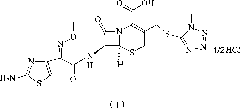
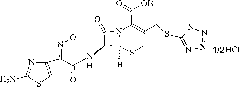
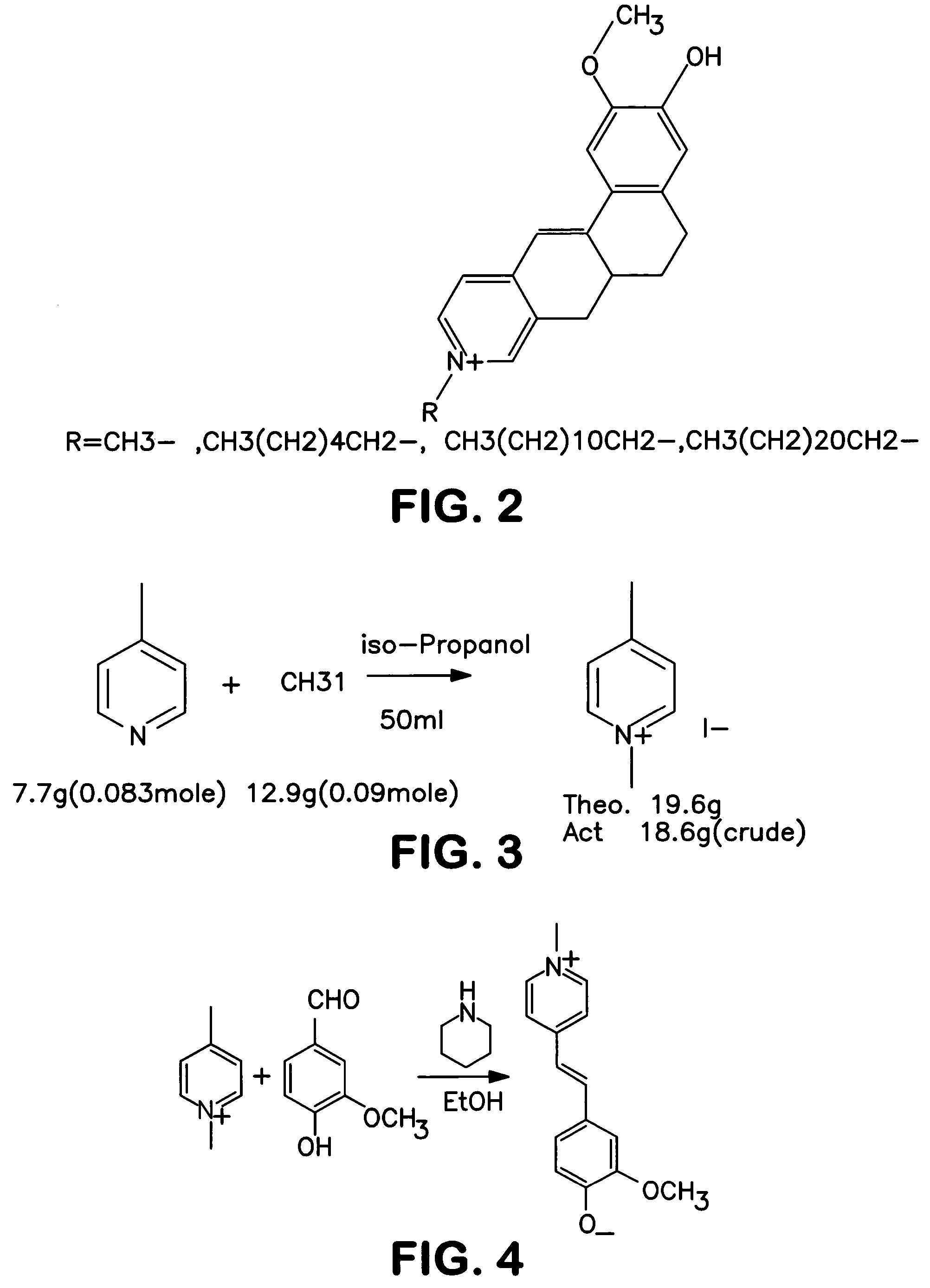
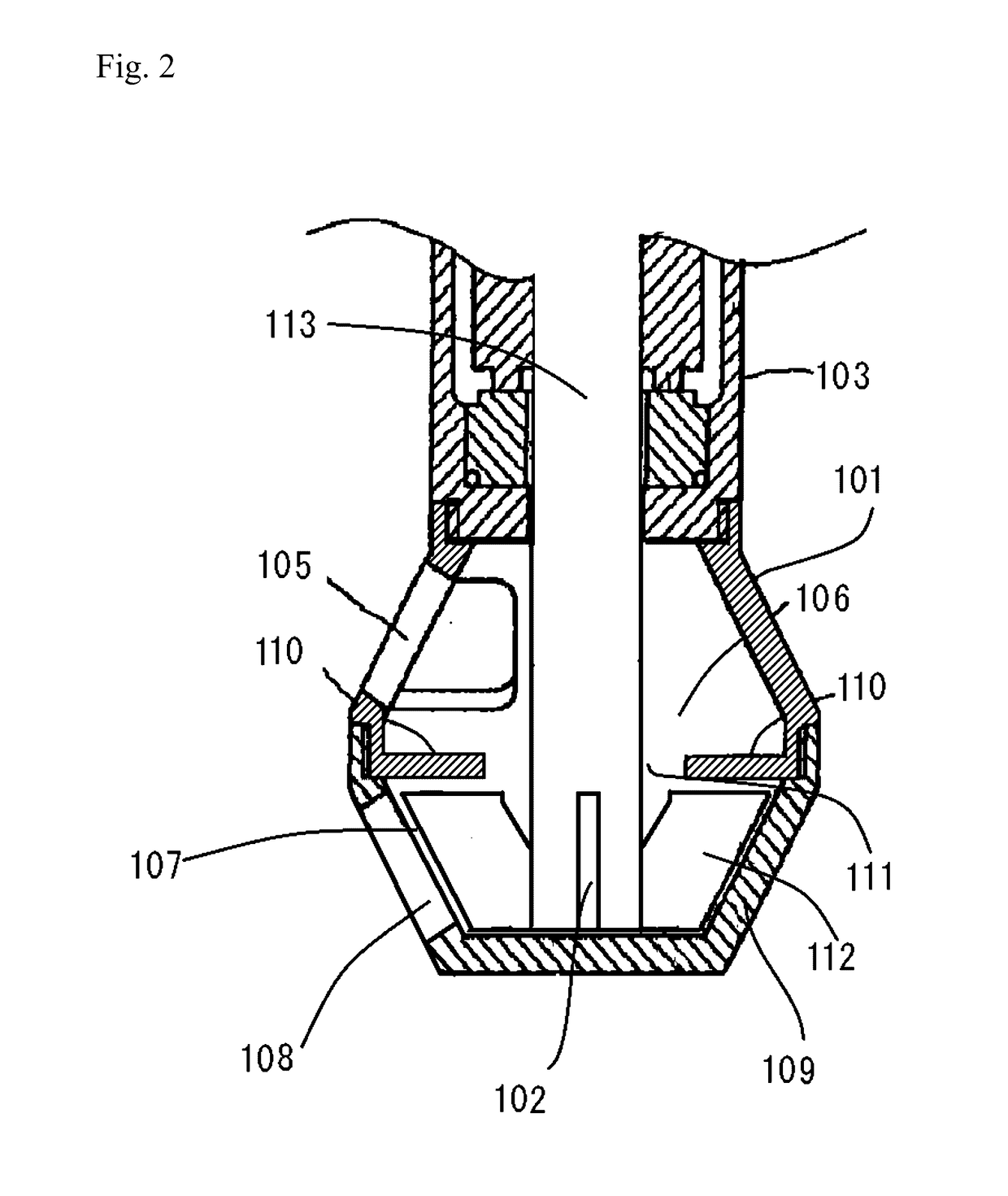
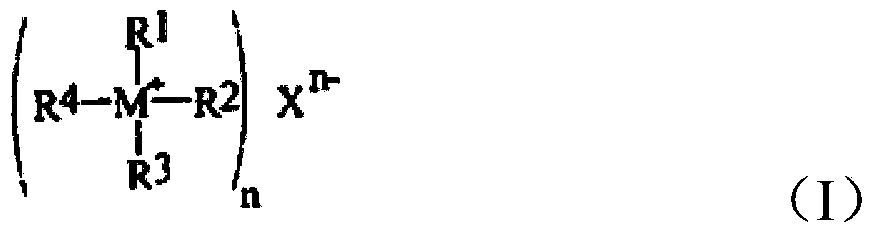Patents
