Radio frequency recognizing privacy authentication method for dynamic cryptographic key update based on rarefaction tree
An authentication method and dynamic key technology, applied in the field of radio frequency identification, can solve the problems of affecting the privacy and security of labels, difficult label maintenance work, lack of key update system, etc., to increase hardware overhead, strong security, Effects of dynamic key update
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
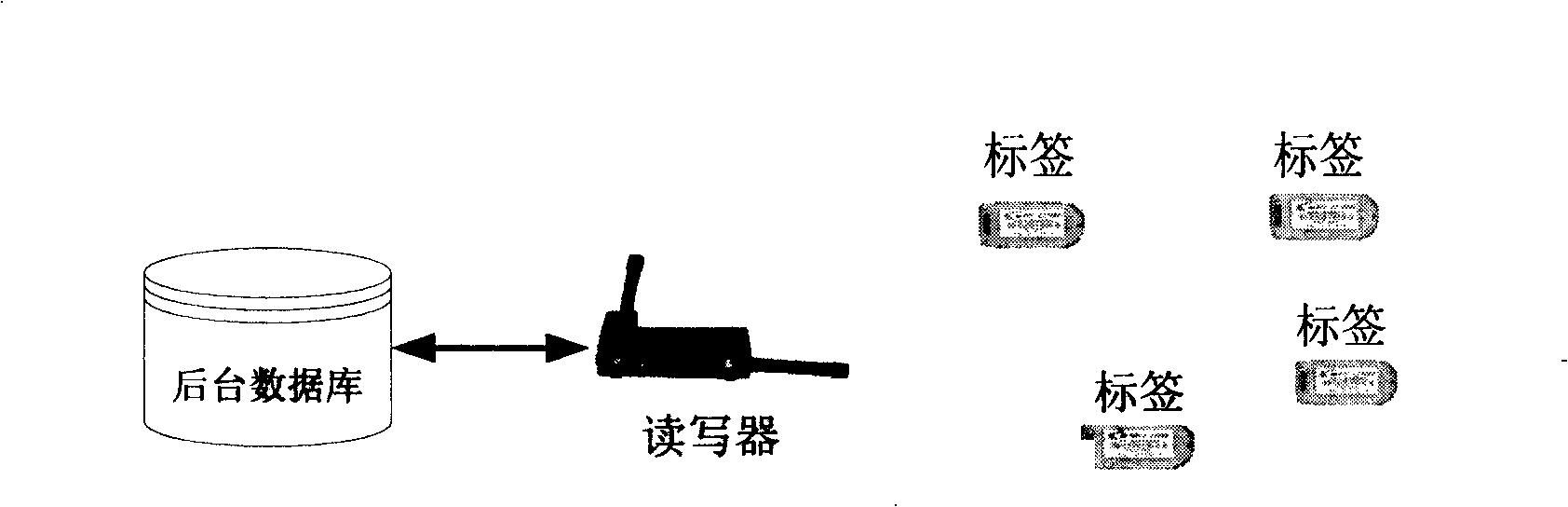
[0040] In order to make the purpose, technical scheme and advantages of the present invention clearer, the following will be combined with the attached Figures 6 to 10 The present invention is further described in detail.
[0041] Let h be a cryptographic hash function { 0,1 } * → { 0,1 } l r , where l r is the security parameter of the RFID system. Suppose there are n tags T in the system i , 1≤i≤n, and reader R. Reader R stores and organizes keys of all tags according to a sparse tree called key tree s. α represents the branching factor of the key tree, and d represents the depth of the key tree. To illustrate this scheme clearly, we only describe this strategy in terms of binary sparse trees, but there is no restriction on binary sparse trees for this schem...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com