Reliable multicast with linearly independent data packet coding
A data grouping, linearly independent technology, applied in the direction of data exchange details, payload distribution, data exchange network, etc., can solve problems such as poor performance, unrecognizable and utilization degrees of freedom, and achieve improved throughput efficiency and energy/energy Utilization, Effects of Reliable Multicast
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0050] Throughout the drawings, the same reference numbers will be used for the same or similar elements.
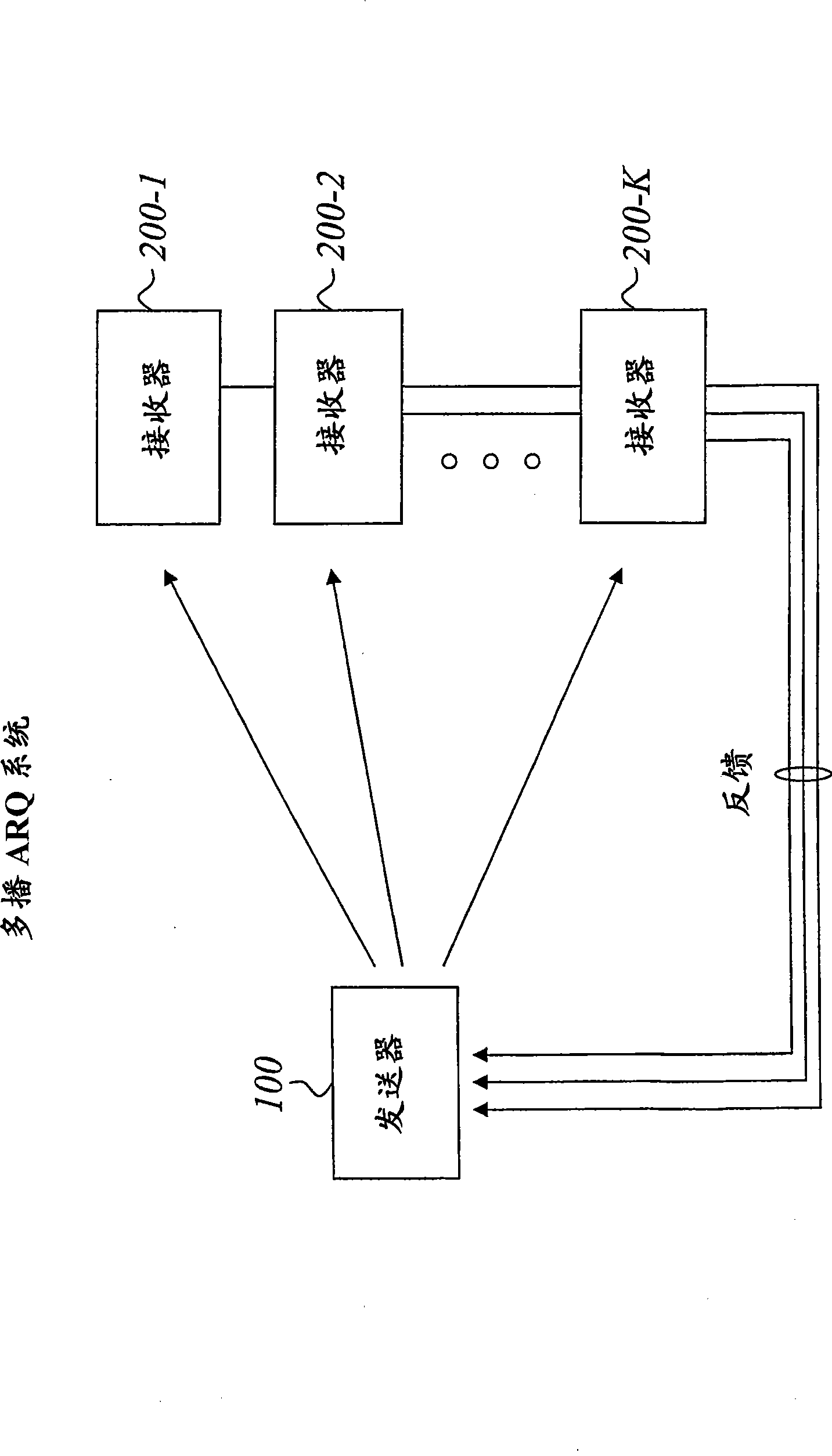
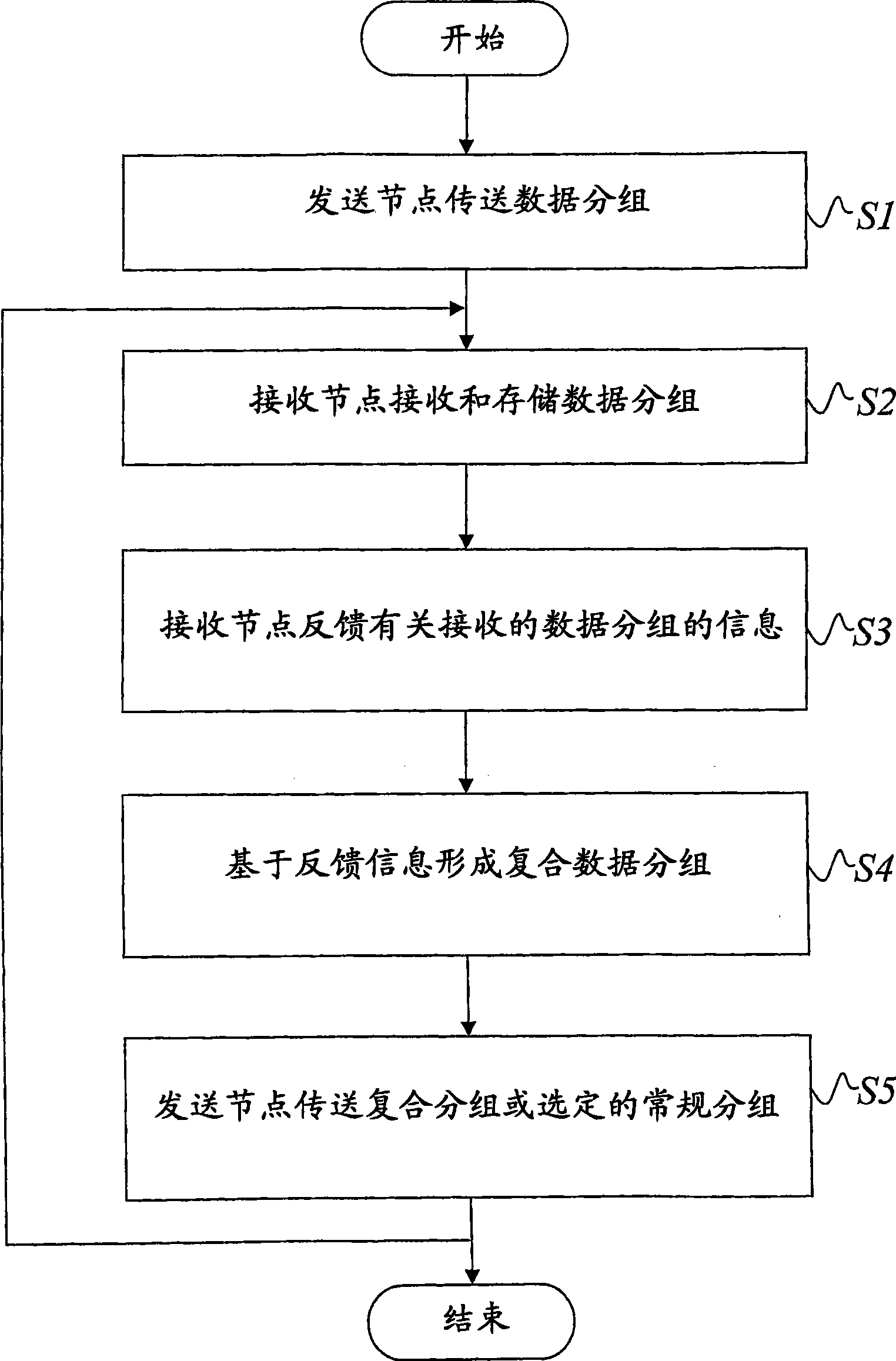
[0051] In the following, the term "regular data packet" denotes a normal (non-compound) data packet (ie just a completely normal data packet), whereas a compound data packet is based on at least two normal data packets. A "multicast data packet" can be a regular data packet or a compound data packet, and in its most general sense such a data packet may be called a "general data packet", a "multicast data packet" or a "generic multicast data packet ".
