Patents
Literature
182 results about "Opposed-piston engine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An opposed-piston engine is a reciprocating internal combustion engine in which each cylinder has a piston at both ends, and no cylinder head.
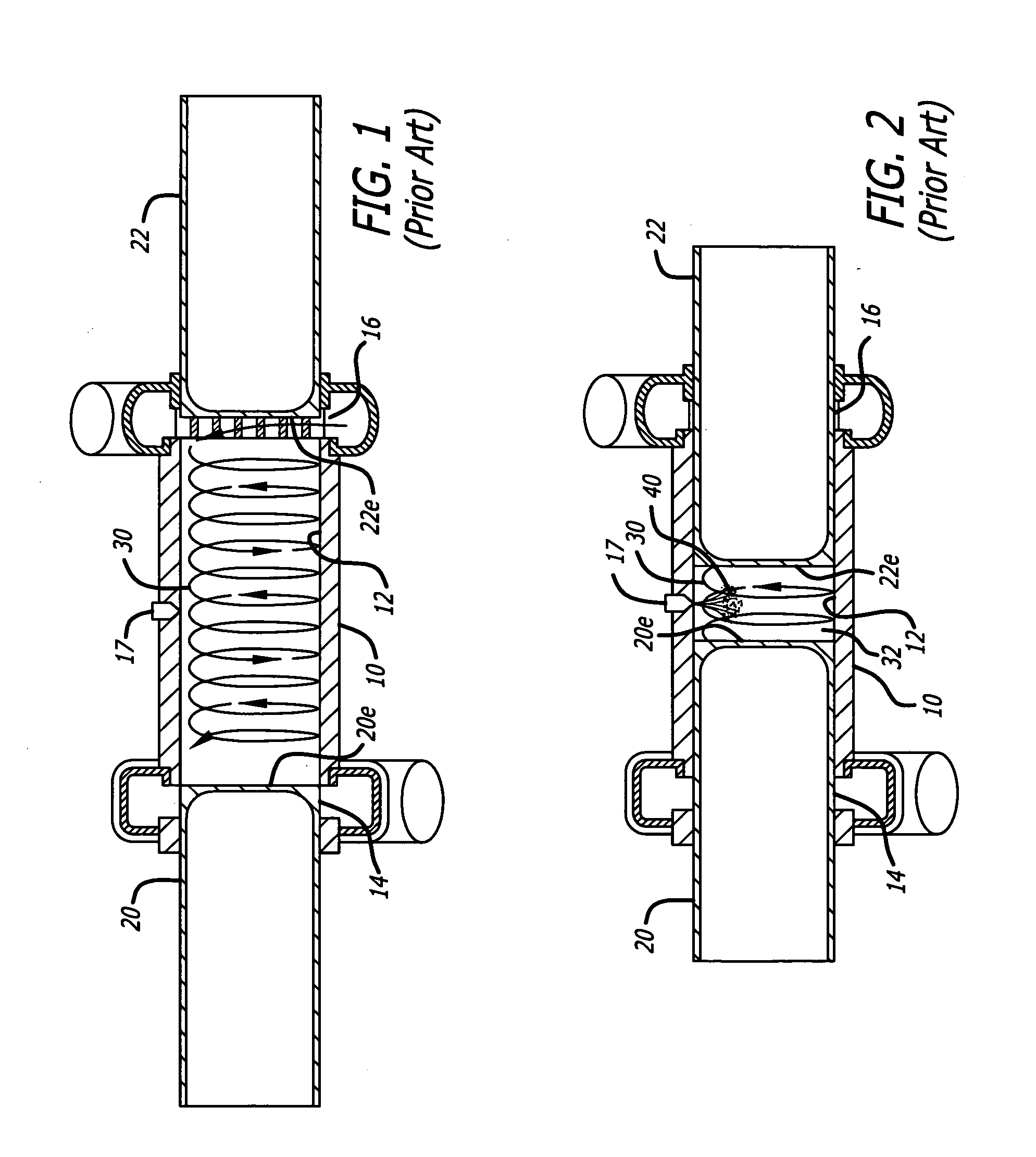
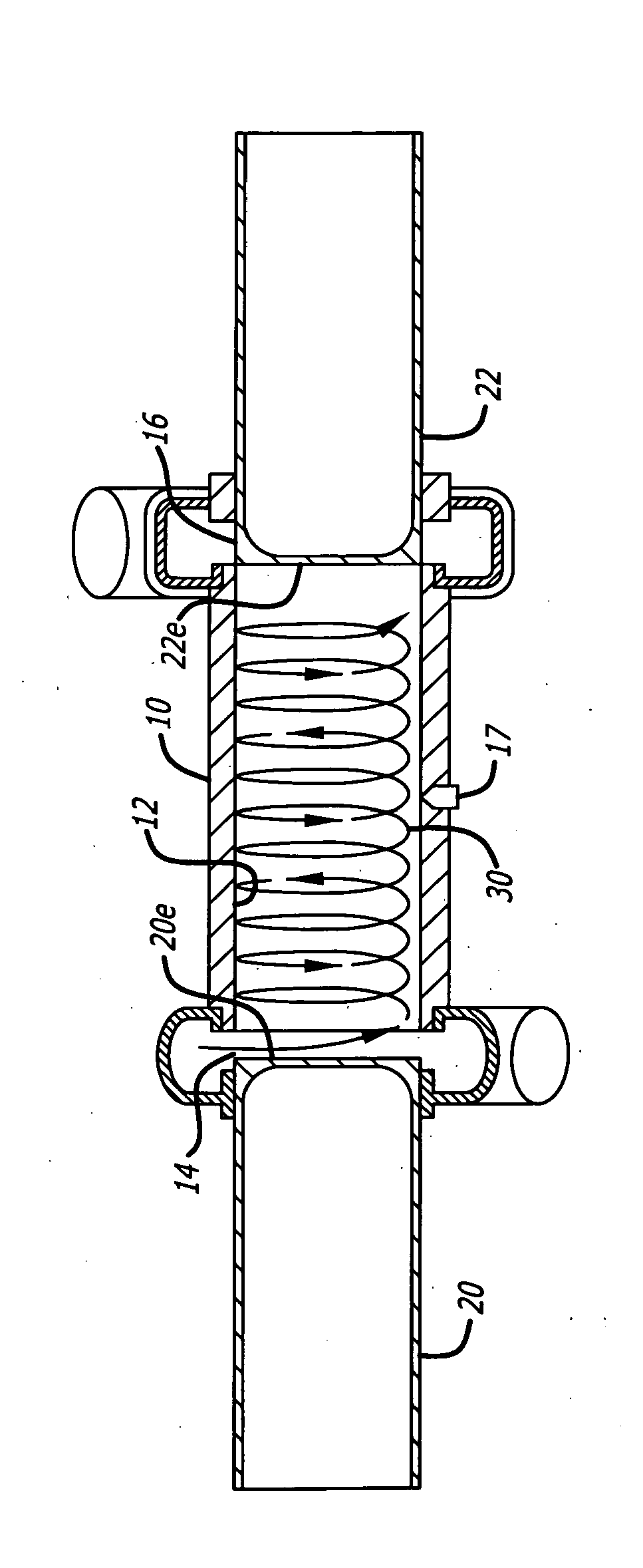
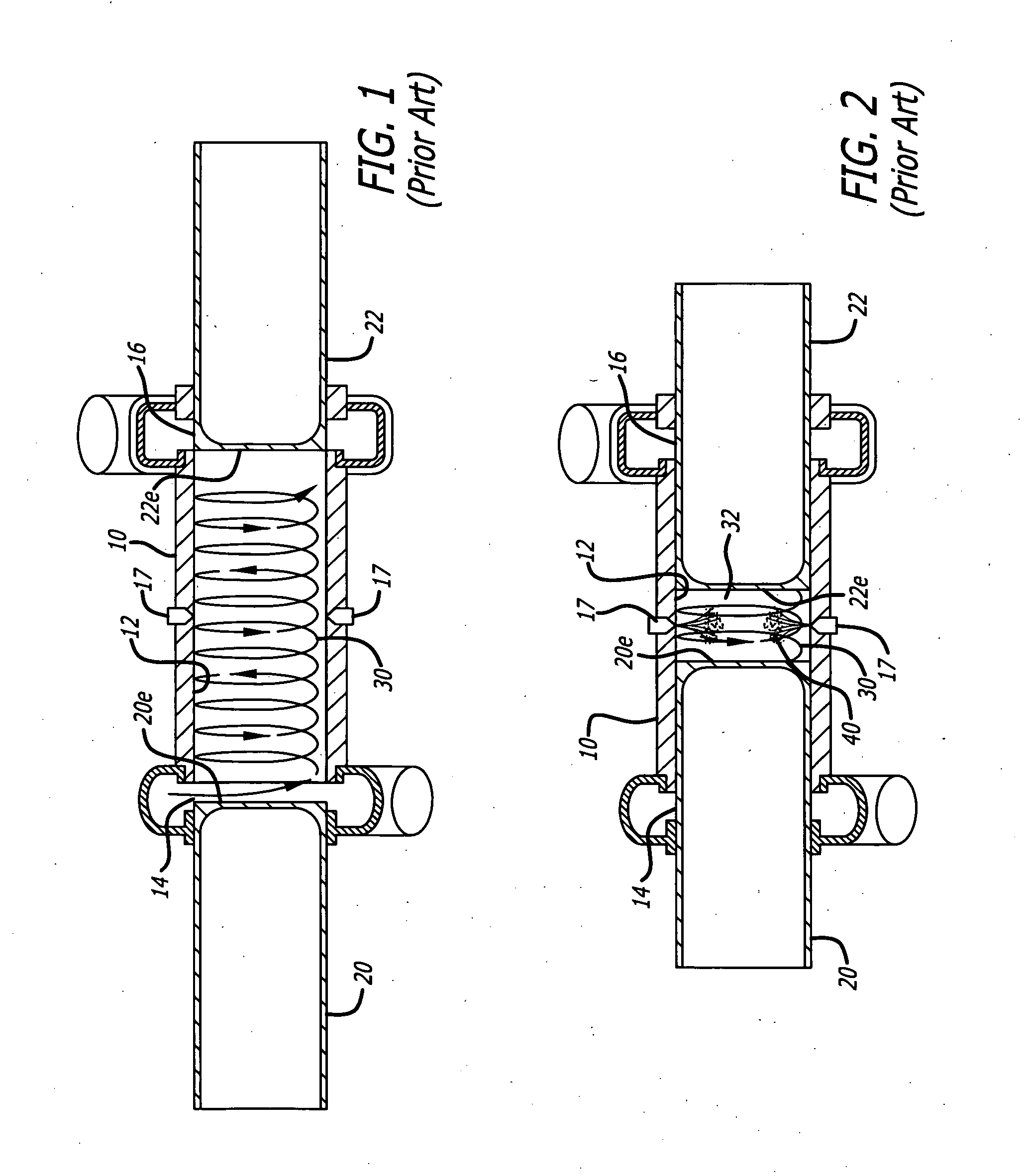
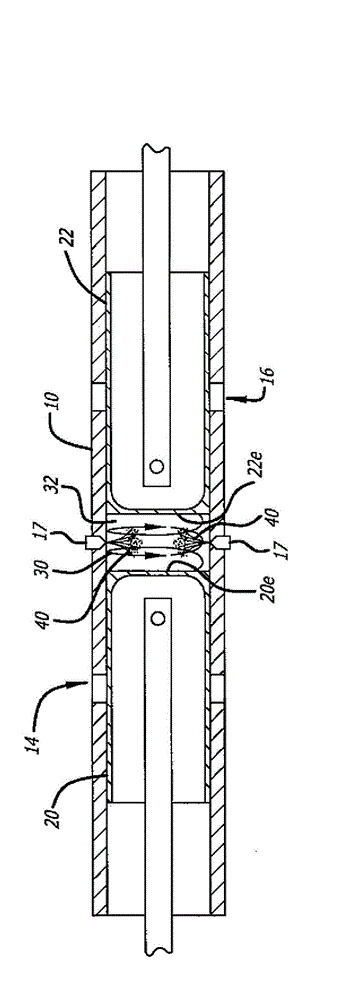
Opposed piston internal combustion engine with inviscid layer sealing
InactiveUS9909492B2Close toleranceAccurate concentricityCombustion enginesReciprocating piston enginesDetonationCombustion
An opposed-piston engine that forms an inviscid layer between pistons and the respective cylinder walls. In an aspect, the opposed-piston engine utilizes a Scotch yoke assembly that includes rigidly connected opposed combustion pistons. In an aspect, the Scotch yoke assembly is configured to transfer power from the combustion pistons to a crankshaft assembly. In an aspect, the crankshaft assembly can be configured to have dual flywheels that are internal to the engine, and can be configured to assist with an exhaust system, a detonation system, and / or a lubrication system.
Owner:PRIME GRP ALLIANCE
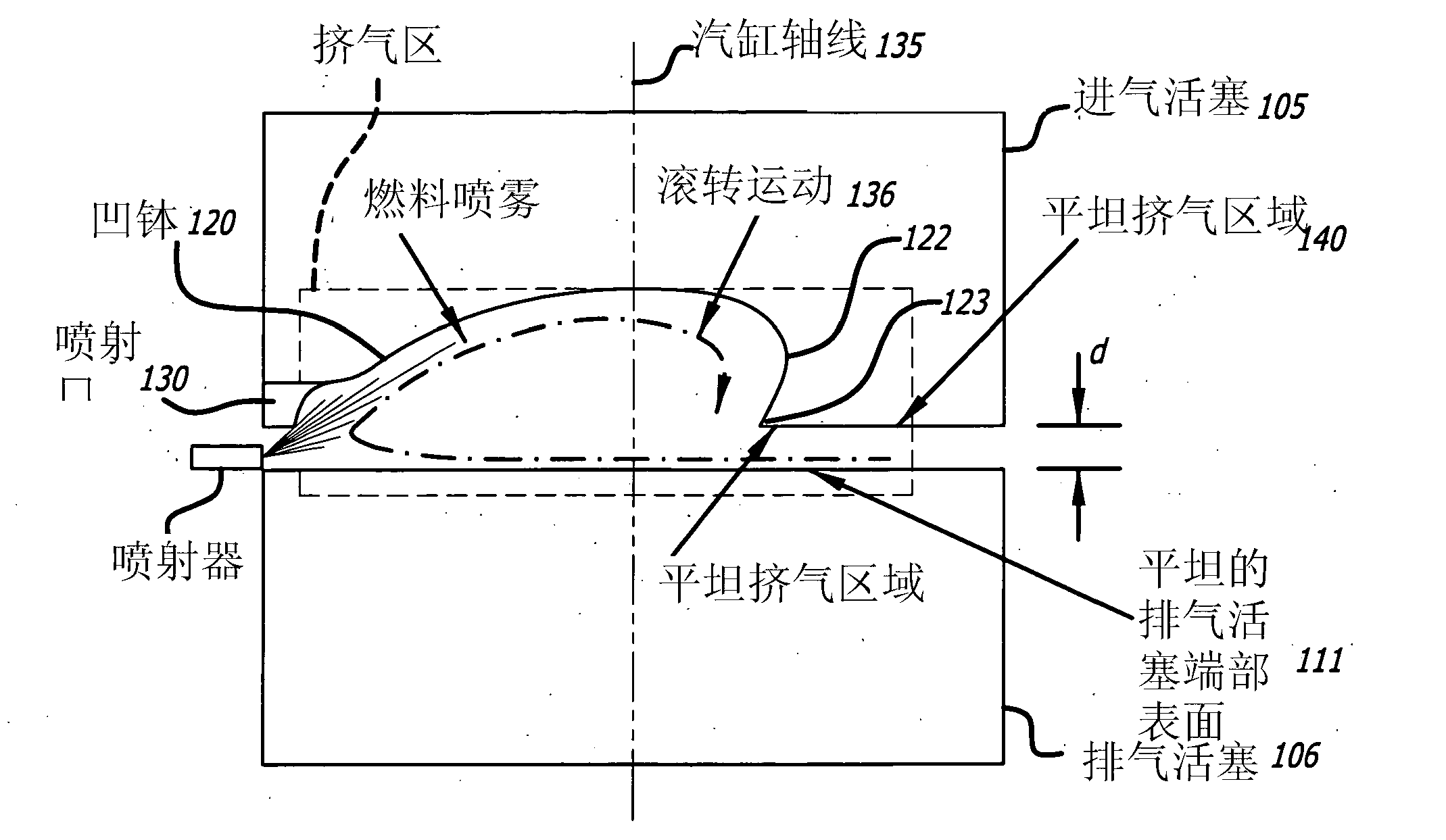
High-Squish Combustion Chamber With Side Injection
InactiveUS20130036999A1Internal combustion piston enginesReciprocating piston enginesCombustion chamberEngineering
A combustion chamber for an internal combustion engine is disclosed in which the piston has a large squish region at a peripheral location on the piston top and a depression in the center of the piston top. A side injector sprays fuel into the depression in the piston top through a channel defined in the squish region. In some embodiments, two injectors are provided that are diametrically opposed to each other. In some embodiments, the engine is an opposed-piston engine in which each piston has the squish regions and depressions in the piston top.
Owner:ECOMOTORS
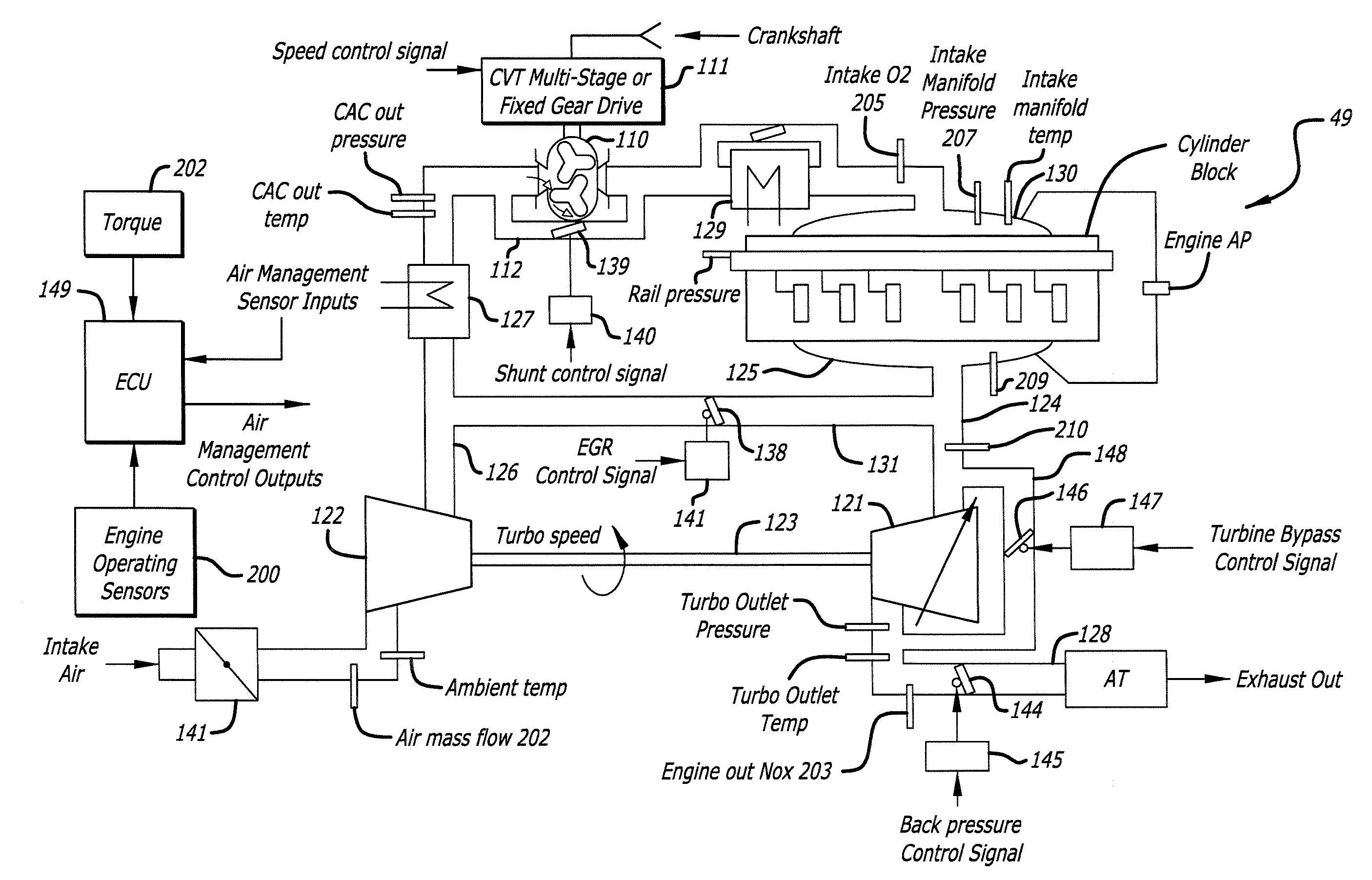
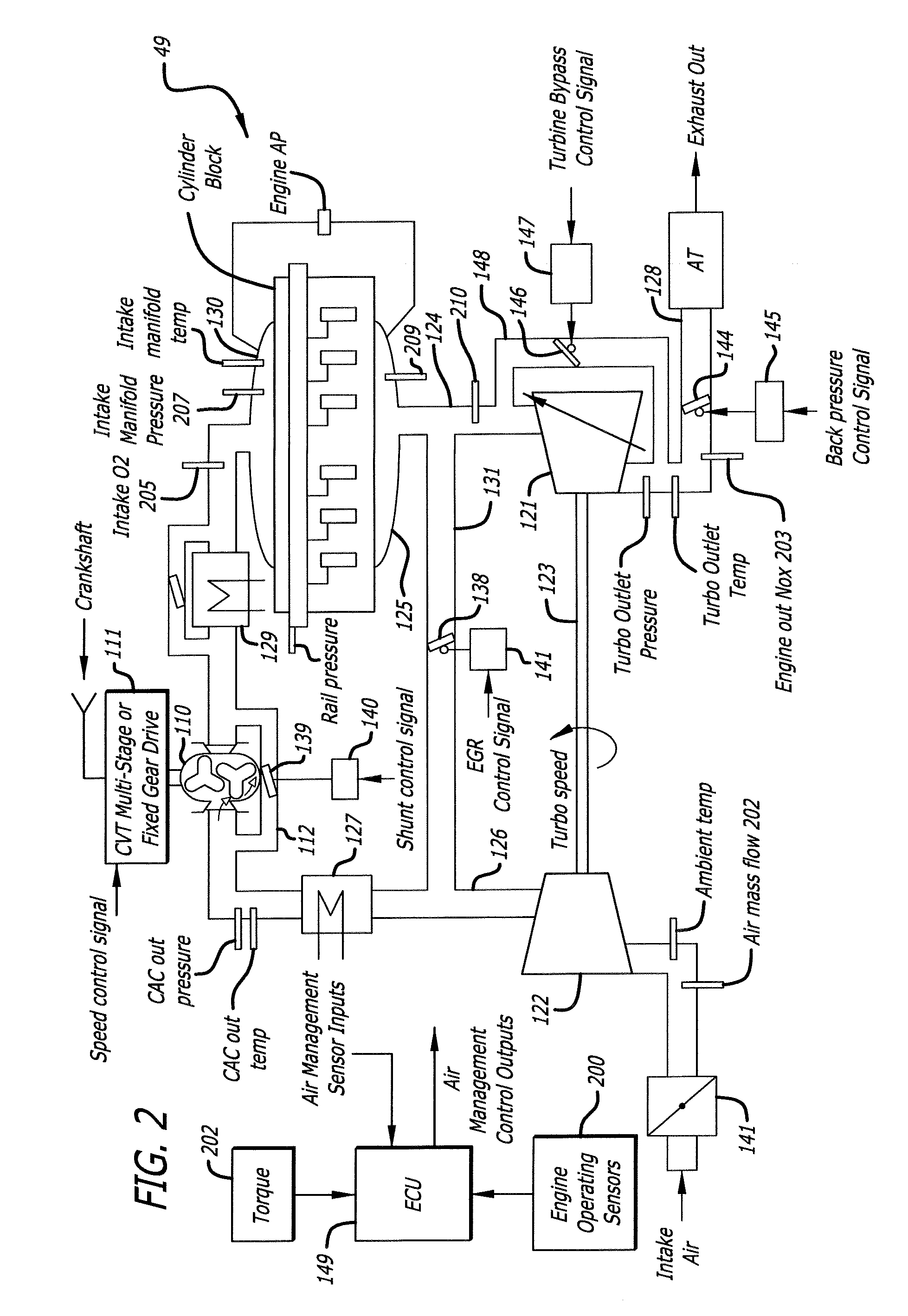
System and Method for Air Handling Control in Opposed-Piston Engines with Uniflow Scavenging
