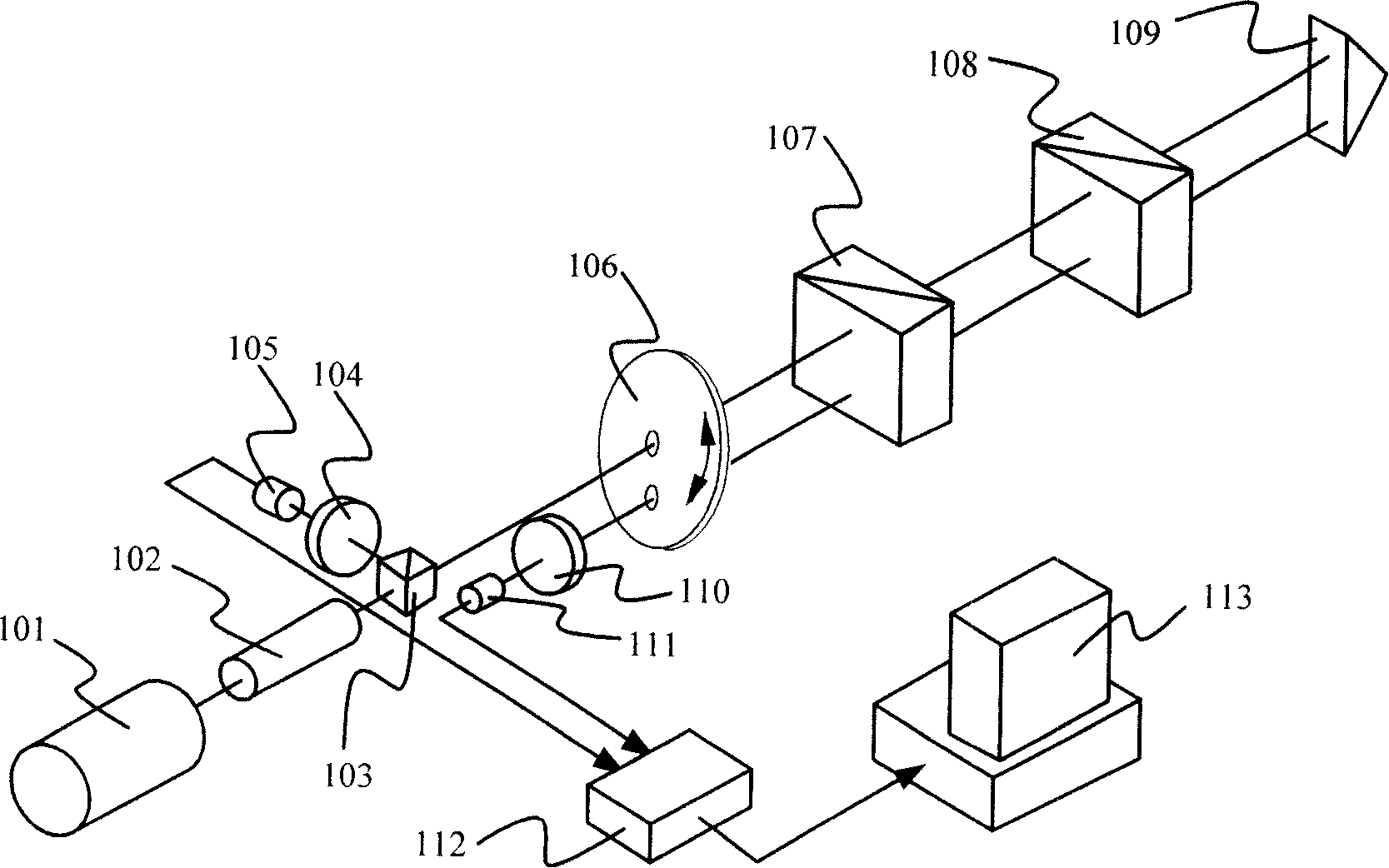
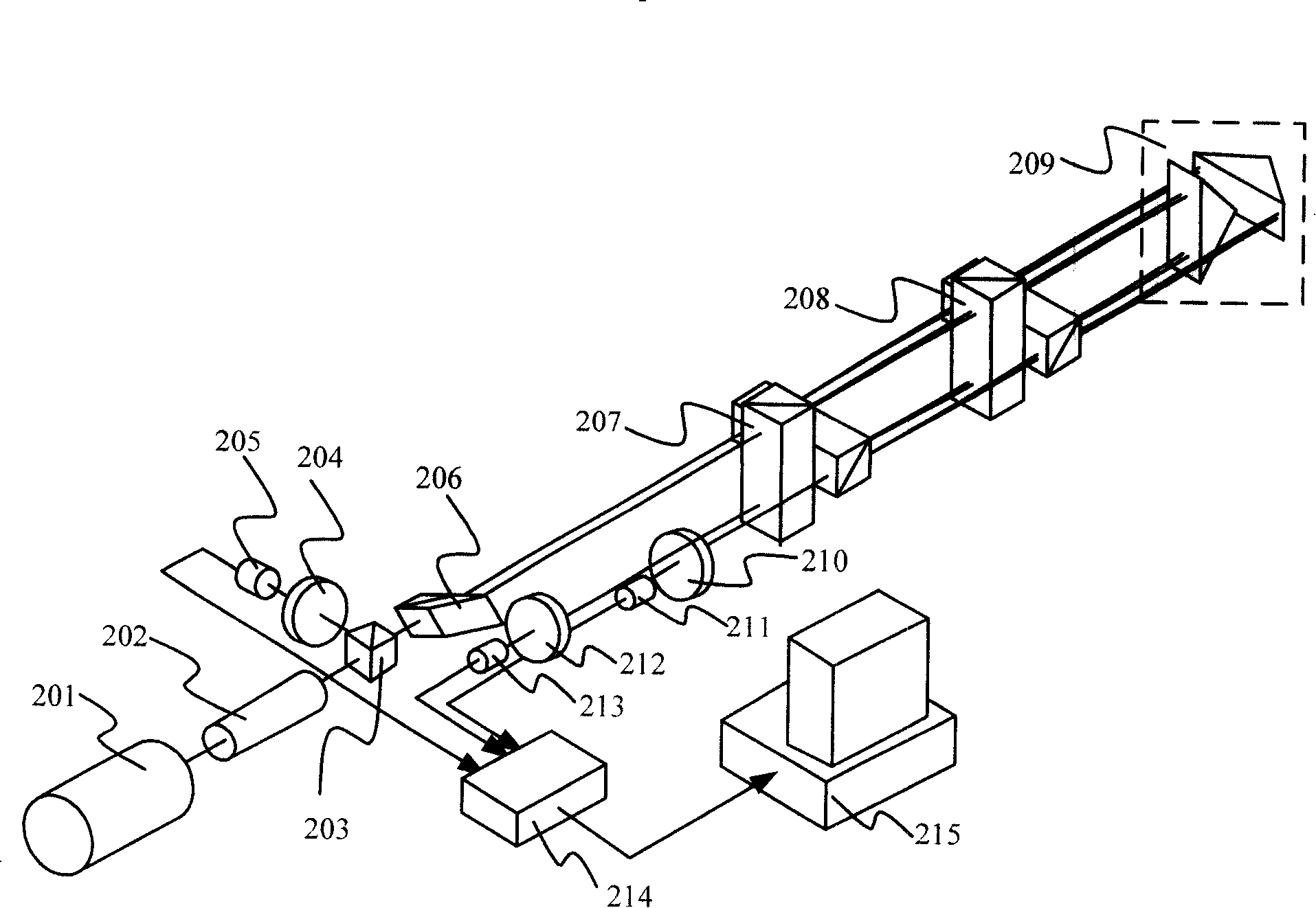
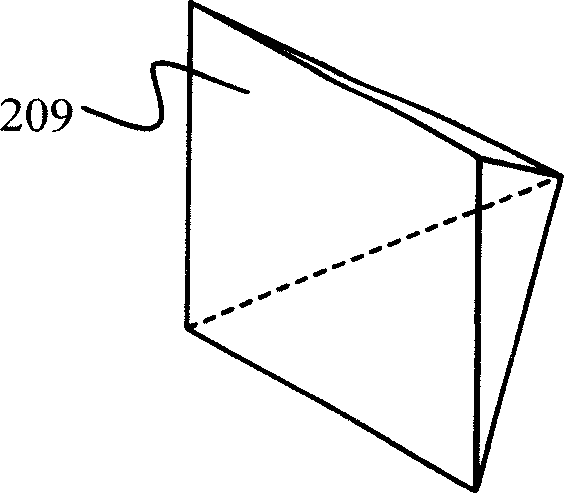
[0044] figure 2 It is a structural schematic diagram of an embodiment of the two-dimensional transverse Zeeman dual-frequency laser straightness / coaxiality measuring device of the present invention. The dual-frequency laser 201 of the device adopts a transverse Zeeman laser, which directly emits two mutually orthogonal linearly polarized lights, two linearly polarized components of different frequencies, and the directions are horizontal and vertical respectively, and both are perpendicular to the light direction. A telescope 202 and a beam splitter 203 are arranged successively on the optical path axis of the laser emitting end, and the beam splitter is a neutral non-polarizing beam splitter; the parallel beam splitter 206 is formed by gluing a rhombic prism and a right-angle prism, and is used for gluing The oblique surface of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com