Reference current circuit
A technology of reference current and reference voltage, applied in the direction of adjusting electrical variables, control/regulating systems, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of low temperature dependence of resistance, reducing the temperature dependence of reference current, and limitation of adjustment range.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
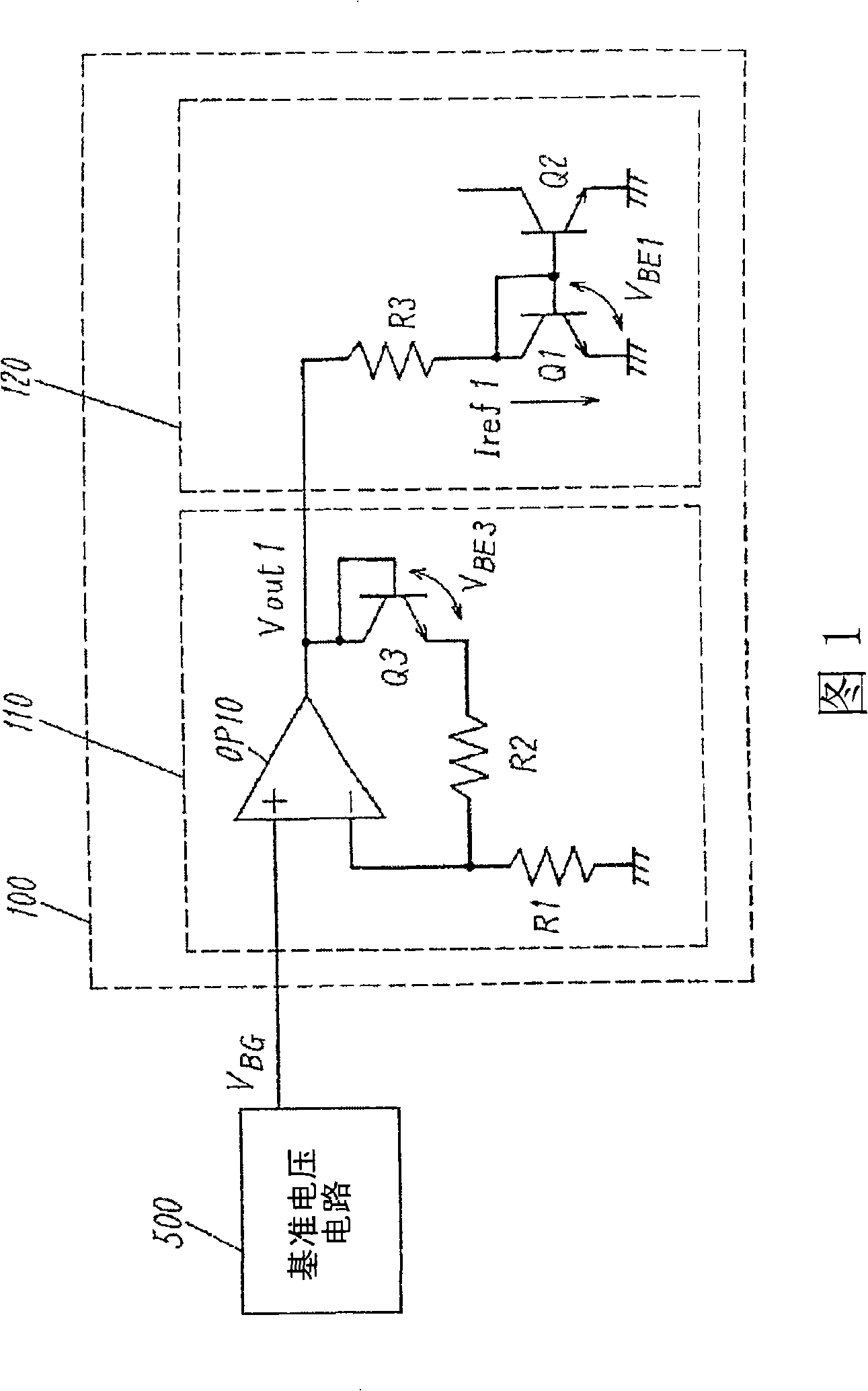
[0040] FIG. 1 shows the structure of a reference current circuit of a first embodiment of the present invention.
[0041] The reference current circuit 100 includes a non-inverting amplifier circuit 110 and a current source circuit 120 receiving an input from the non-inverting amplifier circuit 110 .