ActiveUS20140373816A1Reliable combustionImprove emission performanceElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesControl systemHandling system
In an air handling system of a uniflow-scavenged, two-stroke cycle opposed-piston engine, repeatable trapped mass and composition are achieved by determining provision of air handling setpoints that control operation of the engine's air handling system components. In some aspects, these setpoints govern operations of the air handling system by actively controlling the intake manifold pressure (IMP), EGR flow, and exhaust channel backpressure.
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC
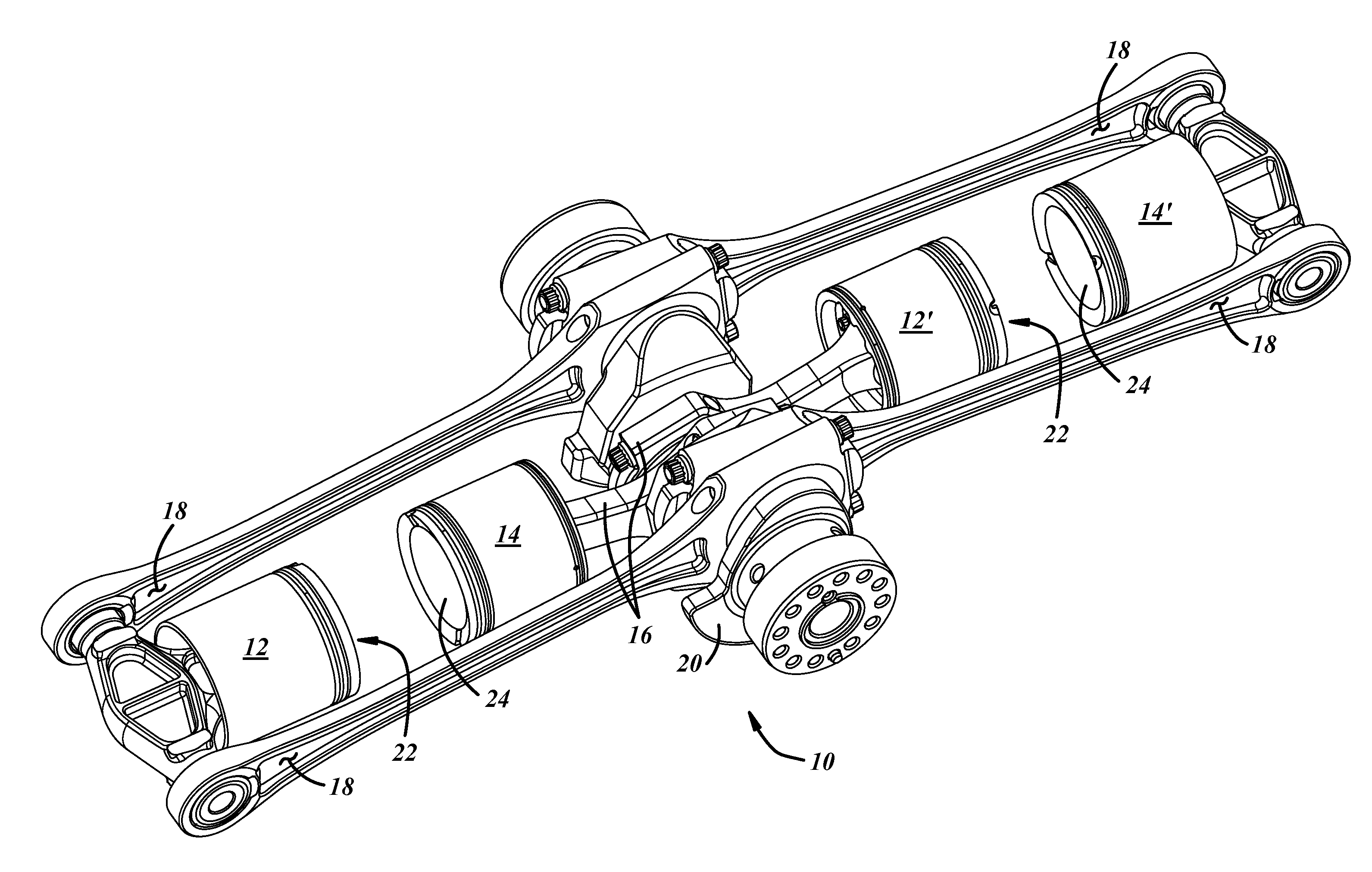
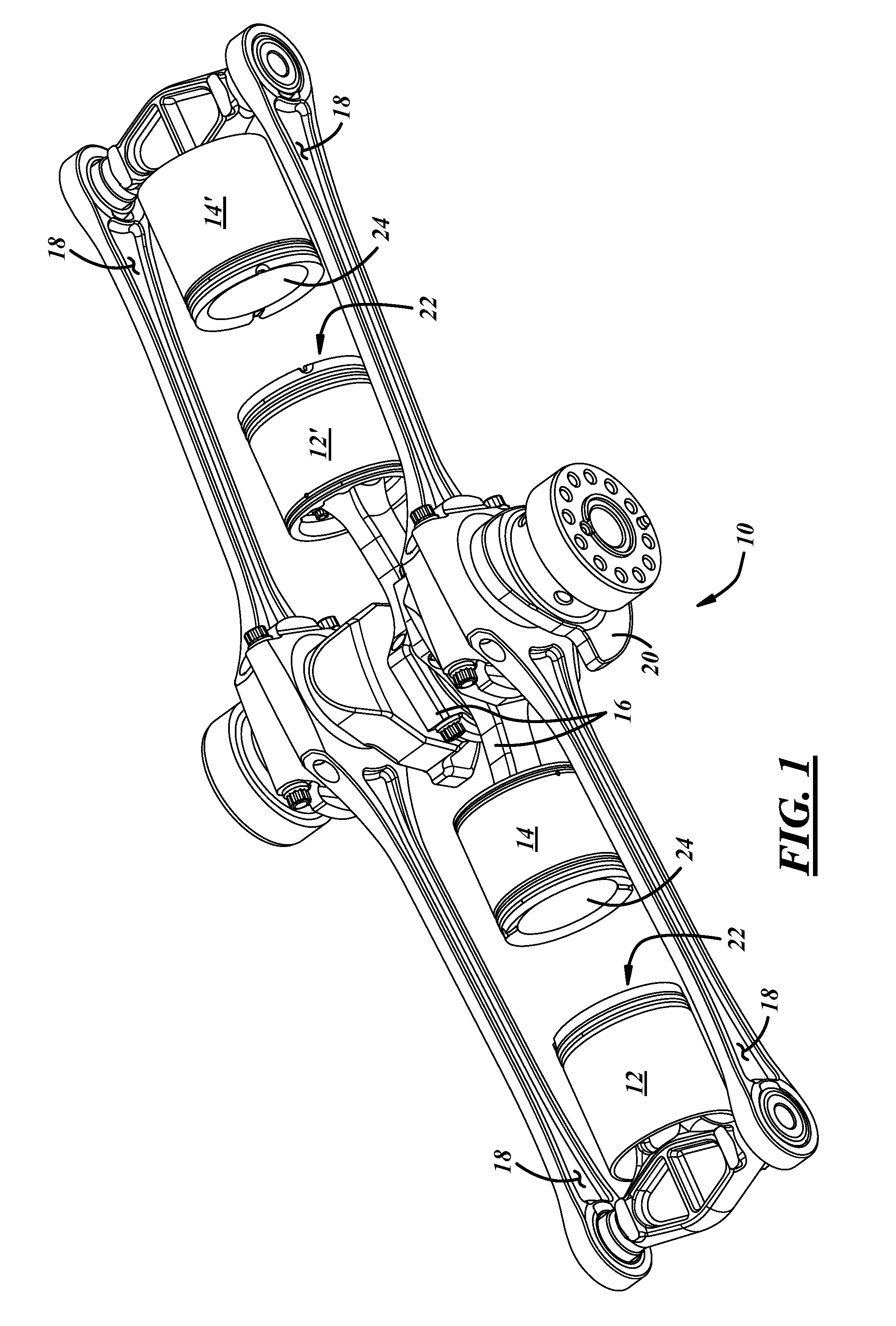
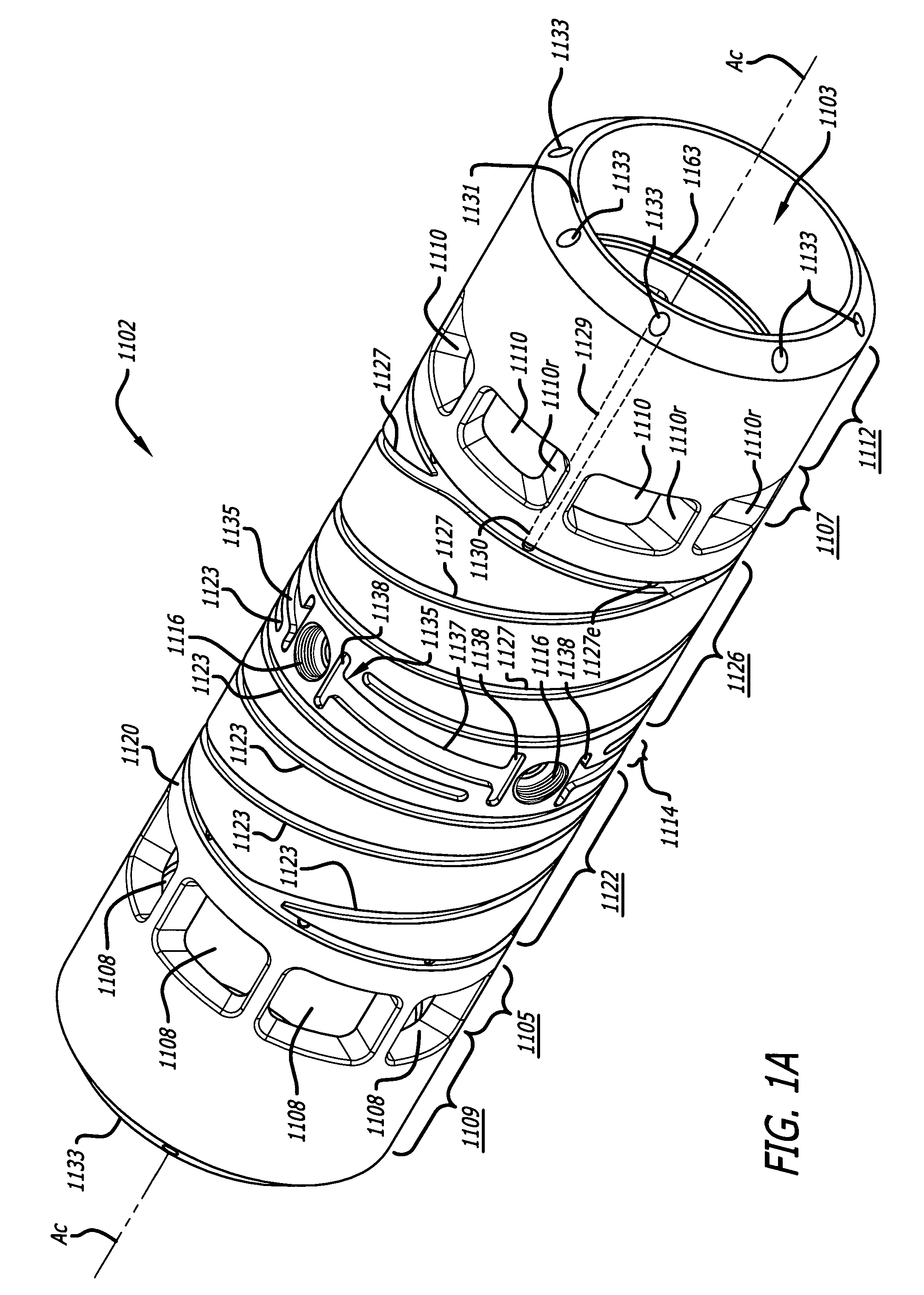
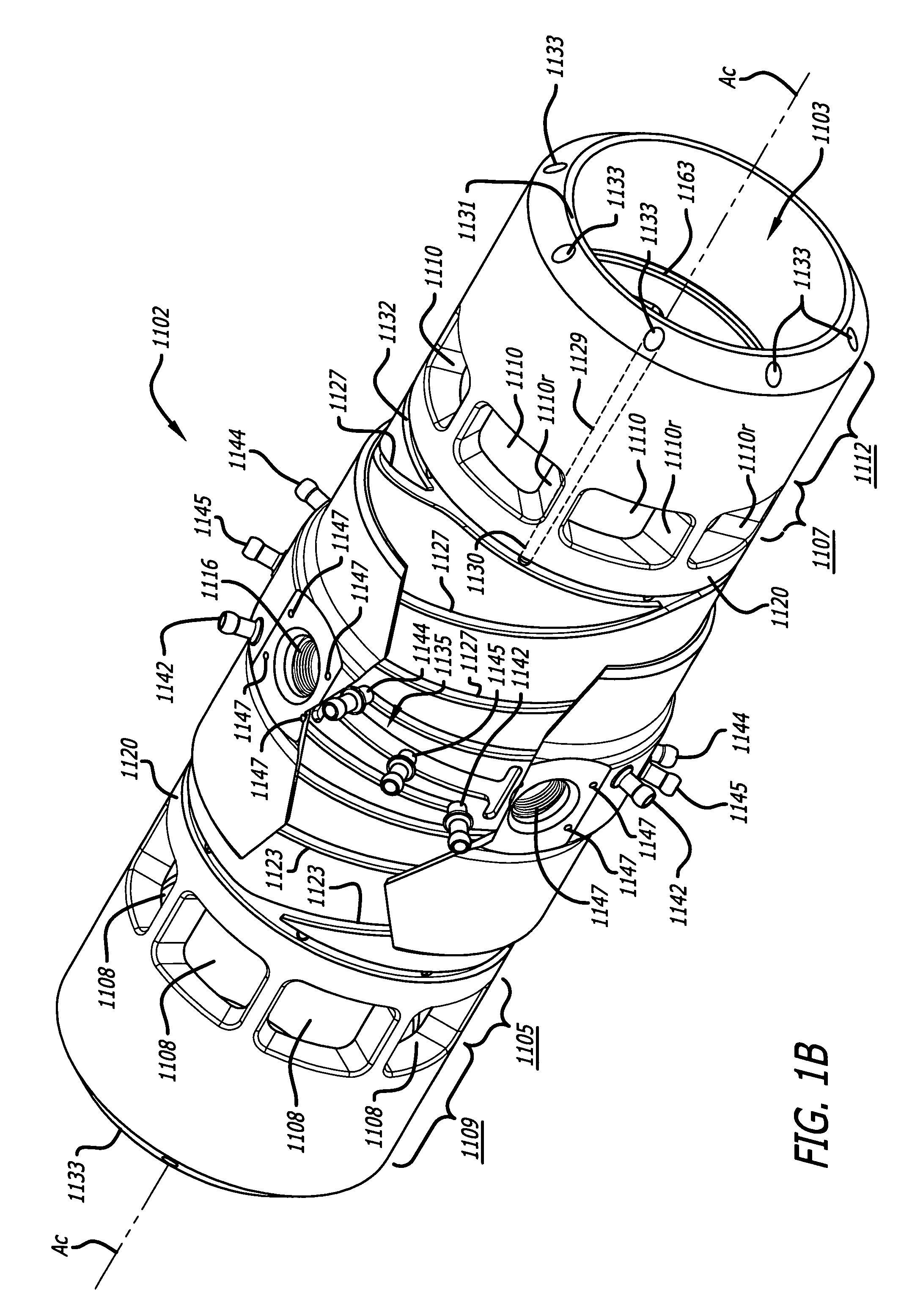
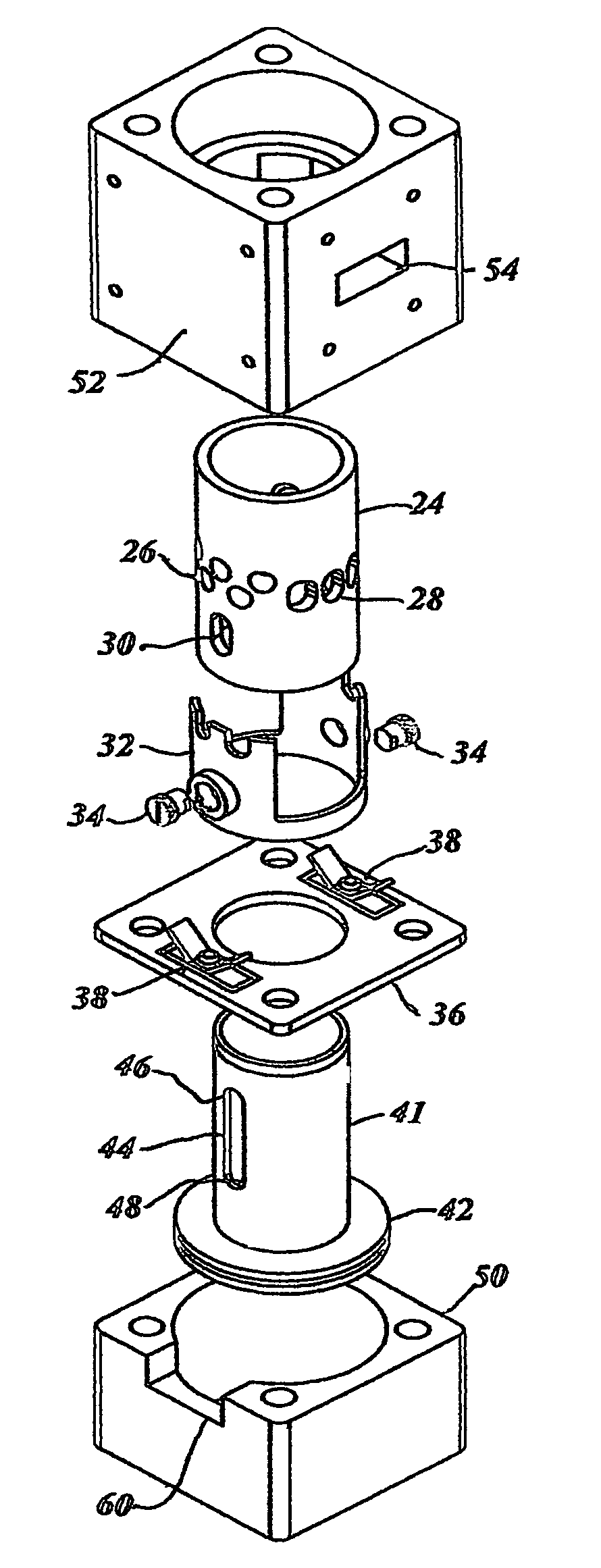
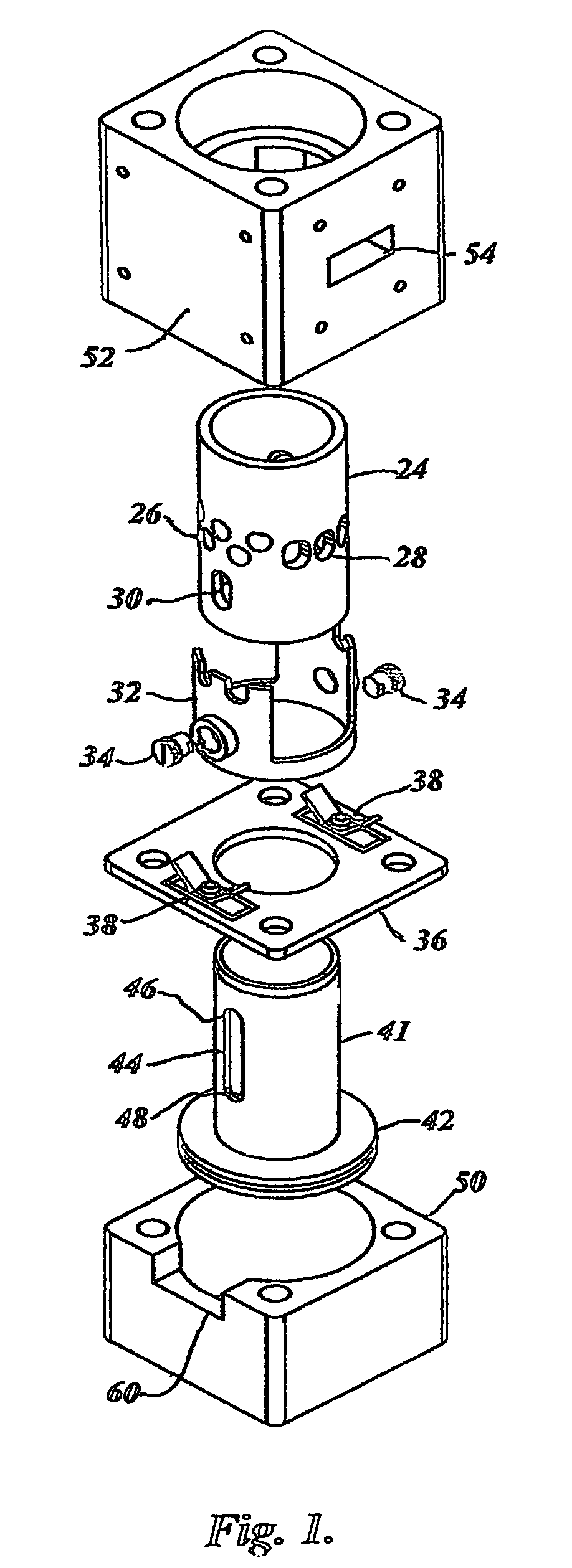
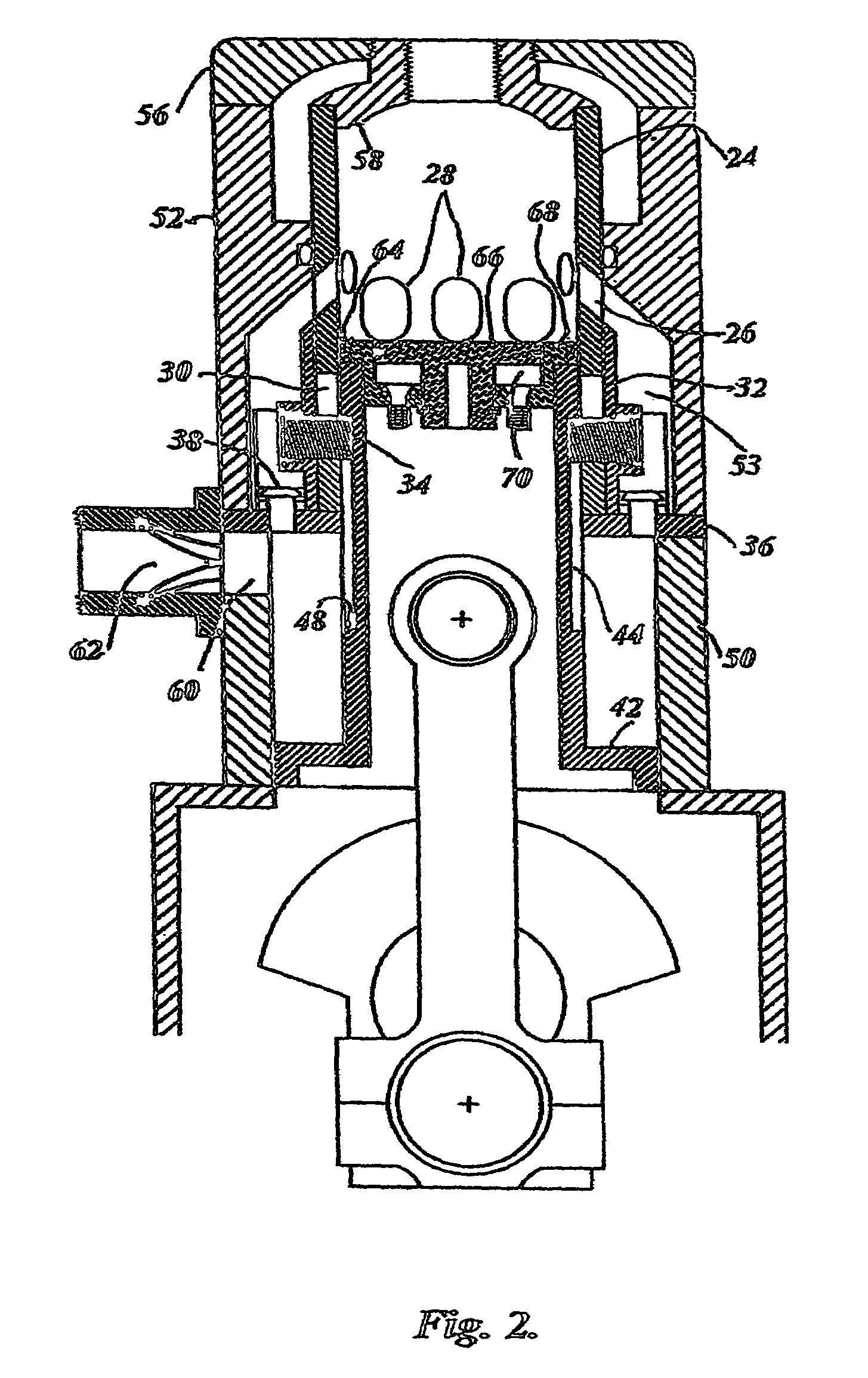
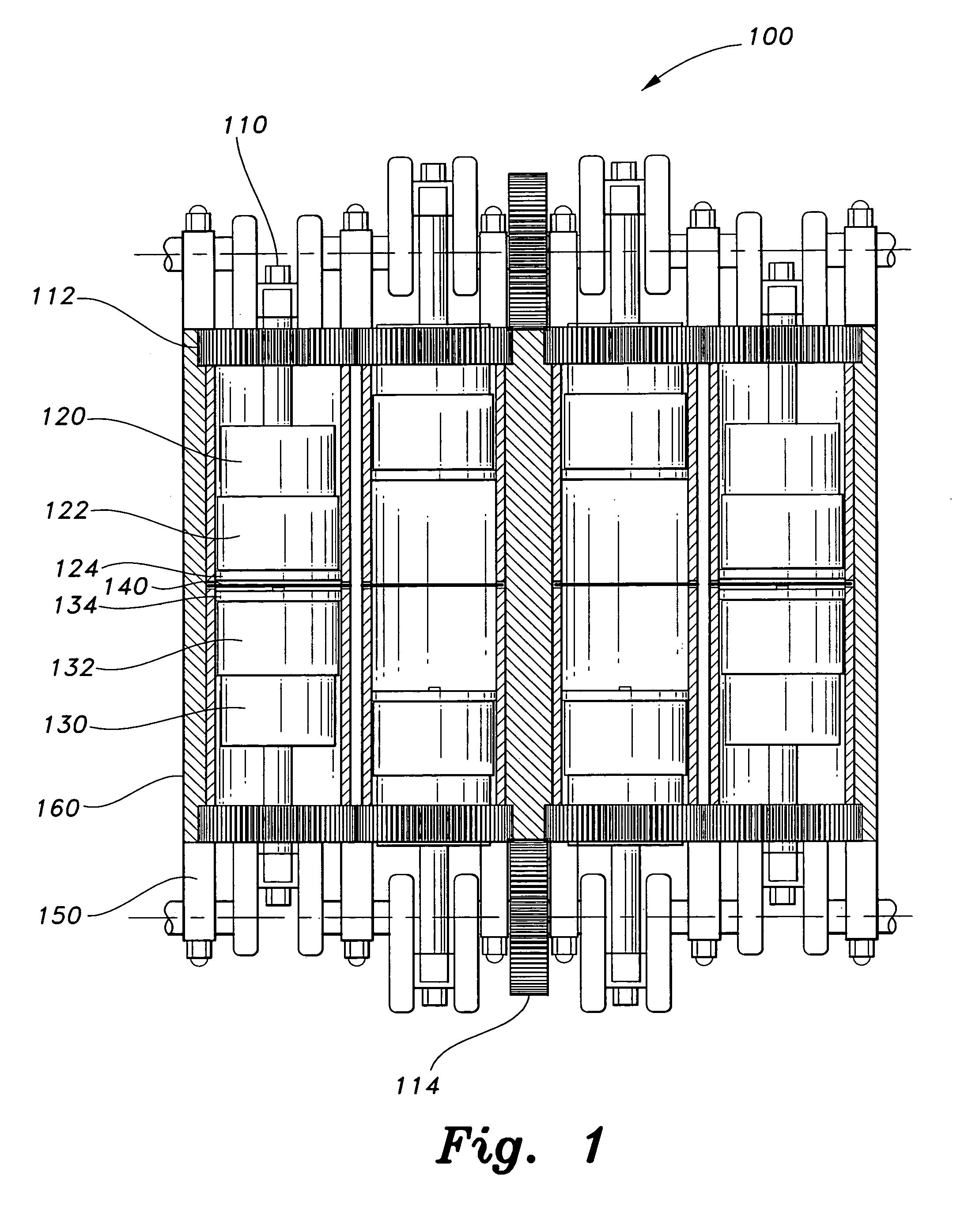
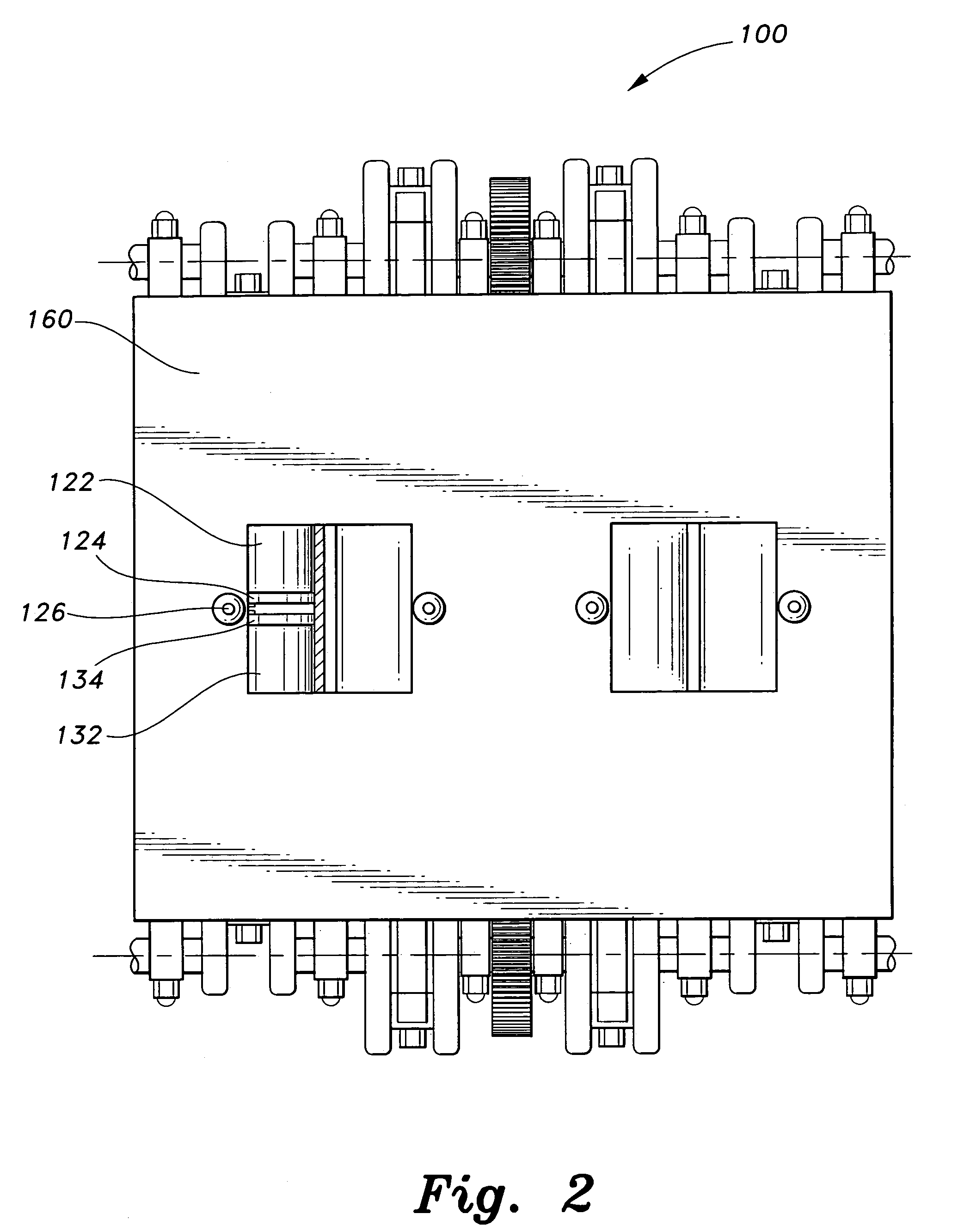
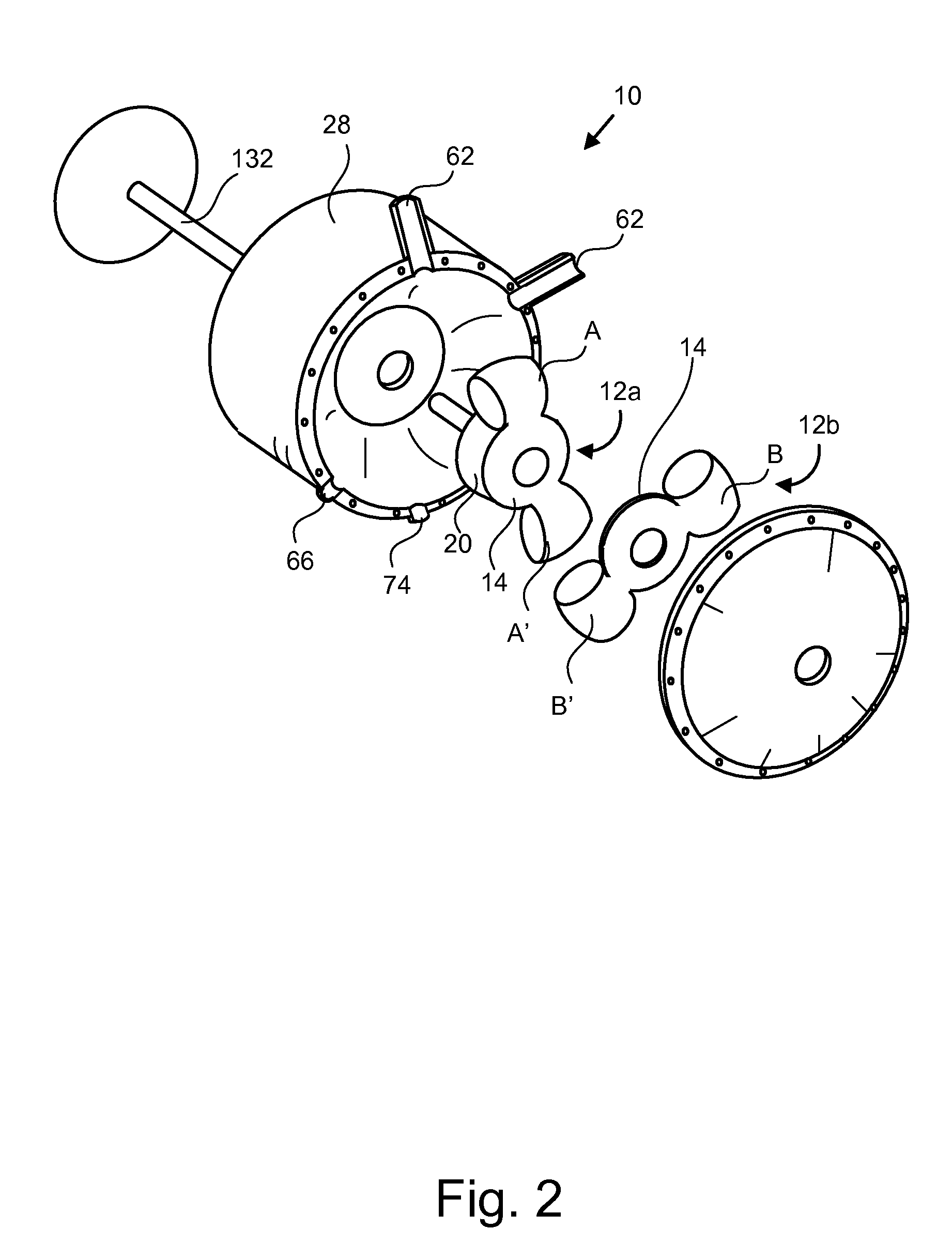
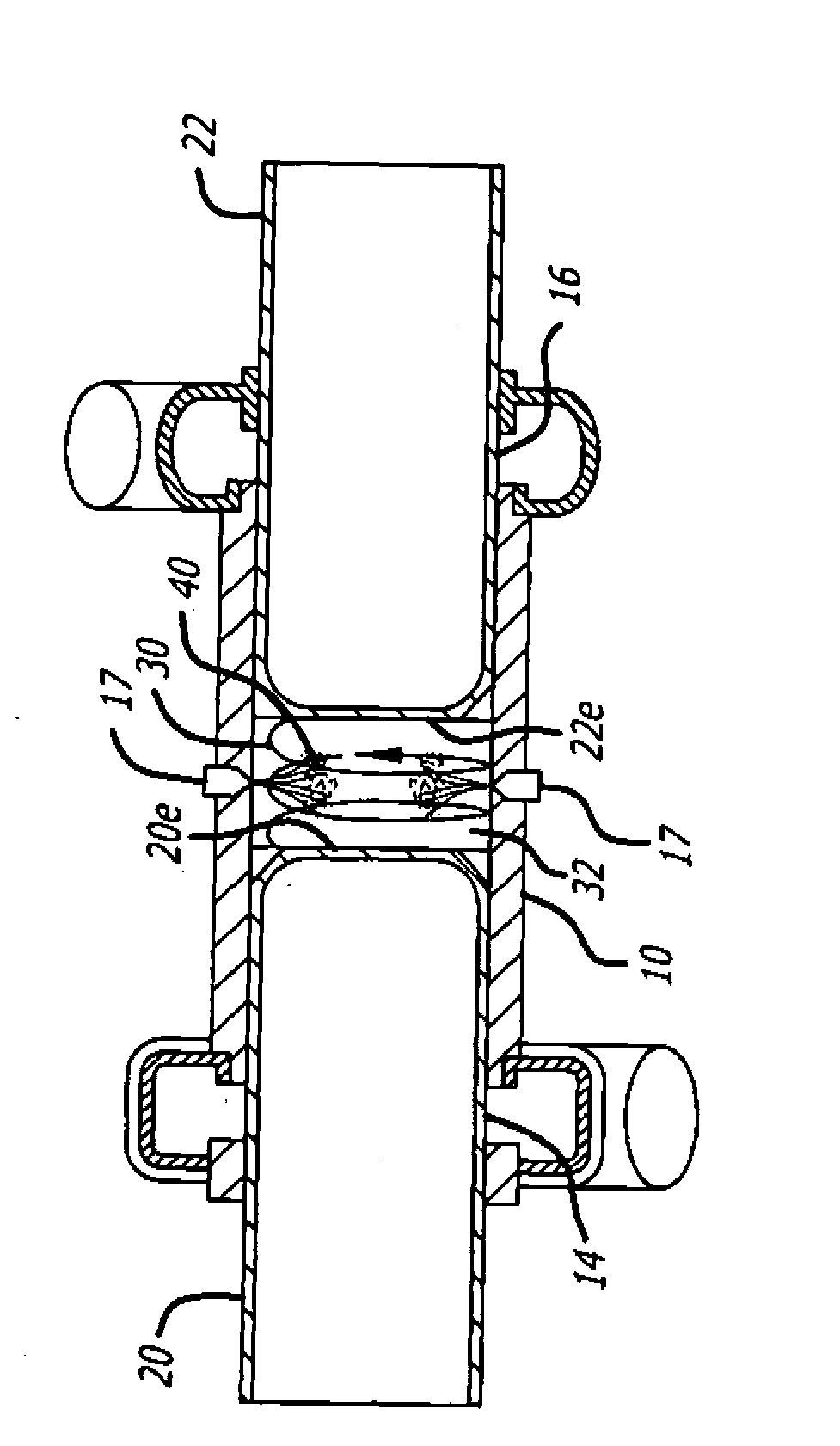
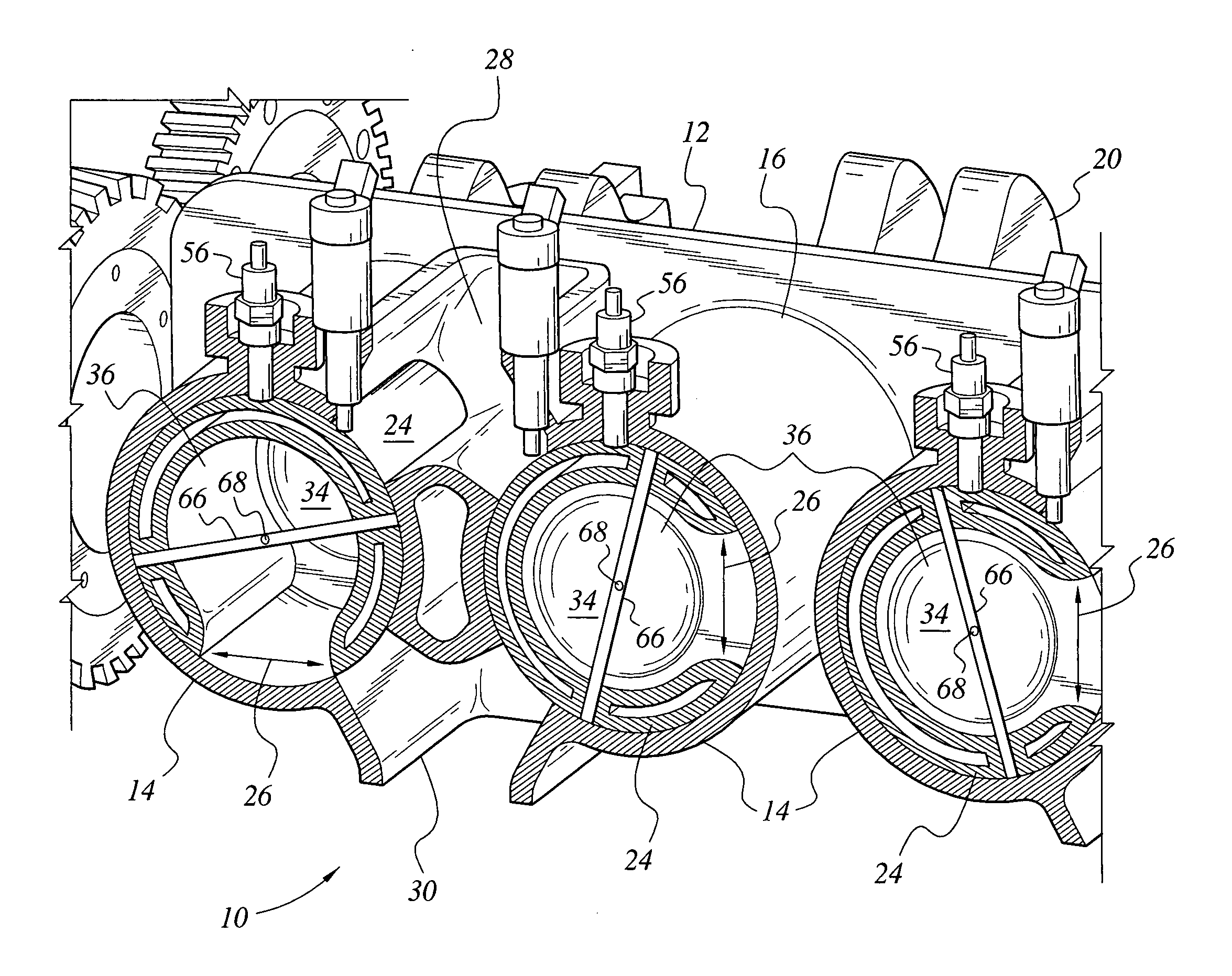
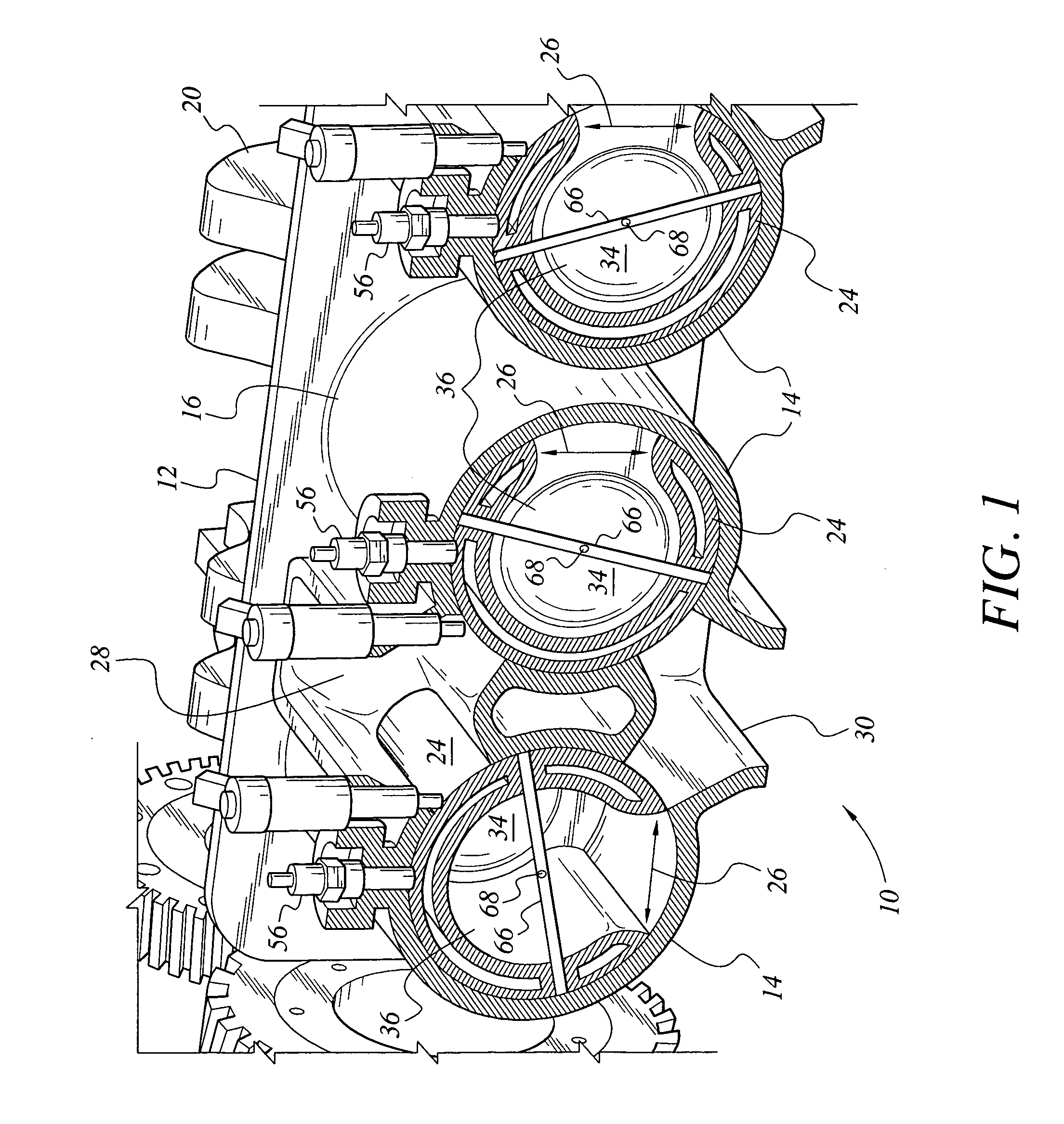
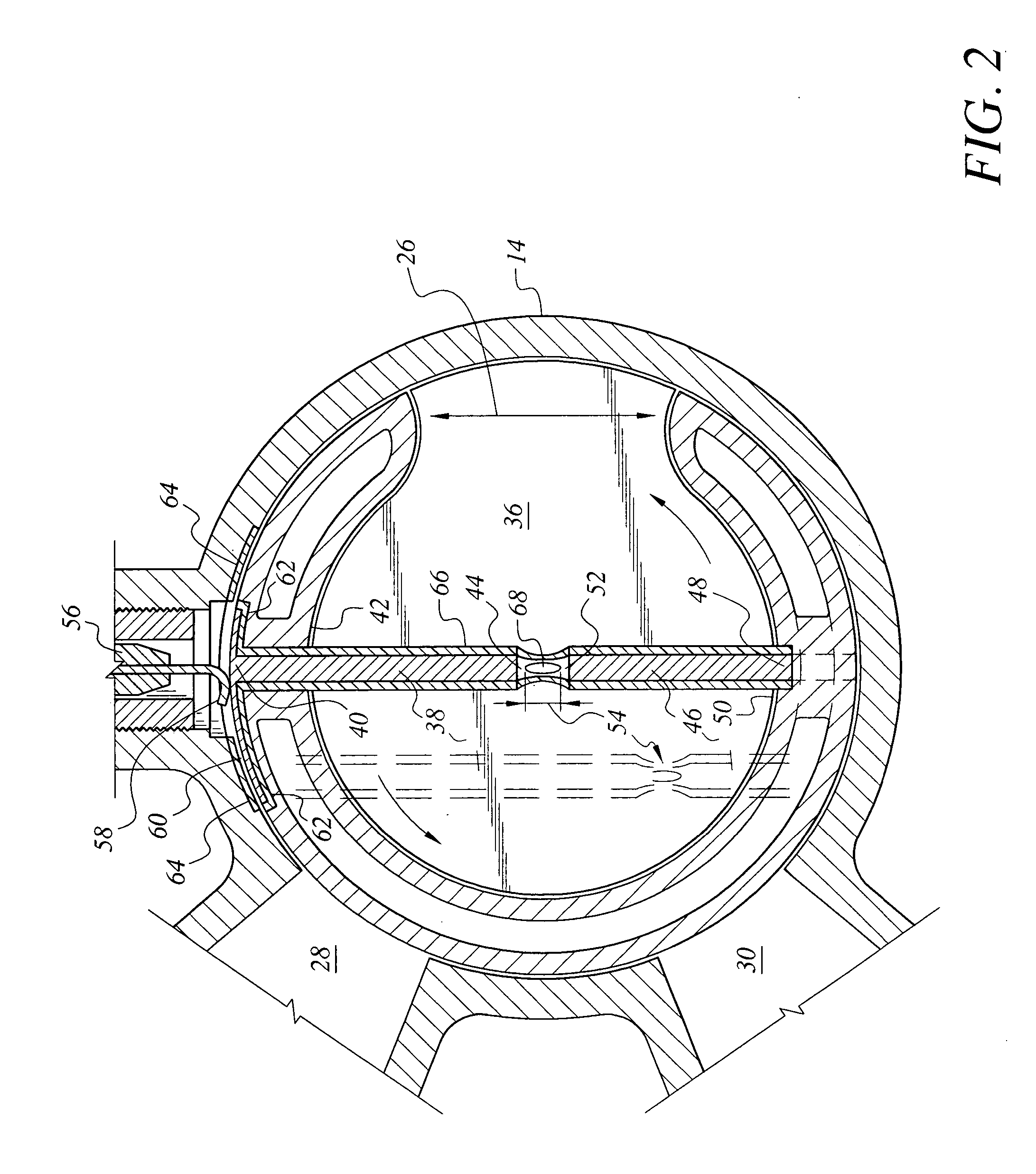
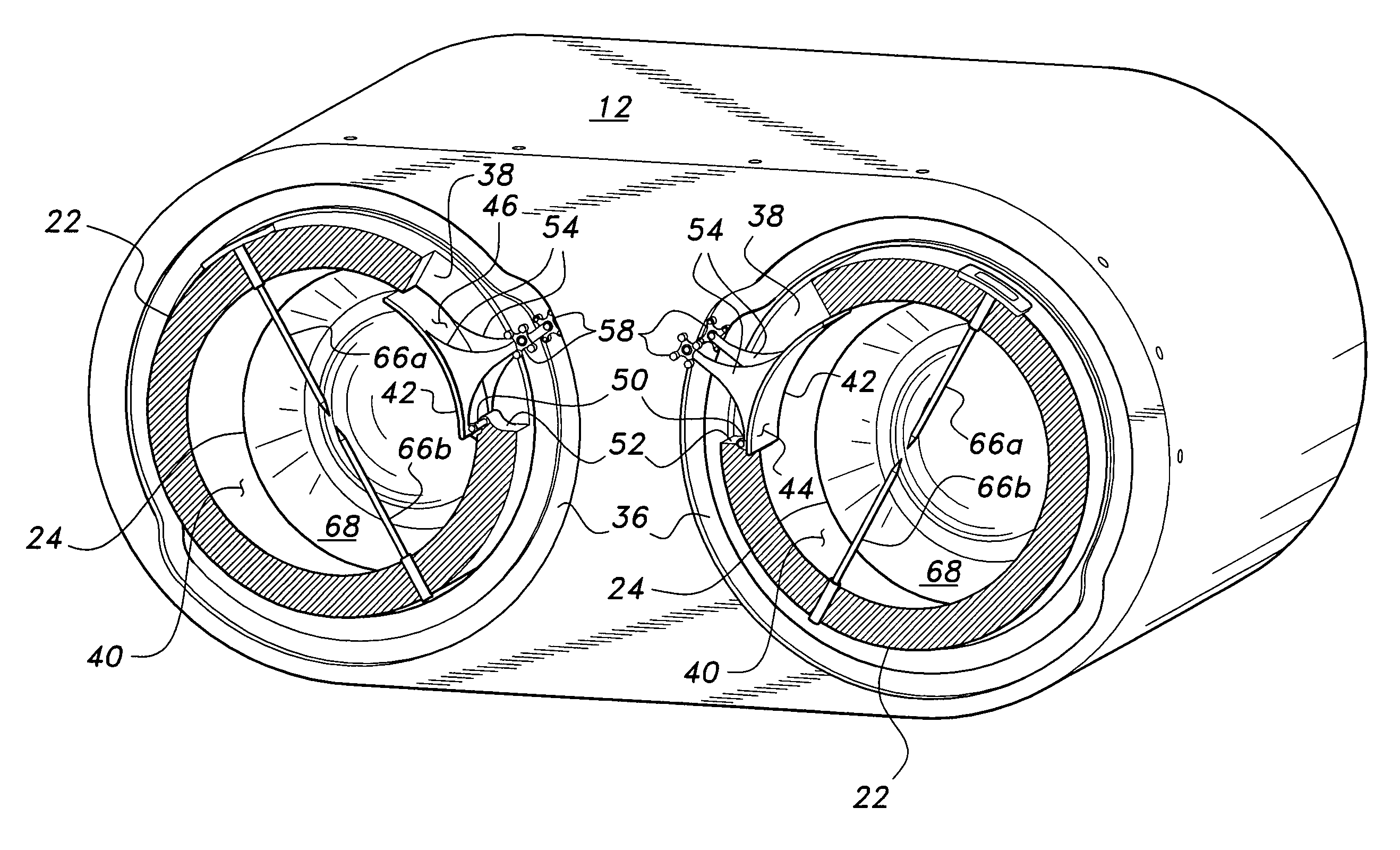
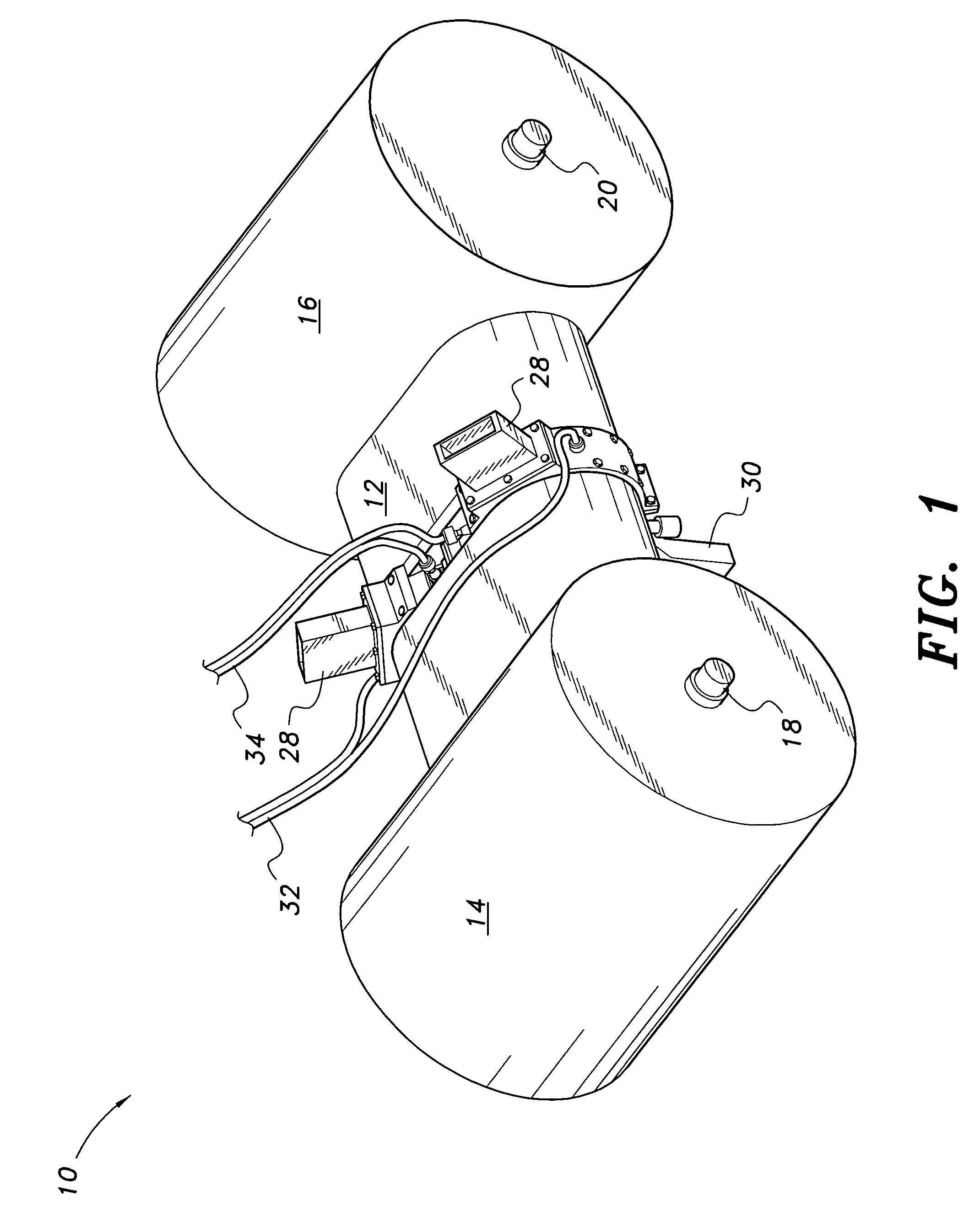
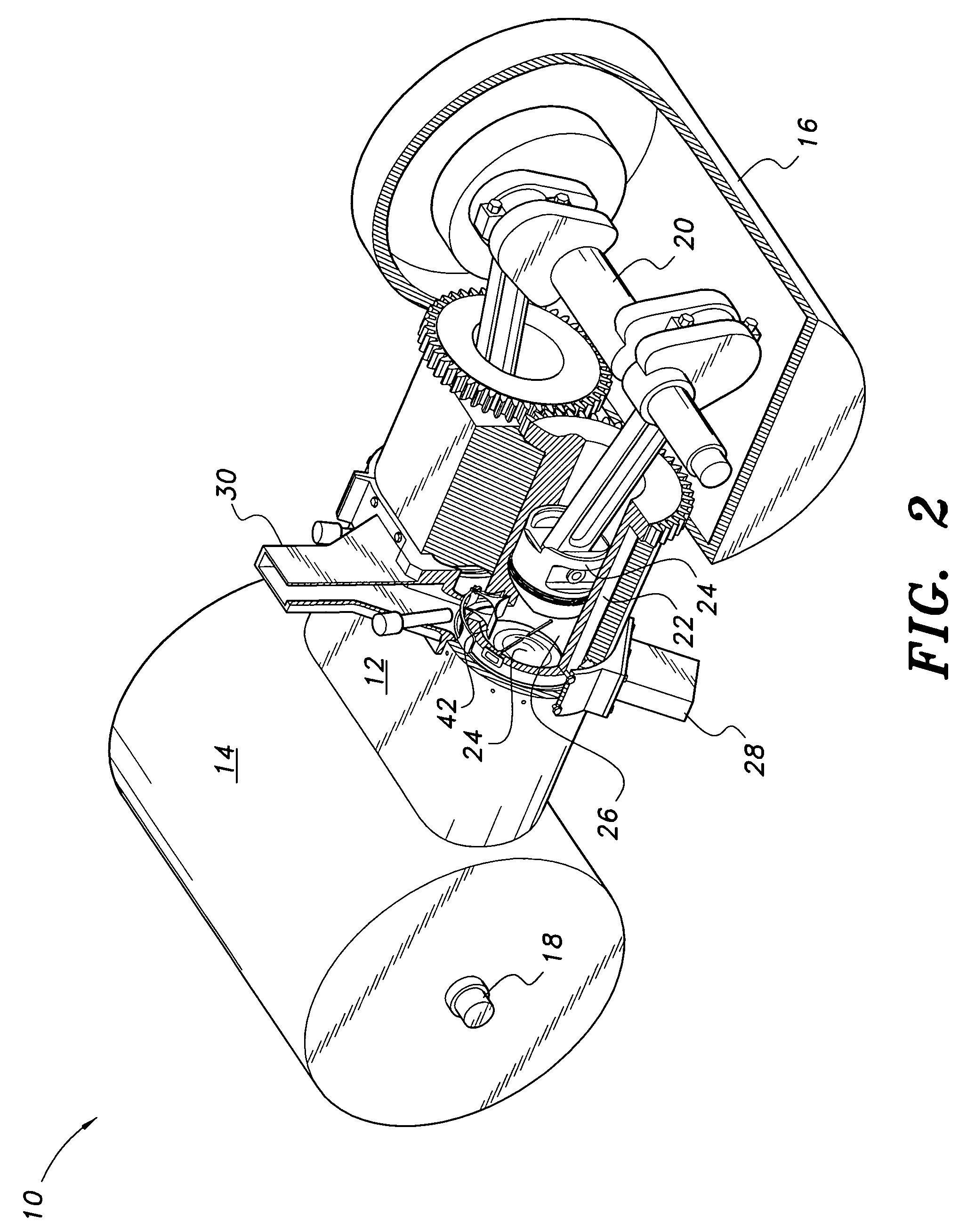
Cylinder and piston assemblies for opposed piston engines
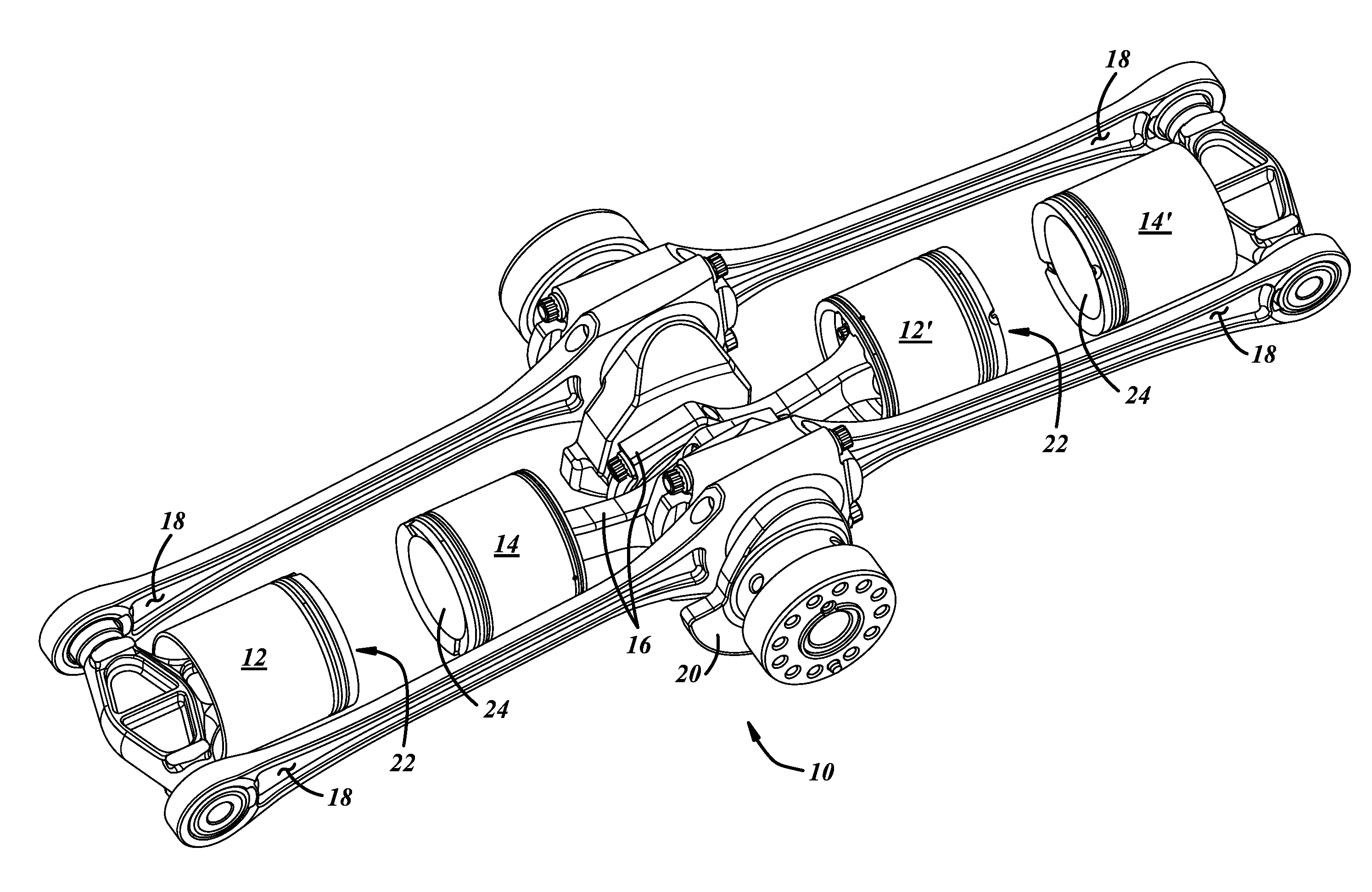
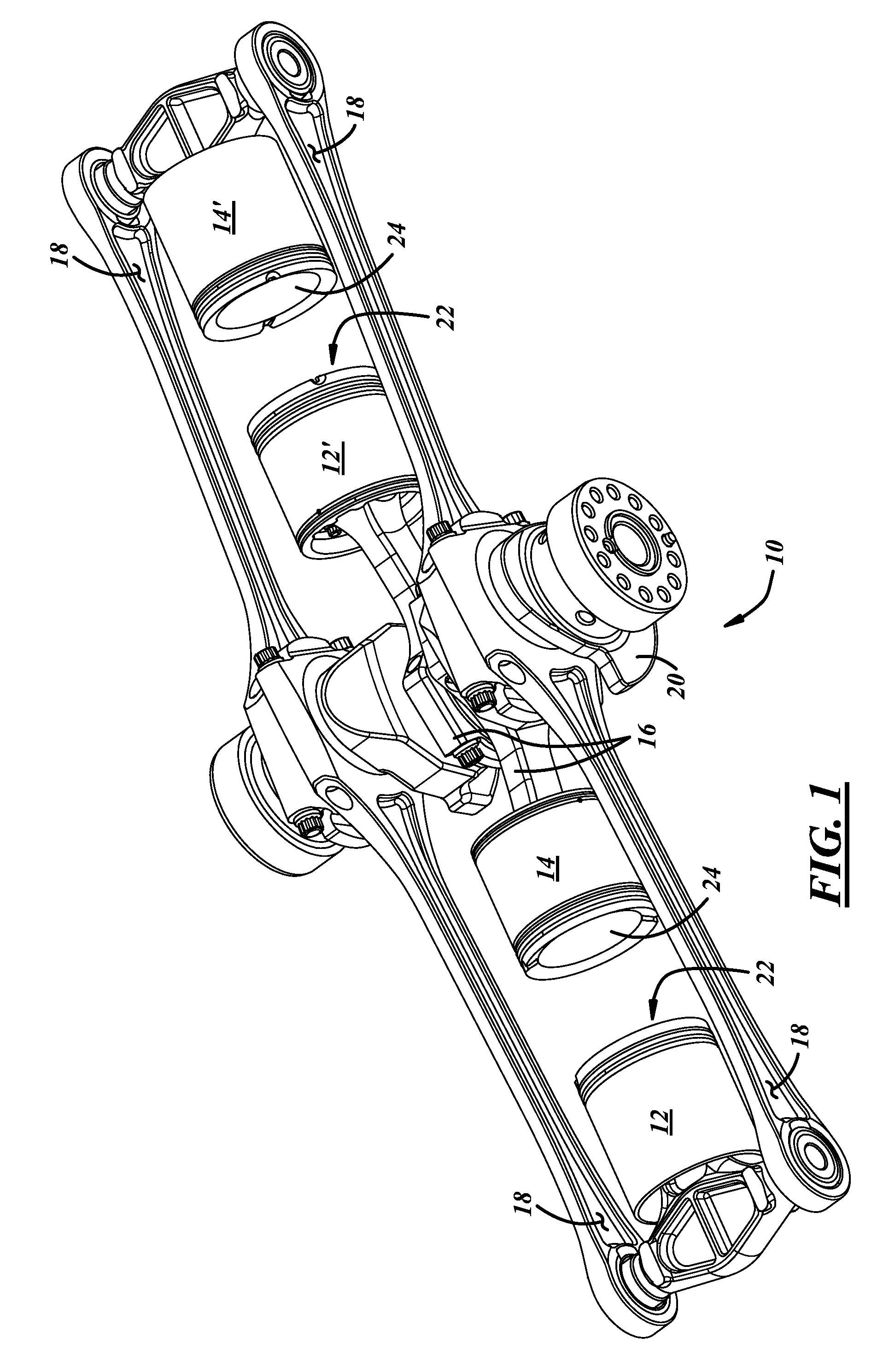
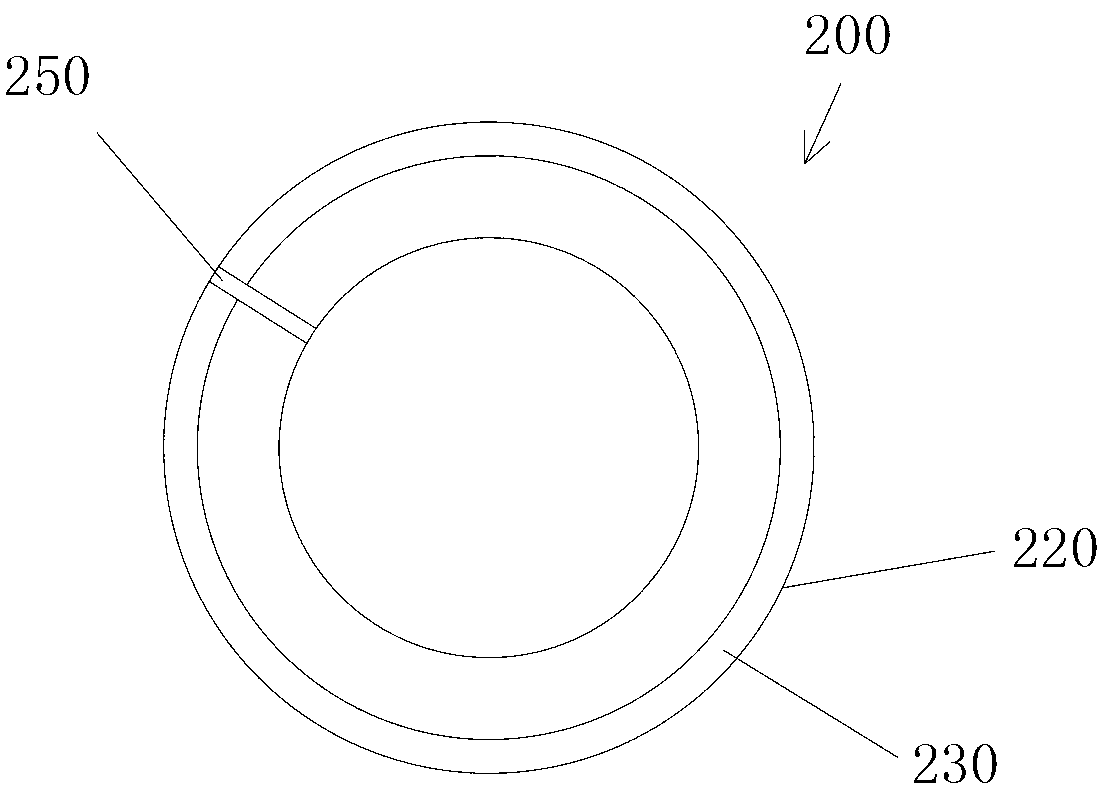
In an opposed piston engine, a pair of pistons are disposed in opposition in the bore of a cylinder. The cylinder includes first liquid coolant grooves having a first cooling capacity to cool a portion of the cylinder extending from a central portion toward an exhaust port, and second liquid coolant grooves having a second cooling capacity, less than the first cooling capacity, to cool a portion of the cylinder extending from the central portion toward an inlet port. Each piston includes a cylindrical skirt with a crown and an open end opposite the crown, a piston rod with a bore, a first end attached to a back surface of the crown, and a second end extending through the open end of the skirt, a radial array of liquid coolant flow passages in communication with the bore and disposed between the first end and the back surface of the crown, and a single wristpin retained on the second end section of the piston rod and positioned externally to the piston.