Literature
194 results about "Acid–base reaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
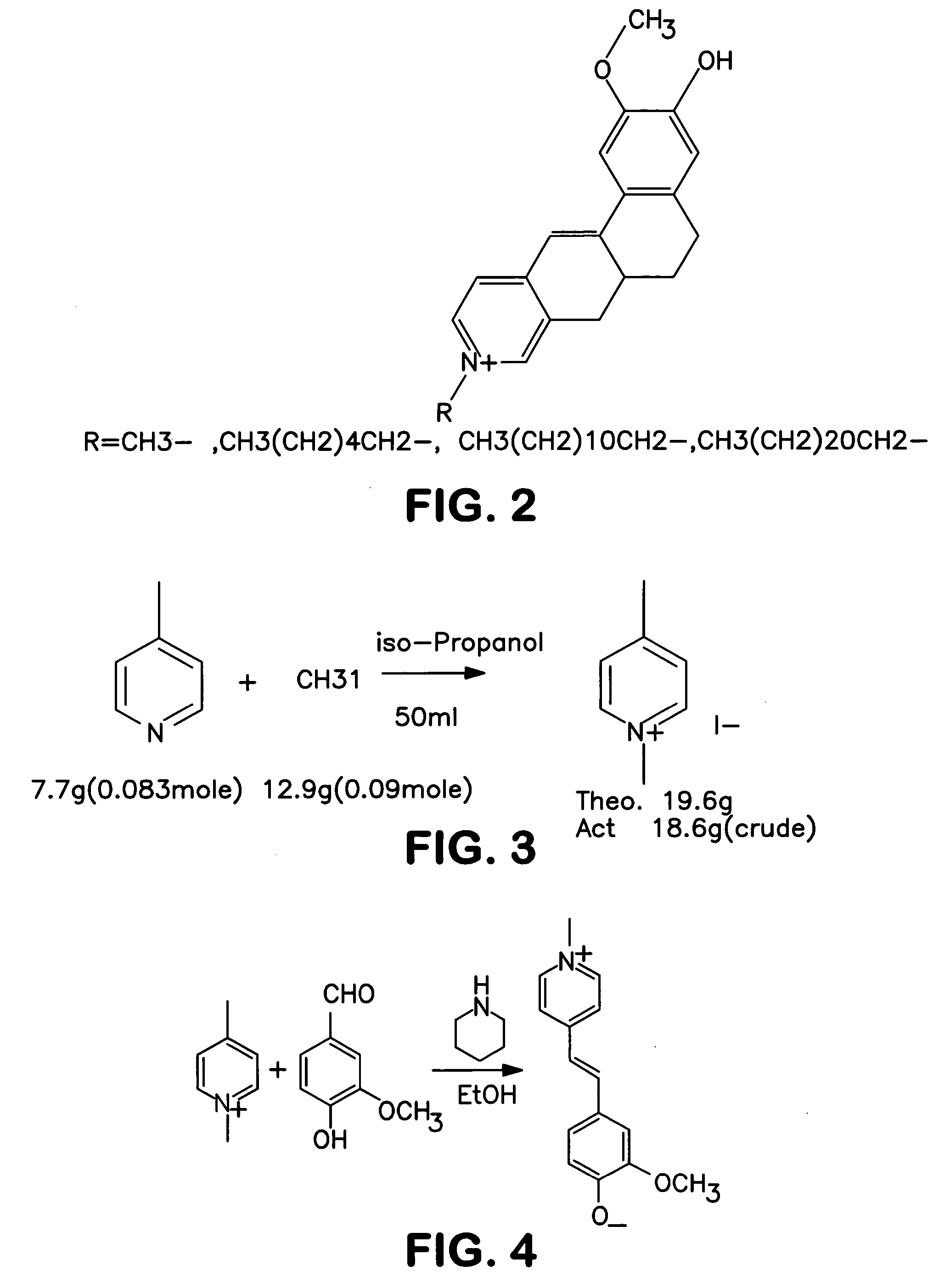
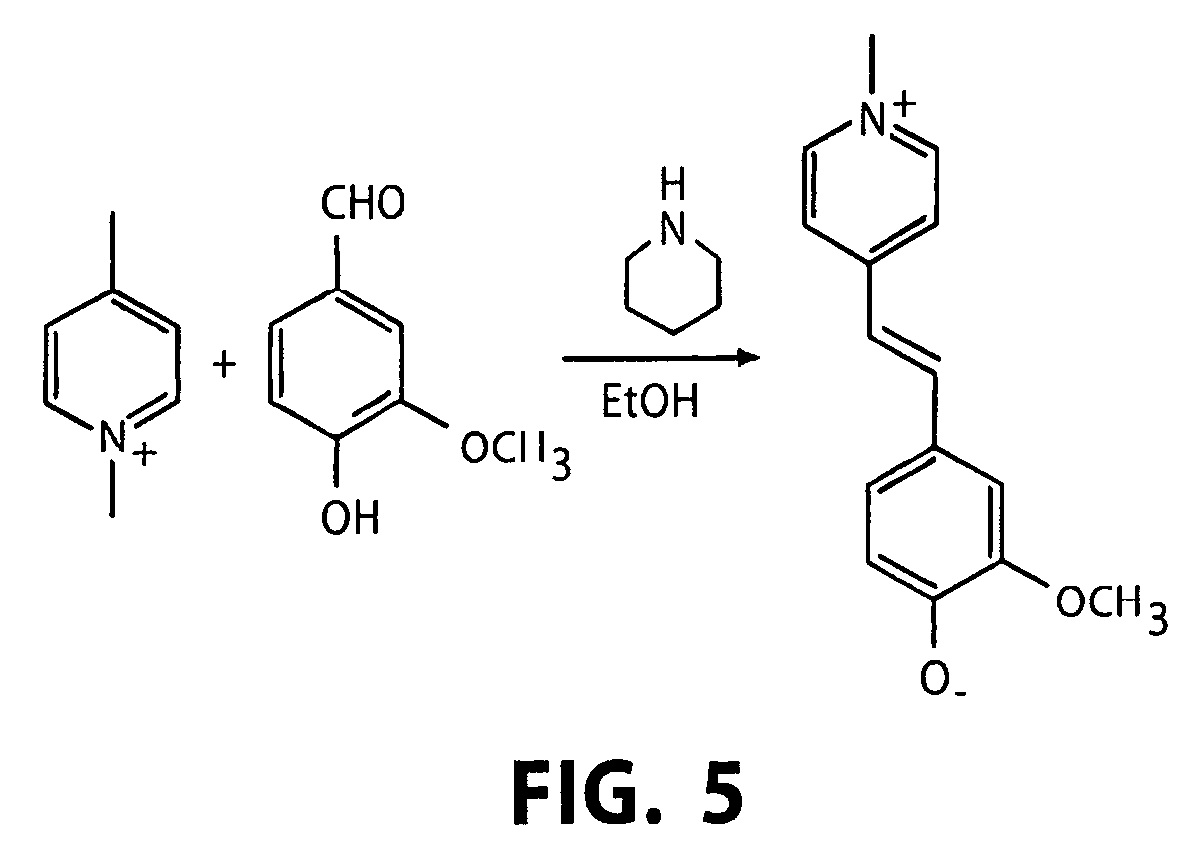
An acid–base reaction is a chemical reaction that occurs between an acid and a base. It can be used to determine pH. Several theoretical frameworks provide alternative conceptions of the reaction mechanisms and their application in solving related problems; these are called the acid–base theories, for example, Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory.
