Encoding method, encoder, and transmitter
A coding method and coding technology, applied in coding, coding components, code conversion, etc., can solve problems such as parallel processing difficulties, difficult coding calculation speed, etc., and achieve the effect of improving coding speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
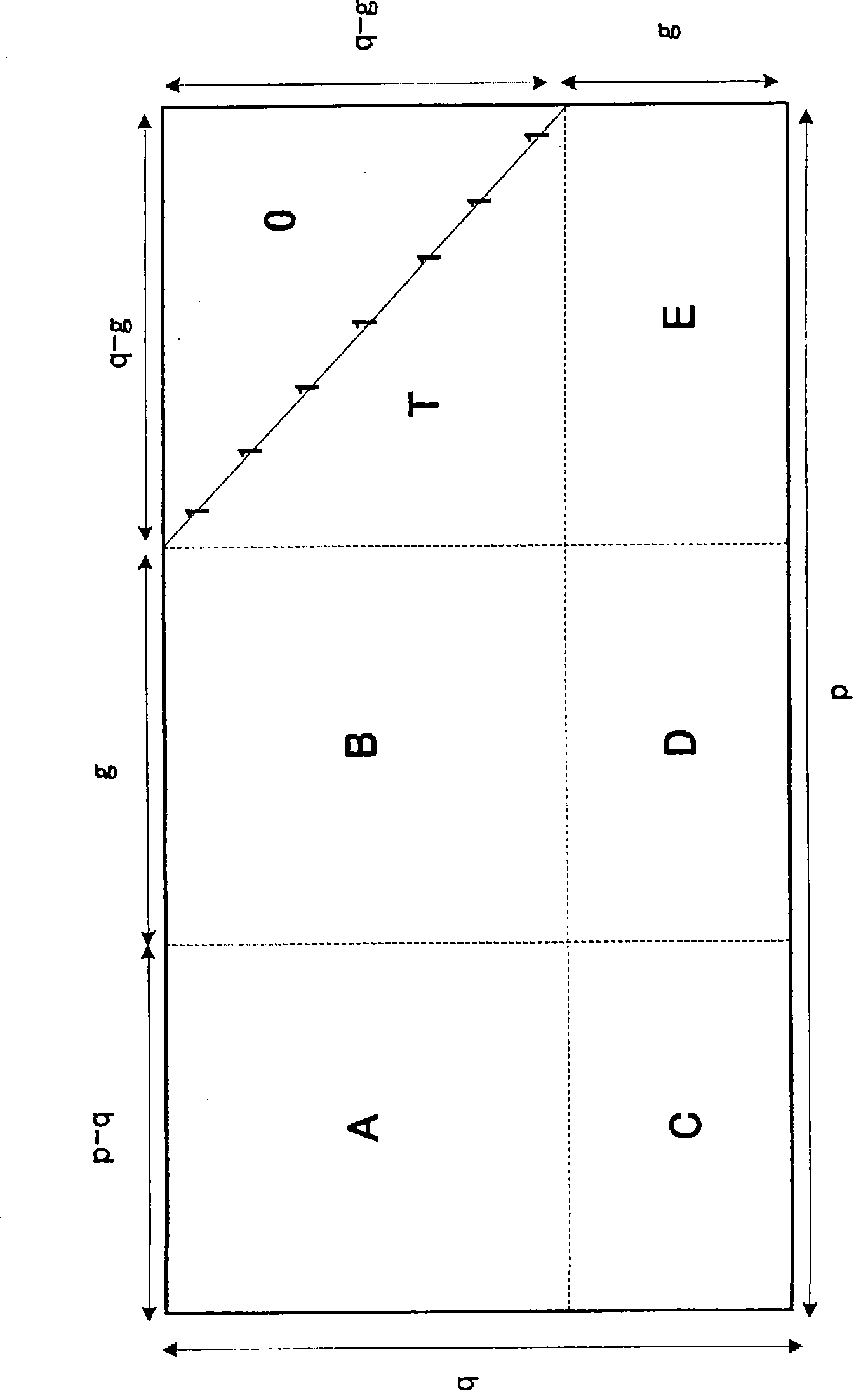
[0156] Figure 4 It is a diagram showing a configuration example of an encoding device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. In this embodiment, an LDPC code word is obtained by multiplying a row vector of an LDPC code generation matrix by a column vector obtained by converting an input data sequence into a column vector. The present embodiment is characterized in that by adopting the above configuration, parity bits of the LDPC code can be obtained at one time, thereby enabling high-speed encoding.
