Opposed piston engine
An opposed-piston, engine technology, applied in engine components, machines/engines, engine cooling, etc., to solve problems such as difficulty in providing effective sealing of cylinders and pistons, inability to maintain tight tolerances, and inability to prevent piston crown expansion.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
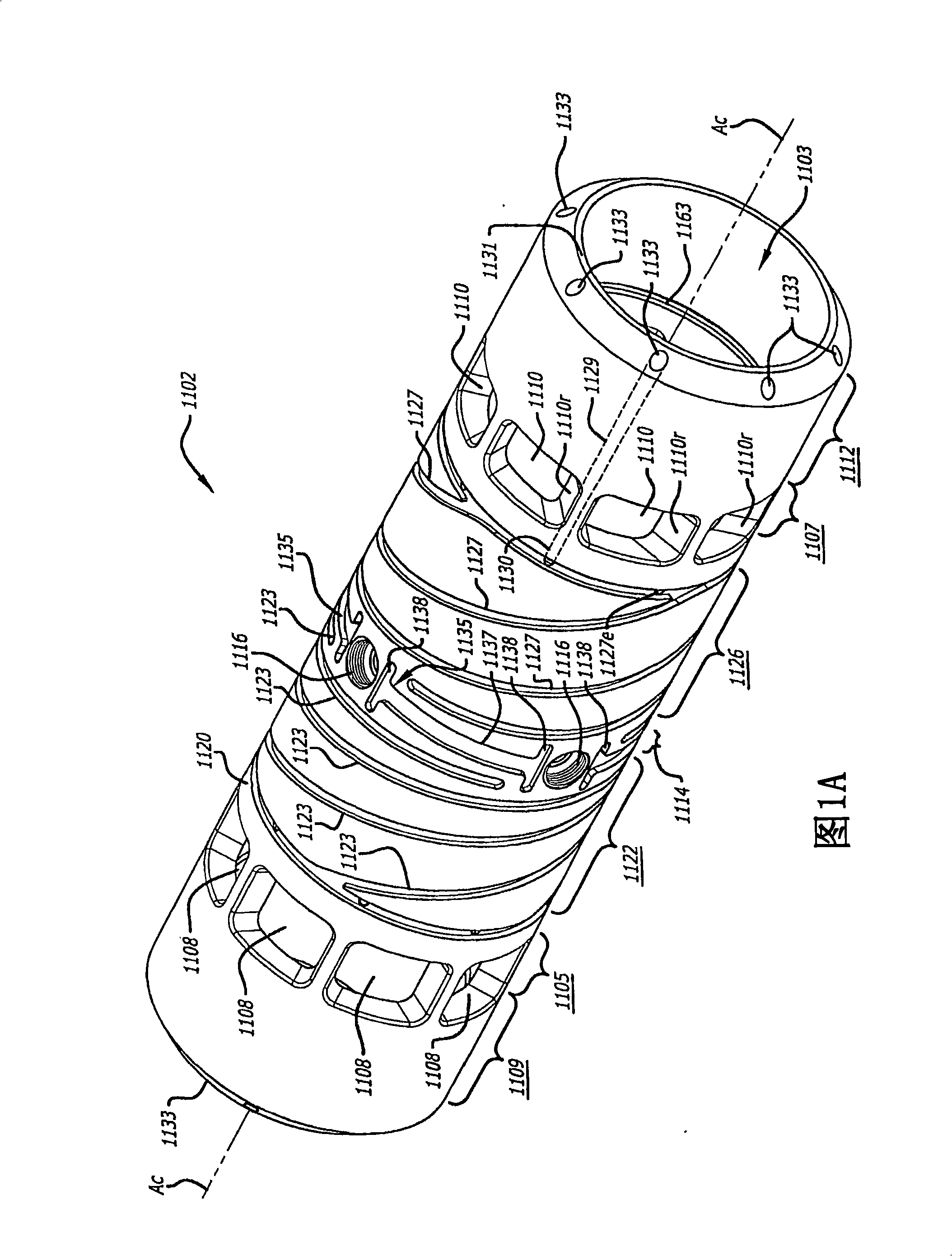
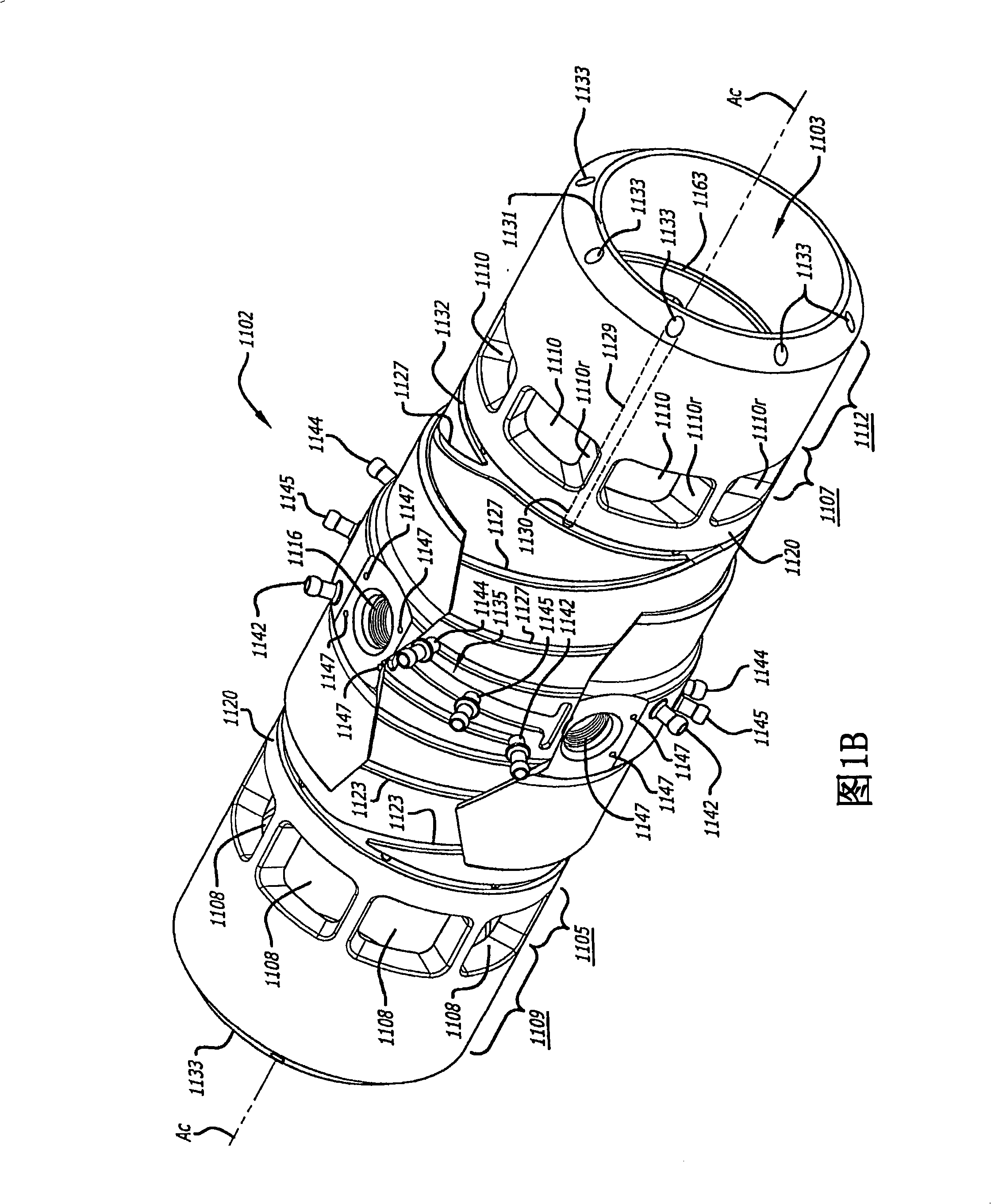
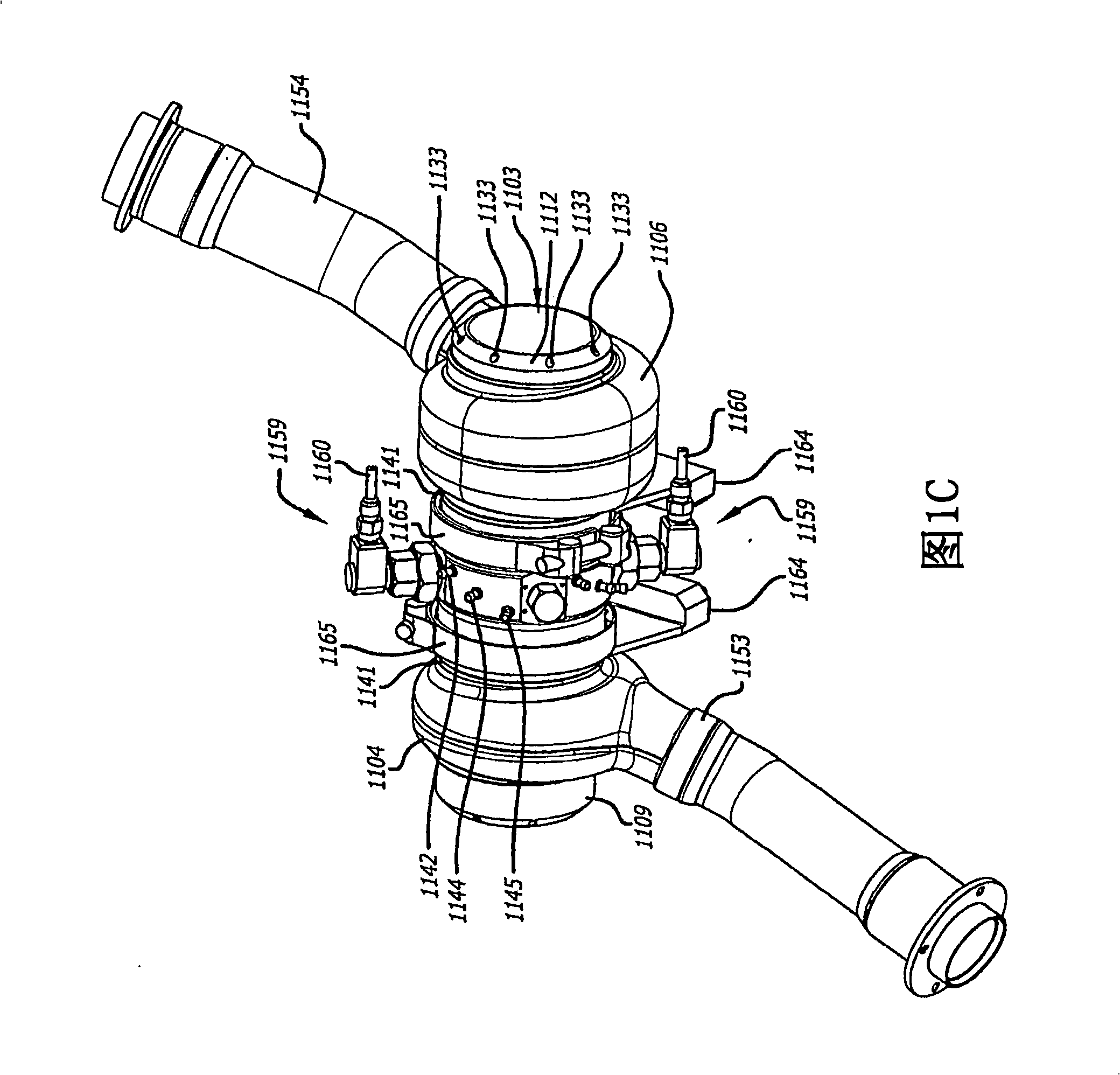
[0021] 1A-1D illustrate a cylinder 1100 that may be used in an opposed-piston internal combustion engine. The cylinder 1100 has four parts: a cylinder liner 1102 formed as an open cylindrical tube with a cylindrical bore 1103 , an exhaust manifold 1104 , an intake manifold 1106 and a cylinder sleeve 1140 . Cylinder 1100 is preferably made of aluminum such as high temperature aluminum alloy and may be cast as a single piece or assembled by securing manifolds 1104 and 1106 to cylinder sleeve 1140 and subsequently securing the subassembly to the outer surface of cylinder liner 1102 form. Longitudinal axis A of cylinder liner 1102 c Also the longitudinal axis of cylinder 1100 .
[0022]As best shown in FIG. 1A , the cylinder liner 1102 has an exhaust port 1105 consisting of a series of circumferentially spaced openings 1108 proximate an exhaust end 1109 of the cylinder liner 1102 . The cylinder liner 1102 also has an intake port 1107 consisting of a series of circumferentially ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com