[0042] The non-inverting amplifier circuit 110 is composed of an amplifier circuit OP10, a resistor R1, a resistor R2, and a transistor Q3. The amplifier circuit OP10 has an inverting input terminal, a non-inverting input terminal, and an output terminal; a resistor R1 is inserted into the wiring to connect the inverting input terminal and a ground terminal; a resistor R2 and a transistor Q3 functioning as a temperature compensation element are inserted into the wiring Connect the output terminal and inverting input terminal. The non-inverting input terminal of the amplifier circuit OP10 receives a reference voltage V that does not depend on the temperature T and the power supp...
no. 2 example
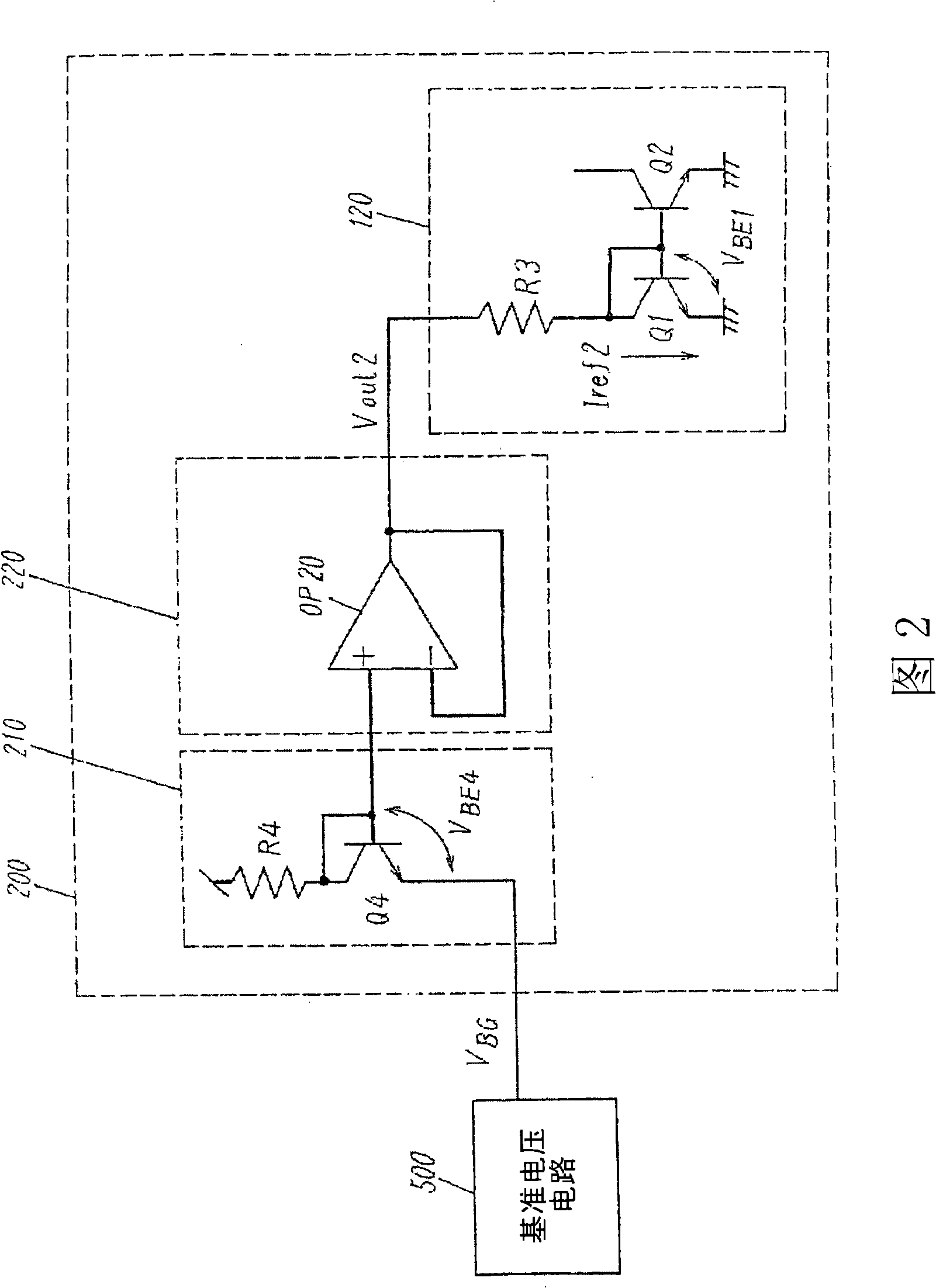
[0071] FIG. 2 shows the structure of a reference current circuit of a second embodiment of the present invention.
[0072] The reference current circuit 200 includes a temperature compensation circuit 210 , a voltage follower 220 receiving an output of the temperature compensation circuit 210 as an input, and a current source circuit 120 receiving an output of the voltage follower 220 as an input.
[0073] The temperature compensation circuit 210 is composed of a transistor Q4 and a resistor R4. Transistor Q4 receives the reference voltage V from its emitter BG input, the collector and base of transistor Q4 are connected to each other. Resistor R4 is inserted into the wiring connecting the power supply terminal and the collector of transistor Q4.