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC
Toroidal Combustion Chamber With Side Injection
InactiveUS20130014718A1Internal combustion piston enginesOscillating piston enginesCombustion chamberInjector
A toroidal combustion chamber shape with a side injector is disclosed for an opposed-piston engine. Fuel is injected into the toroidal volume from a fuel injector in the cylinder wall. In one embodiment, fuel is injected from each injector a plurality of times with the timing between the injections such that fuel clouds from each injection remain substantially isolated from each other.
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC +1
Two stroke, opposed-piston engines with engine braking
ActiveUS20120210985A1Simple and inexpensiveHigh trafficInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelFree-piston engineSwing-piston engine
In a two-stroke opposed-piston engine, a ported cylinder with a pair of opposed pistons is equipped with an engine brake including an engine braking valve that can be opened to release air from the cylinder as the pistons cycle between BDC and TDC positions.
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC
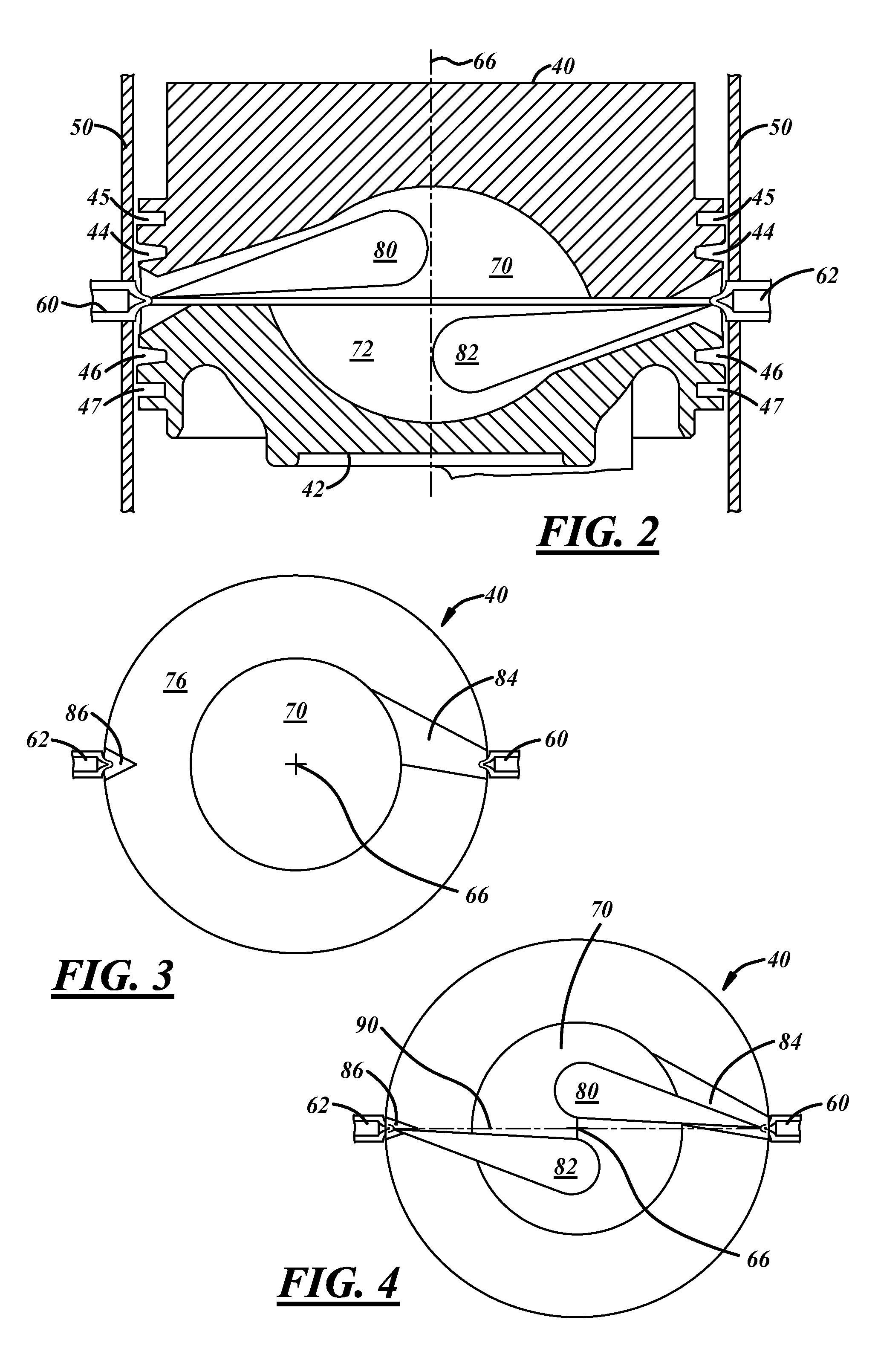
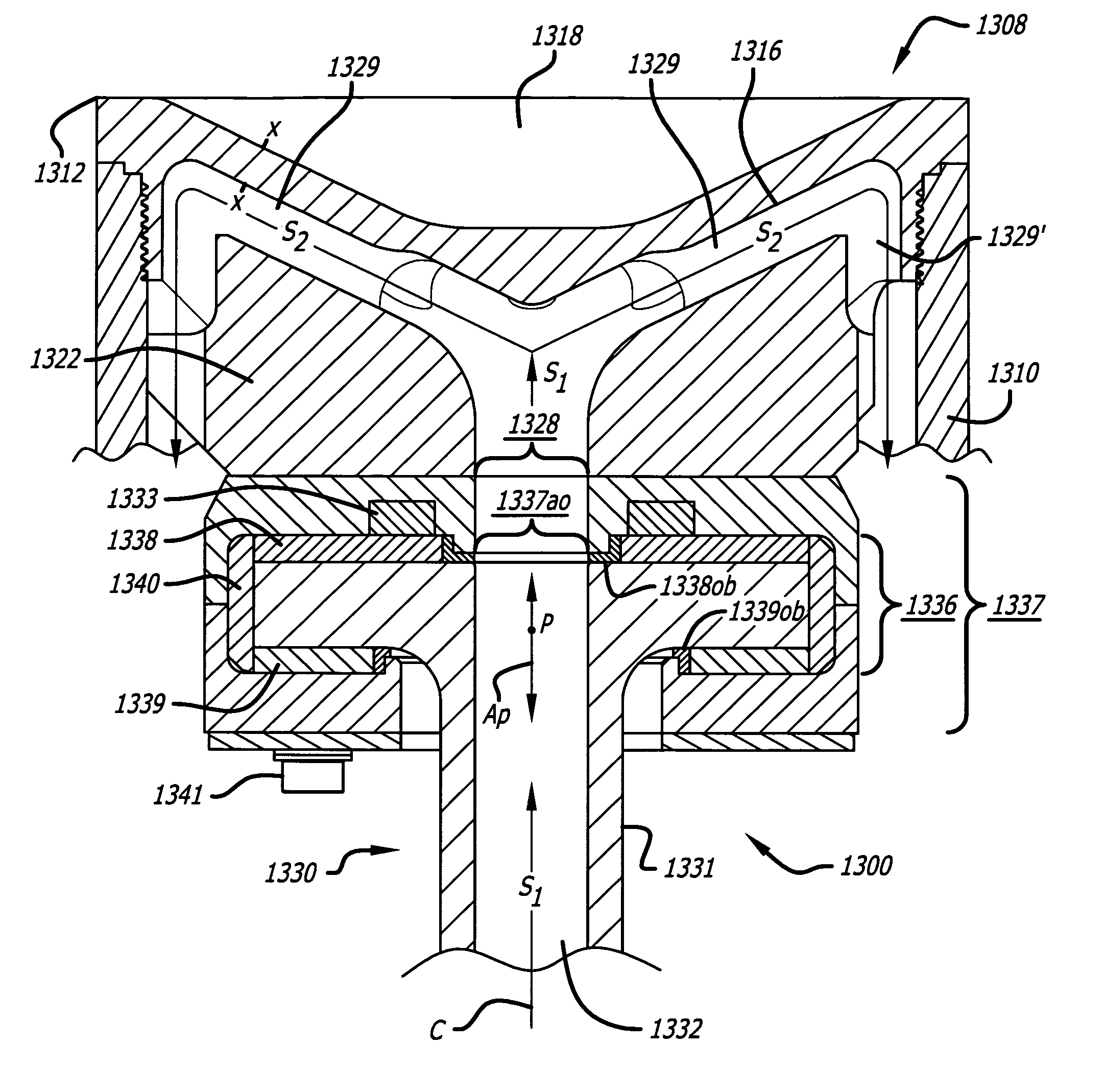
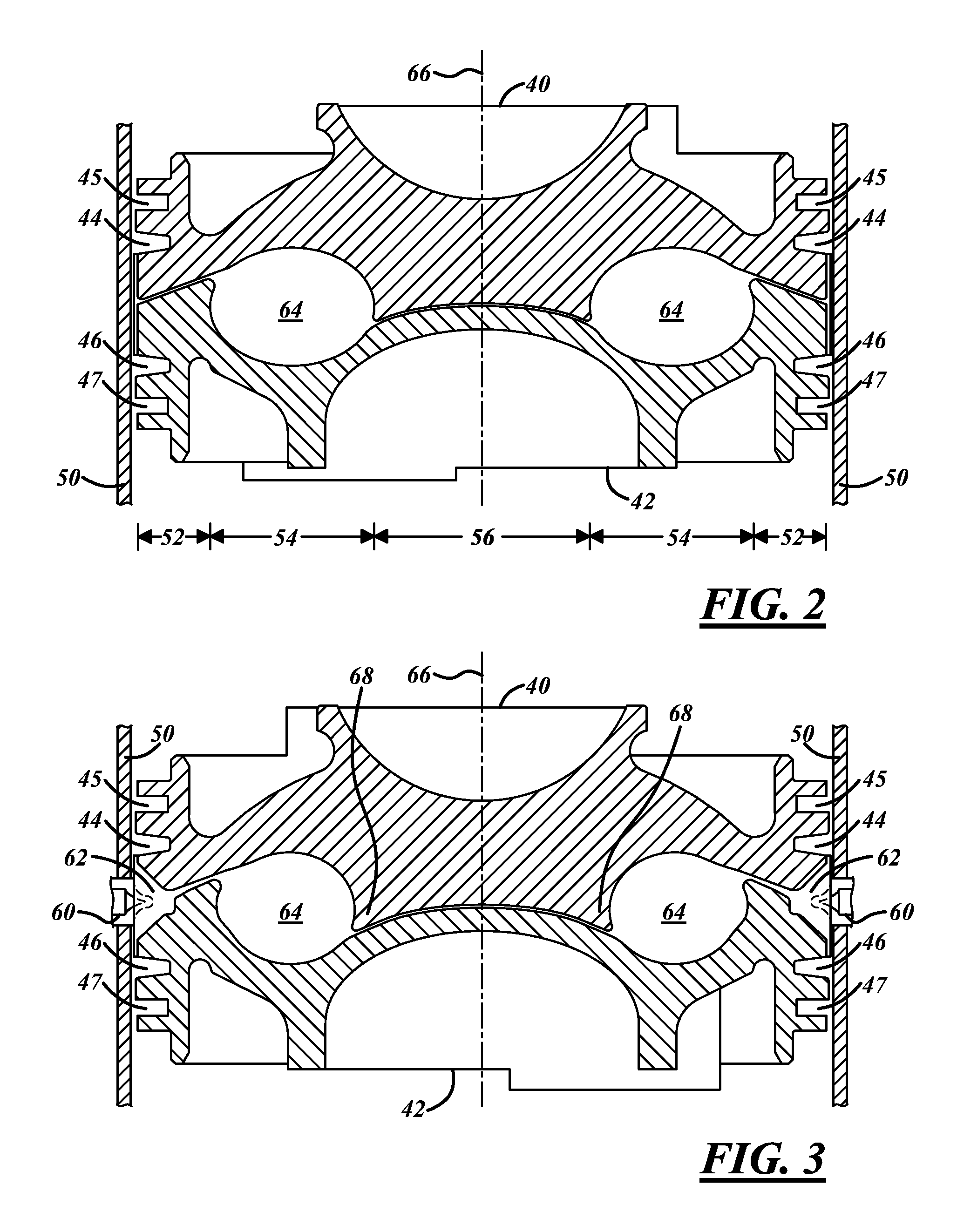
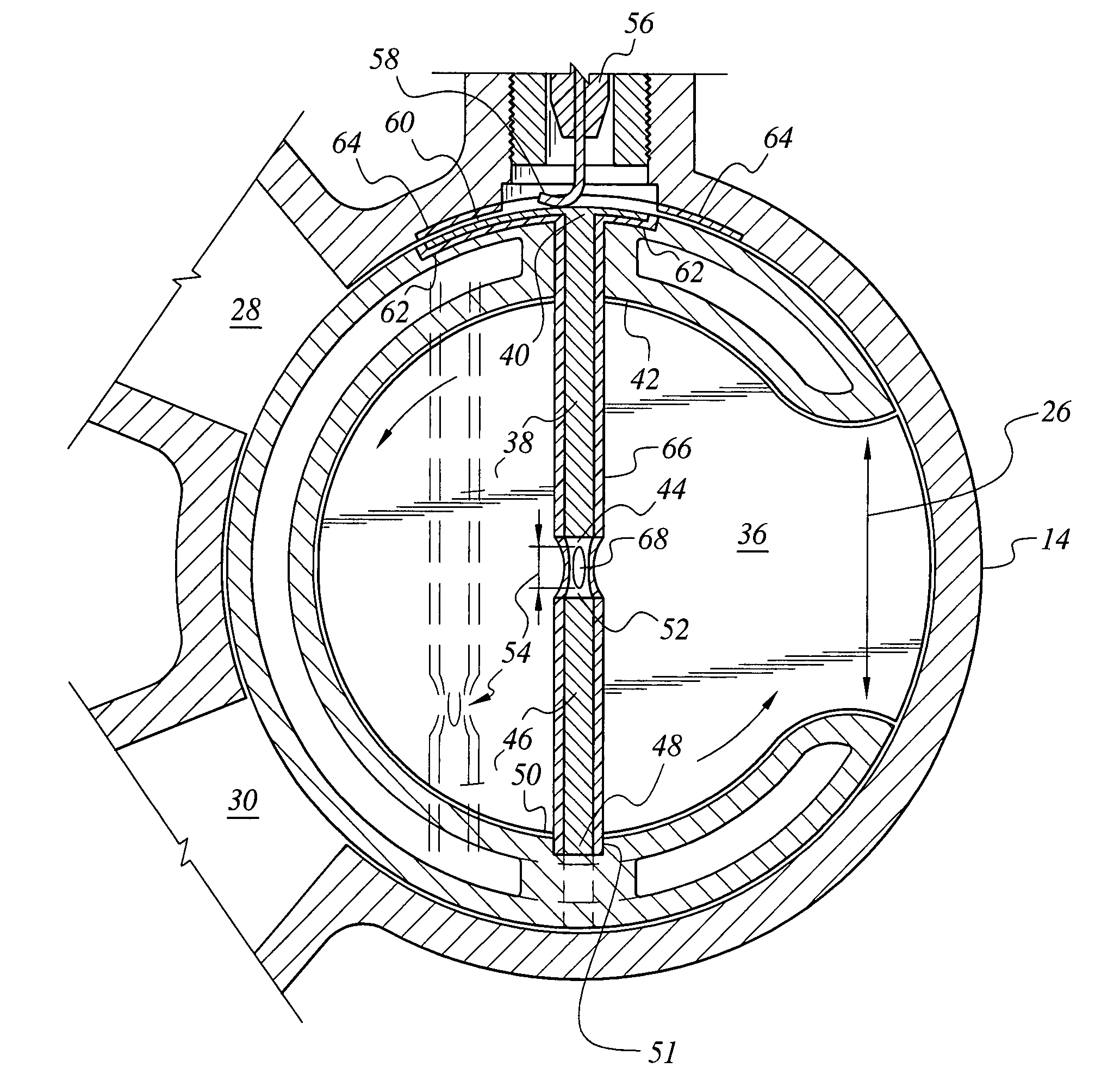
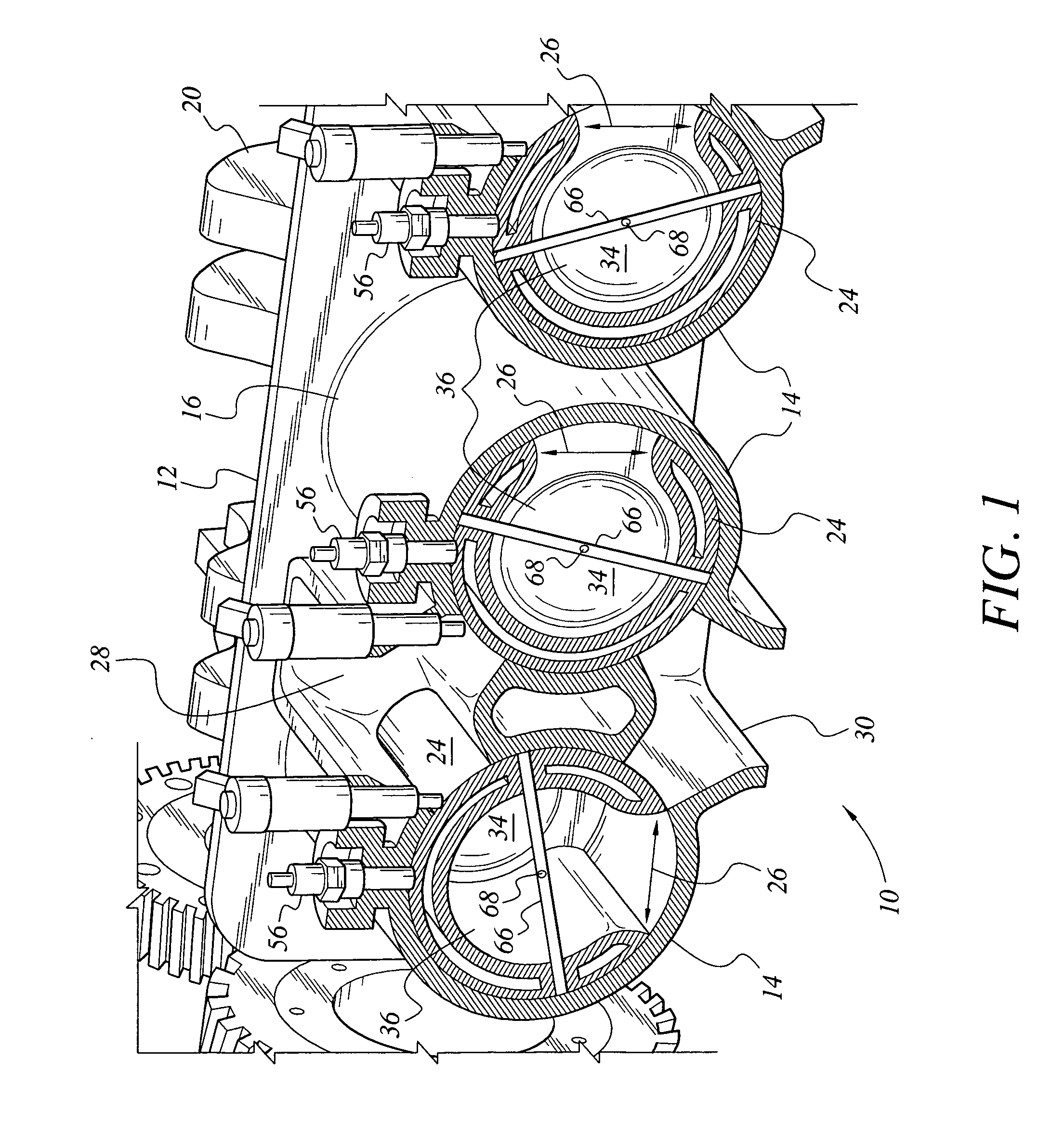
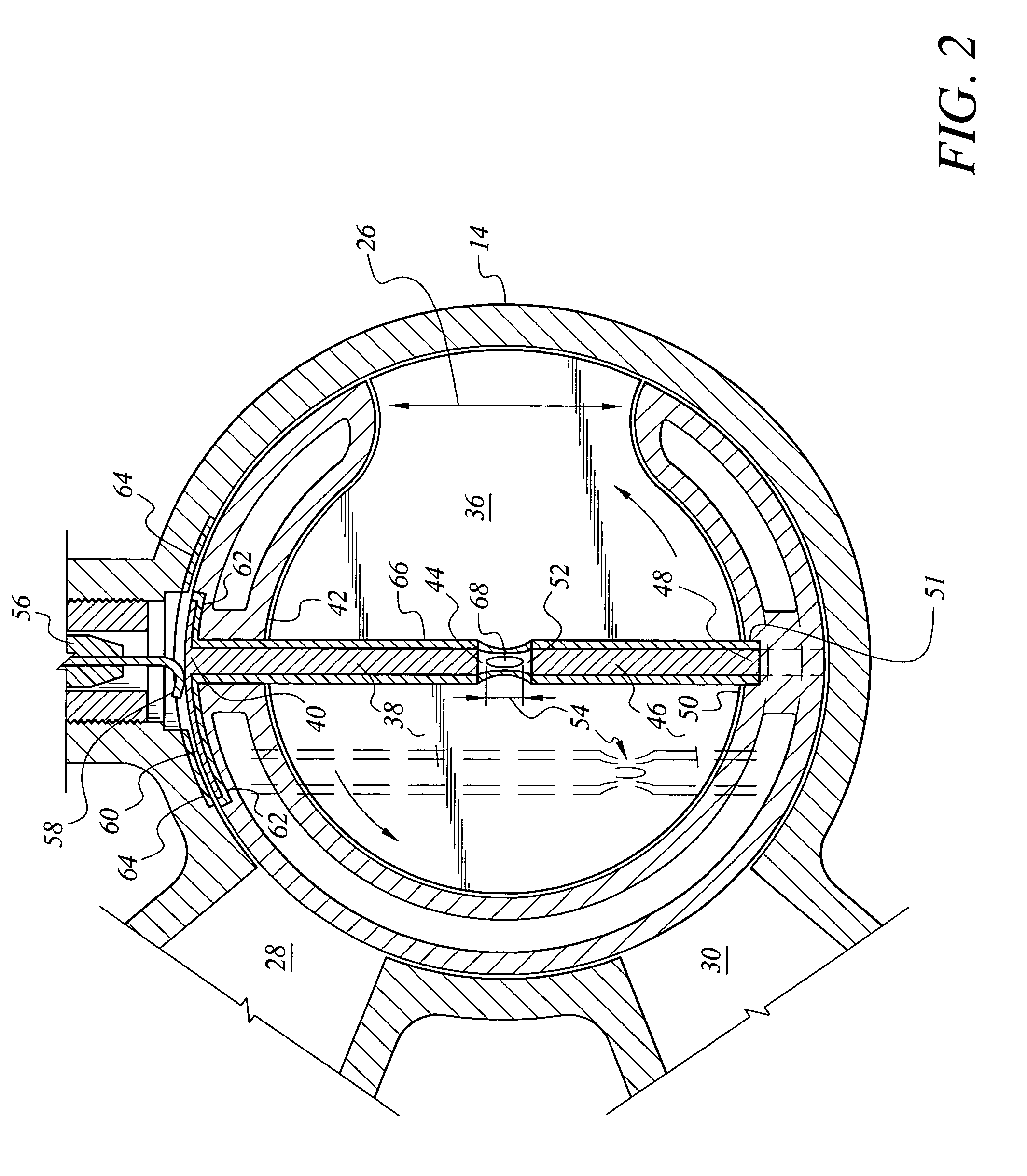
Combustion chamber constructions for opposed-piston engines
A combustion chamber for an opposed-piston engine includes a squish zone defined between circumferential peripheral areas of opposing end surfaces of the pistons, a cavity defined by one or more bowls in the end surfaces, and at least one injection port that extends radially through the squish zone into the cavity. The cavity has a cross-sectional shape that imposes a tumbling motion on air flowing from the squish zone into the cavity.
