Micro-calorimetric method suitable for quickly detecting total amount of microorganisms in food
A technology of microcalorimetry and microorganisms, which is applied in the field of micromethods for the total number of microorganisms, and can solve the problems of reduced practicability and poor parallelism of measurement results, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
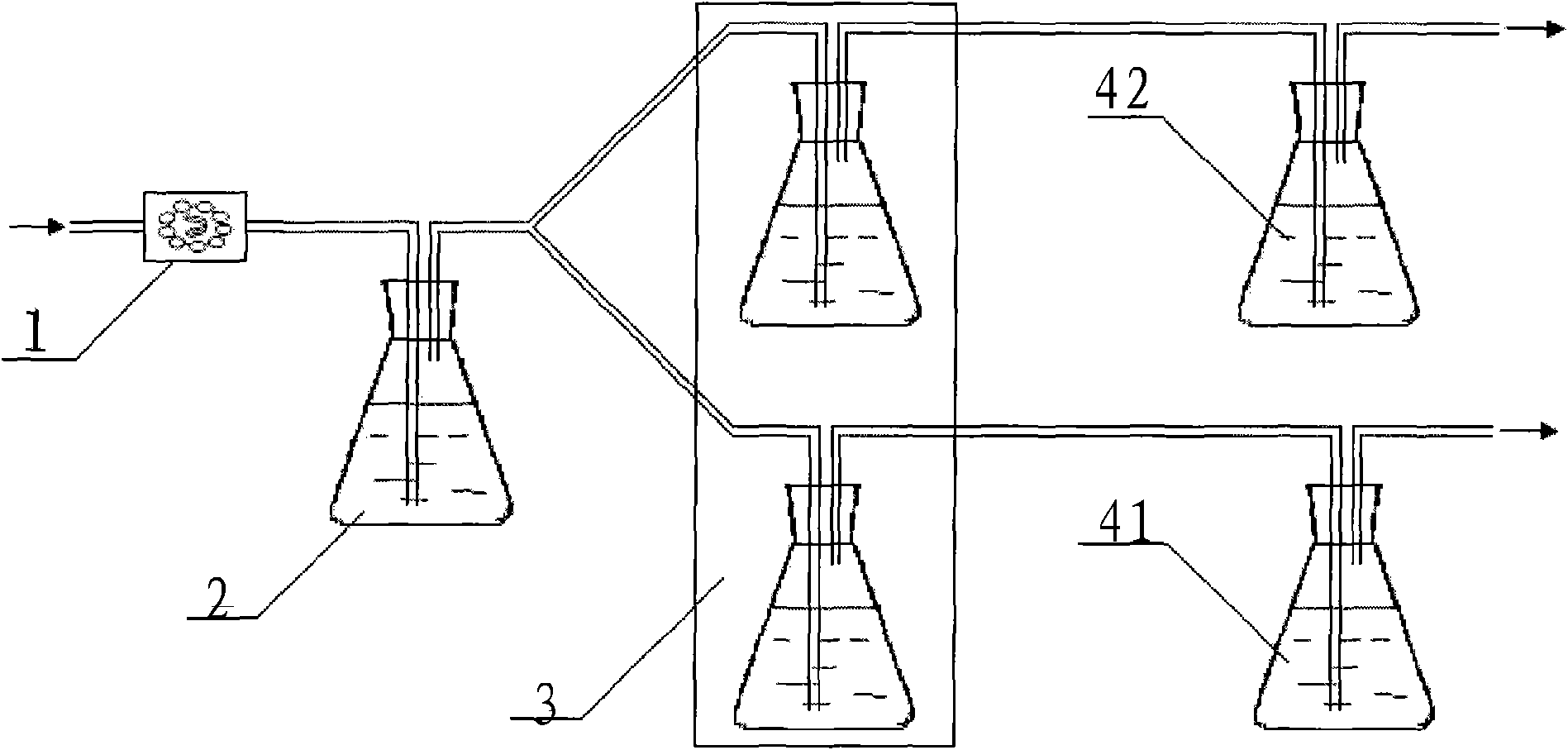
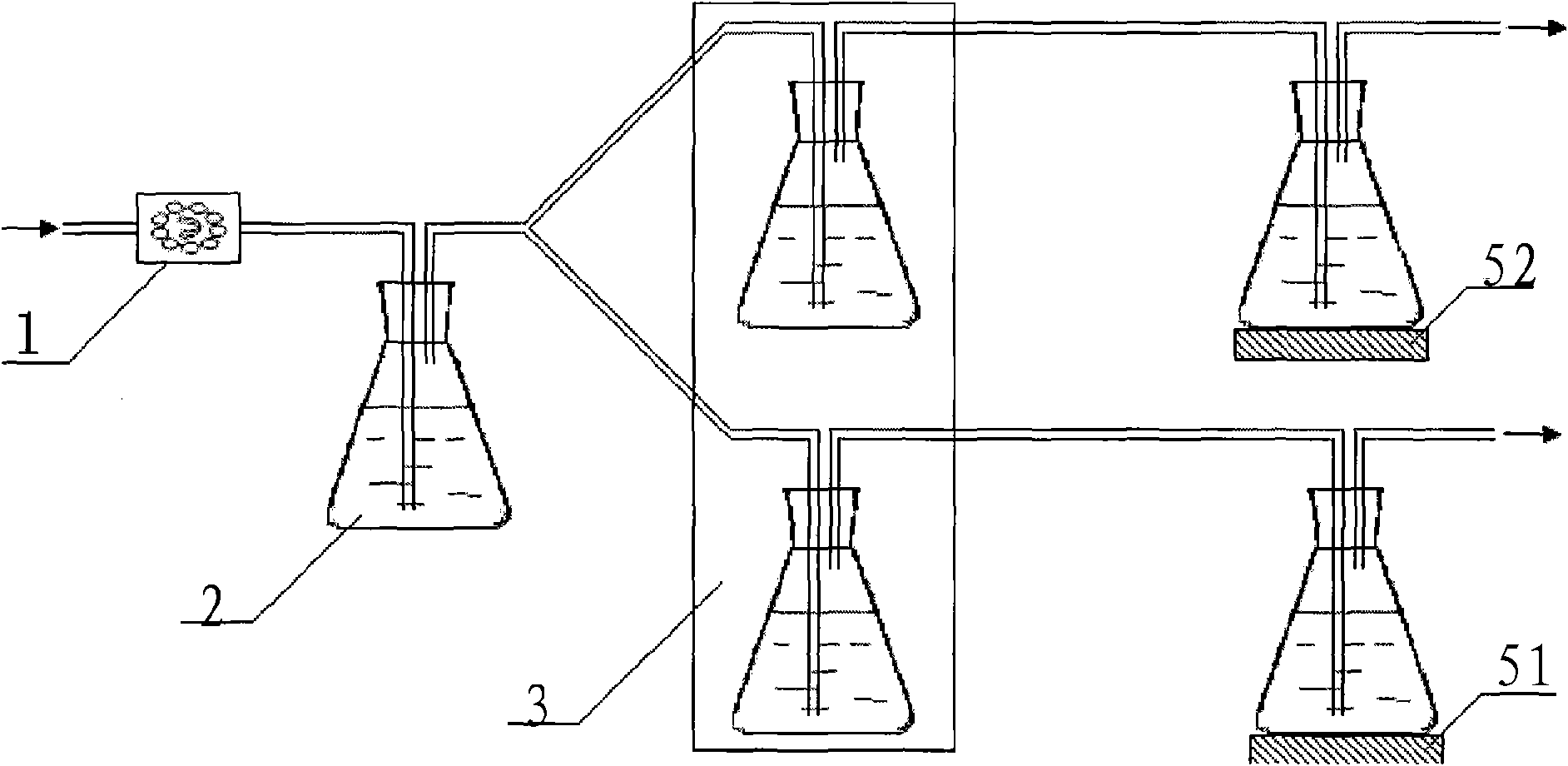
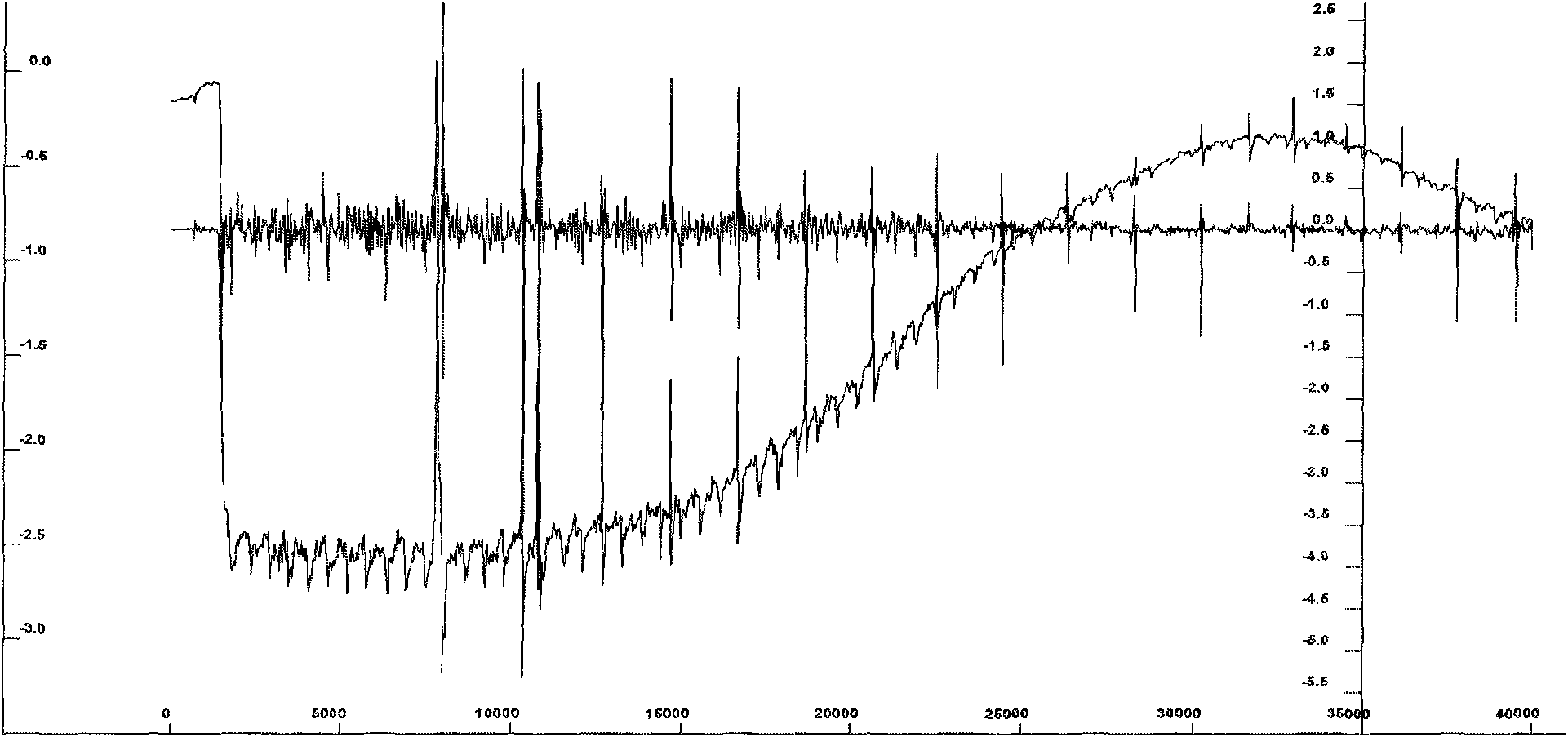
[0018] A microcalorimetric method suitable for rapid detection of the total number of microorganisms in food, by detecting the CO produced during the growth of microorganisms 2 The amount detects the total number of microorganisms in food.
[0019] Since the exotherm of bacterial growth is something that every bacterial species produces, the replacement needs to be equally universal. The basic growth process of microorganisms is:
[0020] C source + O 2 +N source→cell mass+H 2 O+CO 2 +product+heat
[0021] It can be seen from the above equation that microorganisms decompose and utilize various energy substances, in addition to growth, they also produce water, CO 2 , various products and heat. Since the microorganisms are cultivated in a water environment, the water produced cannot be detected, and the heat has been negated. At the same time, the products produced by different microorganisms are different, and no commonality can be found from them. Therefore, CO 2 would ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com