[0074] The voltage follower 220 is constituted by an amplifier circuit OP20 including an inverting input terminal, a non-inverting output terminal, and an output terminal. The collector and base of the transistor Q4 are connected...
no. 3 example
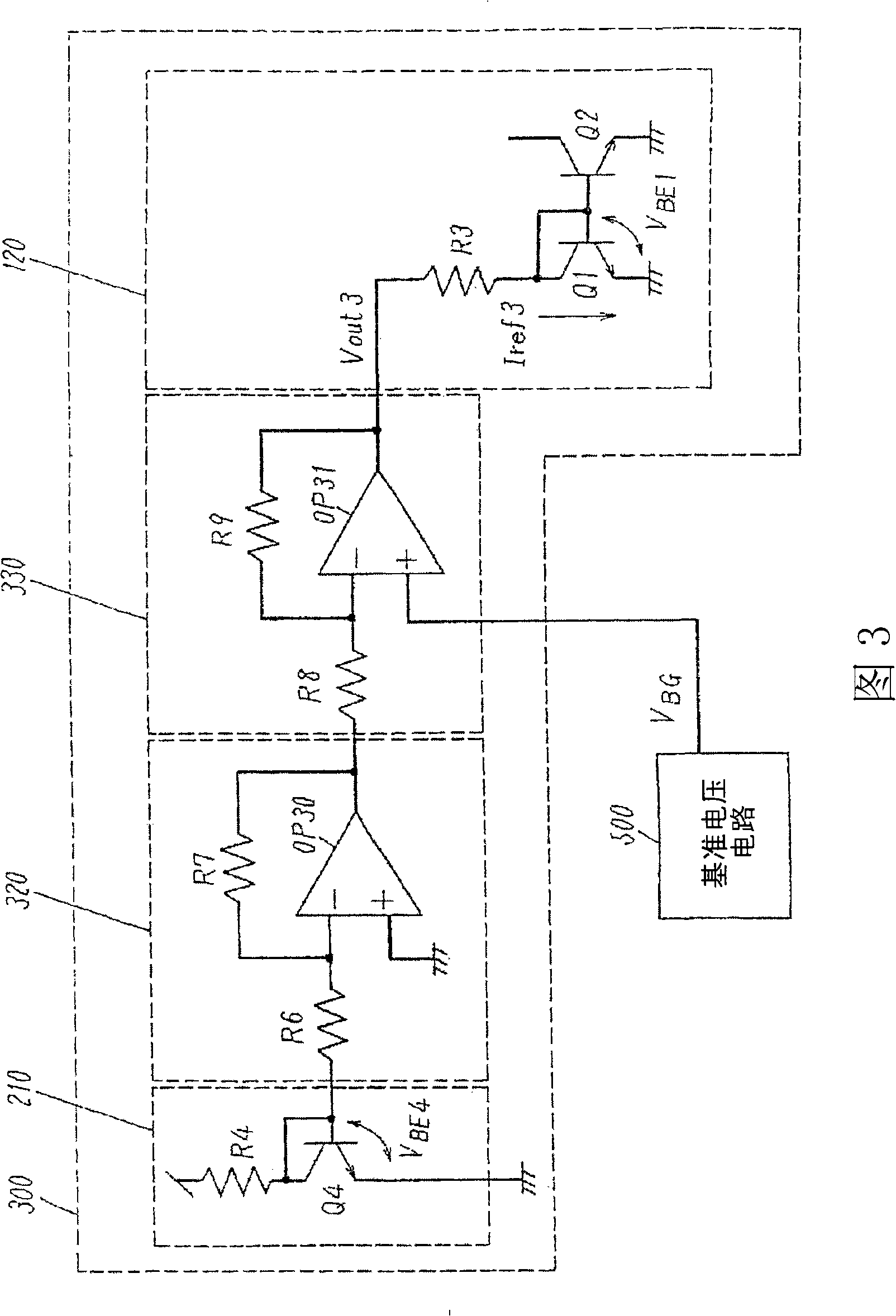
[0099] FIG. 3 shows the structure of a reference current circuit of a third embodiment of the present invention.
[0100] The reference current circuit 300 includes a temperature compensation circuit 210 , an inverting amplifier circuit 320 , an inverting amplifier circuit 330 and a current source circuit 120 . The inverting amplifier circuit 320 receives the output of the temperature compensation circuit 210 as an input; the inverting amplifier circuit 330 receives the output of the inverting amplifier circuit 320 as an input; the current source circuit 120 receives the output of the inverting amplifier circuit 320 as an input.
[0101] The temperature compensation circuit 210 is composed of a transistor Q4 and a resistor R4. The emitter of the transistor Q4 is grounded, and the collector and base of the transistor Q4 are connected to each other. Resistor R4 is inserted into the wiring connecting the power supply terminal and the collector of transistor Q4.
[0102] The inv...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com