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC
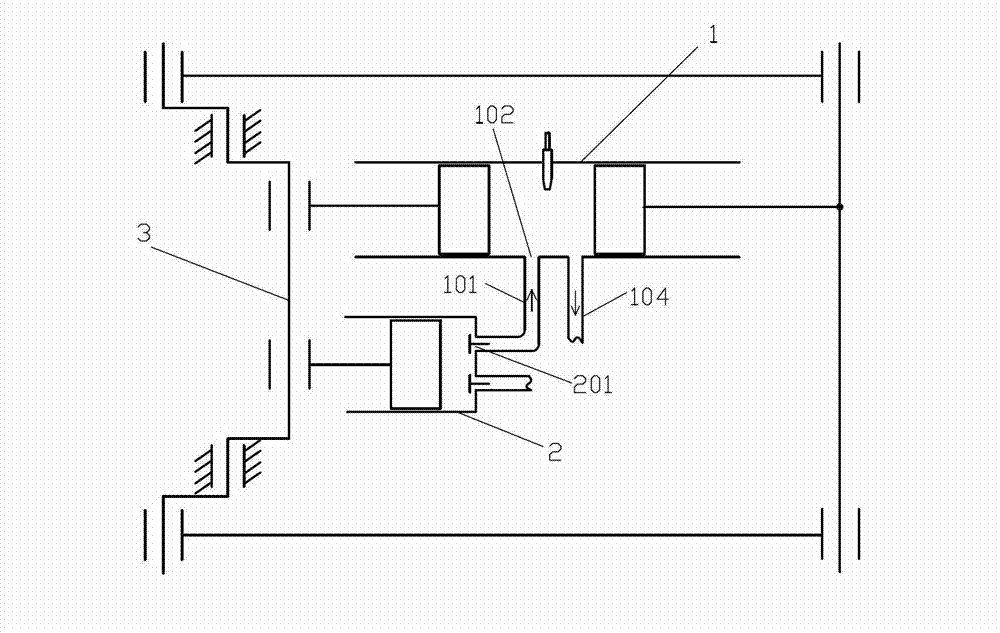
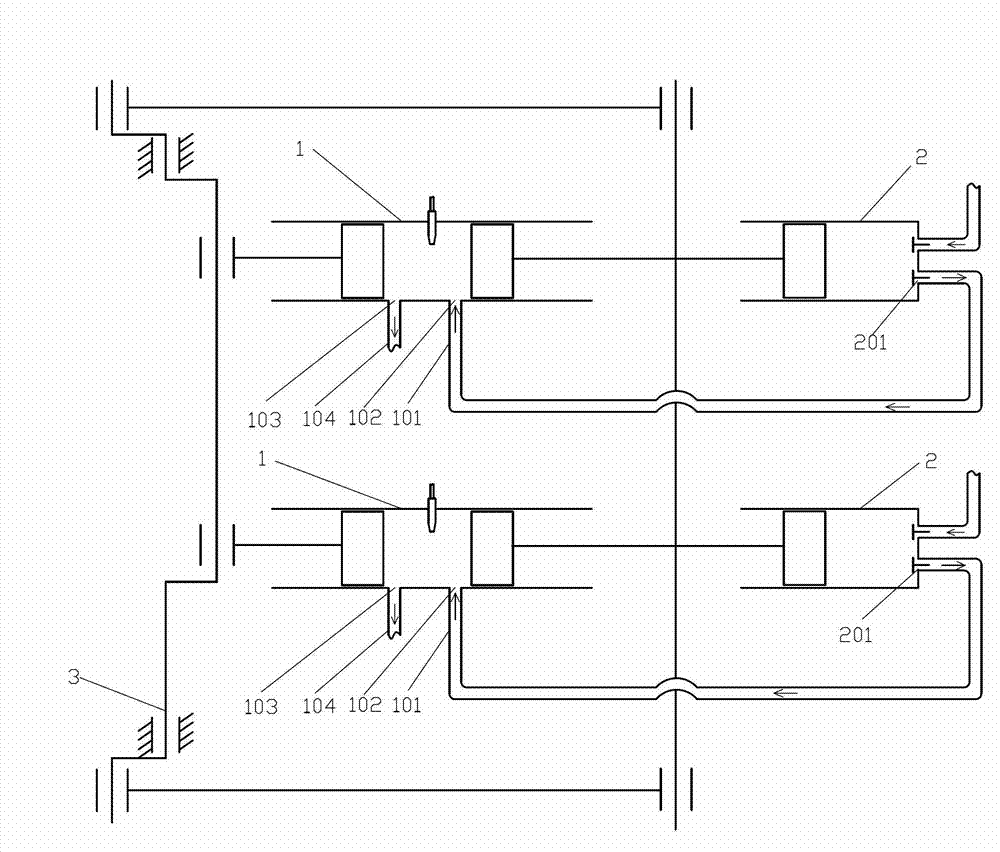
Supercharged two-cycle engines employing novel single element reciprocating shuttle inlet valve mechanisms and with a variable compression ratio
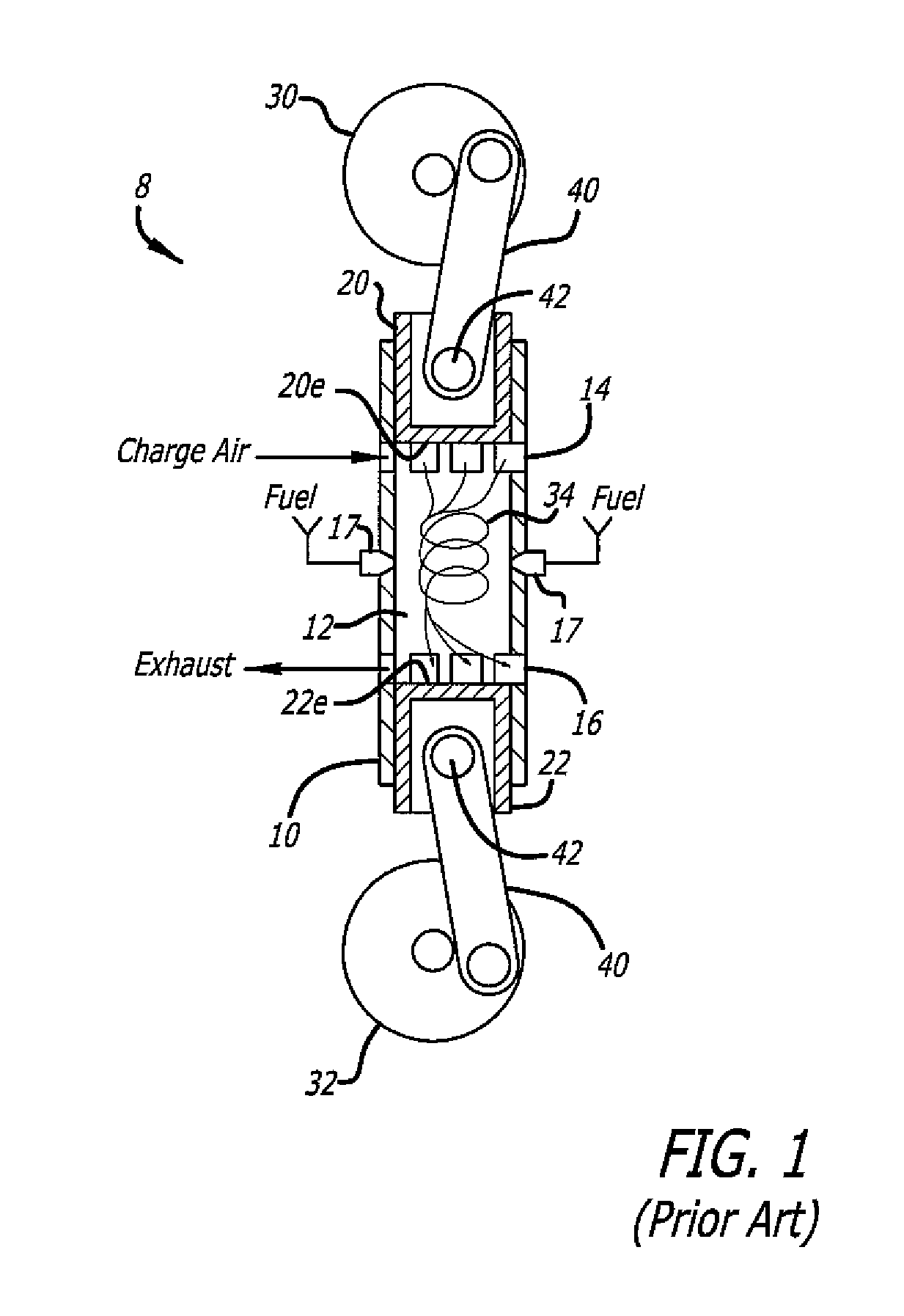
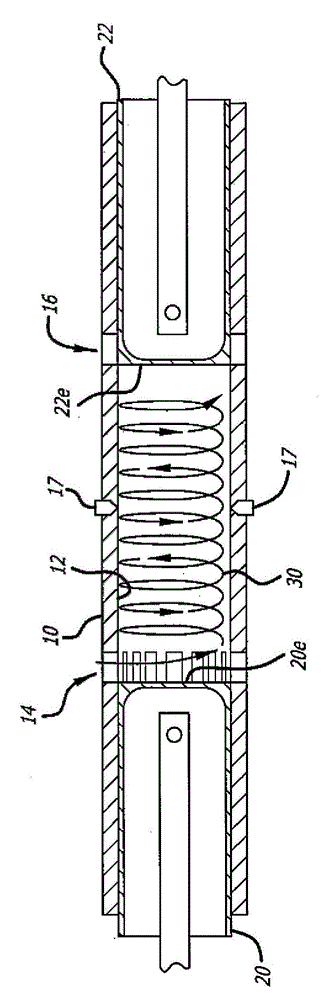
This invention relates to novel reciprocating shuttle inlet valves, effective with every type of two-cycle engine, from small high-speed single cylinder model engines, to large low-speed multiple cylinder engines, employing spark or compression ignition. Also permitting the elimination of out-of-phase piston arrangements to control scavenging and supercharging of opposed-piston engines. The reciprocating shuttle inlet valve (32) and its operating mechanism (34) is constructed as a single and simple uncomplicated member, in combination with the lost-motion abutments, (46) and (48), formed in a piston skirt, obviating the need for any complex mechanisms or auxiliary drives, unaffected by heat, friction, wear or inertial forces. The reciprocating shuttle inlet valve retains the simplicity and advantages of two-cycle engines, while permitting an increase in volumetric efficiency and performance, thereby increasing the range of usefulness of two-cycle engines into many areas that are now dominated by the four-cycle engine.
Owner:WIESEN BERNARD
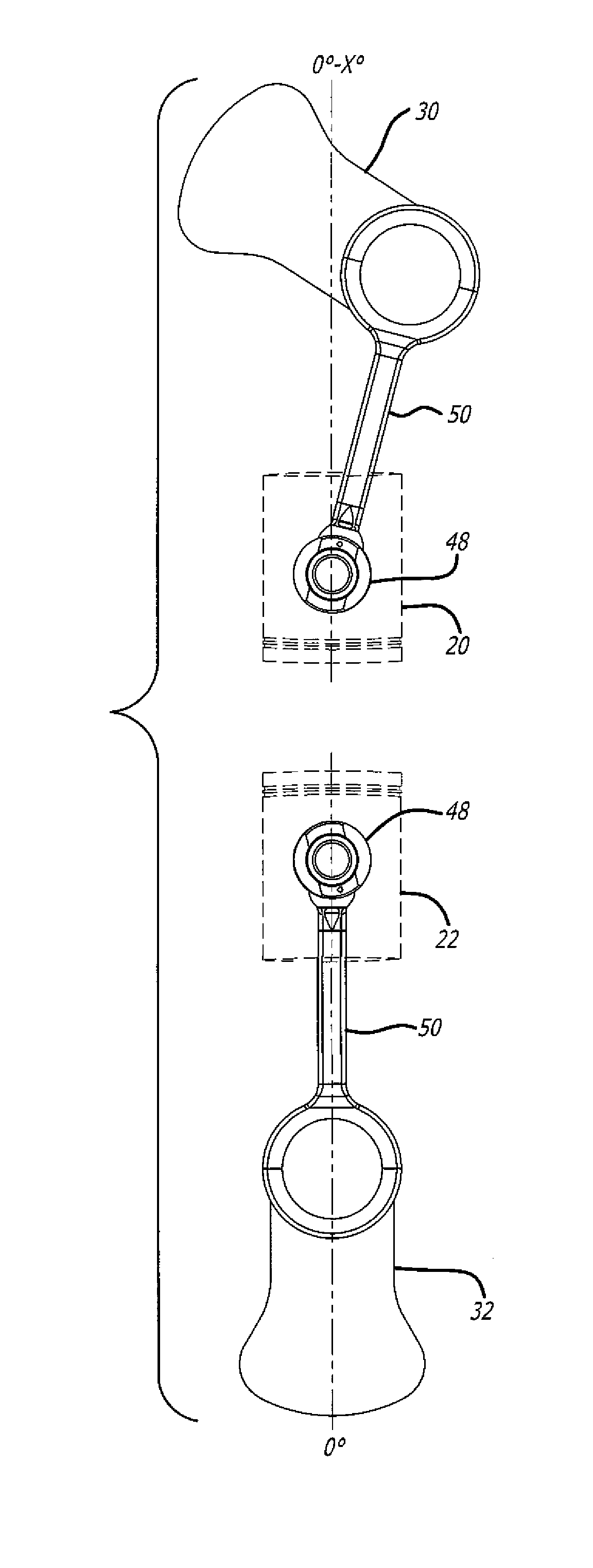
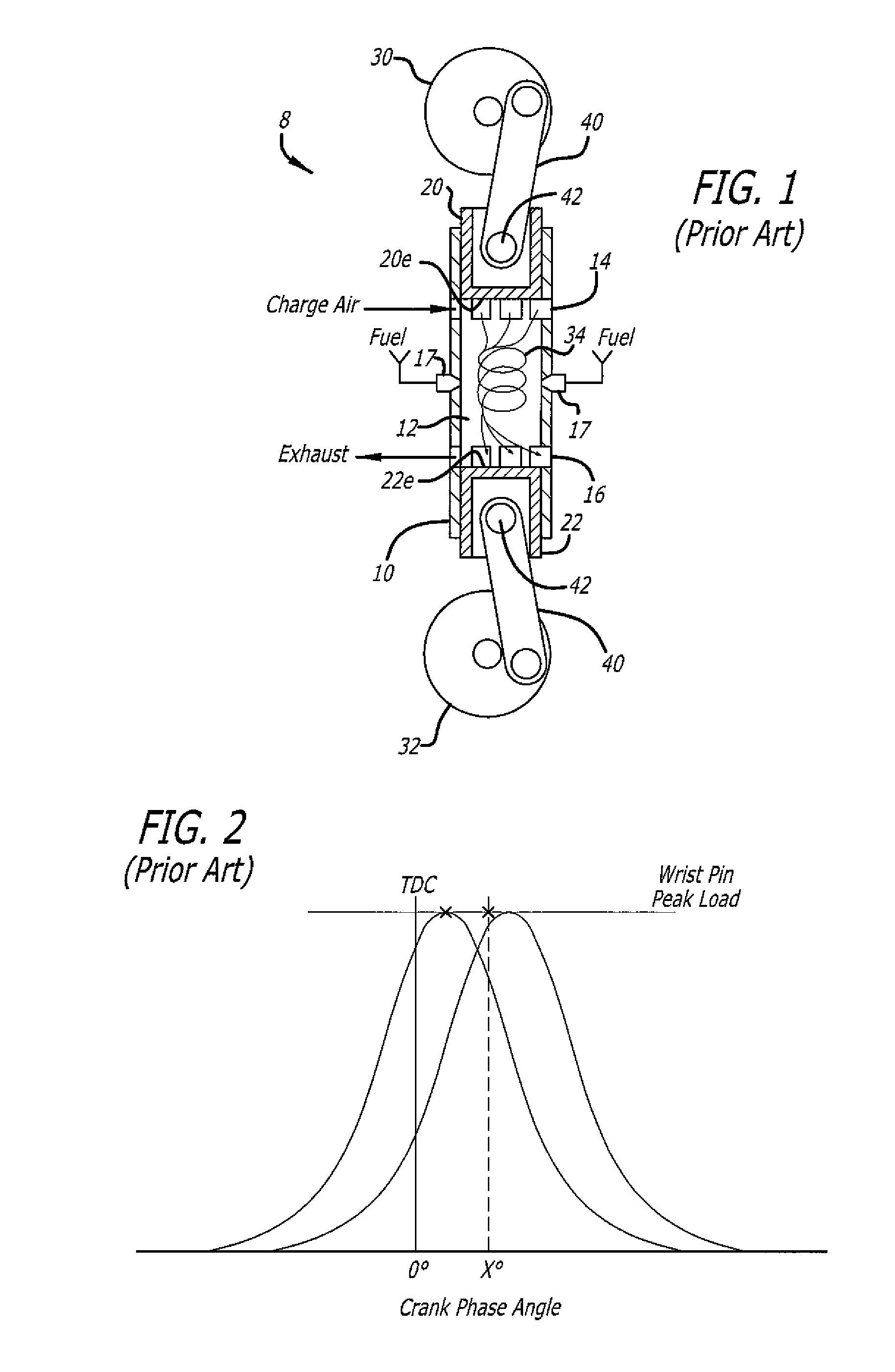
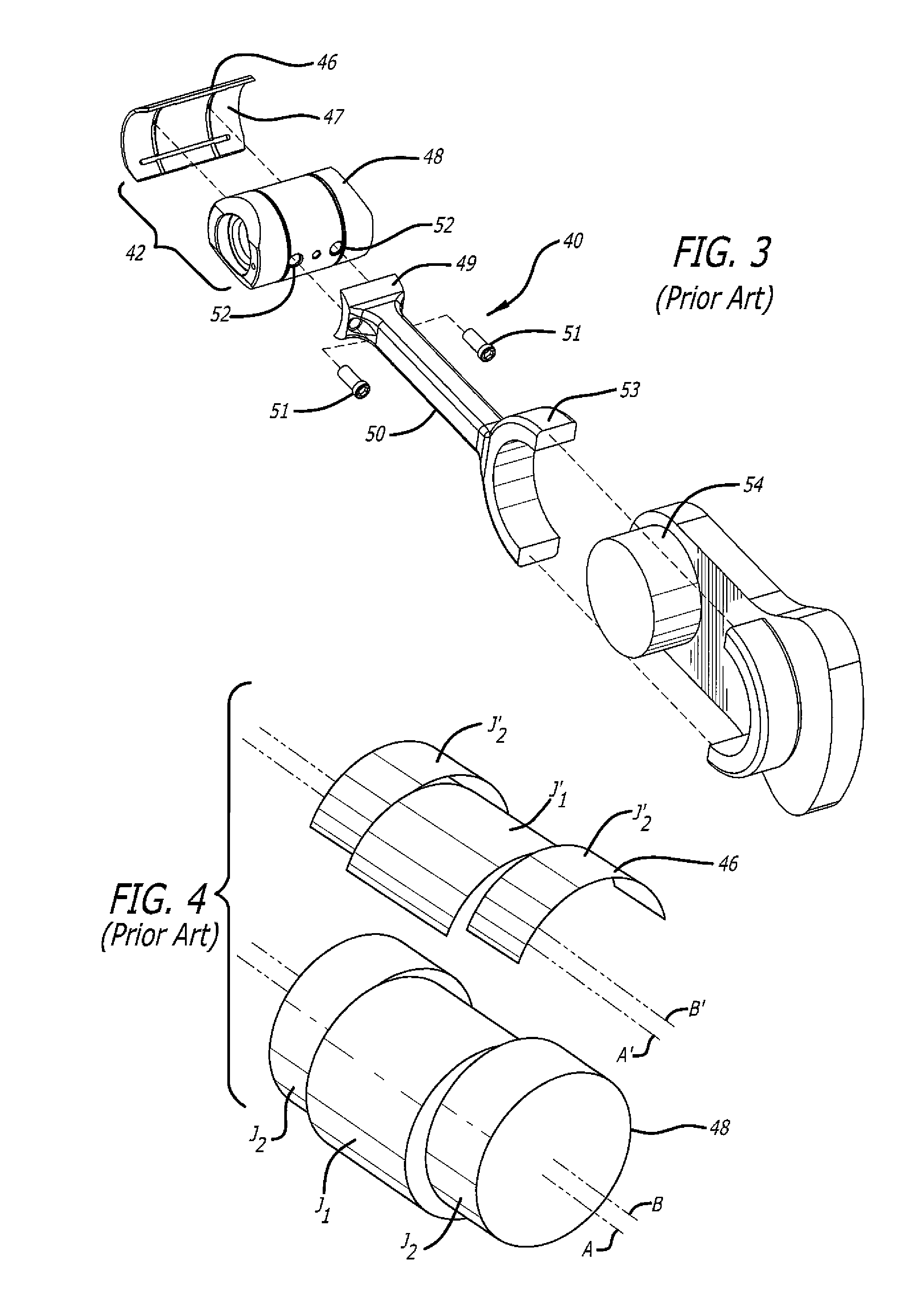
Load Transfer Point Offset Of Rocking Journal Wristpins In Uniflow-Scavenged, Opposed-Piston Engines With Phased Crankshafts
ActiveUS20160356216A1Sufficient oil film thicknessCrankshaftsConnecting rod bearingsCombustionEngineering
Load transfer point offset of rocking journal bearings in uniflow-scavenged, opposed-piston engines with phased crankshafts includes differing offsets for the load transfer points of opposed pistons. More specifically, under the condition that a first crankshaft leads the second crankshaft, an angular offset of a rocking journal wristpin of a piston coupled to the first crankshaft proportional to an offset of the first crankshaft relative to the second crankshaft is made to ensure adequate oil film thickness to the wristpin when it experiences a peak combustion pressure during a power stroke
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC
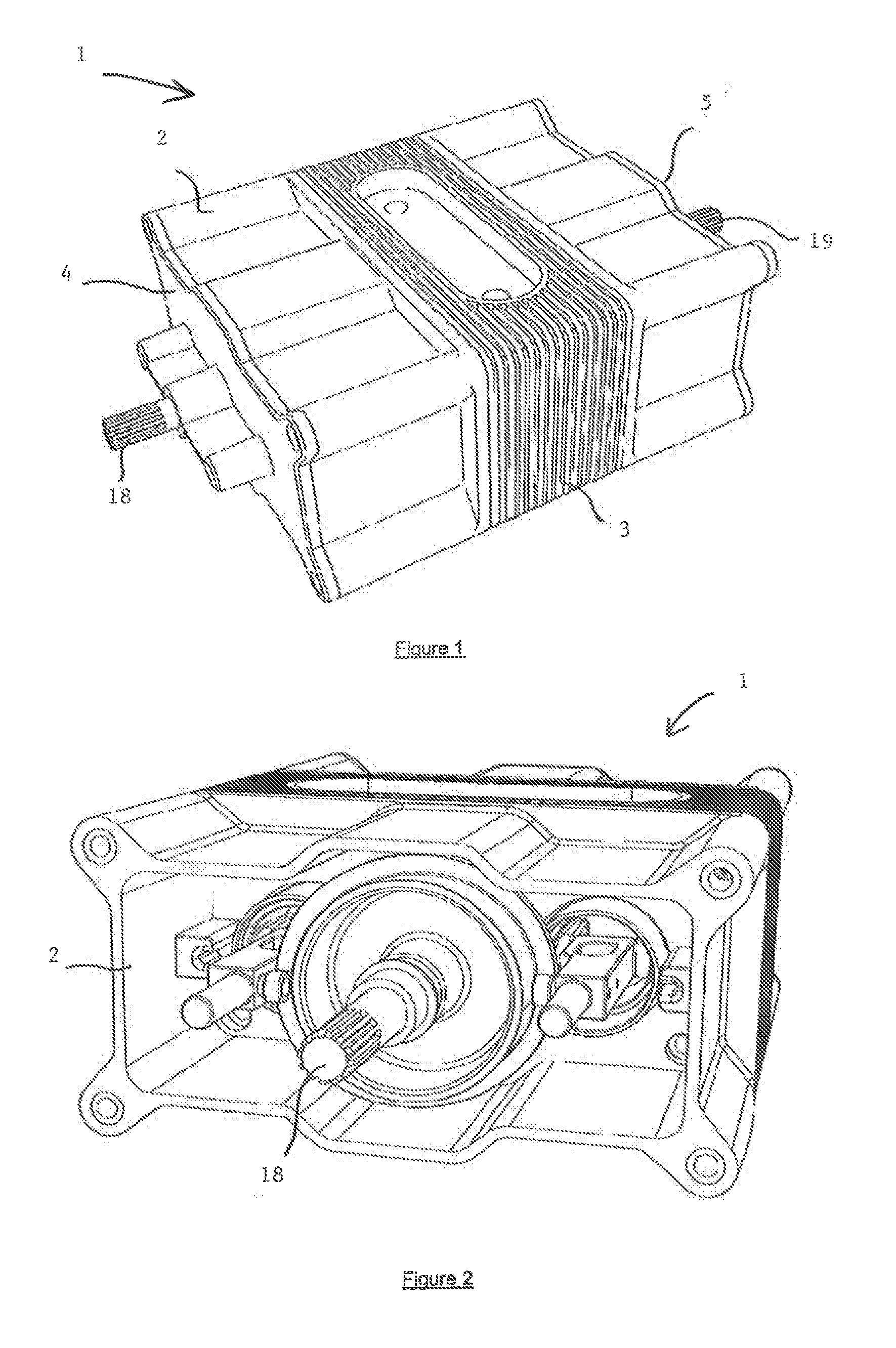
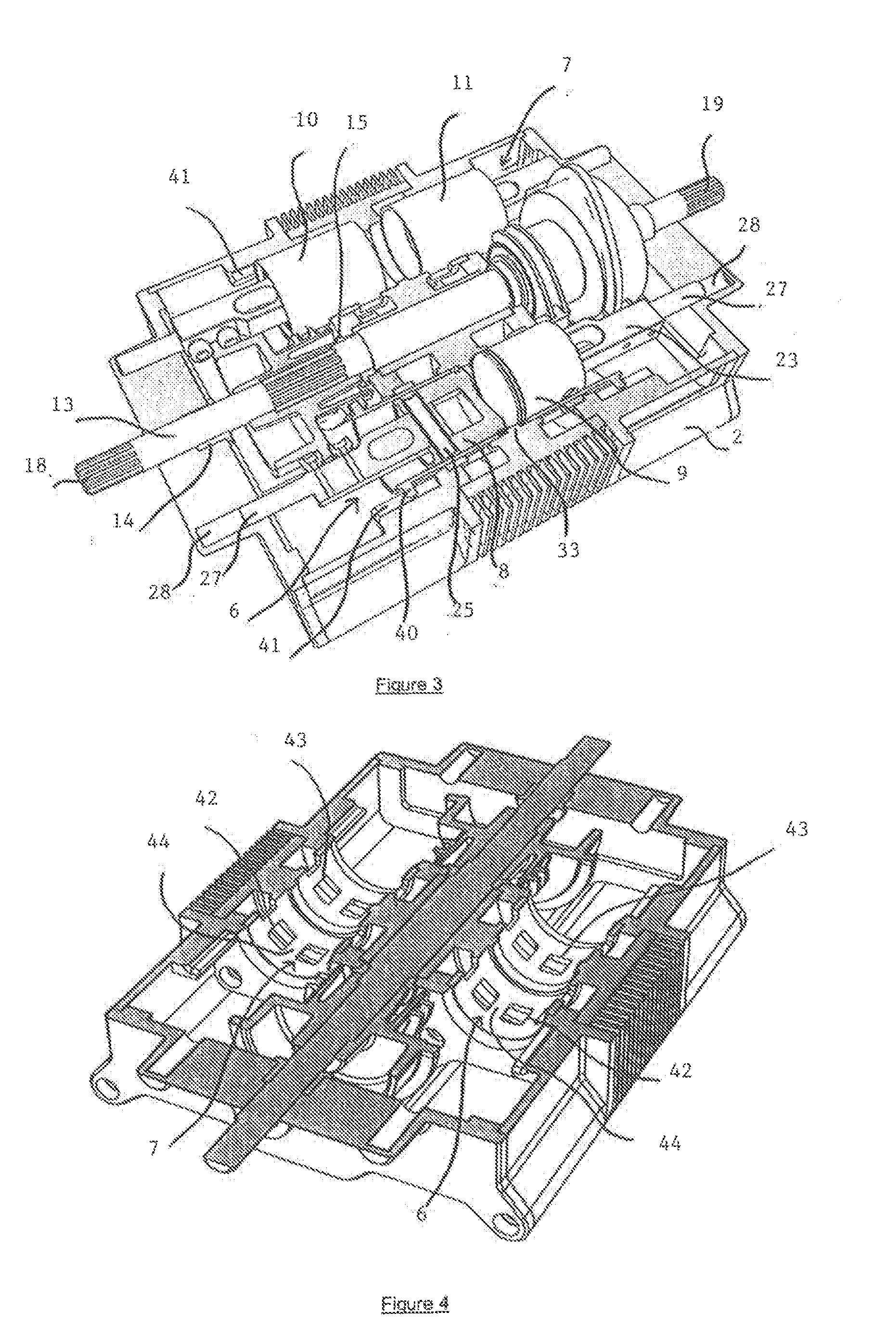
Opposed piston engine
ActiveUS7004120B2Internal combustion piston enginesEngines with rotating cylindersEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:ENGINUITY POWER SYST INC
Differential with guided feedback control for rotary opposed-piston engine
ActiveUS20060225691A1Improve efficiencyImprove pressure resistanceInternal combustion piston enginesOscillating piston enginesCamFeedback control
A gear set is disclosed having a guide, such as a cam, engaging the output shaft of the gear shaft and being indexed thereby. The guide drives one or more followers which in turn drive one or more interfaces of a differential gear set. The output shaft may be driven by a third interface of the differential gear set. The followers may likewise engage piston assemblies in order to control the piston assemblies during execution of a process such as a four stroke combustion process, or other process involving compression or expansion of a gas. The piston assemblies are enclosed within a housing defining an annular chamber, such as a toroid. Apertures formed in the housing allow exhaust gases to leave and air to be taken in. In one embodiment, a hyper expansion port is formed in the housing to release a portion of the air during the compression stroke in order to decrease the pressure of combustion gases.
