Application of rapamycin in preparing medicines for treating addiction to morphine-like drugs
A technology of rapamycin and drugs, applied in the field of rapamycin in the preparation of drugs for the treatment of morphine drug addiction, can solve the problem of not finding rapamycin, etc., and achieve good results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1 Method for establishing a rat model of morphine addiction
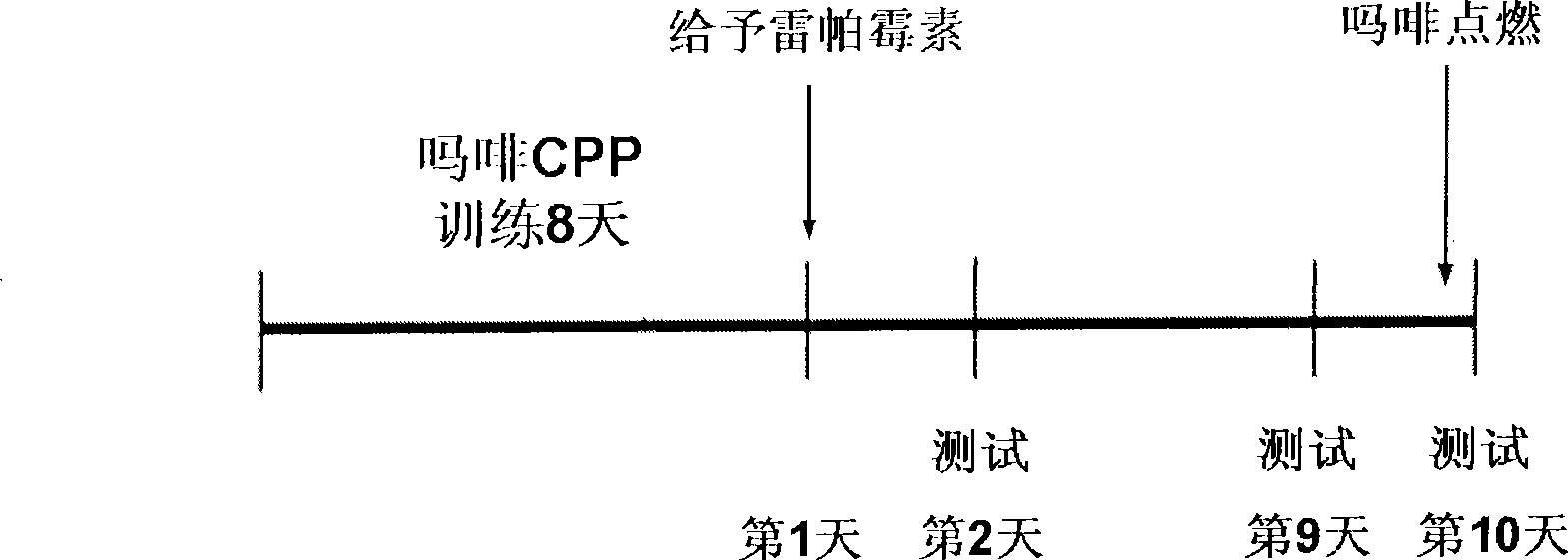
[0023] The present invention adopts conditioned place preference (CPP for short) training mode to establish a rat morphine addiction model. The relevant description is as follows:
[0024] The conditioned position preference training and testing instrument is a conditioned position preference box composed of three boxes (developed by the Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences): two side chambers (L×W×H: 27.9cm×21cm×20.9cm) and one The middle room (L×W×H: 12.1cm×21cm×20.9cm). The three rooms are separated by movable partitions, and the floors are similar.