[0157] In addition, in this embodiment, before parity data is generated from the input data, the input data is first stored in the encoding device. This is because when generating an LDPC codeword, the parity data is arranged after (or before) the input data and output, so it is necessary to match the timing of generating the LDPC code.
[0158] For example, when all input data is input to an encoding device and parity data is generated, there is a generation dela...
Embodiment approach 2
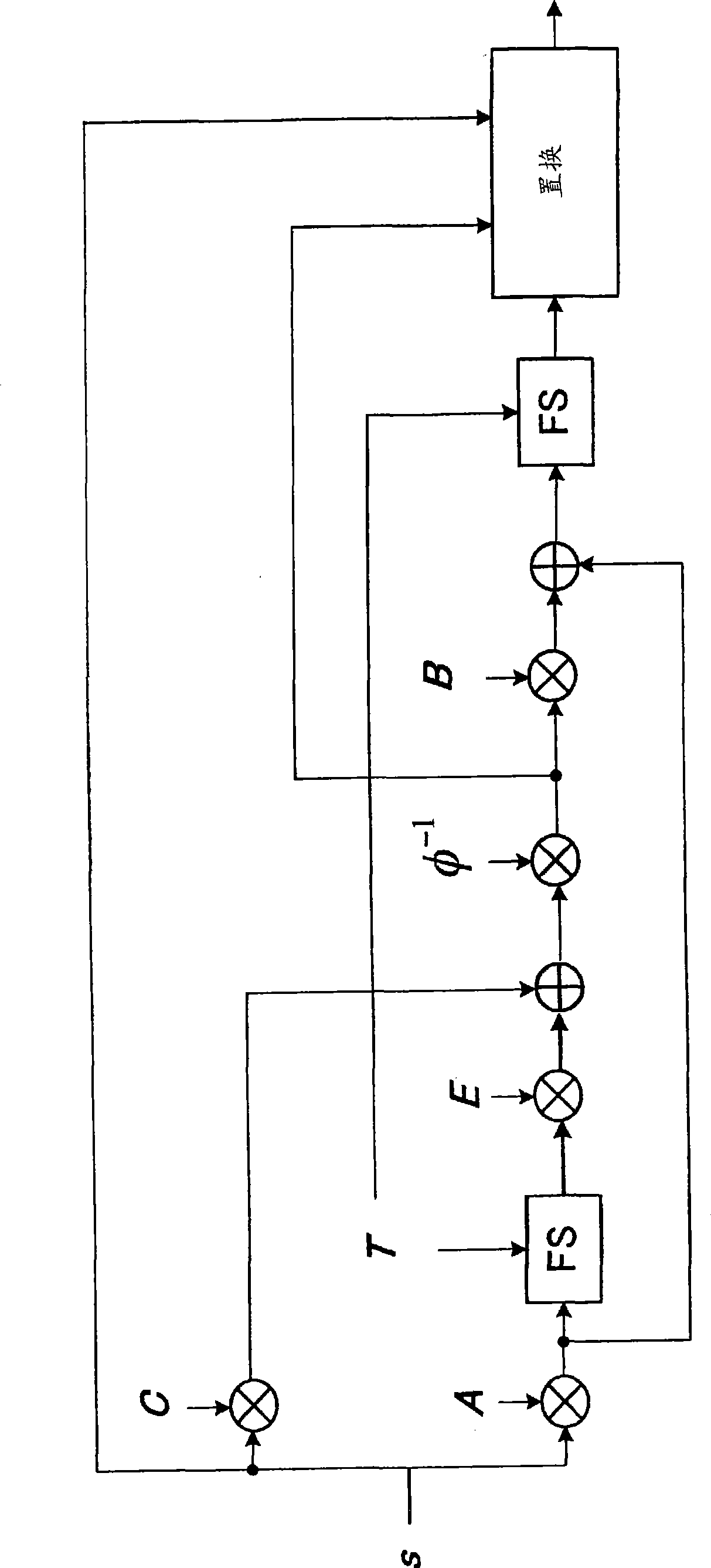
[0172] Figure 5 It is a diagram showing a configuration example of an encoding device 200 according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. In addition, in the second embodiment, the same parts as those in the first embodiment are assigned the same reference numerals (including terms), and redundant descriptions are appropriately omitted.
[0173] In this embodiment, the input data is multiplied by the column vector of the generator matrix, and the result is cumulatively added to obtain parity bits. In this embodiment, the multiplication between the generator matrix and the input data is performed using the column vectors of the generator matrix. Therefore, the input data vector is generated without holding the input data when multiplication is performed. As described above, the encoding device 200 of this embodiment is characterized in that it can reduce the circuit size because it does not require a storage unit for input data, and that it can perform high-speed encodin...
