Method for detecting soil microbial biomass nitrogen
A technology of soil microorganisms and biomass, which is applied in the direction of biological testing, chemical analysis by titration, material inspection products, etc., can solve the problems of exacerbating the difficulty of transferring products, the inadvisability of chromium and potassium sulfate, and the existence of losses. The effect of continuous development, good accuracy and easy cleaning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
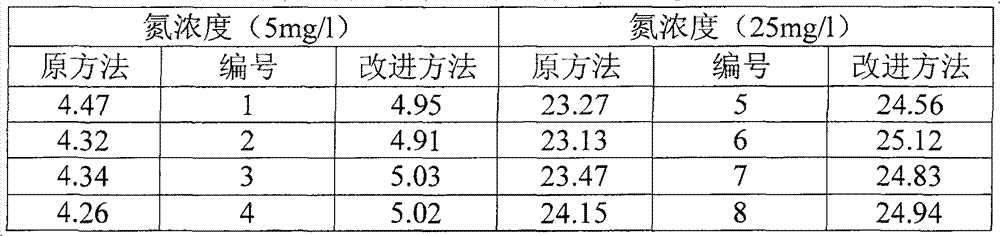
[0032] The nitrogen content in the standard solution of acetanilide was determined by comparing the original method and the improved method.
[0033] With reference to Document 4, the nitrogen content in the imported acetanilide standard solution was determined using the improved method of the present invention. Add 5.0ml of extract solution once in the digestion tube, mix accelerator 3g (accelerator mass composition is K 2 SO 4 : CuSO 4 : Se=90:9:1), and 8ml of concentrated sulfuric acid, shake well; the solution is heated to 340°C by means of gradient temperature rise, constant temperature, after 3h, cool; the solution in the digestion tube is poured into the distillation flask , Wash the digestion tube 2-3 times with distilled water, add NaOH solution for distillation at the same time, receive boric acid, and titrate with standard hydrochloric acid solution.
[0034] The specific process is as follows:
[0035] 1) Preparation of acetanilide standard solution: Take 1.929...
Embodiment 2
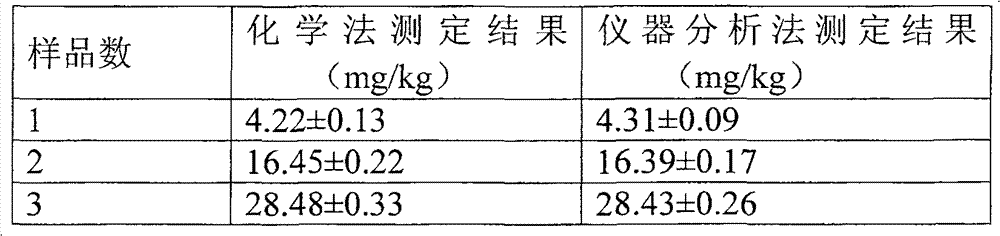
[0062] Determination of microbial biomass nitrogen in soil using a modified method.
[0063] The specific implementation process:
[0064] The test steps are:
[0065] 1) Fumigation-extraction: Take 30g of fresh soil (equivalent to about 25g of dry soil) in a small beaker, put it into a vacuum desiccator with 30ml of chloroform (with zeolite), 30ml of NaOH and wet filter paper, and airtightly pump to Chloroform boiling 3min, close the valve. Cultivate in the dark at 25°C for 24 hours, open the desiccator to check for air leakage, if there is no air leakage, take out the chloroform and NaOH, and repeatedly pump air with a vacuum pump until the soil does not smell the smell of chloroform. In addition, no fumigation was used as a control. Shake the fumigated and non-fumigated soil samples with 100ml potassium sulfate solution for 30min, and filter;
[0066] 2) Determination: Add 5.0ml of extract solution successively in the digestion tube, mix accelerator (mass ratio is K 2 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com