Dermatological compositions
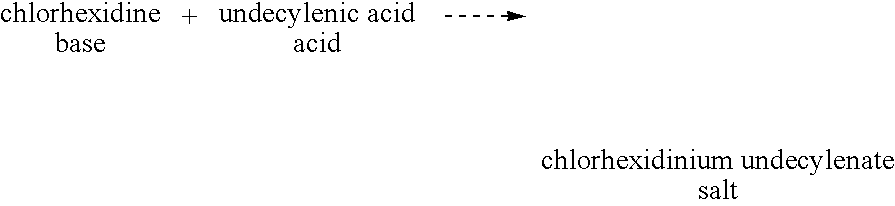
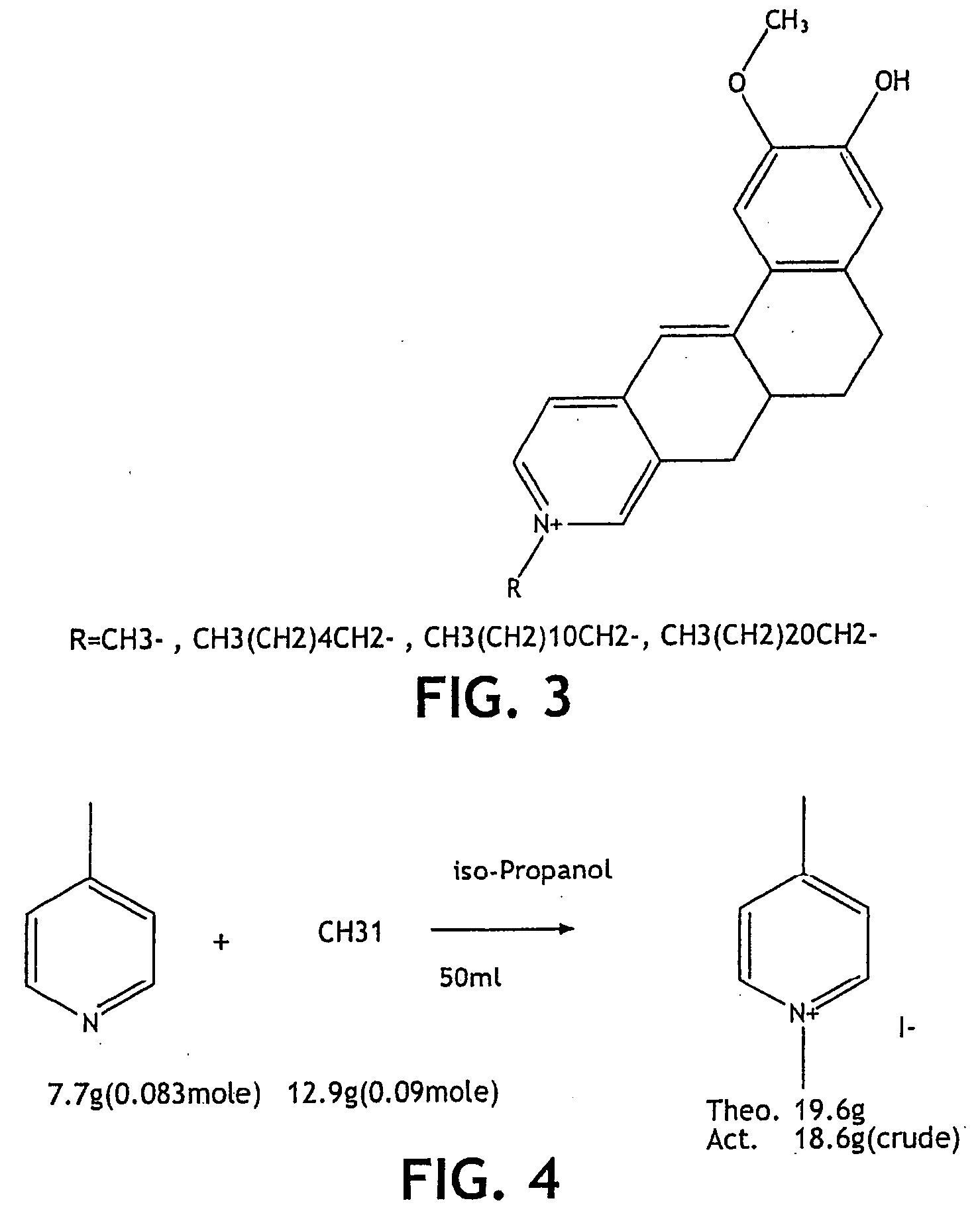
InactiveUS20090318557A1Decrease of bioactivityReduced effectivenessCosmetic preparationsBiocideCarboxylic acidAcid–base reaction
A dermatological composition comprising a salt of a cation and an anion. The cation is derived from a monomeric or polymeric molecule that will generate an amidine moieity, a guanidine moieity or a biguanide moieity. The anion is derived from a monomeric or polymeric molecule that will generate a carboxylic acid moieity. The composition may be prepared by a metathesis or acid-base reaction.
