Phosphorus-containing coarse nickel iron refining dephosphorization method
A crude nickel and dephosphorization technology, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of reducing nickel direct yield, large nickel loss, large slag amount, etc., and achieves the effects of uniform distribution, less slag amount, and low energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
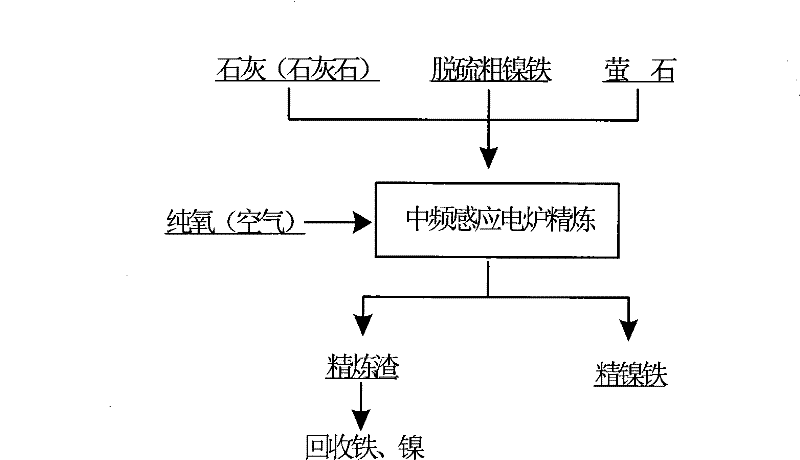
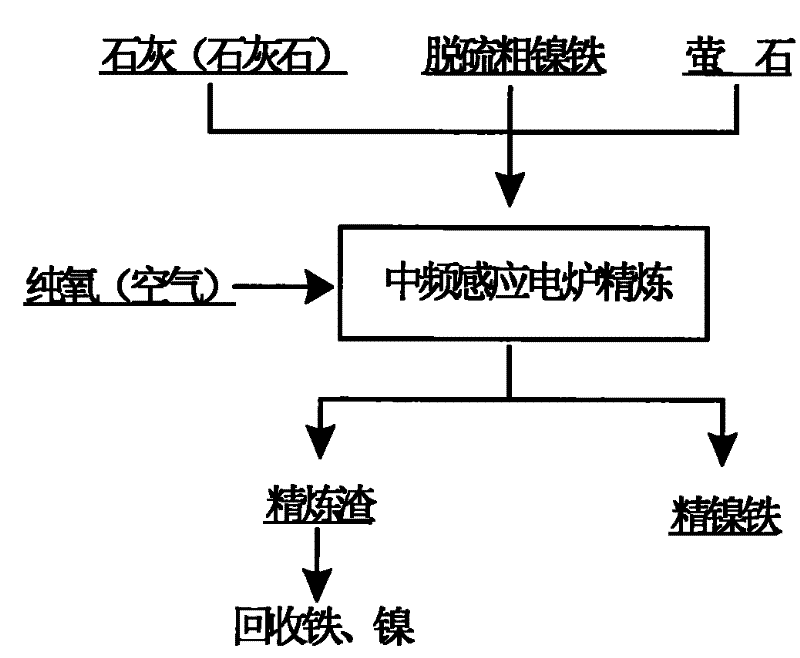
[0021] (1) Put the phosphorus-containing coarse nickel-iron raw material whose main chemical composition is 9.87% Ni, 80.23% Fe and 0.11% P into the medium-frequency induction furnace and heat up to 1500 ° C, and add coarse nickel-iron to the molten thick nickel-iron stirred by electromagnetic stirring Lime powder with 3% nickel-iron mass and 0.5% fluorite powder, lime and fluorite melt rapidly at high temperature;
[0022] (2) Blow industrial oxygen with a pressure of 0.3MPa into the melt in the furnace for top blowing refining, keep the oxygen lance muzzle 40mm away from the melt surface, stop the oxygen supply after blowing for 15 minutes, and tap the iron after slag removal to refine nickel Phosphorus in iron is reduced to 0.012%, both carbon and silicon are reduced to less than 0.015%, the nickel content is 16.23%, and the direct recovery rate of nickel is 95.34%.
Embodiment 2
[0024] (1) Put the phosphorus-containing coarse nickel-iron raw material whose main chemical composition is 8.12% Ni, 84.78% Fe and 0.15% P into the intermediate frequency induction furnace and heat up to 1600 ° C, and add coarse nickel-iron to the molten thick nickel-iron stirred by electromagnetic stirring Limestone powder with 8% nickel-iron mass and 3% fluorite powder, lime and fluorite melt rapidly at high temperature;
[0025] (2) Blow industrial oxygen with a pressure of 0.7MPa into the melt in the furnace for top-blown refining, keep the mouth of the oxygen lance at a distance of 15mm from the melt surface, stop the oxygen supply after 3 minutes of blowing, and tap the iron after slag removal to refine nickel Phosphorus in iron is reduced to 0.009%, both carbon and silicon are reduced to less than 0.015%, the nickel content is 15.88%, and the direct yield of nickel is 95.83%.
Embodiment 3
[0027] (1) Add phosphorus-containing coarse ferronickel raw materials whose main chemical components are 8.74% Ni, 82.76% Fe and 0.14% P into a power frequency induction furnace and heat up to 1550°C, then add 4.5% lime powder and 1.0% fluorite powder by mass of coarse nickel-iron, lime and fluorite melt rapidly at high temperature;
[0028] (2) Blow high-pressure air with a pressure of 0.5Mpa into the melt in the furnace for top blowing refining, keep the mouth of the oxygen lance at a distance of 30mm from the surface of the melt, stop the oxygen supply after blowing for 10 minutes, tap the iron after slag removal, and refine nickel Phosphorus in iron is reduced to 0.009%, both carbon and silicon are reduced to less than 0.015%, the nickel content is 15.19%, and the direct recovery rate of nickel is 96.26%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com