[0025] Basic value test: This experiment uses an unbiased design. On the first day, Sprague-Dawley (SD) male rats (purchased from Beijing Weitong Lihua Laboratory Animal Technology Co., Ltd., license number: SCXK (Beijing) 2002-2003, weight 200-220g) were put into the middle room, Allow him to move freely in the three rooms for...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2: Intraventricular administration of rapamycin to inhibit morphine addiction behavior in rats
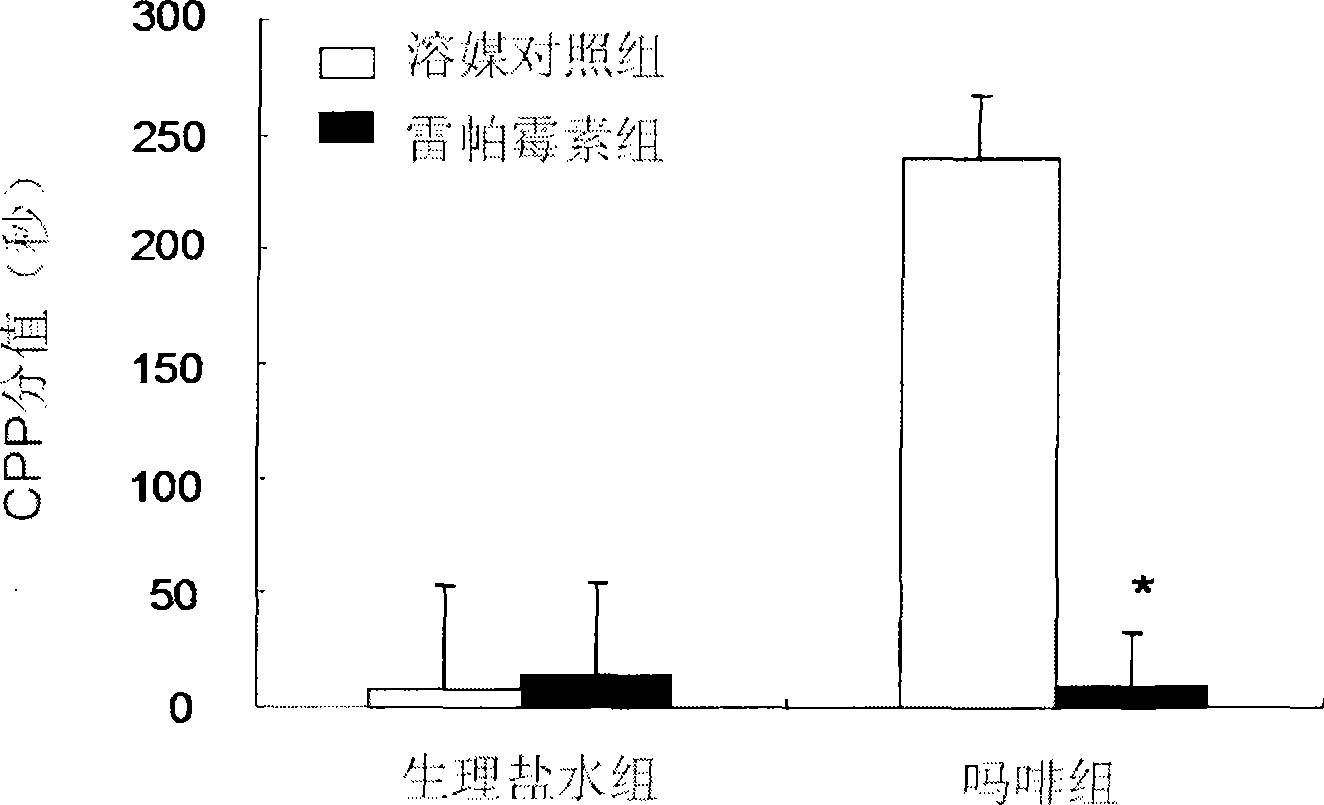
[0030] Forty male SD rats (purchased from Beijing Weitong Lihua Laboratory Animal Technology Co., Ltd.) were randomly divided into two groups, and the conditional positions of physiological saline (1ml / kg, ip) or morphine (10mg / kg, ip) were carried out respectively. Preference training (the method is the same as in Example 1), 60 minutes before each training, each group (20 animals / group) is divided into 2 groups (10 animals / group), respectively, given intraventricular injection of 300μg of rapamycin or solvent DMSO, and observe The formation of CPP. The specific groups are as follows: (1) Normal saline + vehicle control group: Normal saline for CPP training, intraventricular injection of solvent DMSO (n=10) 60 minutes before training; (2) Normal saline + rapamycin group: Normal saline for training For CPP training, 300μg of rapamycin (n=10) was given to the ventricle 60...