Owner:MCCOIN DAN K +1
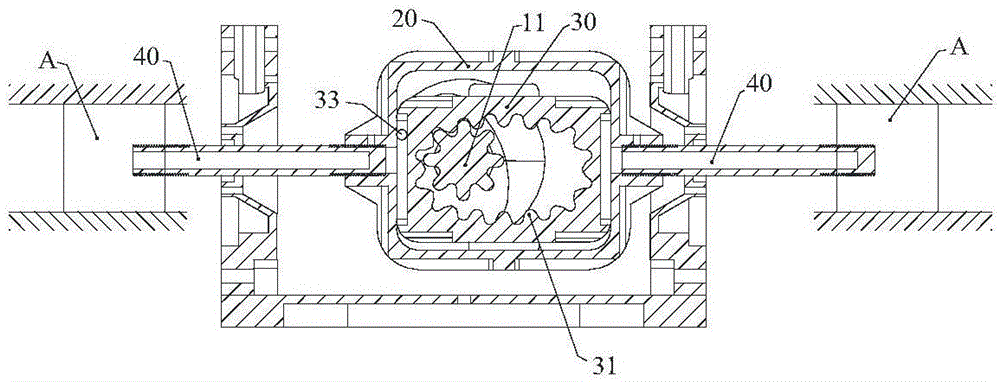
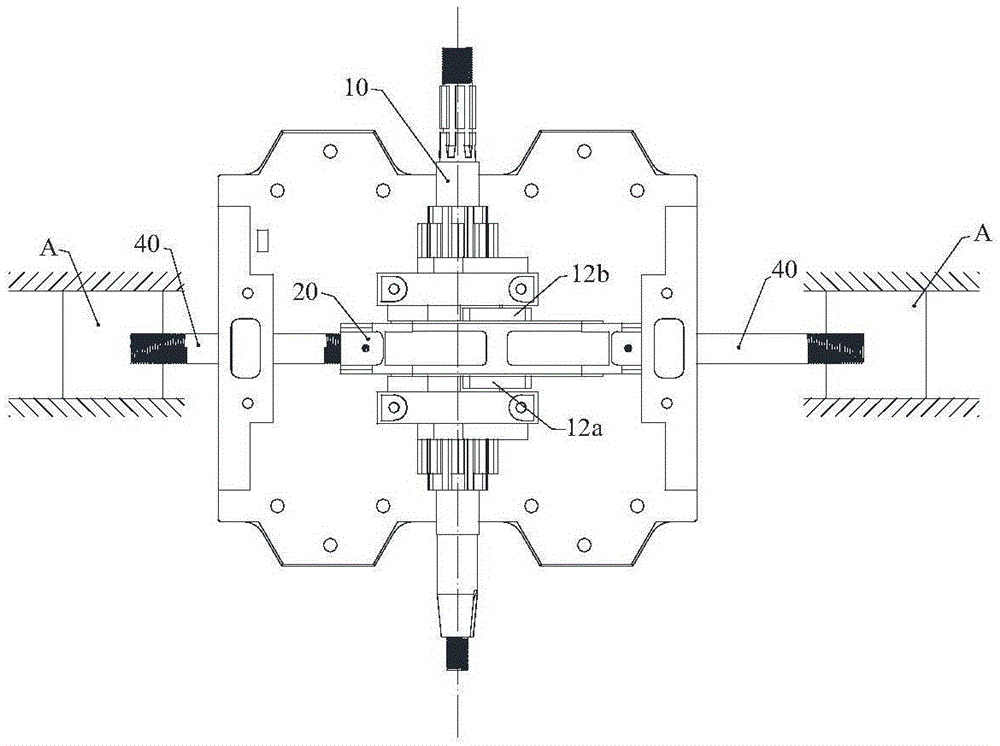
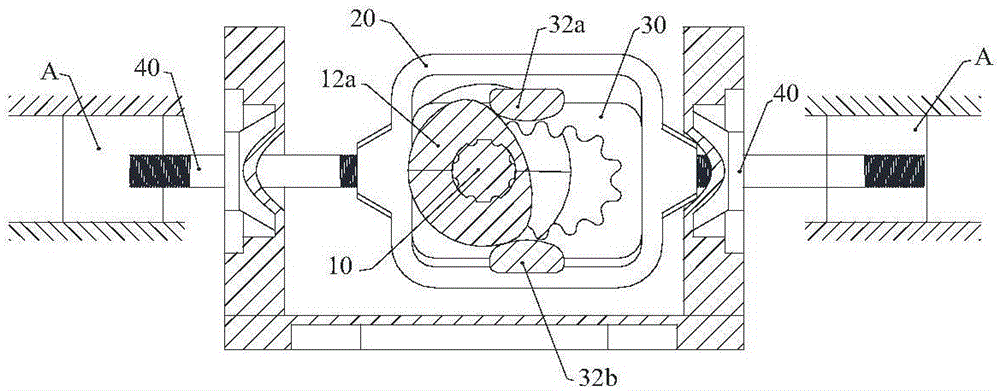
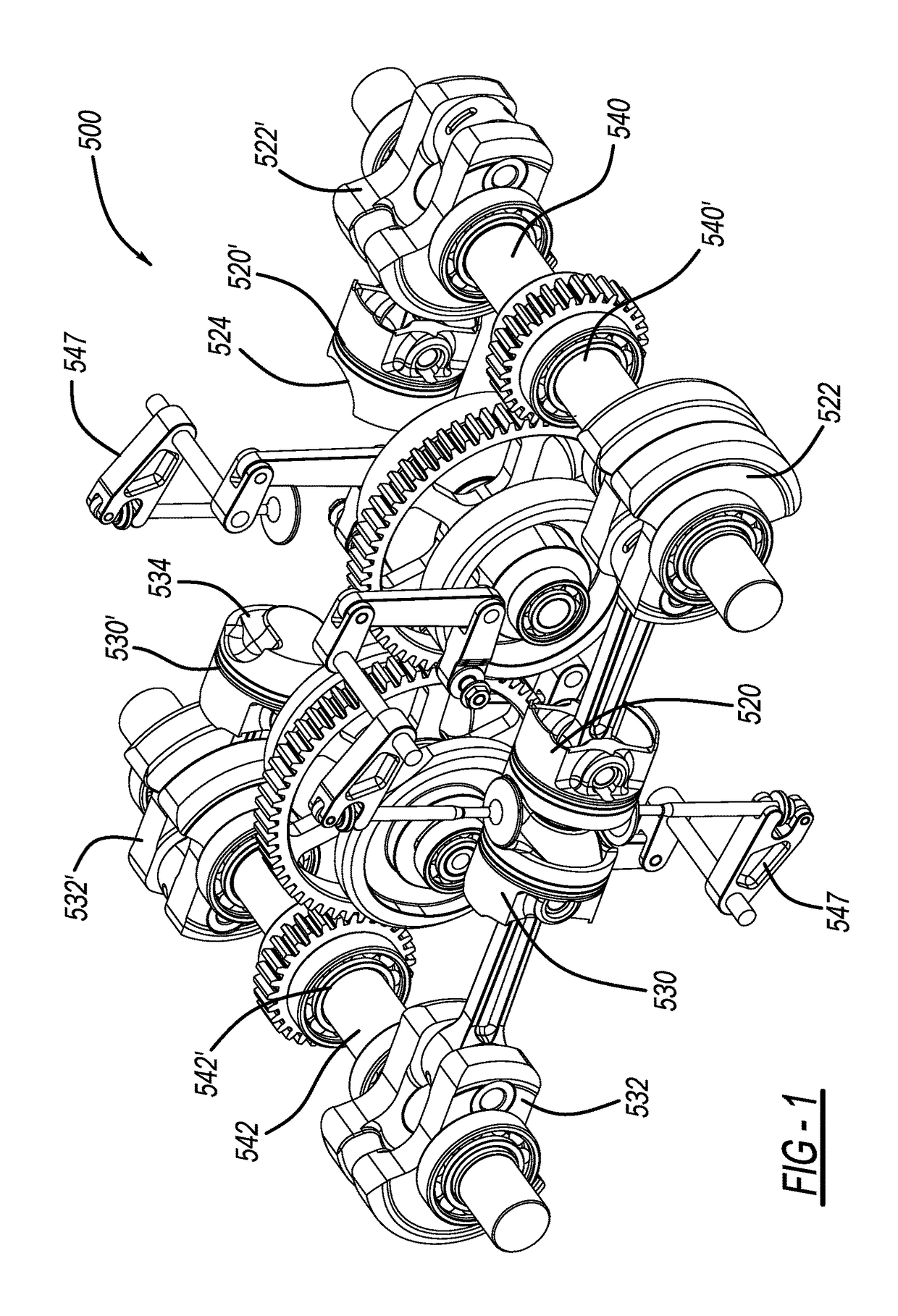
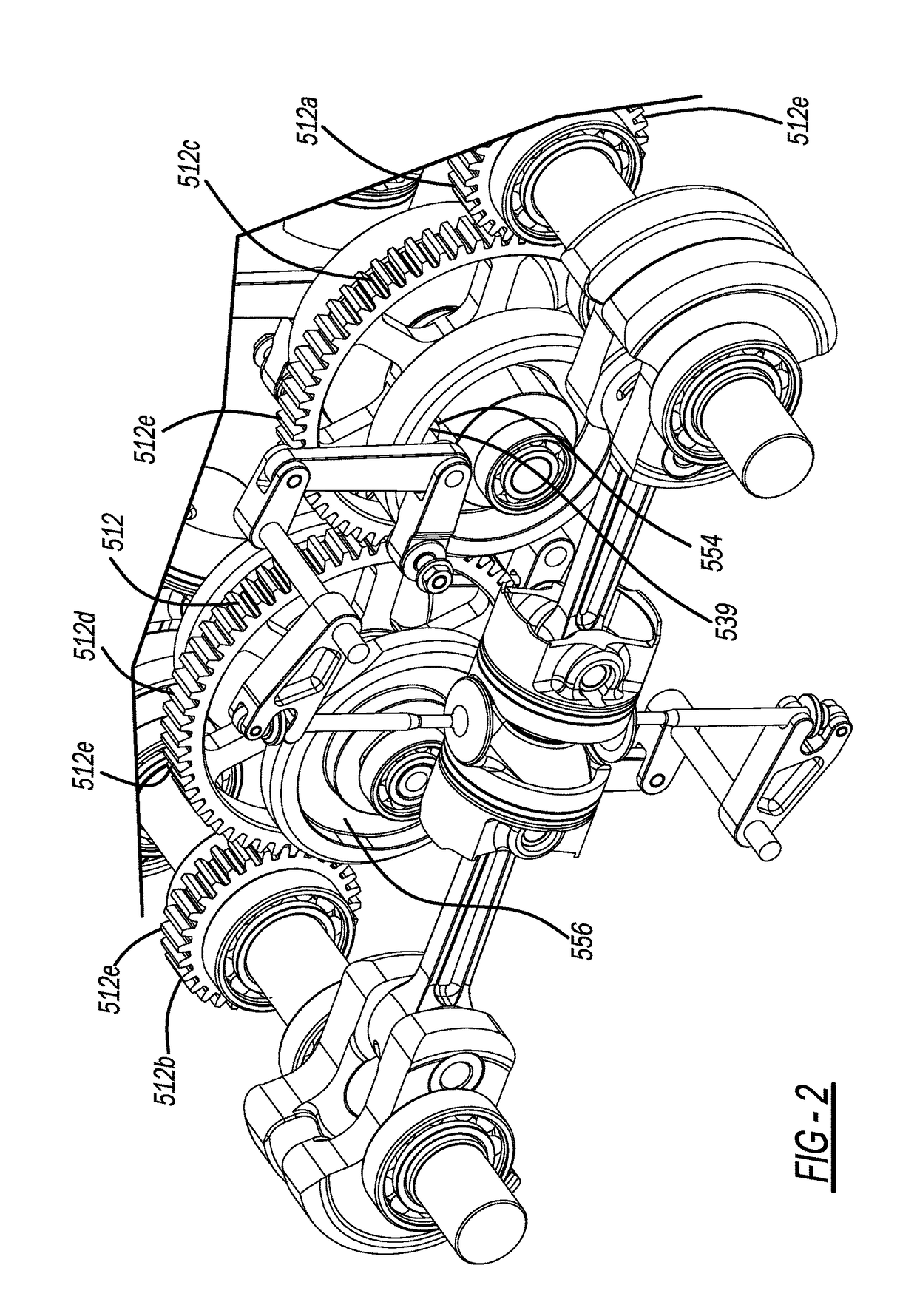
Shaft type connecting rod transmission system and opposed piston engine
ActiveCN105114179AEfficient use ofSimple structureGearingMachines/enginesLinear motionReciprocating motion
The invention discloses a shaft type connecting rod transmission system and an opposed piston engine; and a traditional reciprocating linear motion is converted to a rotating motion in the same direction, so that the reliability of the transmission system is effectively improved, the transmission system is simplified to become more compact, and effective utilization of a space between the back surface of a piston of an internal combustion engine and a cylinder becomes possible. The shaft type connecting rod transmission system comprises a main shaft and at least one linear reciprocating motion unit, wherein the linear reciprocating motion unit comprises at least one linear reciprocating motion body. The linear reciprocating motion bodies are fixedly connected with one ends of corresponding shaft type connecting rods; the other ends of the shaft type connecting rods are fixedly connected with one sides of corresponding push-pull frames; and the axles of the shaft type connecting rods and the main shaft are perpendicular to each other. Slip blocks are arranged in the push-pull frames; two transverse outer side walls of the slip blocks and two transverse inner side walls of the push-pull frames are formed to vertical slide fit; inner rings of the slip blocks have inner teeth with elliptic indexing circles; and the inner teeth are circularly engaged with gears correspondingly arranged on the main shaft. Reversing mechanisms are arranged between the main shaft and the slip blocks.
Owner:郑安庆
Two stroke opposed-piston engines with compression release for engine braking
ActiveCN103314184AAchieve brakingValve arrangementsExhaust gas recirculationTop dead centerControl theory
In a two-stroke opposed-piston engine, a ported cylinder with a pair of opposed pistons is equipped with a decompression port including a valve and a passage with an opening through the cylinder wall that is located between the cylinder's intake and exhaust ports. The decompression port enables the release of compressed air from the cylinder after the intake and exhaust ports are closed. The valve controls airflow through the passage, and is opened to permit compressed air to be released from the cylinder through the passage, and closed to retain compressed air in the cylinder. Engine braking is supported by release of compressed air through the decompression port into an exhaust channel when the pistons are at or near top dead center positions as the cycle transitions from the intake / compression stroke to the power / exhaust stroke. Compression release from the cylinder via the decompression port after intake and exhaust, port closure can also support other engine operations.
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC
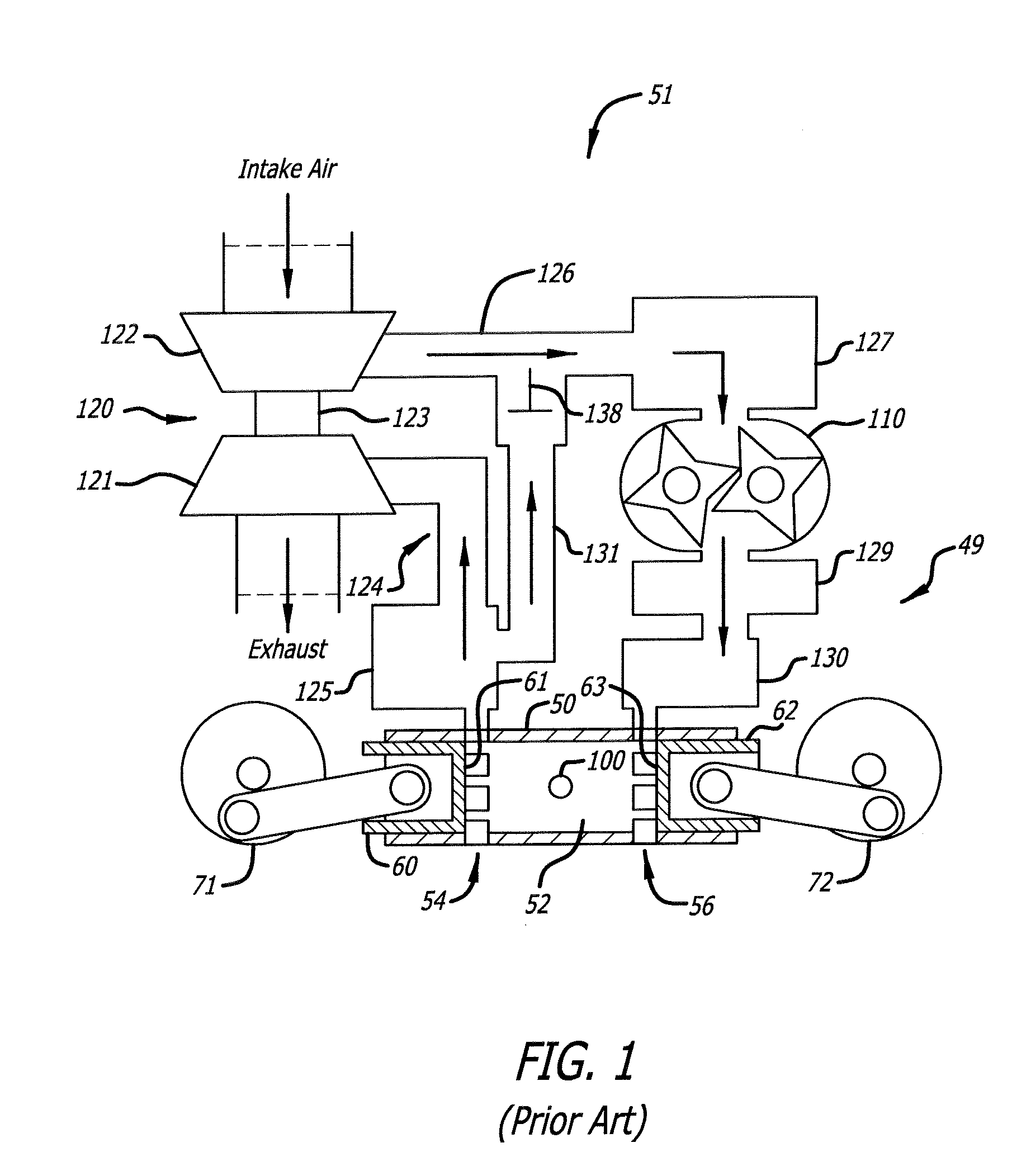
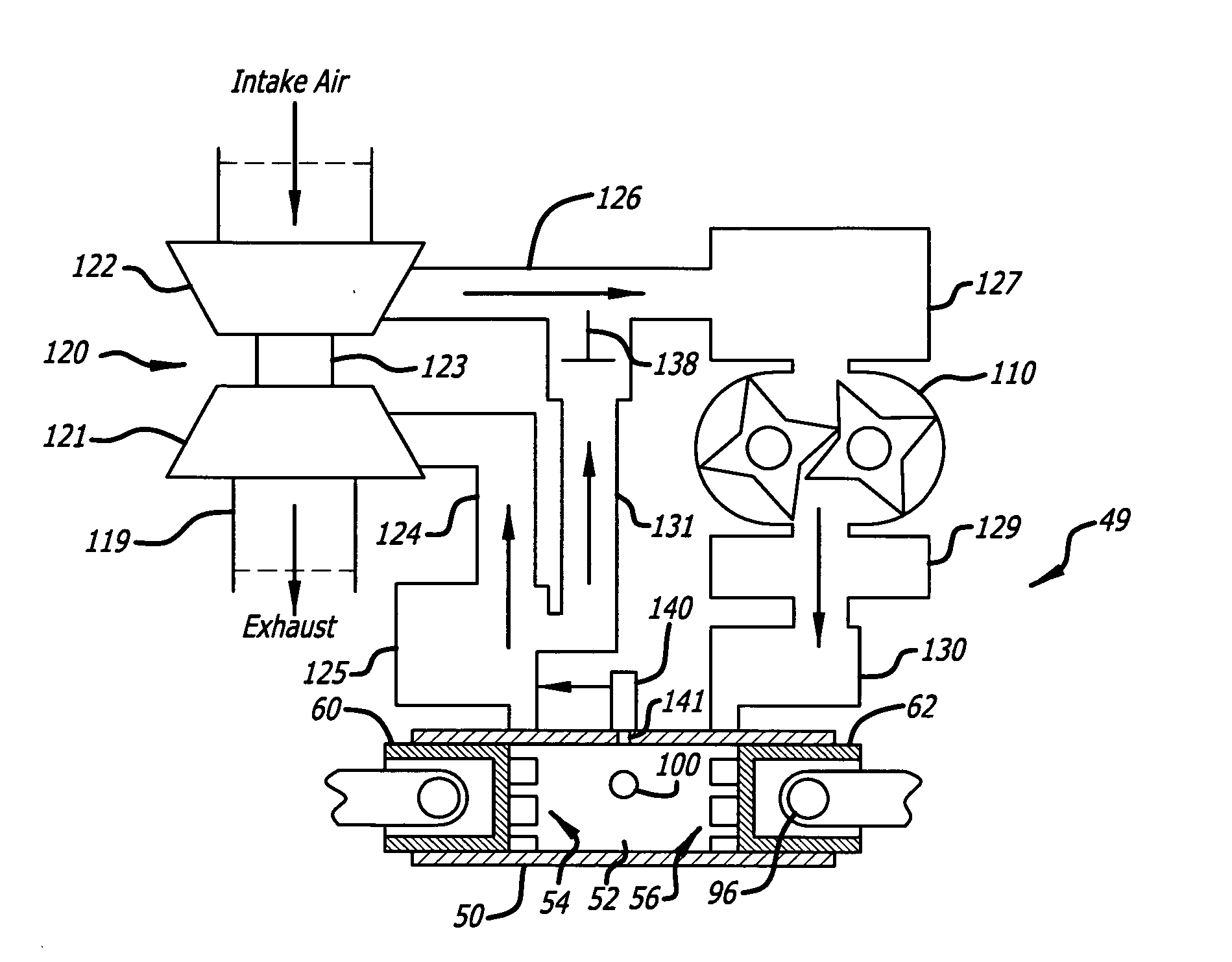
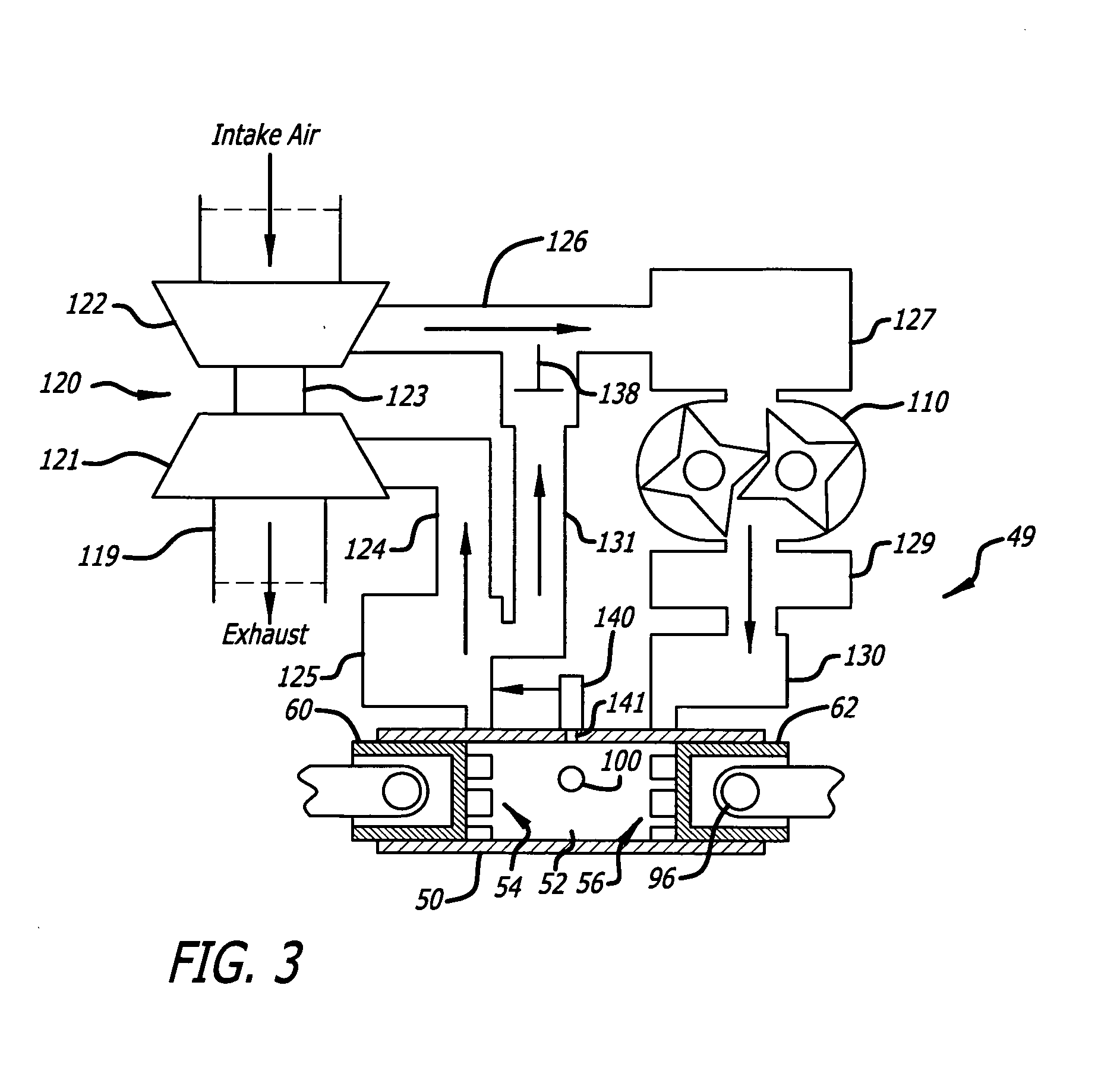
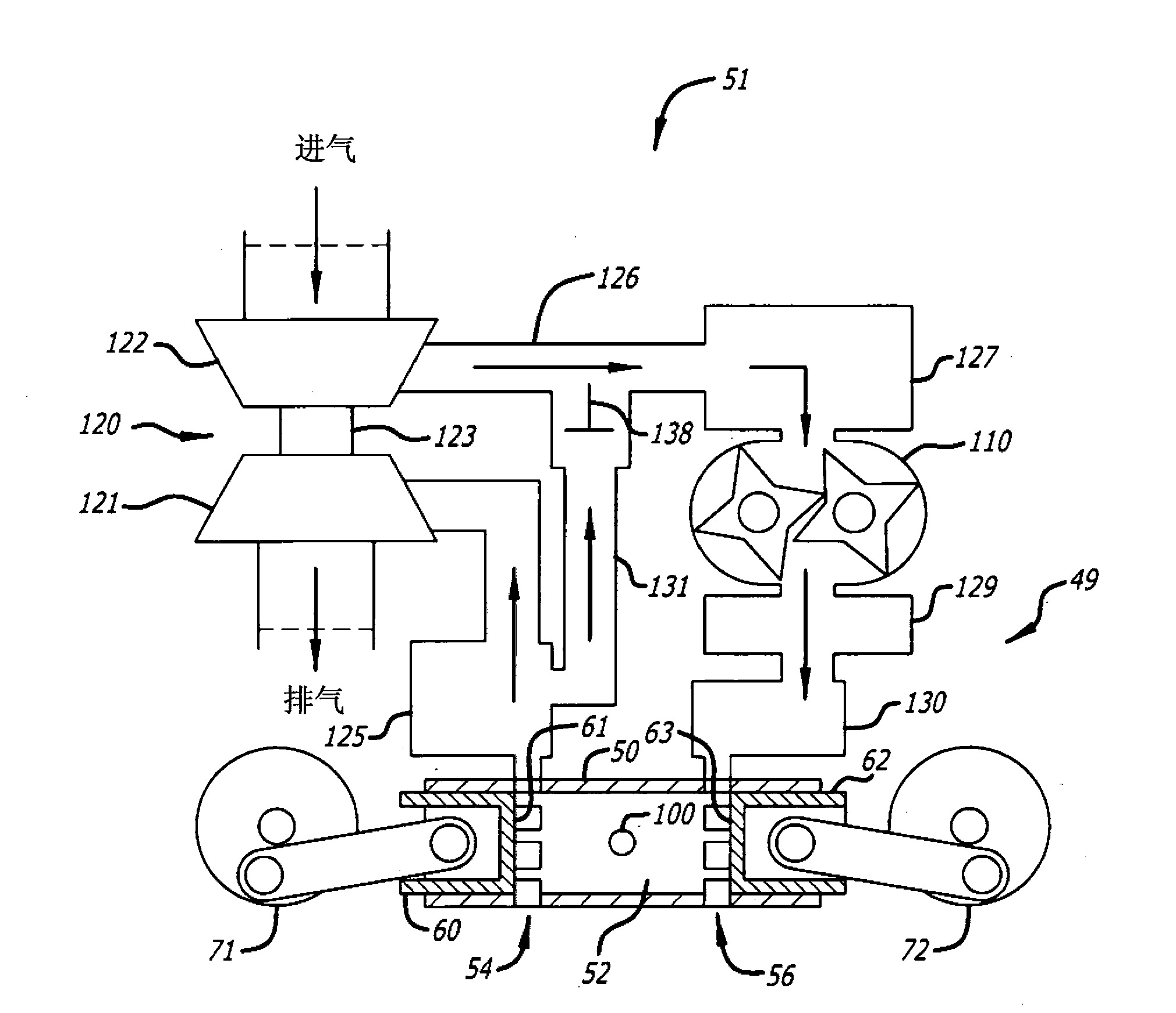
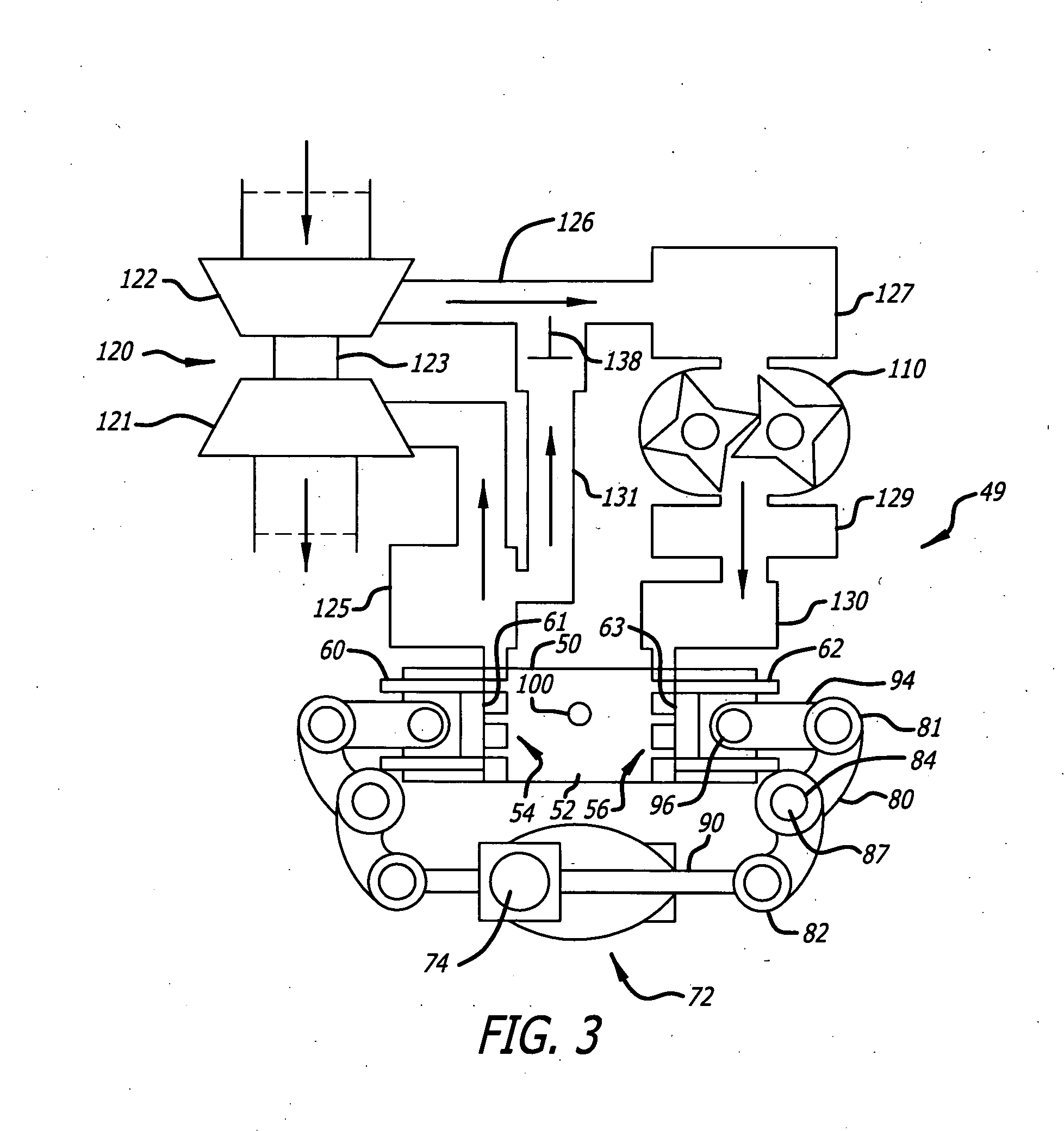
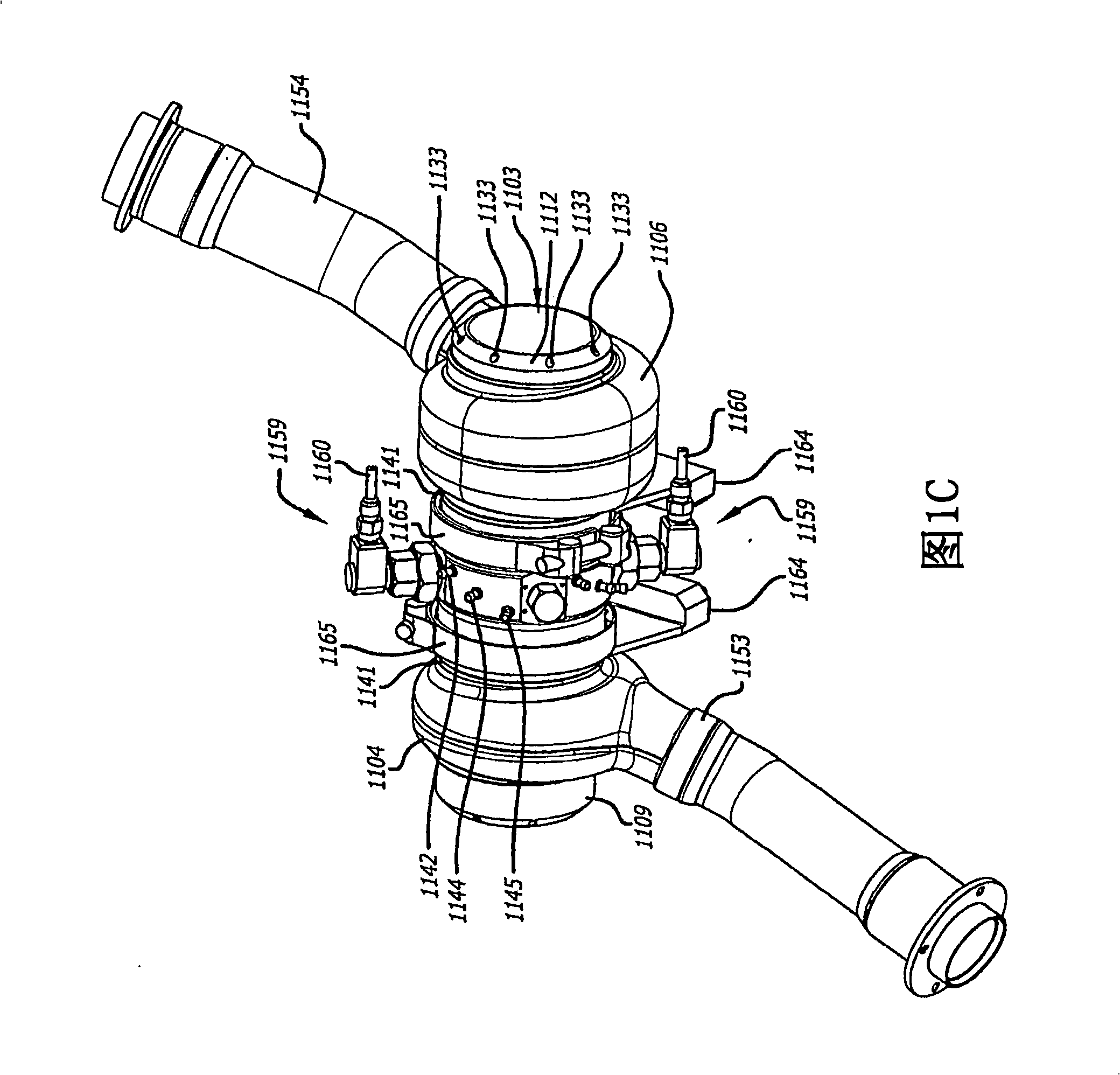
Egr construction for opposed-piston engines
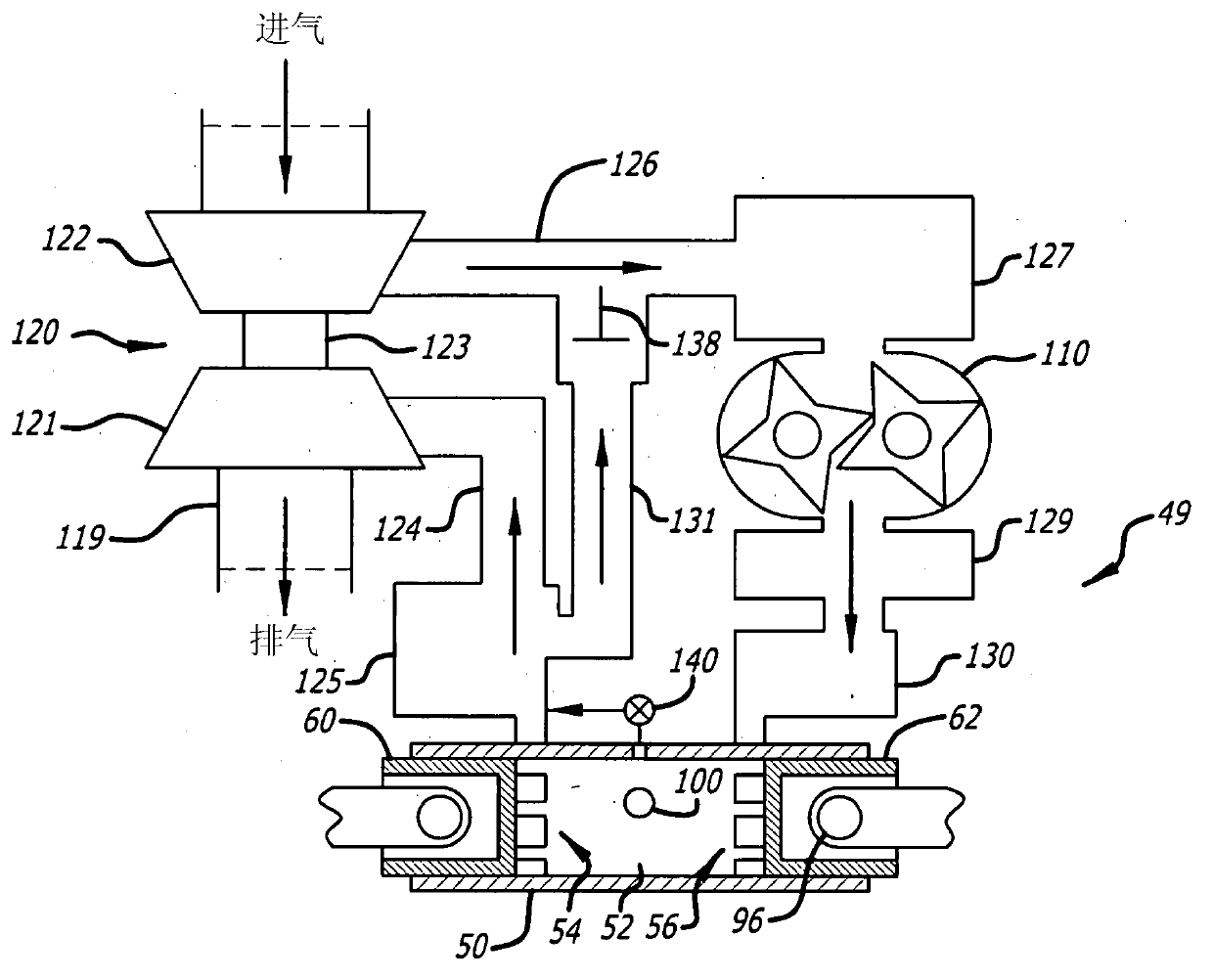
A two-stroke, opposed-piston engine (49) with one or more ported cylinders (c) and uniflow scavenging includes an exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) construction (131) that provides a portion of the exhaust gasses produced by the engine (49) for mixture with charge air to control the production of NOx during combustion.
