Electro-rheological fluid brake and actuator devices and orthotic devices using the same
An electro-rheological fluid and braking device technology, applied in the fields of portable orthoses, cam pivots, and electro-rheological fluid actuators, can solve the problems of increasing overall size, cost and weight, bulky devices, hindering applications, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
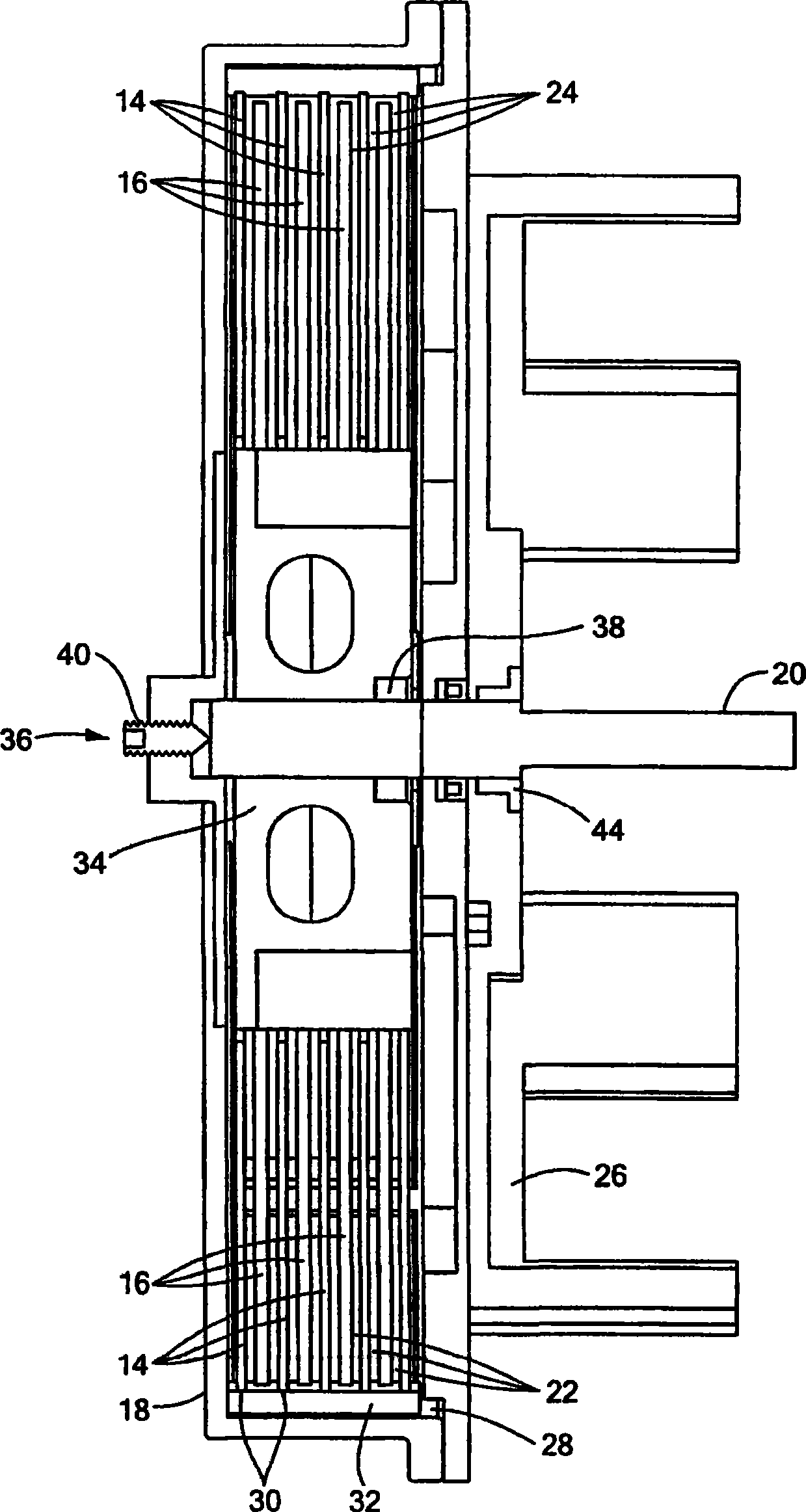
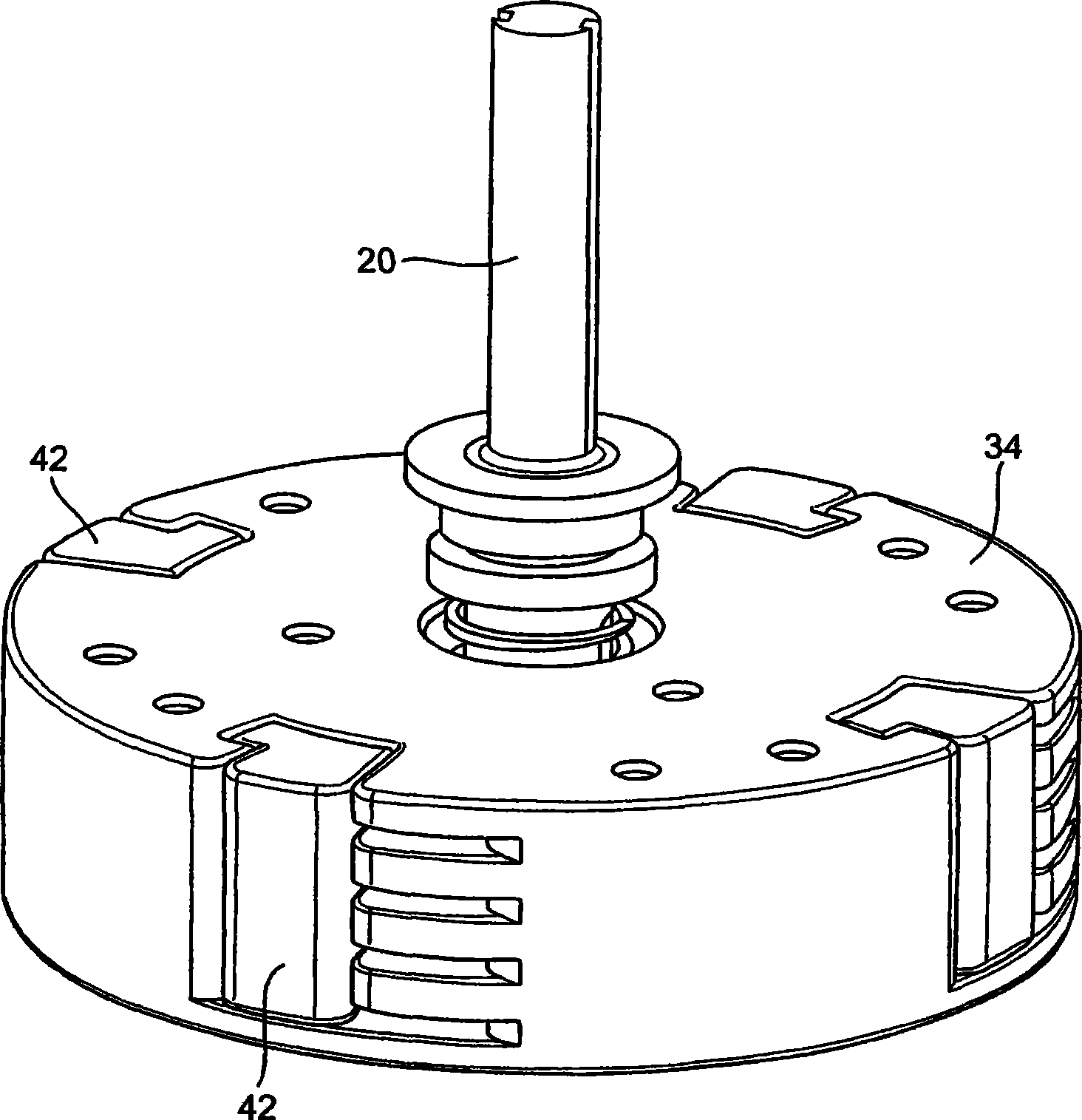
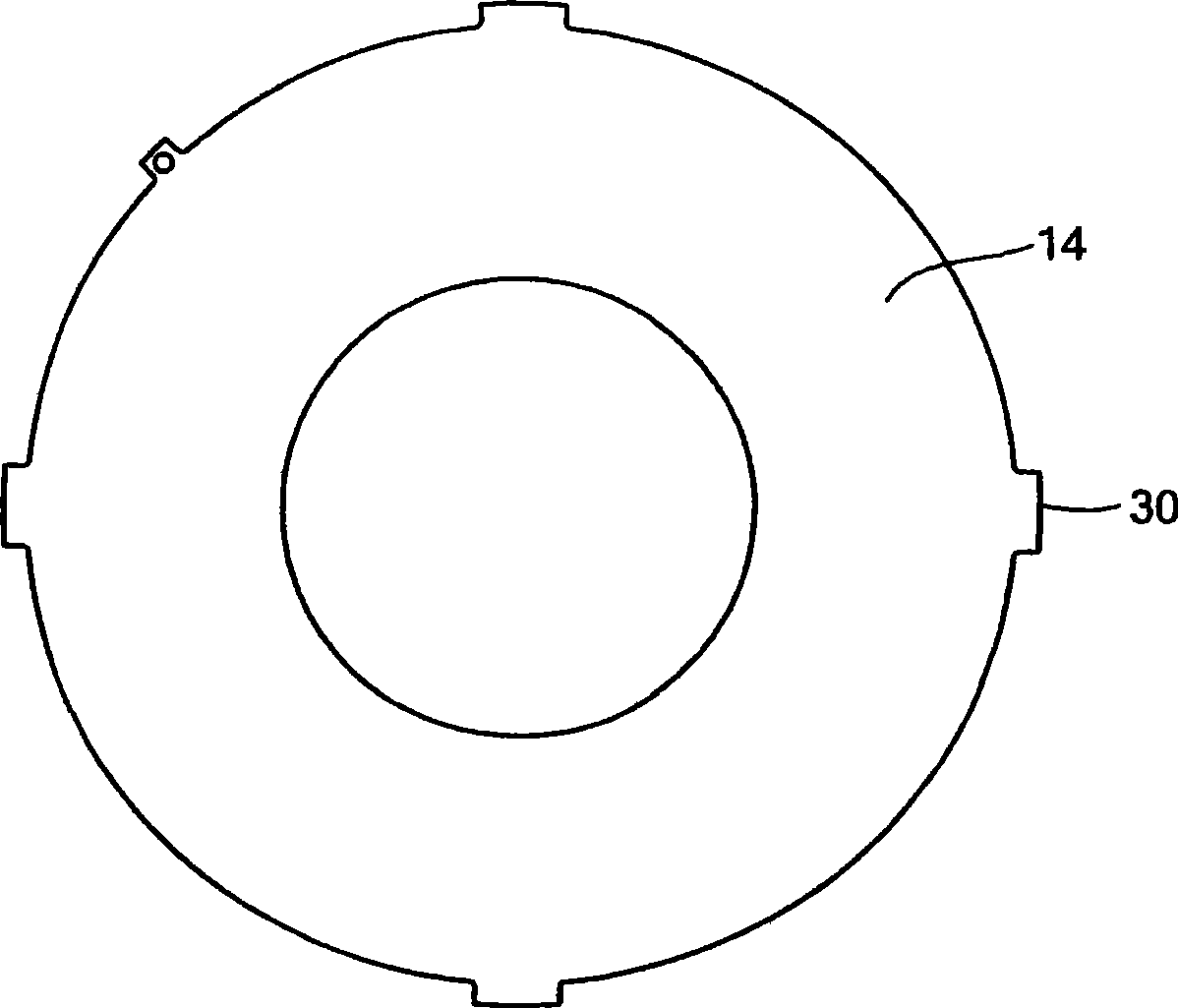
[0049] In the presence of an electric field, electrorheological fluids undergo changes in rheological properties such as viscosity. Such fluids are produced using a suspension of particles with a size of about 0.01 to 0.1 [mu]m in an insulating base fluid such as oil. The volume ratio of particles is usually between 20% and 60%. The electrorheological effect (sometimes called the Winslow effect) is thought to arise from the difference in dielectric constant between the fluid and the particles in electrorheological fluids (ERFs). In the presence of an electric field, the particles form chains along the field lines due to the induced dipole moments. The sensing structure changes the viscosity, yield stress, and other properties of the ERF, allowing the consistency of the ERF to change from a liquid to a viscoelastic-like consistency such as a gel within a millisecond response time. ERFs can exert very high electrically controlled resistance while being small in size (weight an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com