Embodiment 3
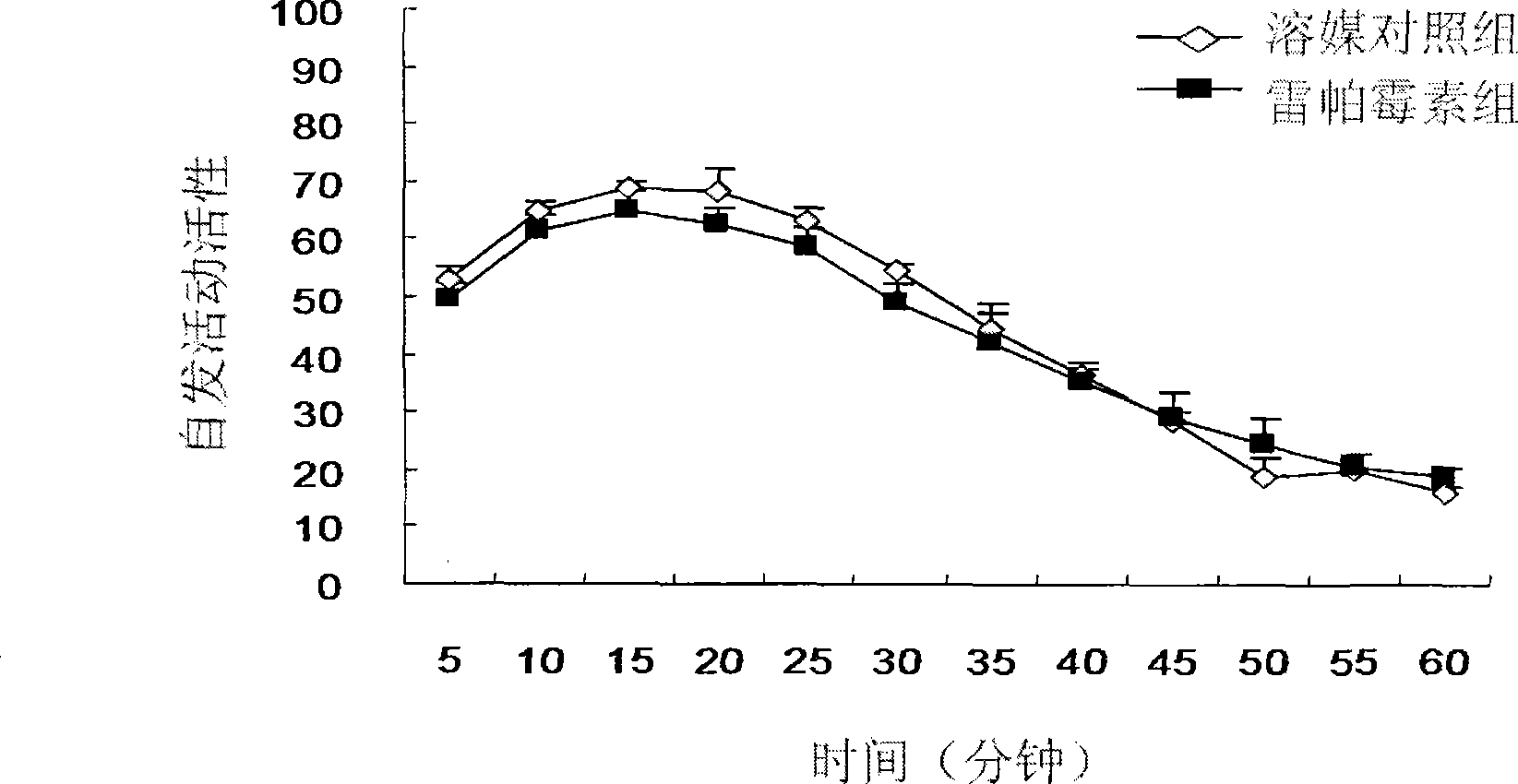
[0032] Example 3: Test of the effect of intracerebroventricular administration of rapamycin on spontaneous activity in rats
[0033] Sixteen rats were randomly divided into two groups, each with 8 rats. One group was injected with 300μg rapamycin into the ventricle, and the other group was injected with DMSO as a solvent. One hour later, they were placed in an autonomous activity test box (purchased from Shanghai Jiliang Software). Technology Co., Ltd.), a computer program automatically observes and records the total number of activities of the rats, which is recorded every 5 minutes for a total of 60 minutes.
[0034] Result (see figure 2 ) After intracerebroventricular injection of rapamycin or solvent DMSO, the spontaneous activity of rats gradually decreased over time (F (11,191) =74.576, p(1,191) =1.785, p>0.05), there is no interaction between the drug and time (F (11,191) =0.656, p>0.05). It shows that rapamycin does not affect the spontaneous activities of rats.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com