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC
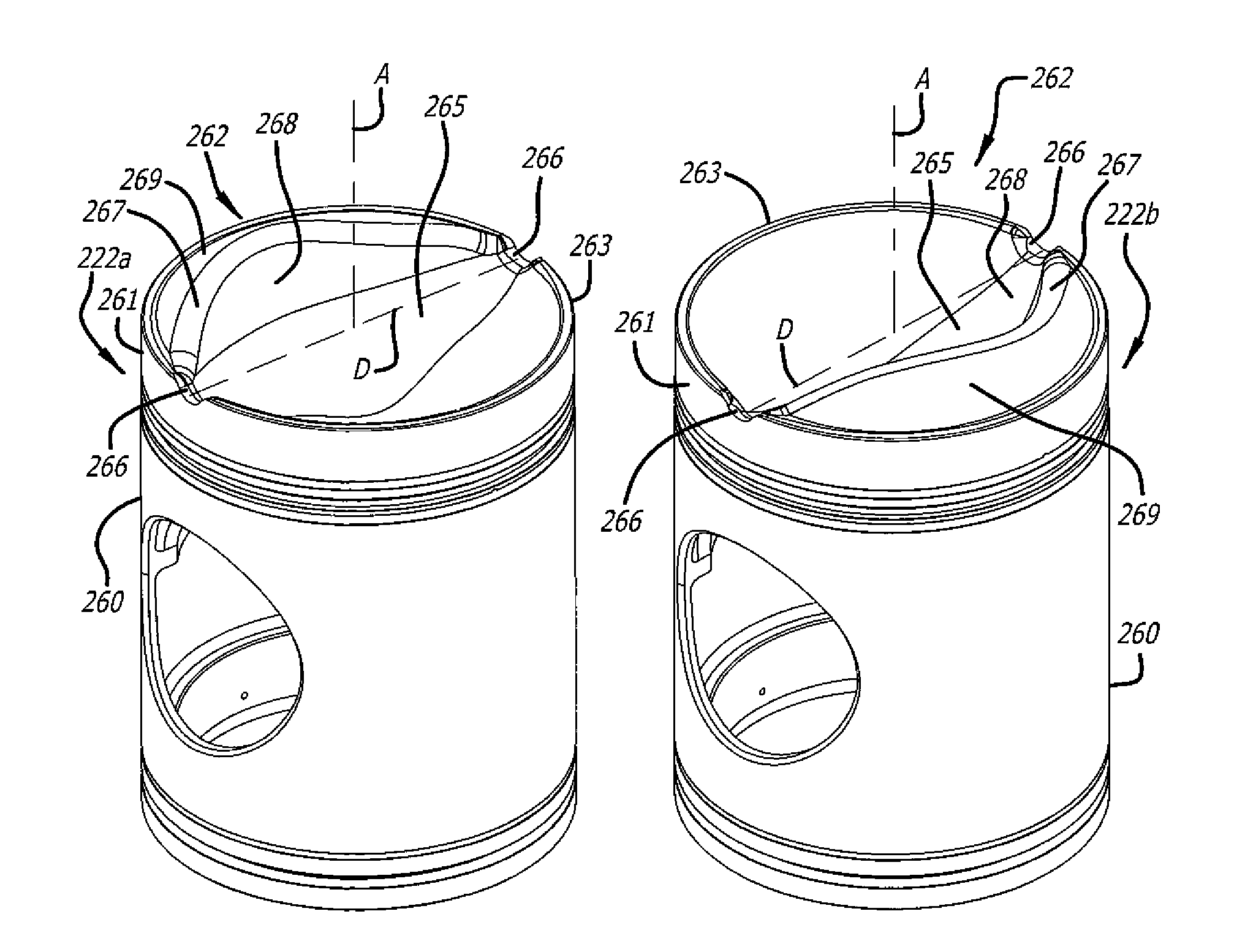
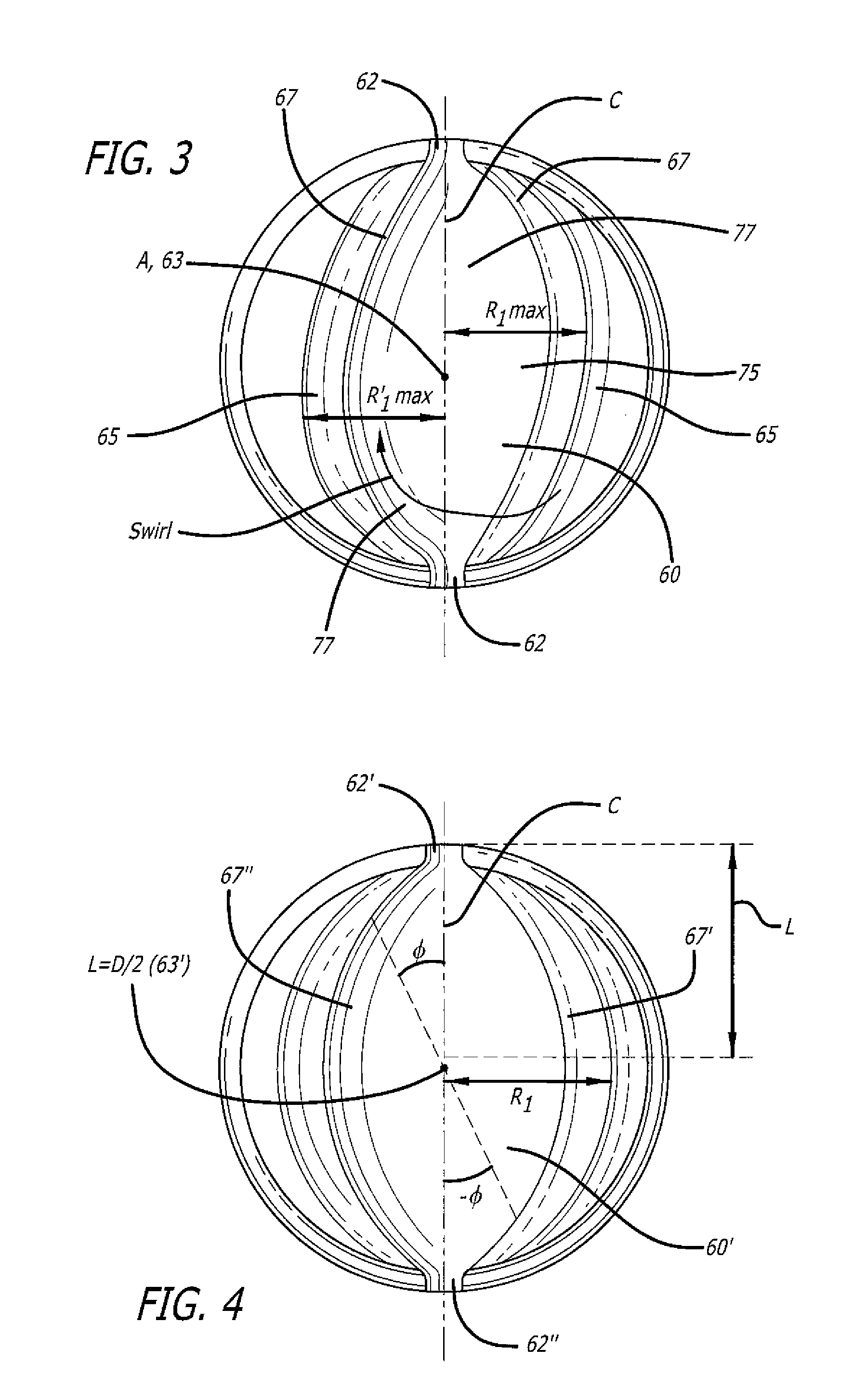
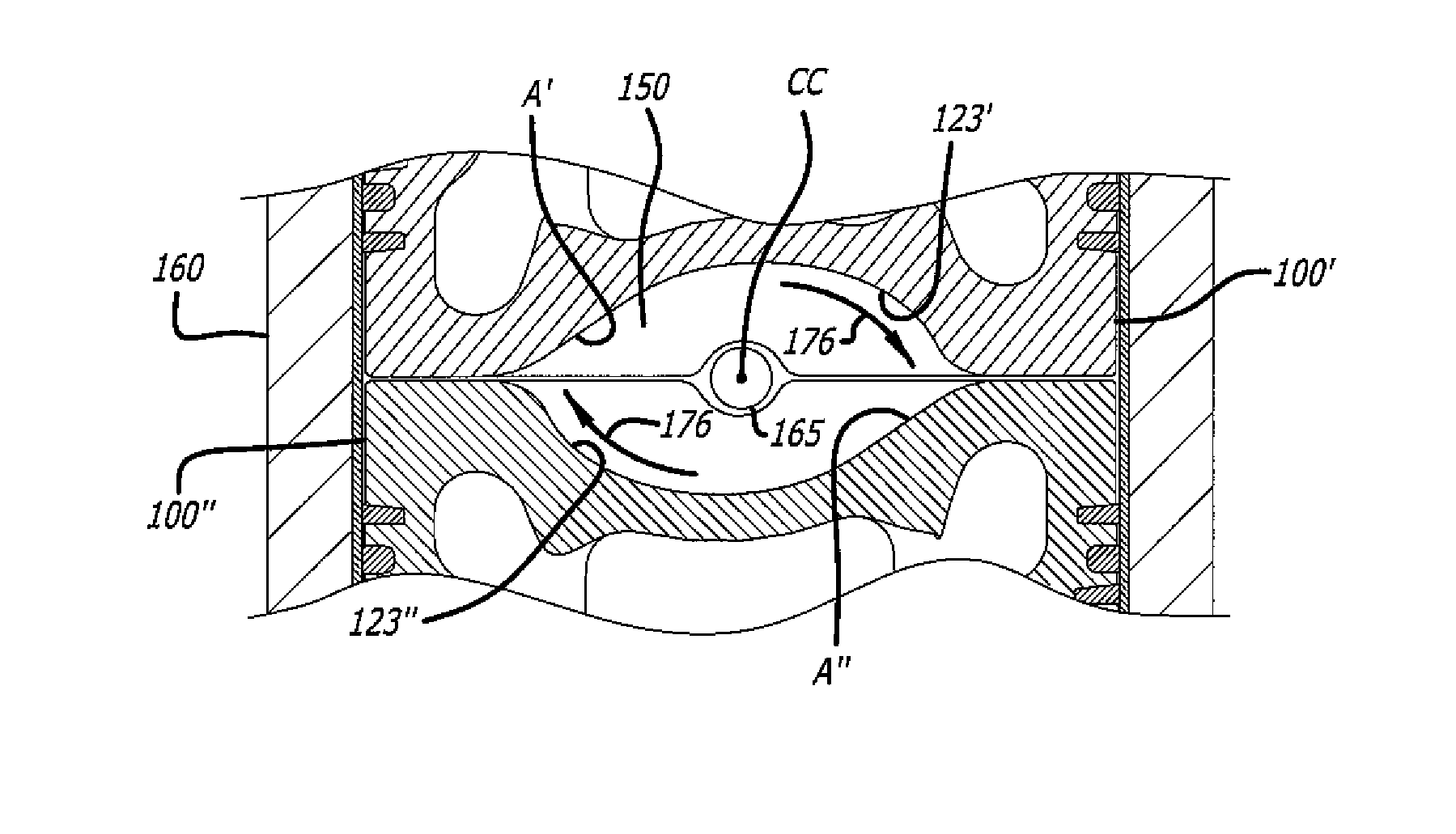
Asymmetrically-Shaped Combustion Chamber For Opposed-Piston Engines
ActiveUS20160290224A1Reduce disadvantagesIncrease the gapInternal combustion piston enginesPistonsCombustion chamberPiston
A combustion chamber for an opposed-piston engine has an elongated asymmetrical shape in longitudinal section that runs along a chamber centerline, between diametrically-opposed openings of the combustion chamber through which fuel is injected. The asymmetry apportions combustion chamber volume to provide additional clearance on a side of the chamber centerline toward which swirl is directed, thereby giving a fuel plume space to swing without hindrance in response to swirl.
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC
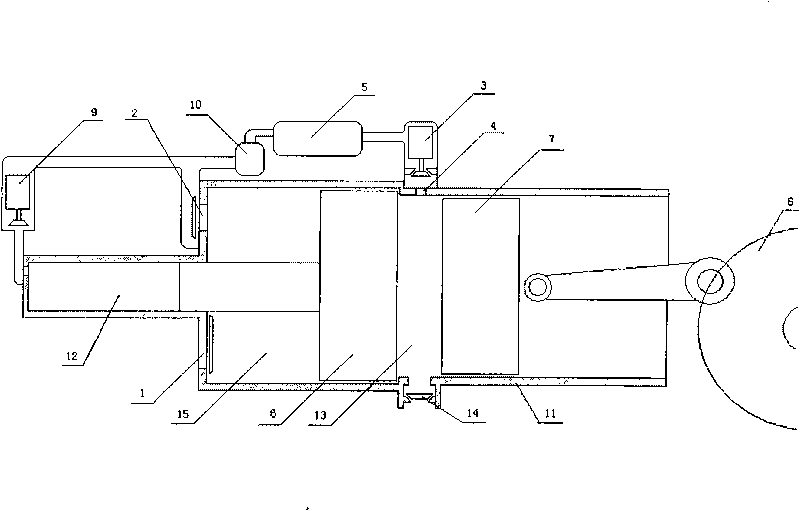
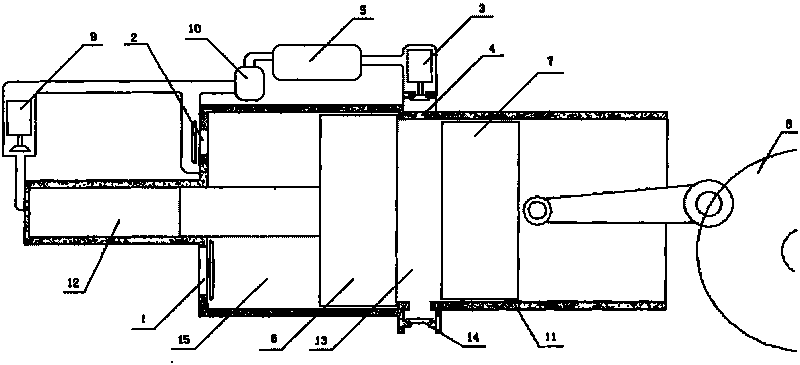
Opposed-piston engine
InactiveCN101737147AExtend your lifeMeet the requirements of fuel saving and efficiency improvementCombustion enginesEngine lubricationFree-piston engineCombustion chamber
Belonging to the field of internal-combustion engine, the invention in particular relates to an opposed-piston engine, comprising a cylinder, a working piston, a crank shaft and the like; wherein the cylinder is provided with an air piston which is opposite to the working piston and moves in opposite direction; the cylinder block face at one side of the air piston is provided with an intake valve and an outtake valve; the intake valve is communicated with the atmosphere, the air piston is provided with a mechanism which can enable the air piston to reset; the air outtake is connected with an air storage mechanism for storing high pressure gas by an oil-gas separating device; the middle part of the cylinder is provided with a combustion chamber which is provided with an air inlet, an air outlet, a fueling injection device and an ignition unit; the air inlet is connected with the gas storage mechanism by a first electromagnetic valve. With the opposed-piston engine adopted, oil fuel consumption and vibration can be reduced by big margins and motorcycles or single-cylinder automobiles with even smaller vibration than the vibration of 4-cylinder automobiles can be produced; in addition, the engine of the invention can serve as auxiliary power of hybrid vehicles.
Owner:曹索格
Improved opposed piston engine
InactiveUS20160025002A1Increase the effective areaIncrease effective lengthValve drivesCombustion enginesSleeve valveReciprocating motion
The invention relates to an opposed piston engine comprising at least one cylinder, at least two pistons arranged to be reciprocated within the same cylinder in an opposed manner, at least one intake port through the cylinder wall, at least one exhaust port through the cylinder wall, at least one shaft arranged to be rotated by reciprocal motion of the opposed pistons, at least one reciprocatable sleeve valve within the cylinder for controlling porting of one or both of the at least one intake port and the at least one exhaust port, a sleeve valve driving mechanism for controlling reciprocal motion of the at least one sleeve valve, and a dwell mechanism. The dwell mechanism is configured to induce at least one period of dwell of the at least two pistons during their respective cycles of piston motion.
Owner:TWO STROKE DEV
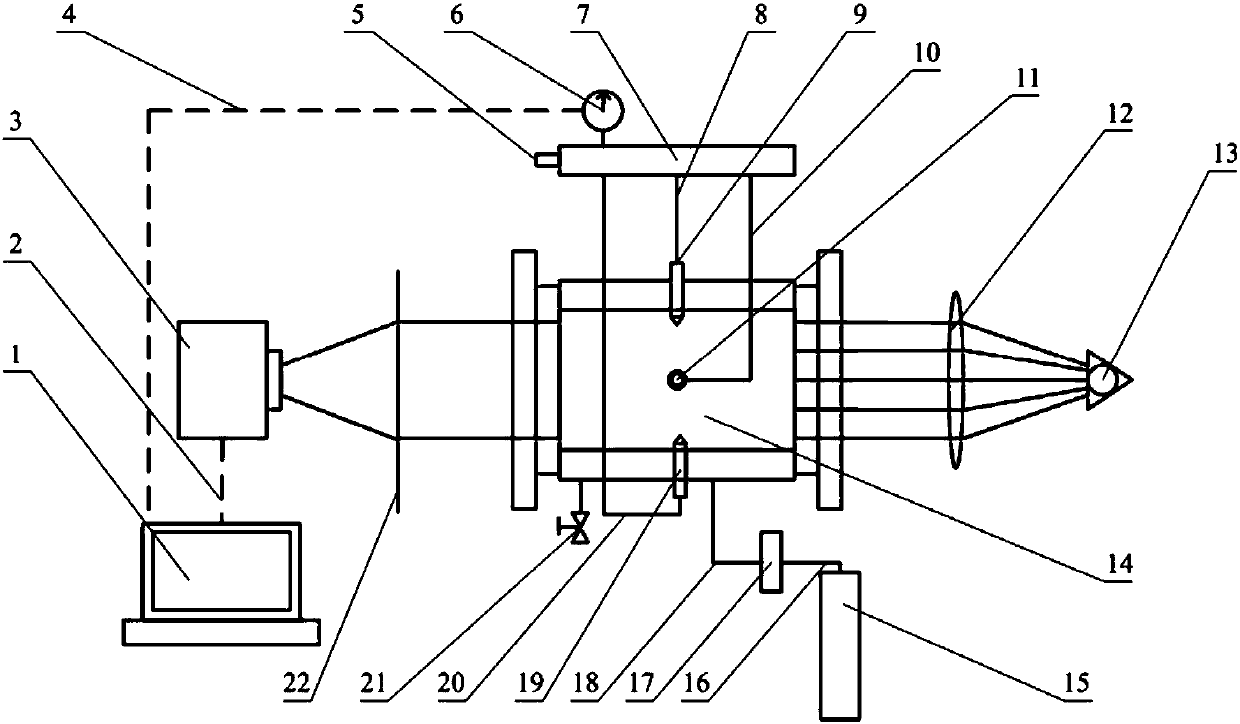
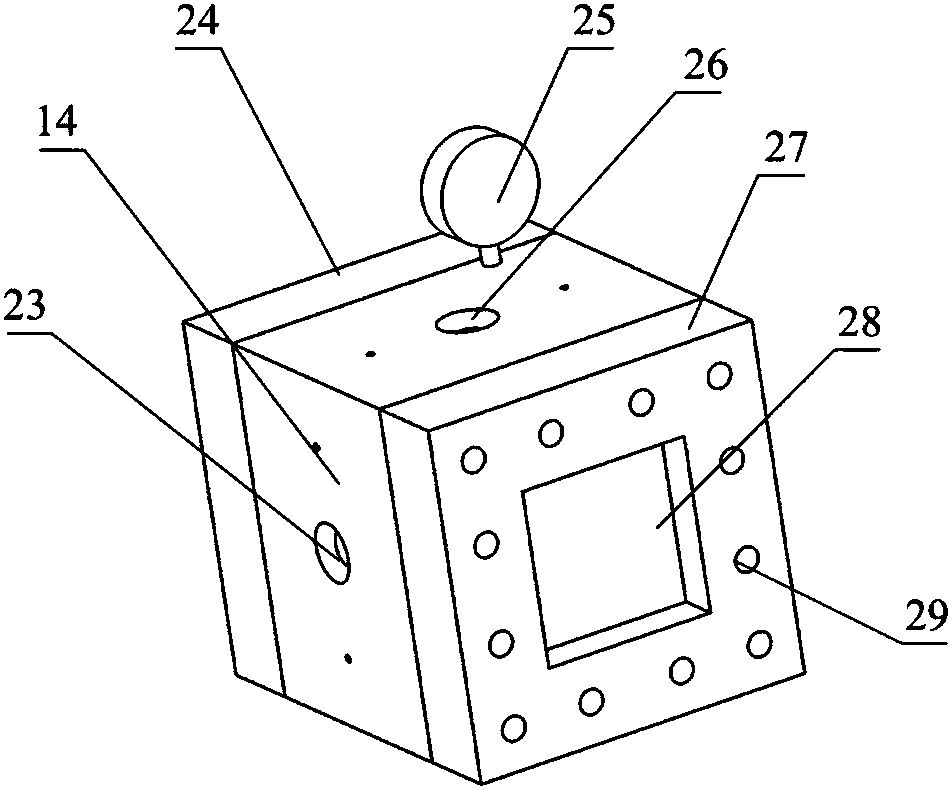
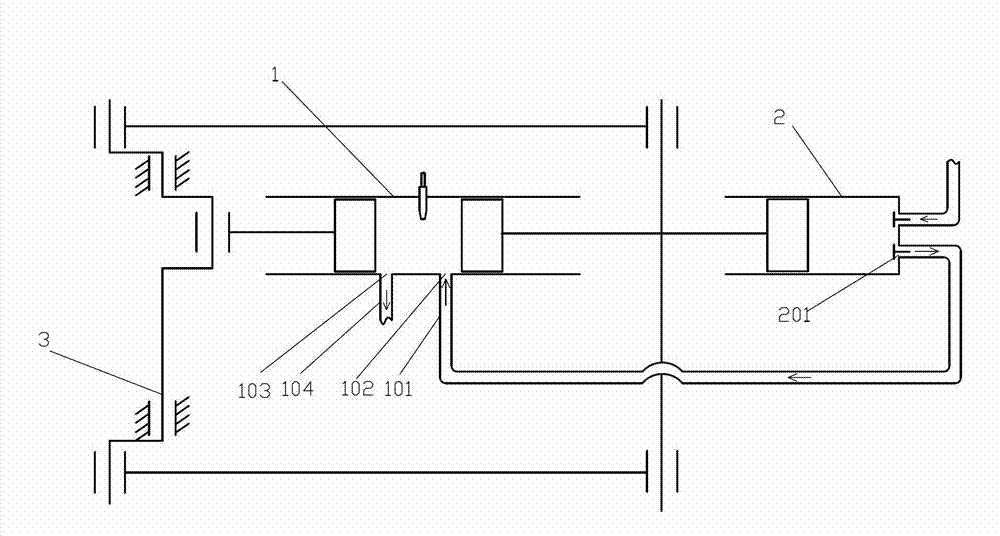
Interference spray test device for opposed piston engine
The present invention discloses an interference spray test device for an opposed piston engine. The device comprises a constant volume bomb system, an air intake and exhaust system, a fuel oil jettingsystem, a high-speed photographing system and a control and acquisition system; the constant volume bomb system is used for simulating the internal condition of a combustion chamber when opposed pistons are located at inner dead points so as to realize a fuel oil jetting, collision and atomization experiment; the air intake and exhaust system is used for providing corresponding jetting back pressure for the interior of the constant volume bomb of the constant volume bomb system and discharging oil mist exhaust gases in the process of the experiment; the fuel oil jetting system is used for establishing oil pressure meeting the requirements of the experiment and realizing fuel oil jetting; and the high-speed photographing system is used for capturing and recording spray structures in a spray field; and the control and acquisition system controls a spray direction, oil jetting pressure and a photographing process, realizes the photographing control of fuel oil jetting and atomization andobtains the process image of spray development, and completes the acquisition of test data. With the test device of the invention adopted, on the one hand, jetting back pressure in a cylinder can beeffectively simulated, and on the other hand, flexible adjustment of interference spray at different angles can be realized.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
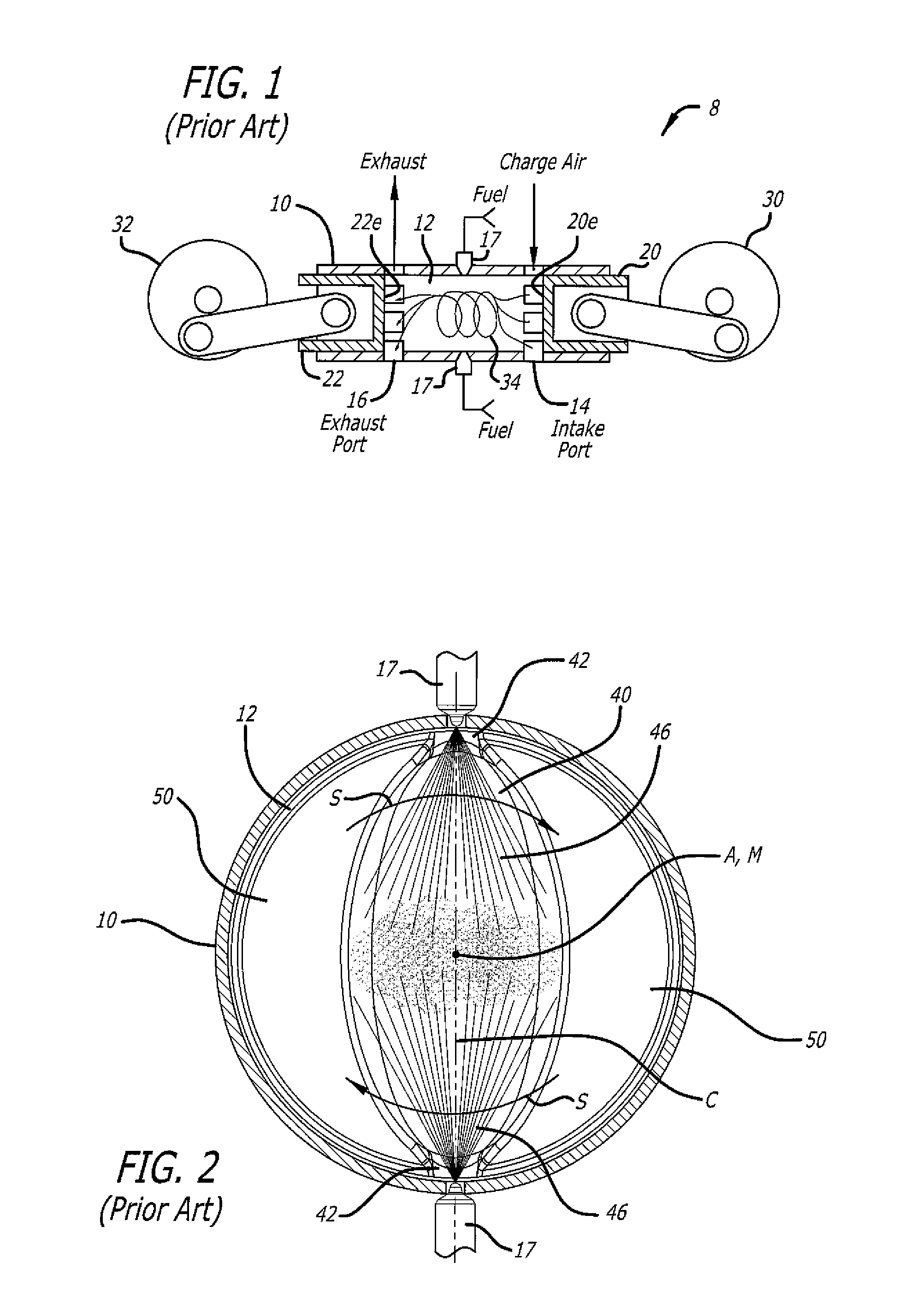
Centrally located ignition source in a combustion chamber
ActiveUS20070095320A1Readily apparentElectric ignition installationMachines/enginesElectrical conductorCombustor
The centrally located ignition source in a combustion chamber is an electrical conductor spanning the general center of the combustion chamber, with a spark gap at the general center of the conductor. The device may be offset from the combustion chamber centerline, and / or the spark gap may be offset from the conductor center, as required. The centrally located ignition source is particularly well suited for use in an opposed piston engine having a rotary sleeve valve mechanism, with the conductor rotating with the sleeve valve and crossing the combustion chamber between the two pistons. An arcuate commutator section may be disposed upon the exterior of the rotary sleeve valve, with a contact finger making electrical contact between the electrical energy source and the commutator section to supply electrical energy to the ignition source. The device is also suitable for use in stationary installations, e.g., gas furnace combustors, etc.