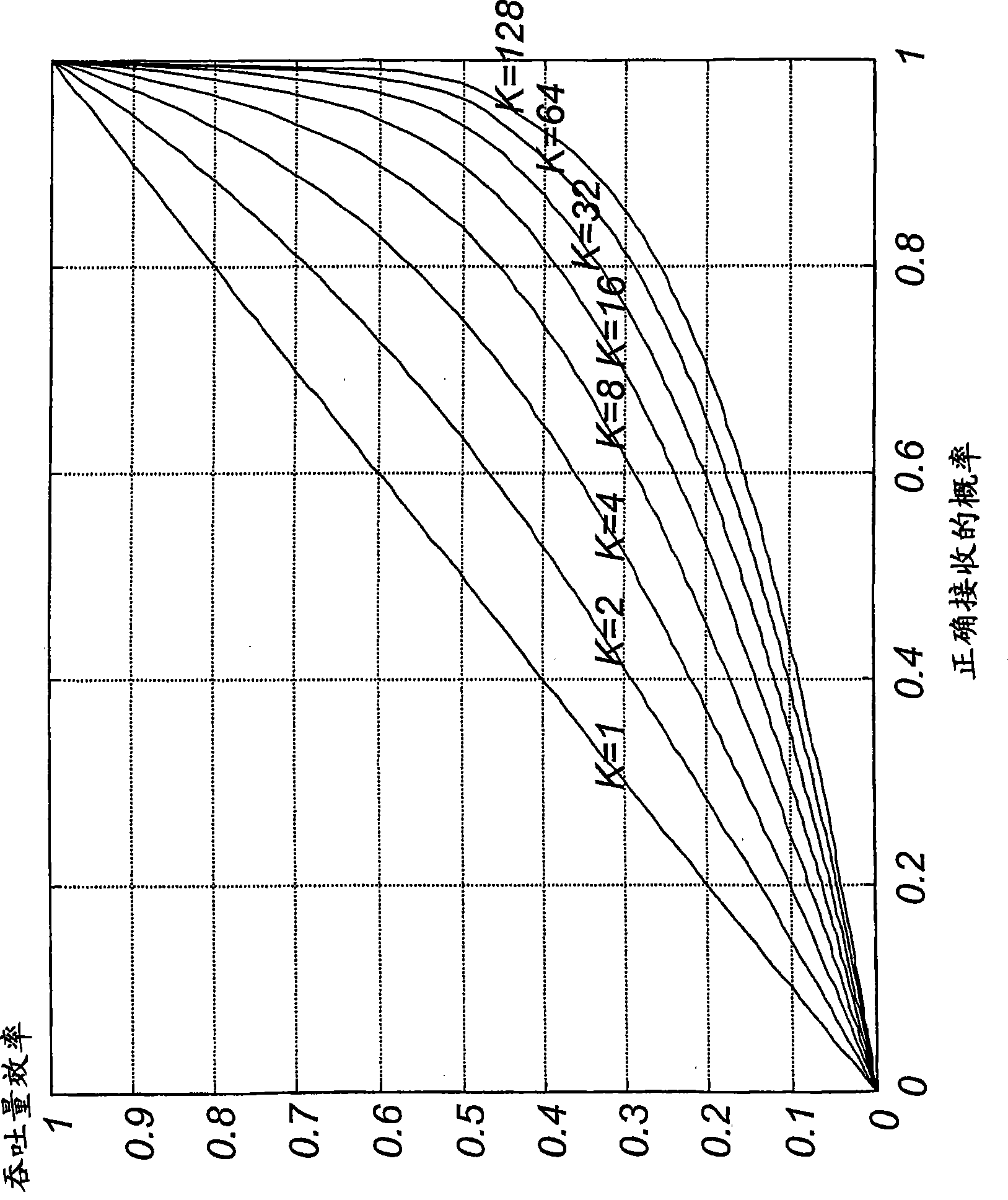
[0052] The problem with conventional multicast ARQ is generally that the performance is extremely poor when the number K of receivers / users is large. figure 1 The throughput efficiency of fully reliable multicast ARQ, K=1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64 and 128 is shown as a function of the probability of correct reception. The leftmost curve shows the case of K=1. As can be seen, the performance degrades as the number of nodes K ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com