Constant-current constant-voltage circuit
A technology of constant current, constant voltage and voltage stabilizing circuit, which is applied in the direction of electric light source, electrical components, adjusting electric variables, etc. It can solve the problem that the channel current cannot be cut off, and achieve the effect of saving power consumption, high efficiency, and reducing circuit components
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
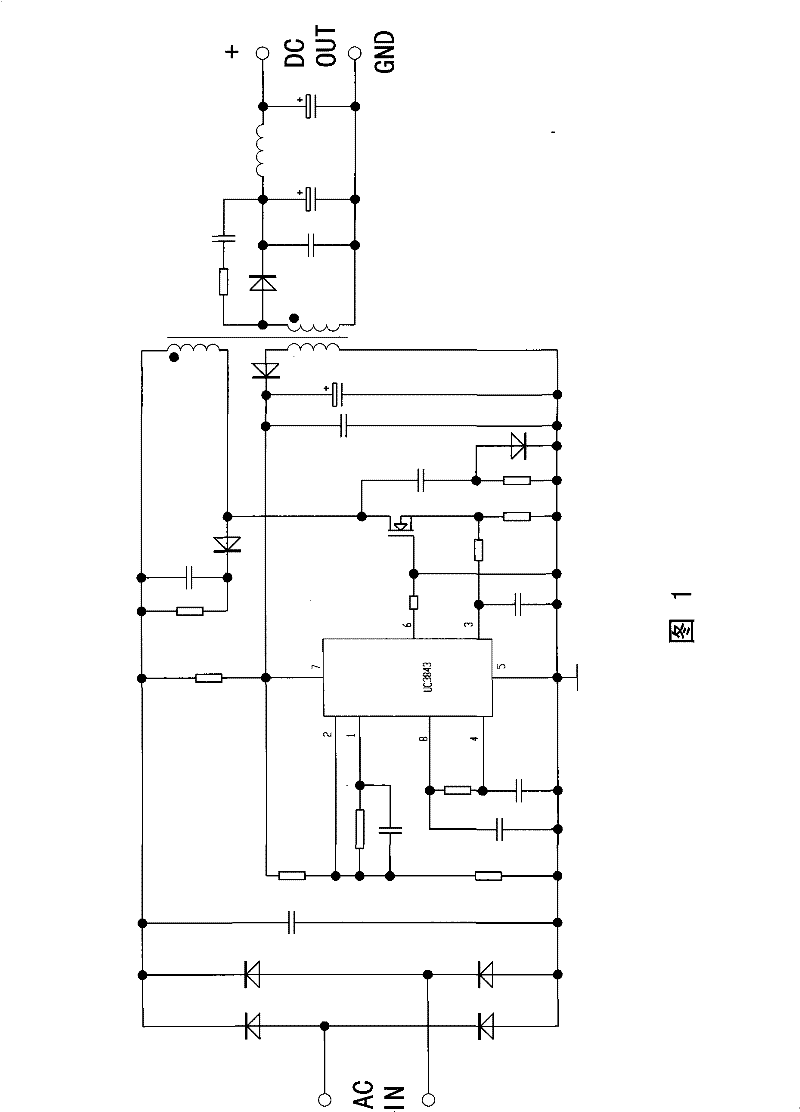
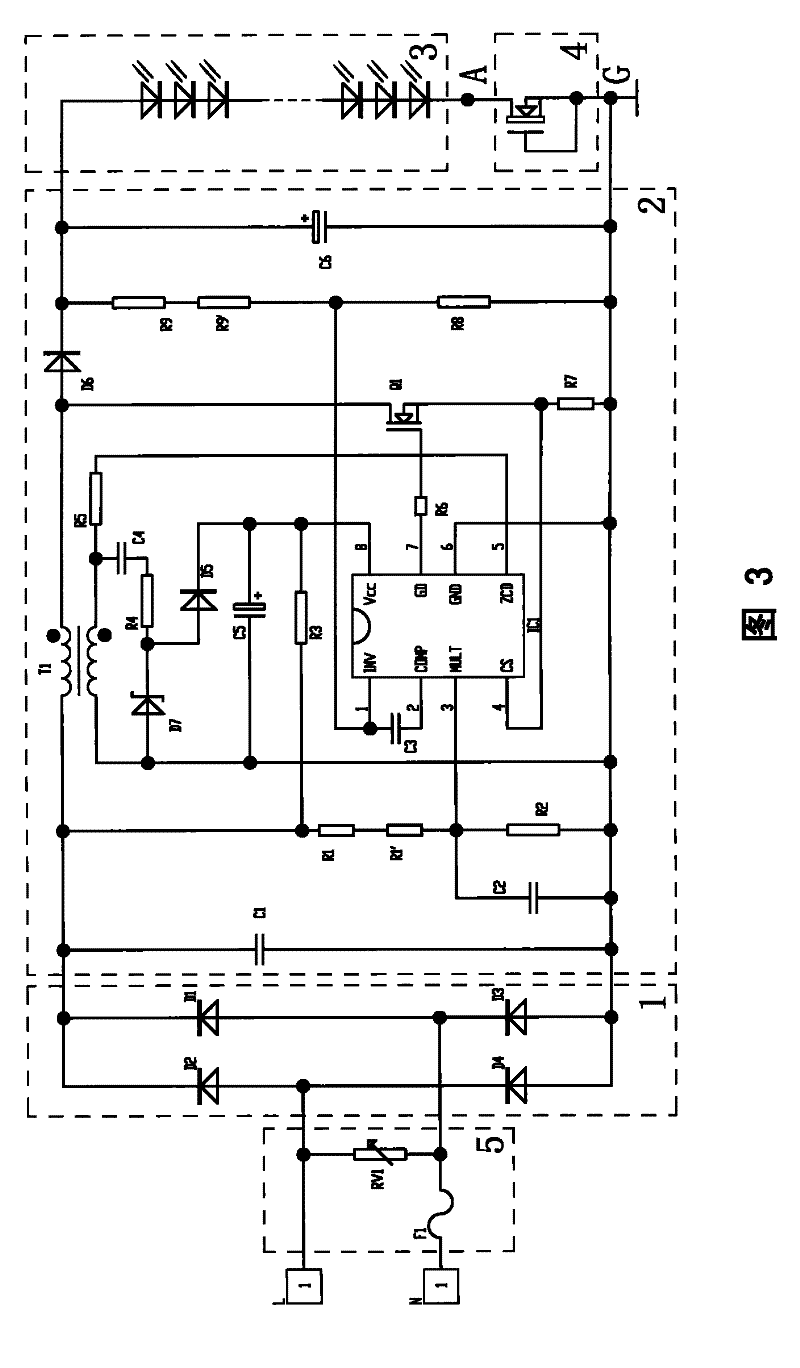
[0022] Such as image 3 As shown, the constant current and constant voltage circuit of this embodiment includes a rectification circuit 1, a voltage stabilization circuit 2, a load 3, a constant current source device 4, and a short circuit protection circuit 5. The output of the output terminal of the circuit 2 becomes constant-voltage direct current and then flows through the load 3. The rectifier circuit 1 adopts a bridge rectifier circuit composed of four rectifier diodes D1, D2, D3, and D4. The short-circuit protection circuit 5 includes a fuse F1 and a varistor RV1 for overcurrent and short circuit protection, connected between the input terminal of the AC power supply and the rectifier circuit 1, the voltage stabilizing circuit 2 is a switching power supply, and the constant current source device 4 is a depletion type field effect transistor, the drain of the depletion type field effect transistor is a contact, the source and the gate of the depletion type field effect t...
Embodiment 2
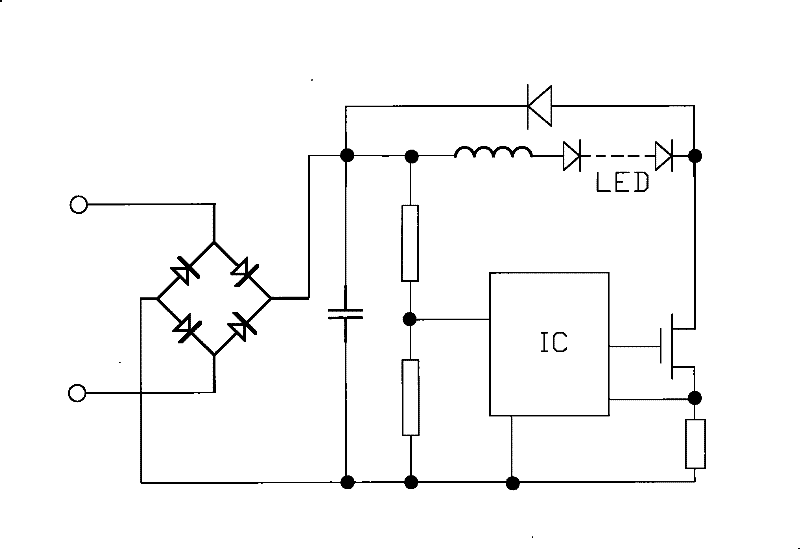
[0032] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the load 3 of this embodiment includes four groups of several LEDs connected in series, and each group of LEDs is connected in series with one of the constant current source devices 4, The four groups connected in series are connected in parallel between the output terminal of the voltage stabilizing circuit 2 and the ground terminal G to form a loop, so there are four constant current source devices 4 in this embodiment. In this embodiment, the method for calculating the number of LEDs connected in series in each group is the same as that in Embodiment 1.
[0033] The remaining features of this embodiment are the same as those of Embodiment 1.
Embodiment 3
[0035] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that: the load 3 of this embodiment includes four groups of several LEDs connected in series, each group of LEDs is connected in parallel and then connected with one of the constant current source devices 4. connected in series and in parallel between the output end of the voltage stabilizing circuit 2 and the ground end G to form a loop. That is, there is only one constant current source device 4 in this embodiment.
[0036] The remaining features of this embodiment are the same as those of Embodiment 1.
[0037] Of course, the load 3 of the present invention can also be other loads such as DC powered electronic circuits or DC motors or high-resistance electrothermal loads. When using these loads, the constant current and constant voltage circuit of the present invention also has the advantages of the above-mentioned embodiments advantage.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com