Owner:ENGINUITY POWER SYST INC
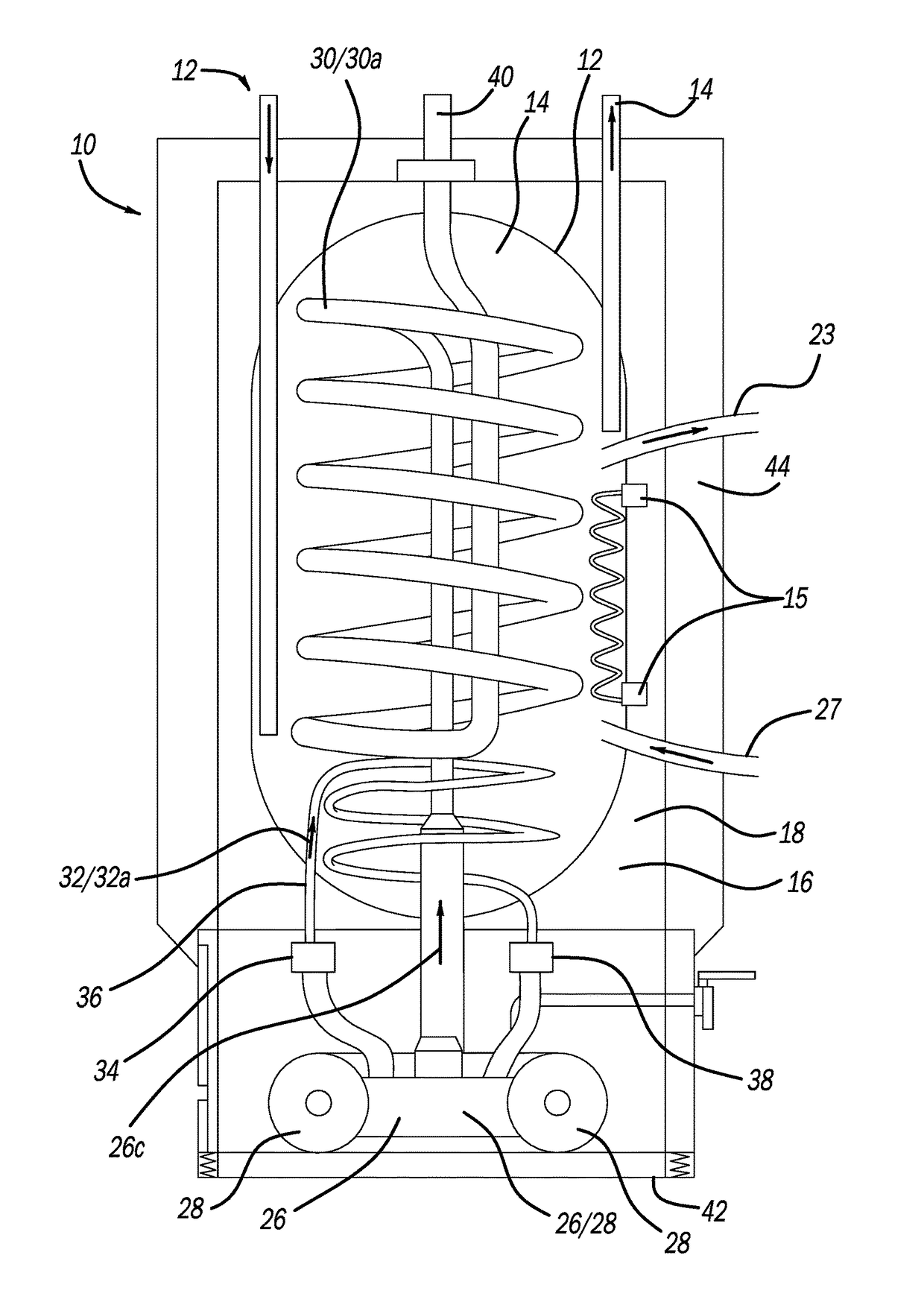
Energy Recovery System
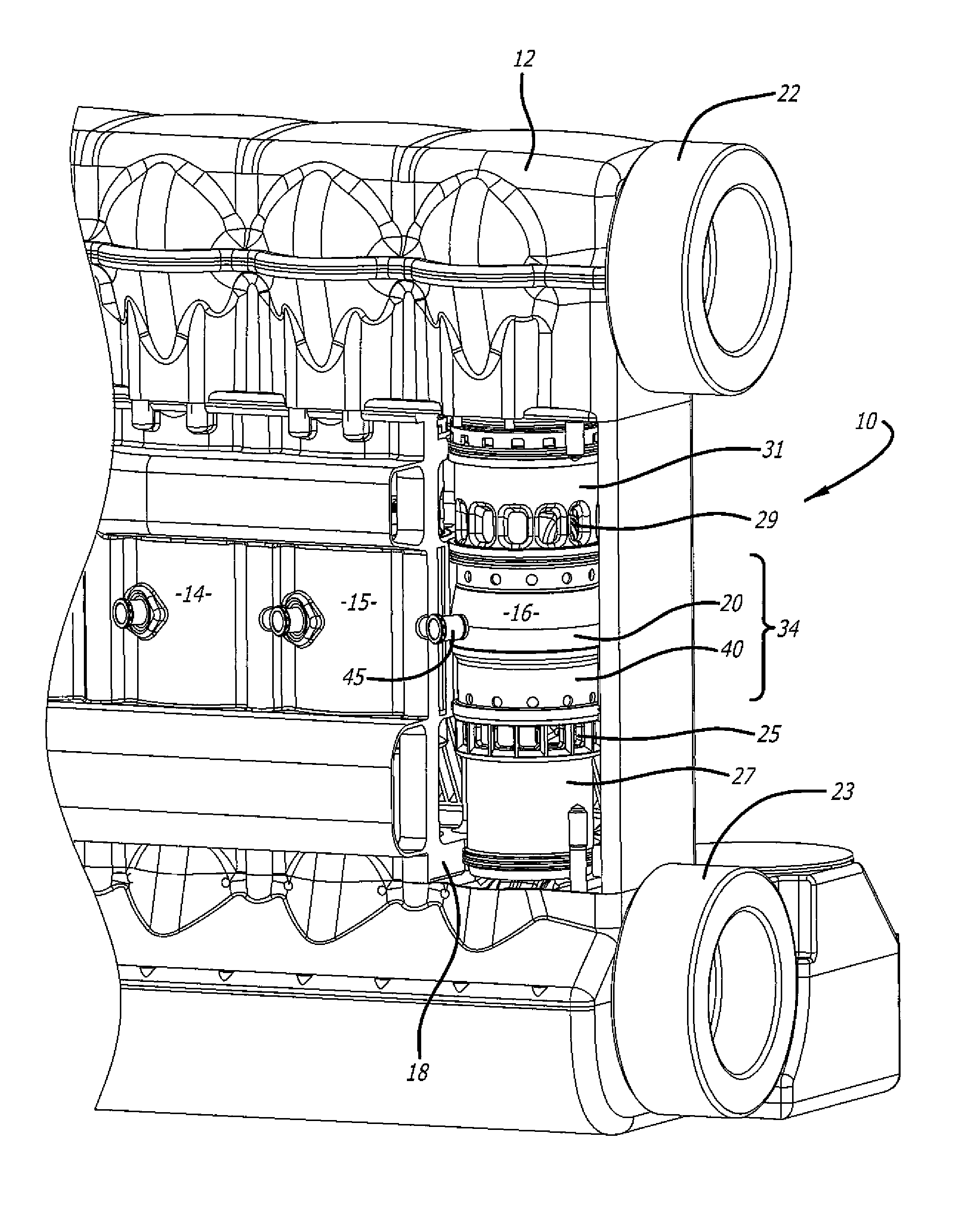
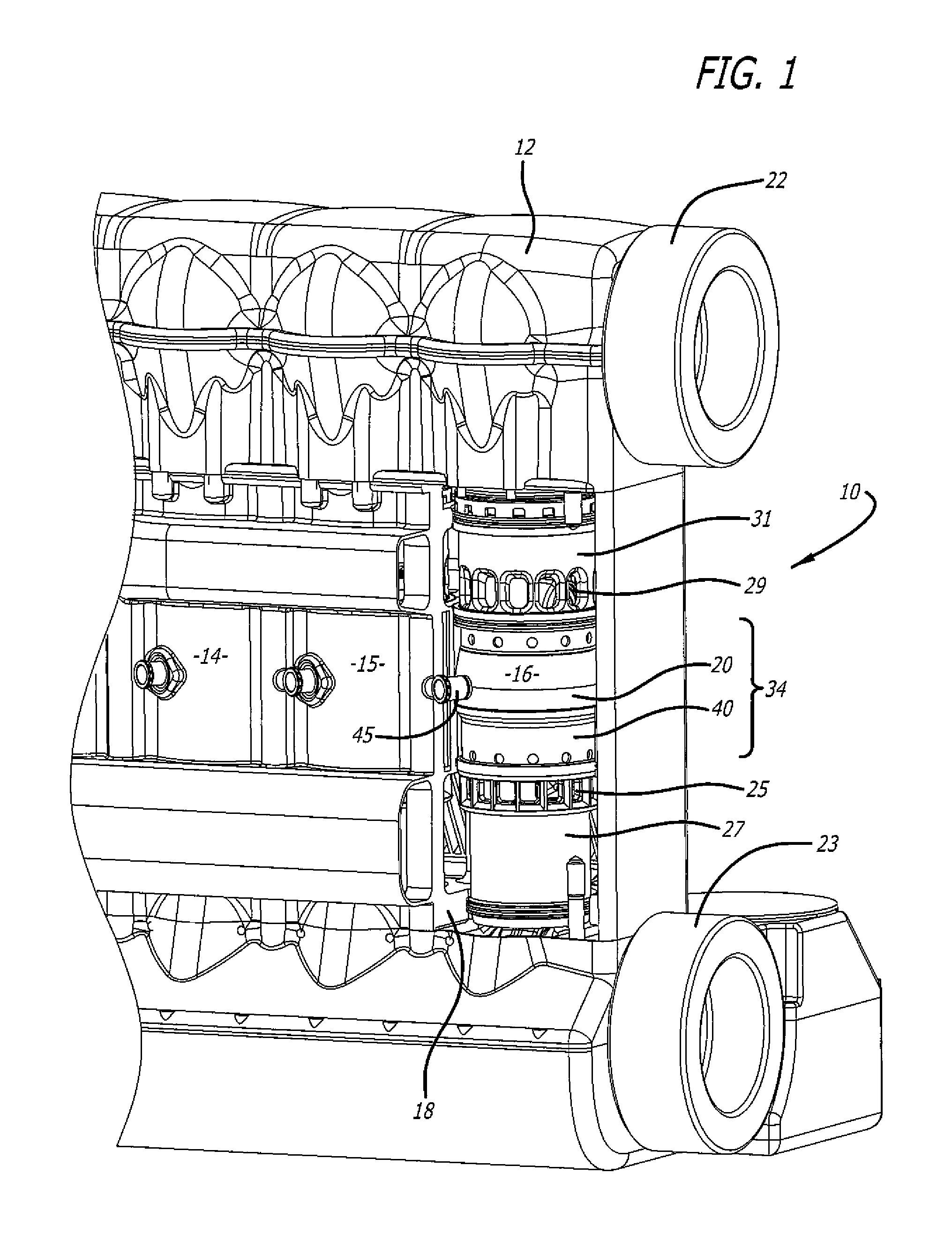
ActiveUS20170356310A1Efficient packagingMaximize applicationFuel cell heat exchangeInternal combustion piston enginesEnergy recoveryProcess engineering
A combined heat and power system, or an energy system, is provided. A four-stroke opposed-piston engine provides efficient power from a generator set or genset. A heat exchange system is provided within the energy system to provide efficient waste heat recovery as the engine is operated.
Owner:ENGINUITY POWER SYST INC
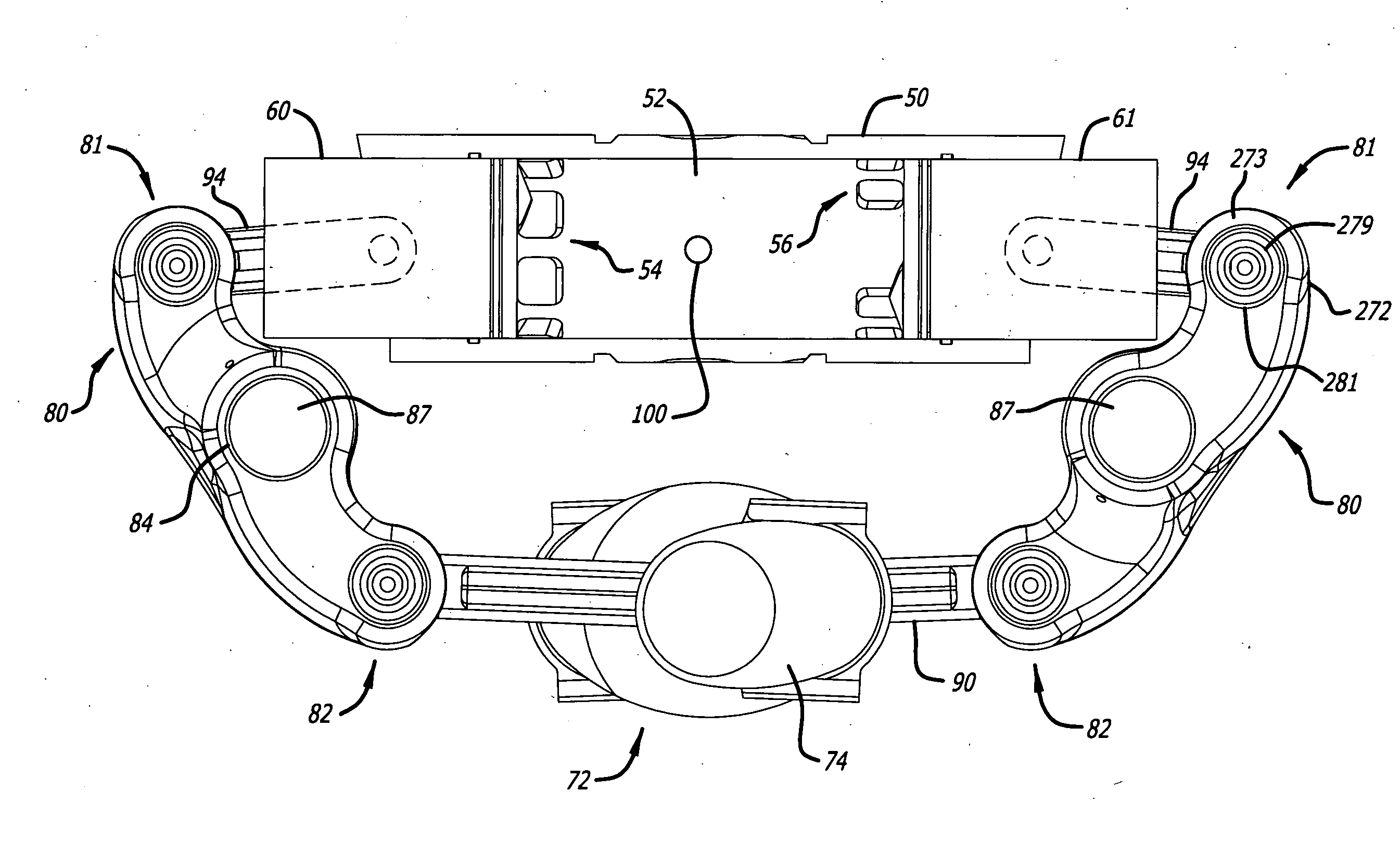
Opposed-piston engine having a single crankshaft coupled to the opposed pistons by linkages with pivoted rocker arms
ActiveUS20120037130A1Alleviates lubricant-blocking effectImprove durability of bearingConnecting rod bearingsInternal combustion piston enginesTop dead centerSwing-piston engine
An opposed-piston engine with a single crankshaft has a rocker-type linkage coupling the crankshaft to the pistons that utilizes a rotatable pivot rocker arm with full-contact plain bearings. A rocker-type linkage utilizes a rotatable pivot bearing with an eccentric aspect to vary translation of piston linkage along the axial direction of a cylinder, which shifts the top dead center (TDC) and bottom dead center (BDC) locations of a piston so as to change the volume of charge air compressed during the power stroke.
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC
Lubrication system of piston ring of internal-combustion engine and upper portion scraper ring of adjacent cylinder sleeve
InactiveCN103174540ASolve problems such as increased wearPiston ringsMachines/enginesCombustorCombustion chamber
The invention discloses a lubrication system of a piston ring of an internal-combustion engine and an upper portion scraper ring of an adjacent cylinder sleeve. The lubrication system comprises a cylinder body of an opposed piston opposed cylinder engine. The cylinder body is provided with an outer piston and an inner piston. At least one piston ring is arranged on the top of the outer piston. The scraper ring is arranged under the piston ring and used for scraping off lubricating oil at the lower portion of the cylinder body, and the scraped lubricating oil is transmitted to the upper portion of the cylinder body. The scraper ring is provided with an oil storage tank used for storing the scraped lubricating oil. When the outer piston and the inner piston reach an upper dead center in an operating cycle, the lubricating oil is left from the oil storage tank under the effect of piston deceleration, and certain amount of the lubricating oil enters the inner surface of the upper portion of the cylinder body. Due to the fact that the piston scraper ring is arranged on the top of the piston, engine oil left on the cylinder wall below an air inlet of a cylinder is collected by the scraper ring and the engine oil is transmitted to the cylinder wall close to a combustor.
Owner:ANHUI ZHONGDING POWER
Centrally located ignition source in a combustion chamber
ActiveUS7448352B2Sparking plugsInternal combustion piston enginesElectrical conductorCombustion chamber
The centrally located ignition source in a combustion chamber is an electrical conductor spanning the general center of the combustion chamber, with a spark gap at the general center of the conductor. The device may be offset from the combustion chamber centerline, and / or the spark gap may be offset from the conductor center, as required. The centrally located ignition source is particularly well suited for use in an opposed piston engine having a rotary sleeve valve mechanism, with the conductor rotating with the sleeve valve and crossing the combustion chamber between the two pistons. An arcuate commutator section may be disposed upon the exterior of the rotary sleeve valve, with a contact finger making electrical contact between the electrical energy source and the commutator section to supply electrical energy to the ignition source. The device is also suitable for use in stationary installations, e.g., gas furnace combustors, etc.
Owner:ENGINUITY POWER SYST INC
Skewed Combustion Chamber For Opposed-Piston Engines
ActiveUS20170030262A1Reduce disadvantagesInternal combustion piston enginesFuel injection apparatusCombustion chamberPiston
A combustion chamber for an opposed-piston engine has a rotationally skewed shape in a longitudinal section that is orthogonal to a chamber centerline, between diametrically-opposed openings of the combustion chamber through which fuel is injected. The rotationally skewed shape interacts with swirl to generate a tumble bulk charge air motion structure that increases turbulence.
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC
Combustion chamber construction for opposed-piston engines
ActiveCN103562515AInternal combustion piston enginesReciprocating piston enginesCombustion chamberTop dead center
An opposed-piston engine includes a ported cylinder and a pair of pistons disposed to reciprocate in the bore of the cylinder. A combustion chamber is defined by opposing shaped piston end surfaces as the pistons approach respective top dead center (TDC) locations in the bore. At the end of scavenging, the shaped end surfaces of the pistons interact with swirl to produce turbulence in the charge air motion in the combustion chamber; the additional bulk motions include tumble. Fuel is injected into the turbulent charge air motion along a major axis, of the combustion chamber.
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC
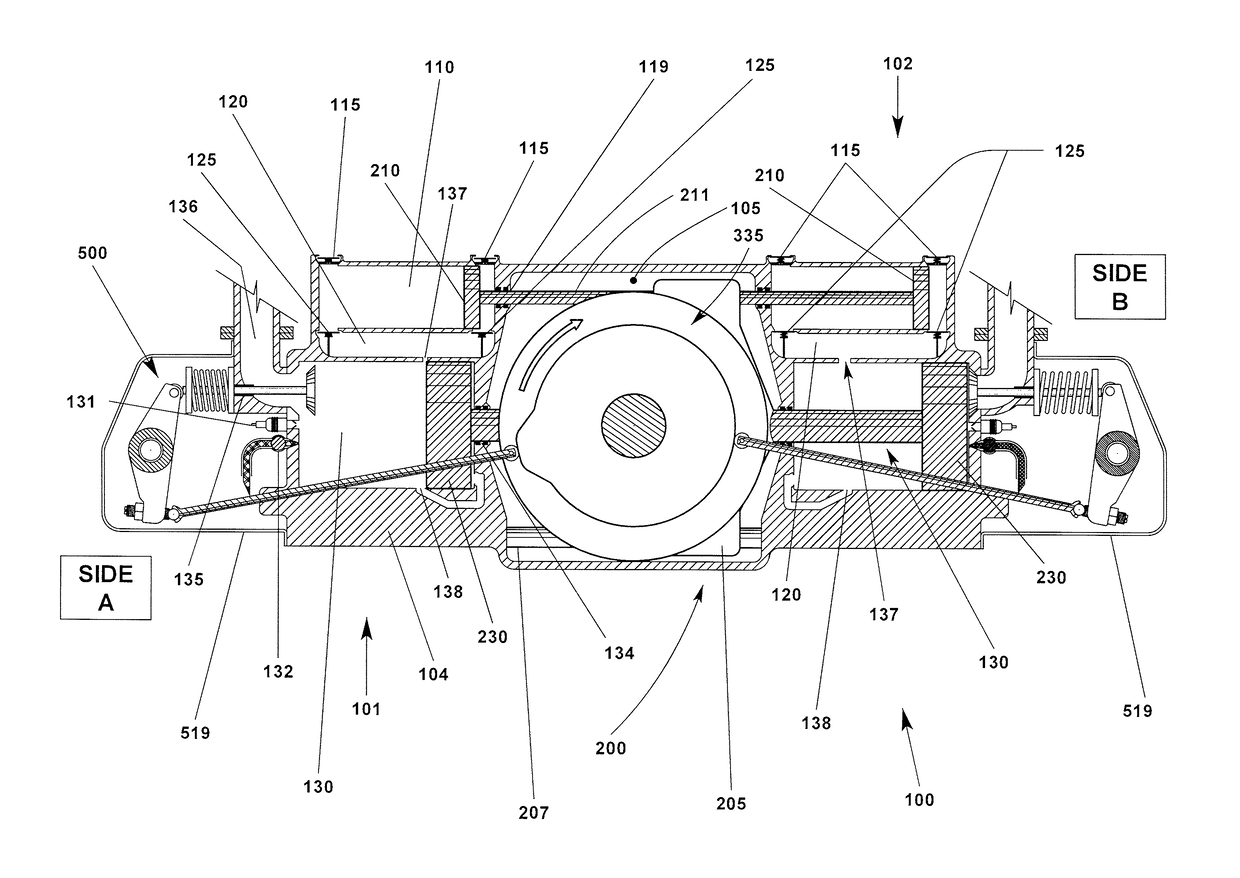
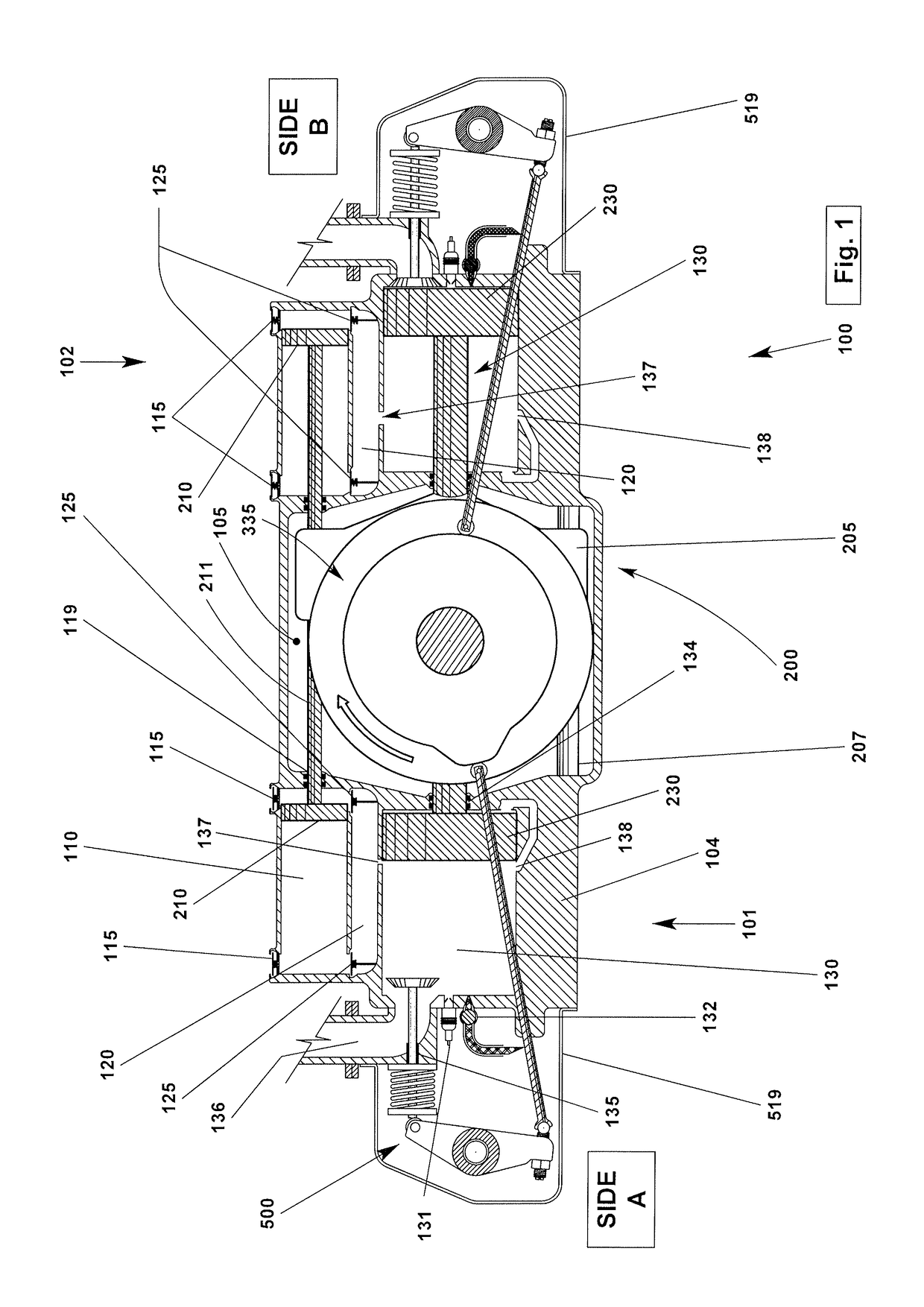
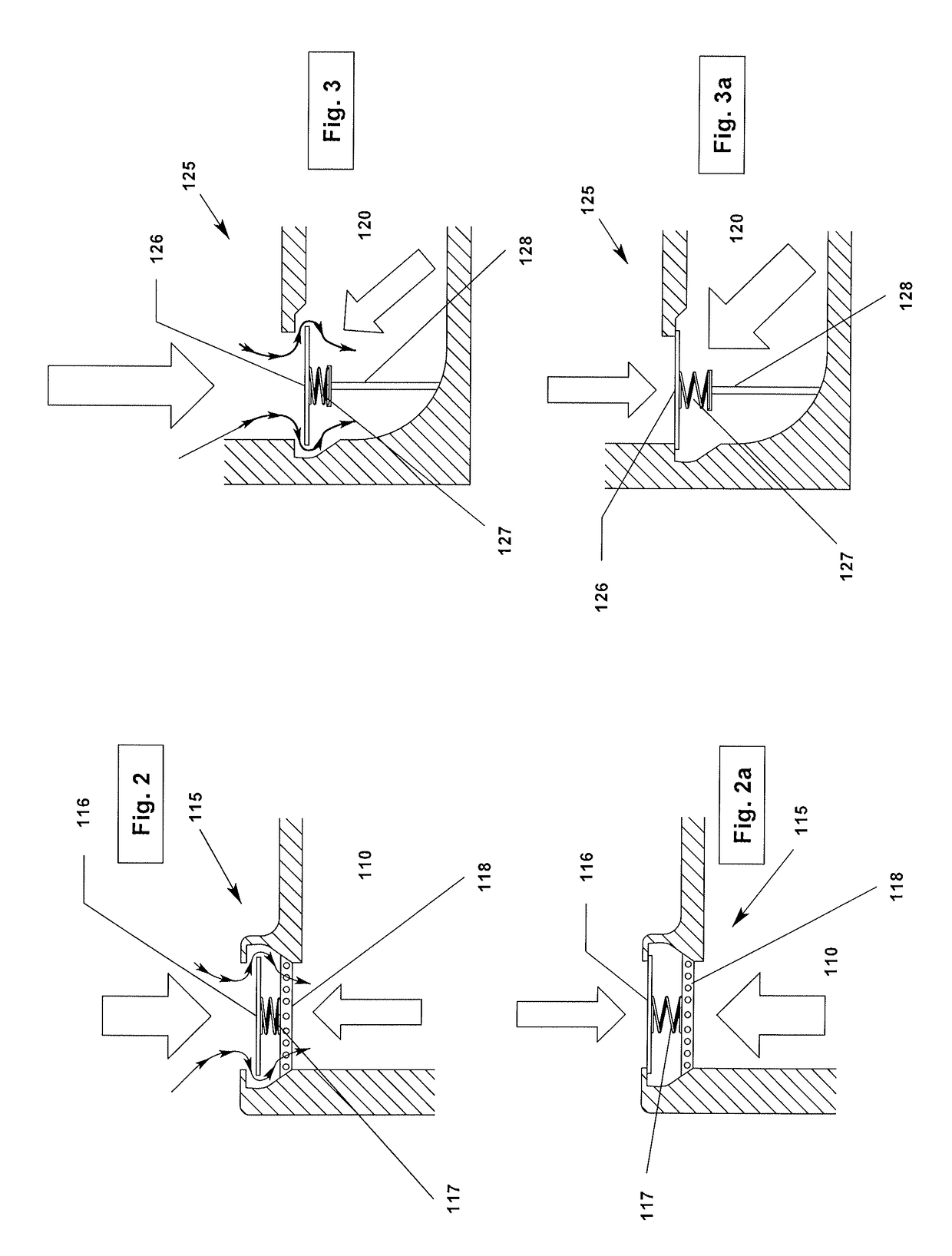
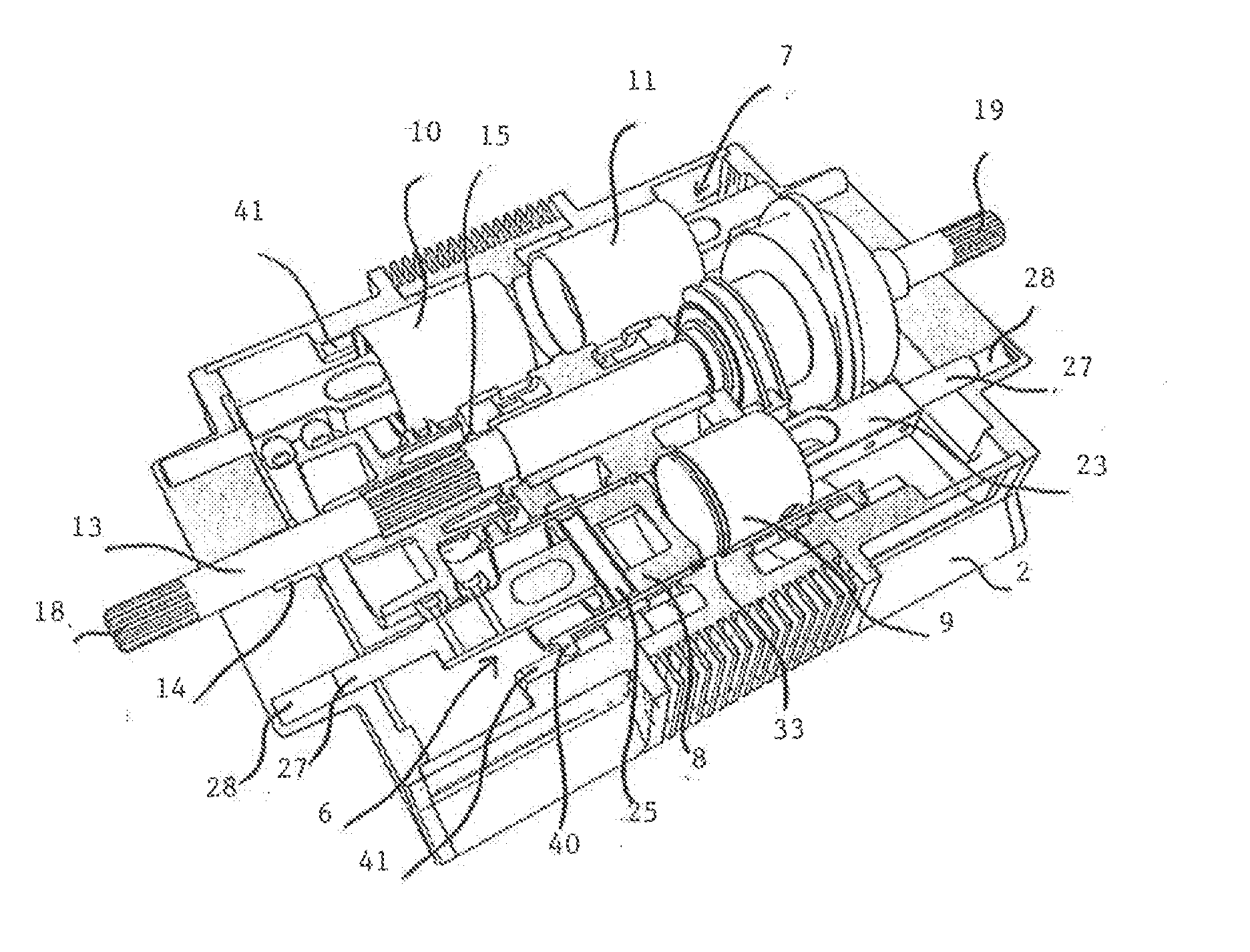
Opposed piston engine
A two-cycle, opposed piston engine with side-mounted crankshafts and cylinders isolated from mechanical stresses of the engine includes tailored cooling of cylinders and symmetrical cooling of the interior surfaces of piston crowns. Each opposed piston includes a compliant member that permits movement of an axially-centered rod mounted in the piston in order to maintain axial alignment with the bore of a cylinder in which the piston is disposed during engine operation. A single wristpin is disposed externally of the piston to connect the piston with connecting rods that run between the piston and the crankshafts.
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC
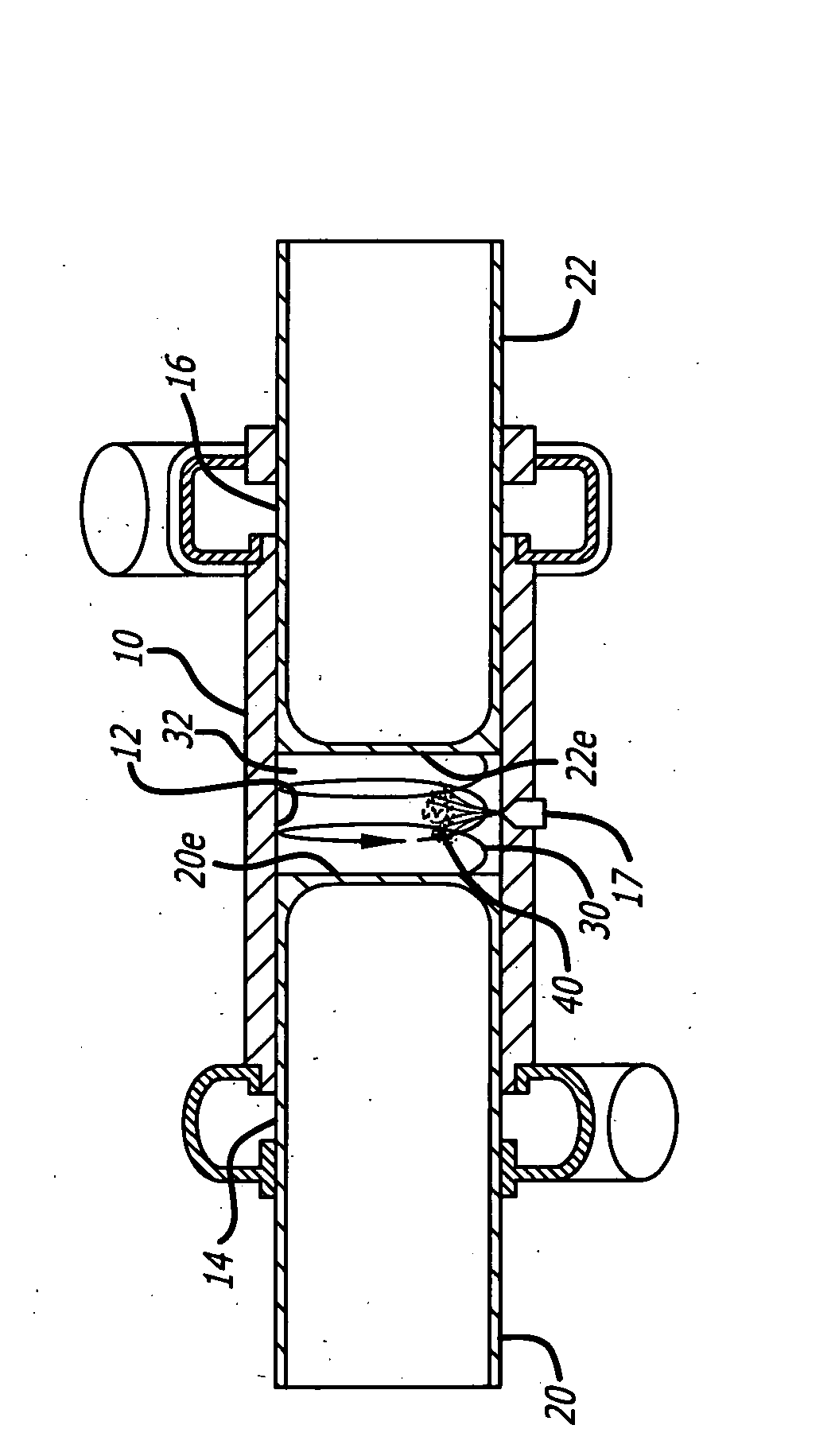
Opposed piston internal combustion engine with inviscid layer sealing
InactiveUS20140318518A1Accurate concentricityWell mixedCombustion enginesReciprocating piston enginesCombustionDetonation
An opposed-piston engine that forms an inviscid layer between pistons and the respective cylinder walls. In an aspect, the opposed-piston engine utilizes a Scotch yoke assembly that includes rigidly connected opposed combustion pistons. In an aspect, the Scotch yoke assembly is configured to transfer power from the combustion pistons to a crankshaft assembly. In an aspect, the crankshaft assembly can be configured to have dual flywheels that are internal to the engine, and can be configured to assist with an exhaust system, a detonation system, and / or a lubrication system.