Embodiment approach 3
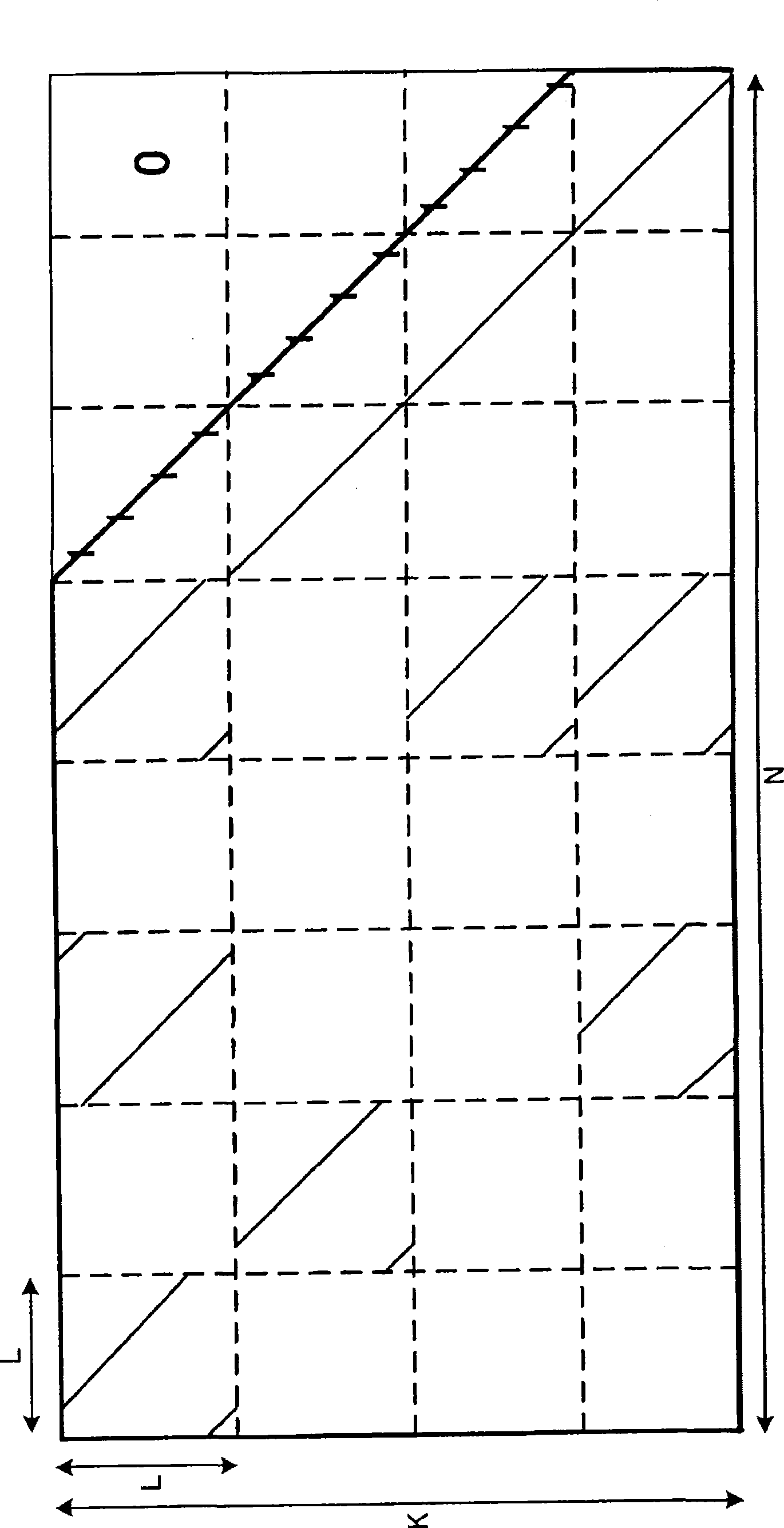
[0187] Figure 6 It is a diagram showing a configuration example of an encoding device 300 according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. In addition, in the third embodiment, the same parts as those in the first embodiment are assigned the same reference numerals (including terms), and redundant descriptions are appropriately omitted.
[0188] In this embodiment, the parity check data is obtained by multiplying the input data by the generator matrix calculated from the QC (Quasi Cyclic) simulated lower triangular check matrix. Then, LDPC encoding is performed using the reference vectors of the blocks that generate the matrix. The multiplication between the generator matrix and the input data multiplies the vector obtained by cyclically shifting the reference vector of the block of the generator matrix and the input data, and performs cumulative addition on the result to obtain parity data. By adopting the above configuration, in the encoding device 300, the circuit sca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com