Method for detecting purity of GFP transgene cotton crossbreed
A hybrid purity and detection method technology, applied in the field of biological breeding, can solve the problems of low seed production efficiency, mixed, incomplete flower peeling, etc., and achieve the effect of simple detection process, accurate and reliable results, and high identification efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
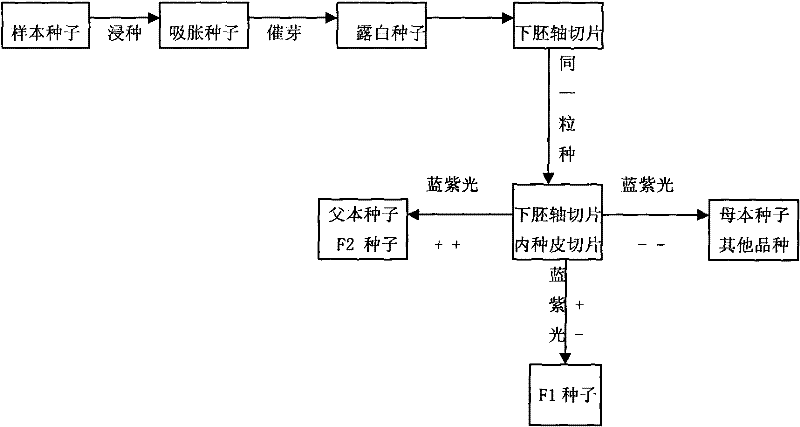
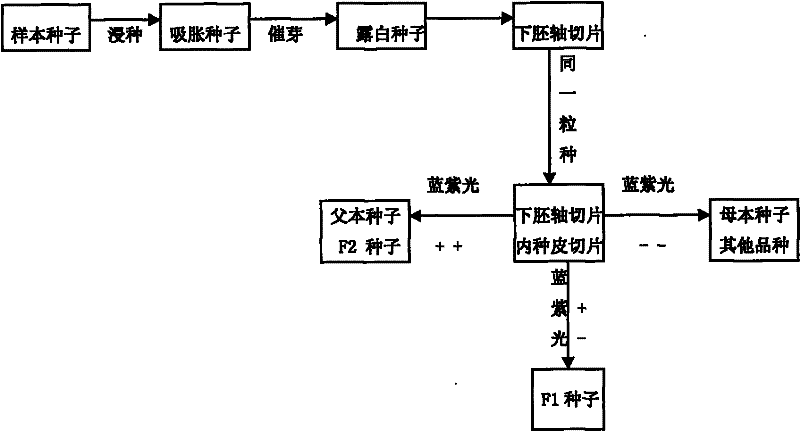
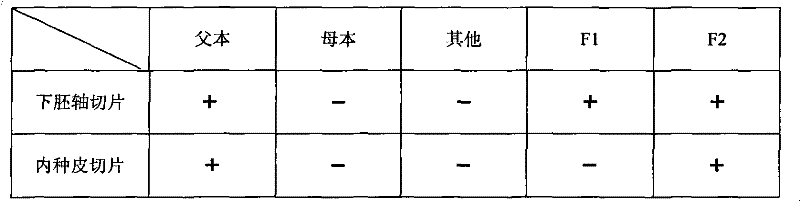
[0022] A method for detecting the purity of GFP transgenic cotton hybrids, which specifically includes the following steps: 1) F1 hybrids obtained by using GFP homozygous varieties (lines) as male parents and non-GFP varieties (lines) as female parents; 2) F1 extraction Substitute seed test samples, after soaking seeds in warm water at 26°C for 20 hours, germinate at 30°C for 30 hours, remove the outer testa, and save the hypocotyl and inner testa of the same seed as a section and place on the same glass; 3) Illuminate with blue-violet light of a fluorescence microscope, observe the fluorescence performance of the two sections, check with Table 1 to determine whether this seed belongs to F1 hybrids, only the hypocotyl section has green fluorescence and the endocarp section has no green When fluorescent, it can be judged that the seed is an F1 hybrid; when both the hypocotyl slice and the endothelial slice have green fluorescence, the seed can be judged to be the male parent or G...
Embodiment 2
[0027] A method for detecting the purity of GFP transgenic cotton hybrids, specifically including the following steps:
[0028] 1) F1 hybrids obtained by using GFP homozygous varieties (lines) as male parents and non-GFP varieties (lines) as female parents;
[0029] 2) Take the F1 generation seed test sample, soak the seeds in 28℃ warm water for 20, incubate the germination at 28℃ for 30h, remove the outer testa, save the hypocotyl and inner testa of the same seed as a slice respectively On glass
[0030] 3) Use the blue-violet light of a fluorescence microscope to observe the fluorescence performance of the two sections. When only the hypocotyl section has green fluorescence and the endocarp section has no green fluorescence, it can be determined that the seed is an F1 hybrid; when the hypocotyl section and When both endometrium slices have green fluorescence, it can be judged that the seeds are male parent or GFP F2 generation seeds; when the hypocotyl slices and endothelial slice...
Embodiment 3
[0032] A method for detecting the purity of GFP transgenic cotton hybrids, specifically including the following steps:
[0033] 1) F1 hybrids obtained by using GFP homozygous varieties (lines) as male parents and non-GFP varieties (lines) as female parents;
[0034] 2) Take the F1 generation seed test sample, soak the seeds in 30℃ warm water for 24 hours, incubate the germination at 30℃ for 24 hours, remove the outer testa, and save the hypocotyl and inner testa of the same seed as a section and place them in the same On glass
[0035] 3) Use the blue-violet light of a fluorescence microscope to observe the fluorescence performance of the two sections. When only the hypocotyl section has green fluorescence and the endocarp section has no green fluorescence, it can be determined that the seed is an F1 hybrid; when the hypocotyl section and When both endometrium slices have green fluorescence, it can be judged that the seeds are male parent or GFP F2 generation seeds; when the hypocot...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com