Owner:PRIME GRP ALLIANCE
Valve system for opposed piston engines
The valve system for opposed piston engines essentially comprises a single poppet valve opening into the common combustion chamber between the two opposed pistons of each piston and cylinder pair. The engine for which the mechanism is adapted includes a rotating internal cylinder surrounding each piston pair, with a stationary outer cylinder or case surrounding the rotating cylinder. The valve is pivotally attached at one side or end thereof to the edge of the valve port of the rotating cylinder, and is actuated by an arm or arms having guides (rollers, etc.) at the distal end(s) thereof, which are captured in corresponding cam track(s) or channel(s) formed in the fixed outer cylinder or case of the engine. The cam track has a variable radius, with the valve arm(s) and guide(s) alternately lifting and lowering as the guide(s) travel(s) in the variable radius cam track(s), thereby closing and opening the valve.
Owner:ENGINUITY POWER SYST INC
Pneumatic opposed-piston engine
InactiveCN102852640ASimple structureImprove efficiencyCombustion enginesInternal combustion engineGas supply
The invention discloses a pneumatic opposed-piston engine which comprises internal combustion cylinders, pneumatic cylinders and a crankshaft, wherein two internal combustion pistons are arranged in one internal combustion cylinder in an opposed mode, pneumatic pistons are arranged in one pneumatic cylinder and connected with the internal combustion pistons, one internal combustion piston in the internal combustion cylinder is rotatablely connected with a rod journal of the crankshaft through a connecting rod, the other internal combustion piston is rotatablely connected with another rod journal of the crankshaft through another connecting rod, a phase difference exists between the two rod journals, a compressed gas inlet of the pneumatic cylinder is communicated with a gas inlet channel of an internal combustion engine of the internal combustion cylinder, and the displacement of one pneumatic cylinder or the displacement sum of all the pneumatic cylinders is greater than the displacement sum of all the internal combustion cylinders. The pneumatic opposed-piston engine disclosed by the invention is simple in structure and high in efficiency.
Owner:ZEROQ SCI & TECH
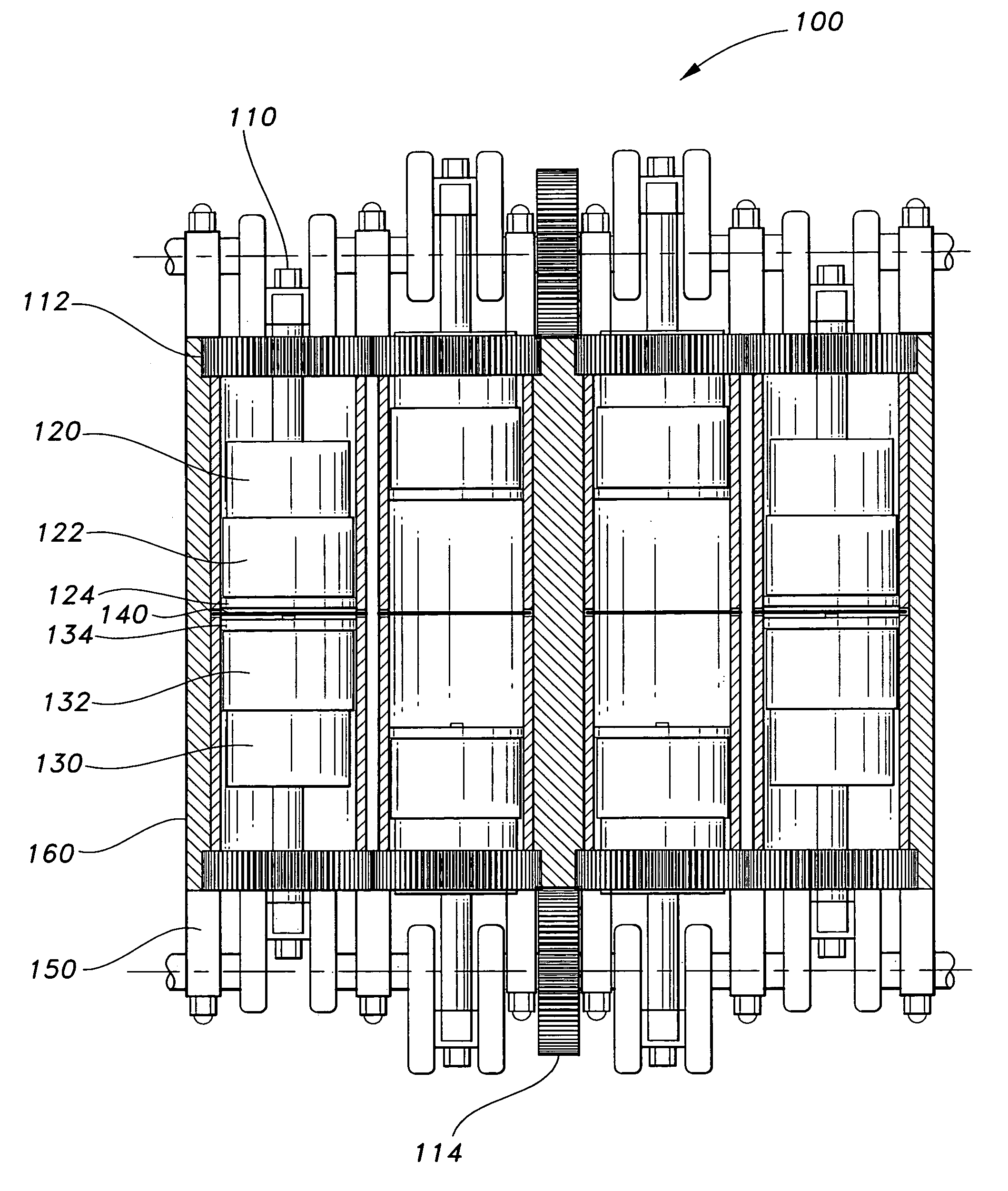
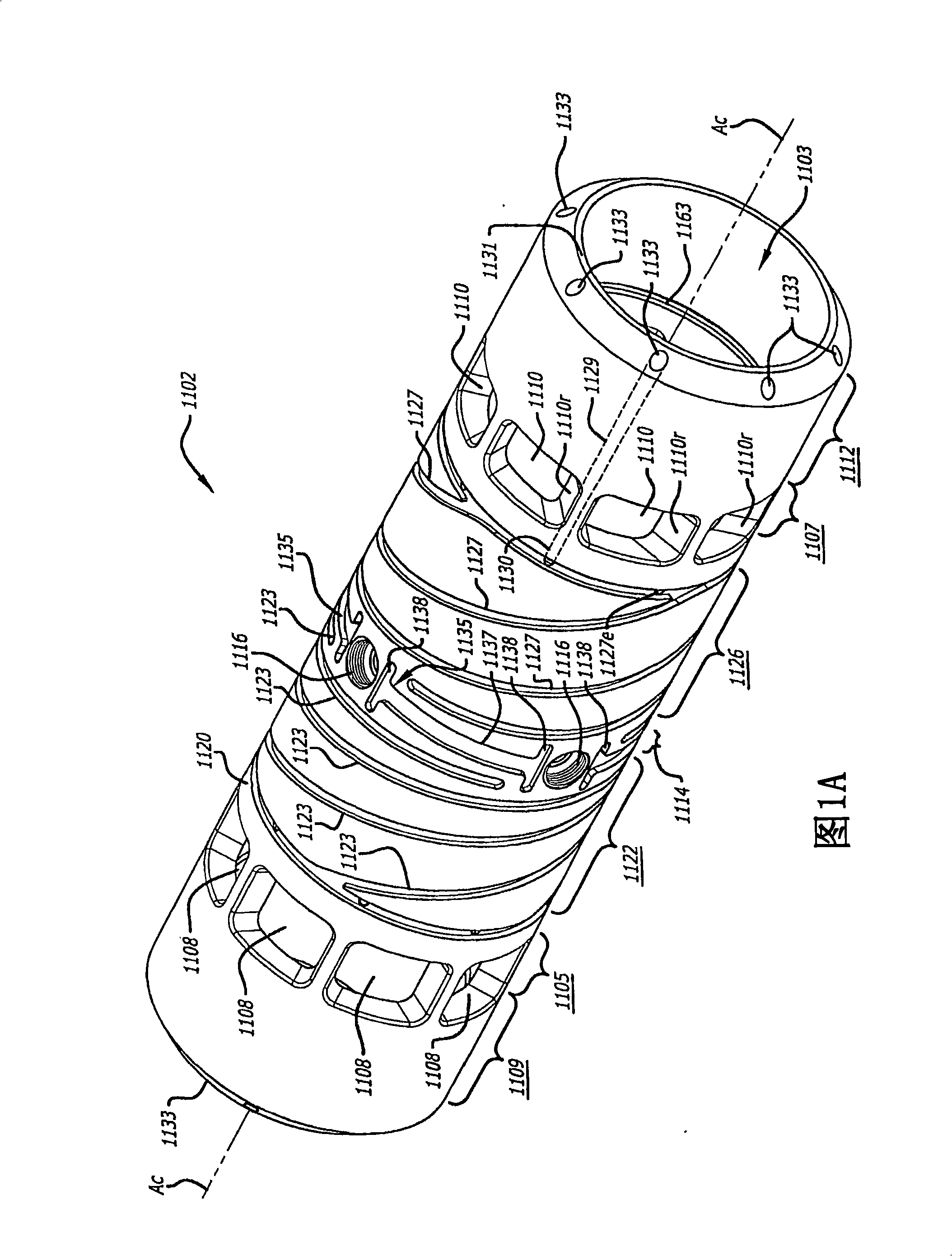
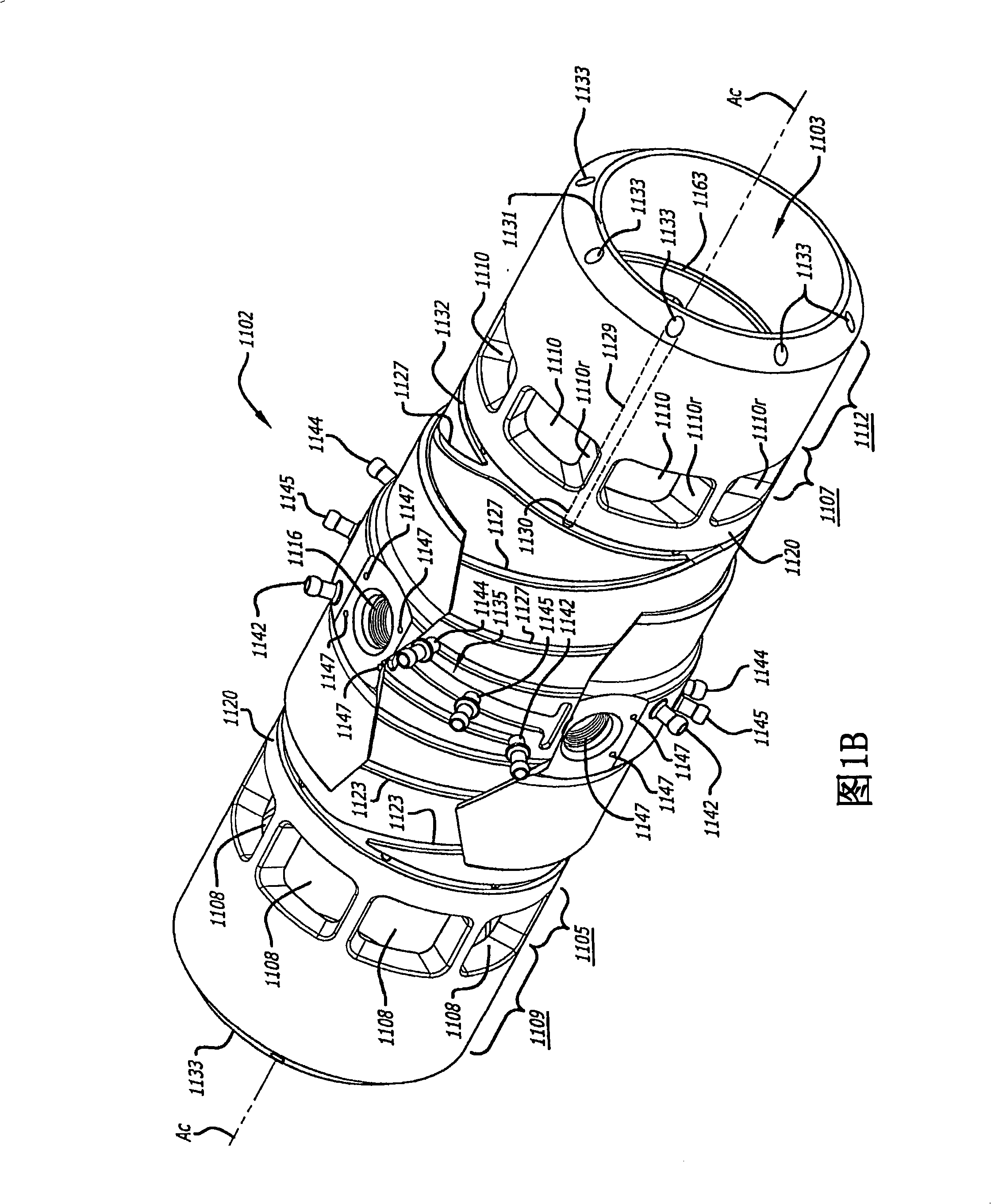
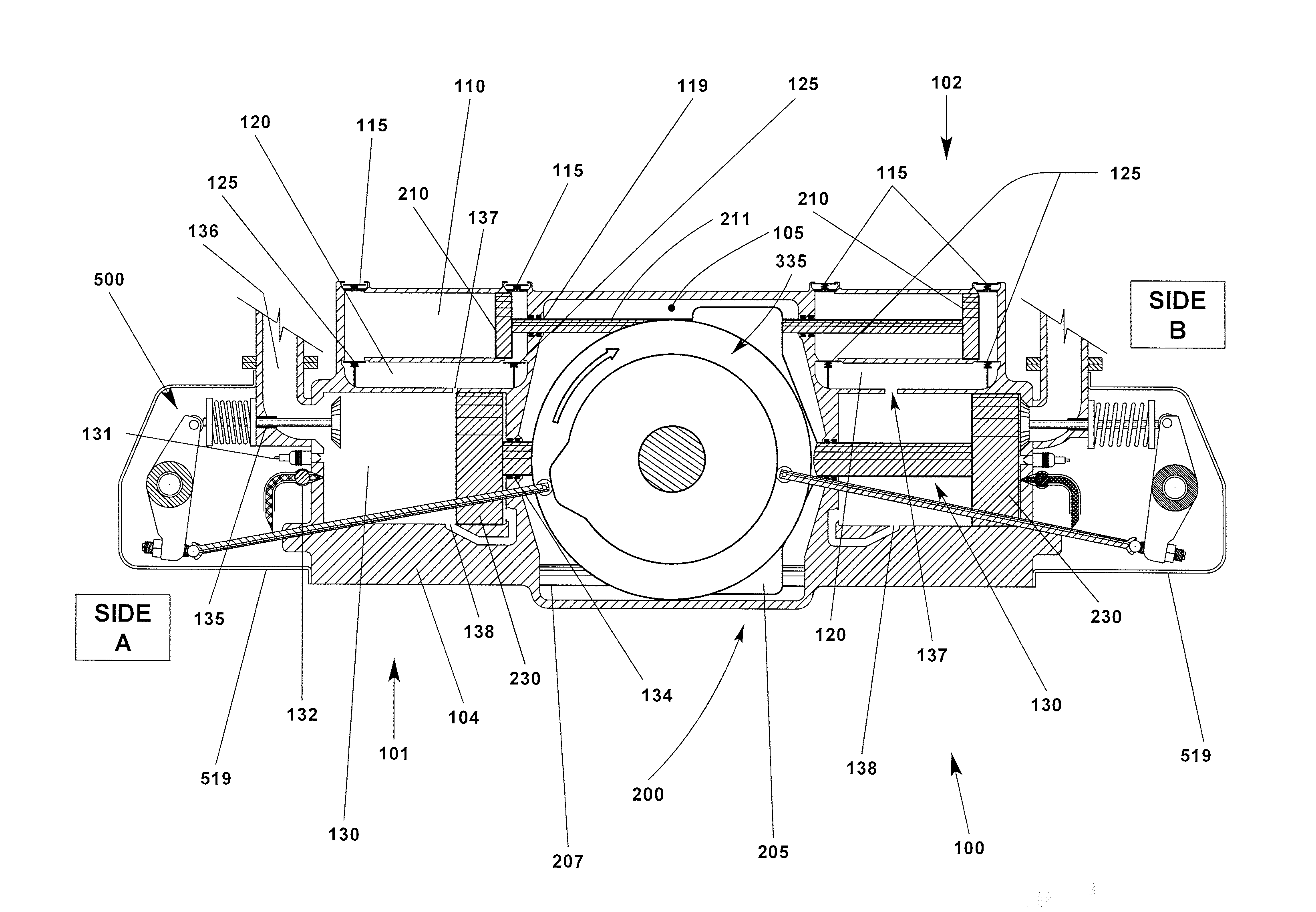
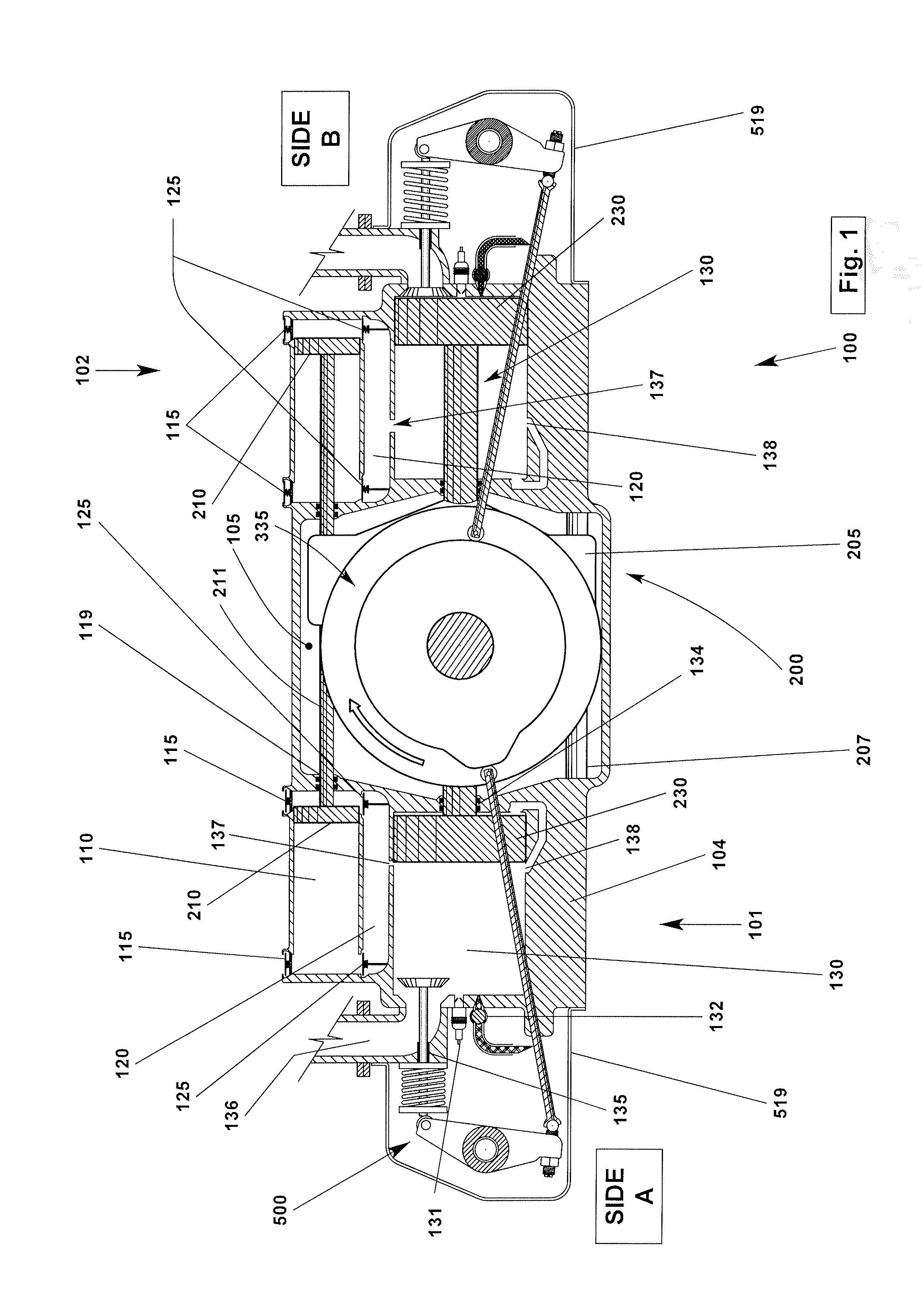
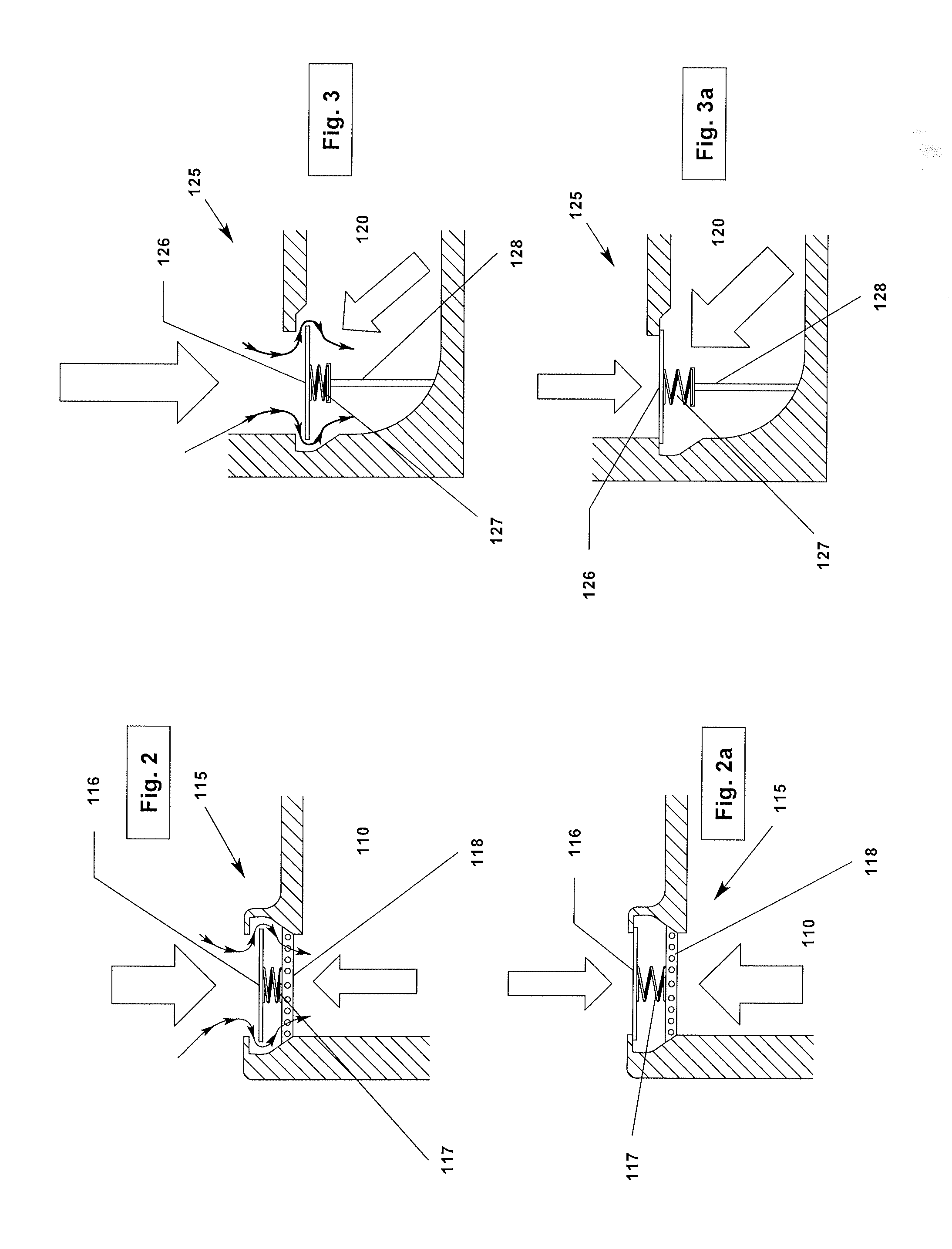
Cylinder For Opposed-Piston Engines
ActiveUS20160356241A1Network can be so complexEasy to manufactureLiquid coolingCylinder headsCombustion chamberEngineering
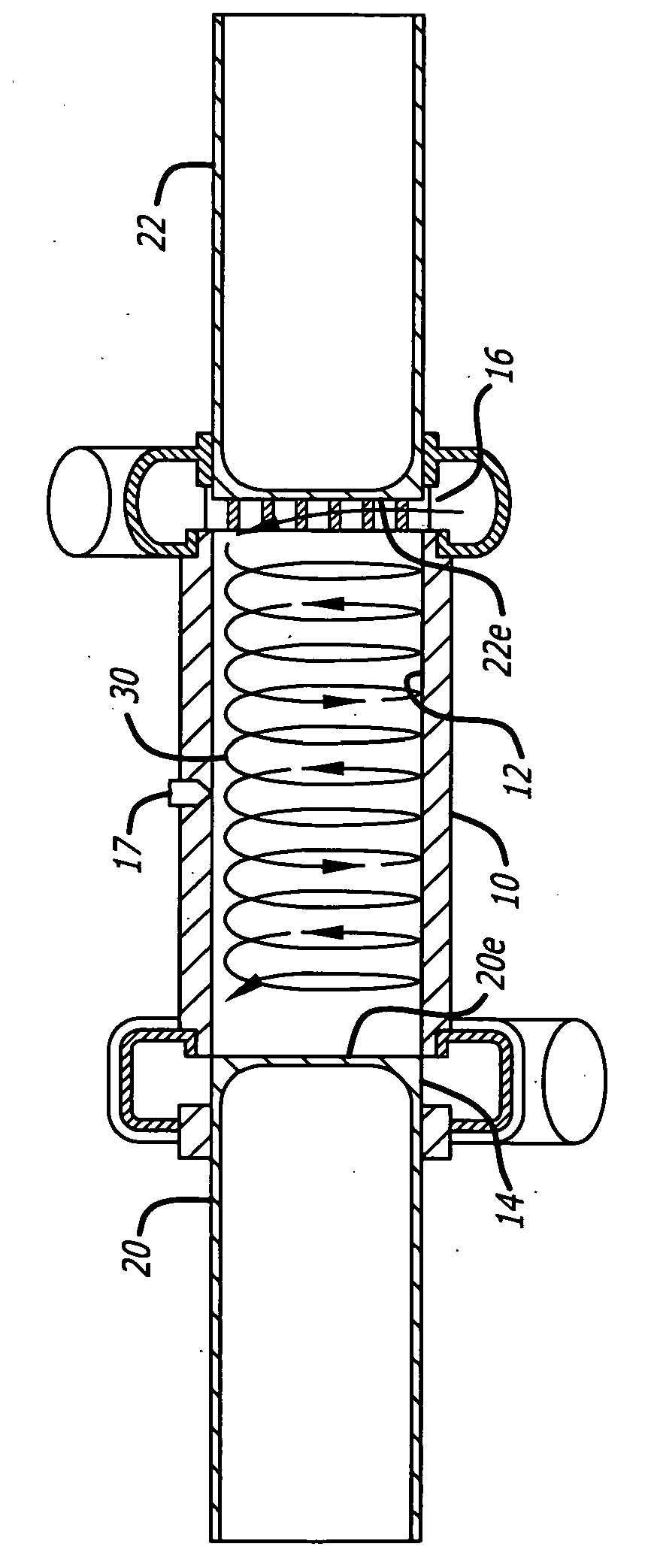
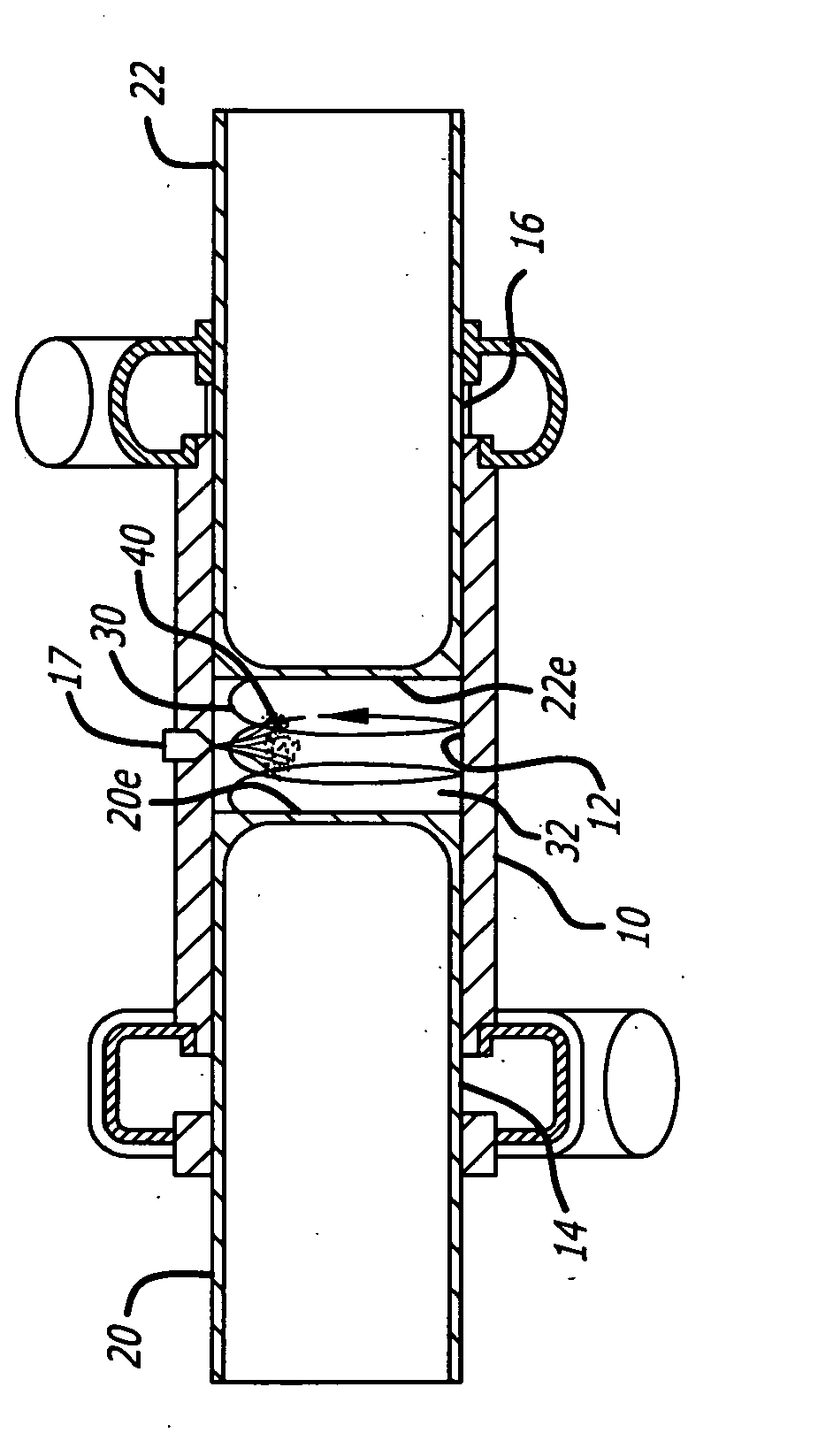
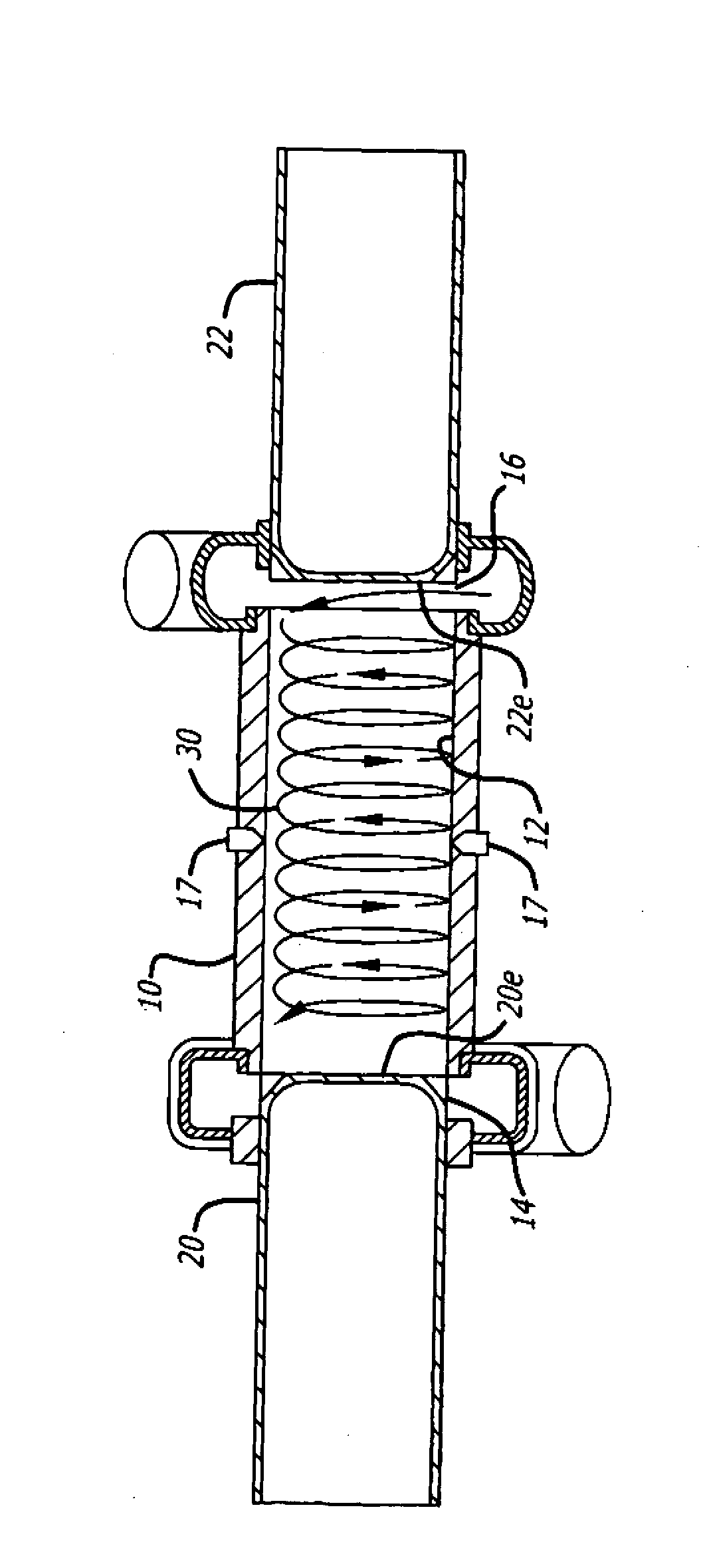
A cylinder for opposed-piston engines includes a liner with a bore and longitudinally displaced intake and exhaust ports near respective ends thereof. An intermediate portion of the liner between the exhaust and intake ports contains a combustion chamber formed when the end surfaces of a pair of pistons disposed in opposition in the bore are in close mutual proximity. A compression sleeve encircles and reinforces the intermediate portion of the liner. An annular grid of pegs disposed between the intermediate portion and the compression sleeve supports the compression sleeve against the liner and defines a turbulent liquid flow path extending across the intermediate portion in a direction that parallels the longitudinal axis of the liner.
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com