Owner:STOCKEL RICHARD F
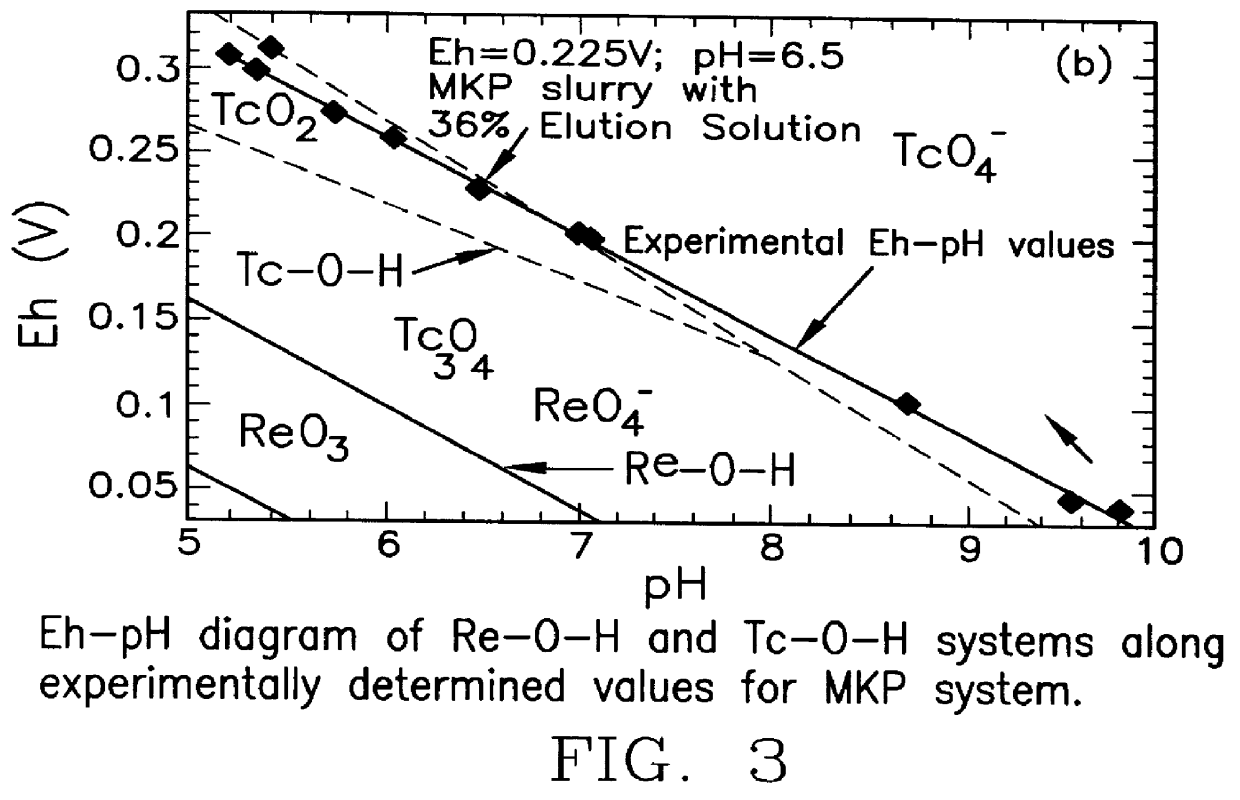
Method for producing chemically bonded phosphate ceramics and for stabilizing contaminants encapsulated therein utilizing reducing agents
Known phosphate ceramic formulations are improved and the ability to produce iron-based phosphate ceramic systems is enabled by the addition of an oxidizing or reducing step during the acid-base reactions that form the phosphate ceramic products. The additives allow control of the rate of the acid-base reactions and concomitant heat generation. In an alternate embodiment, waste containing metal anions are stabilized in phosphate ceramic products by the addition of a reducing agent to the phosphate ceramic mixture. The reduced metal ions are more stable and / or reactive with the phosphate ions, resulting in the formation of insoluble metal species within the phosphate ceramic matrix, such that the resulting chemically bonded phosphate ceramic product has greater leach resistance.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Microbial detection and quantification
InactiveUS20060134728A1Increase brightnessGood colorBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismCell membrane
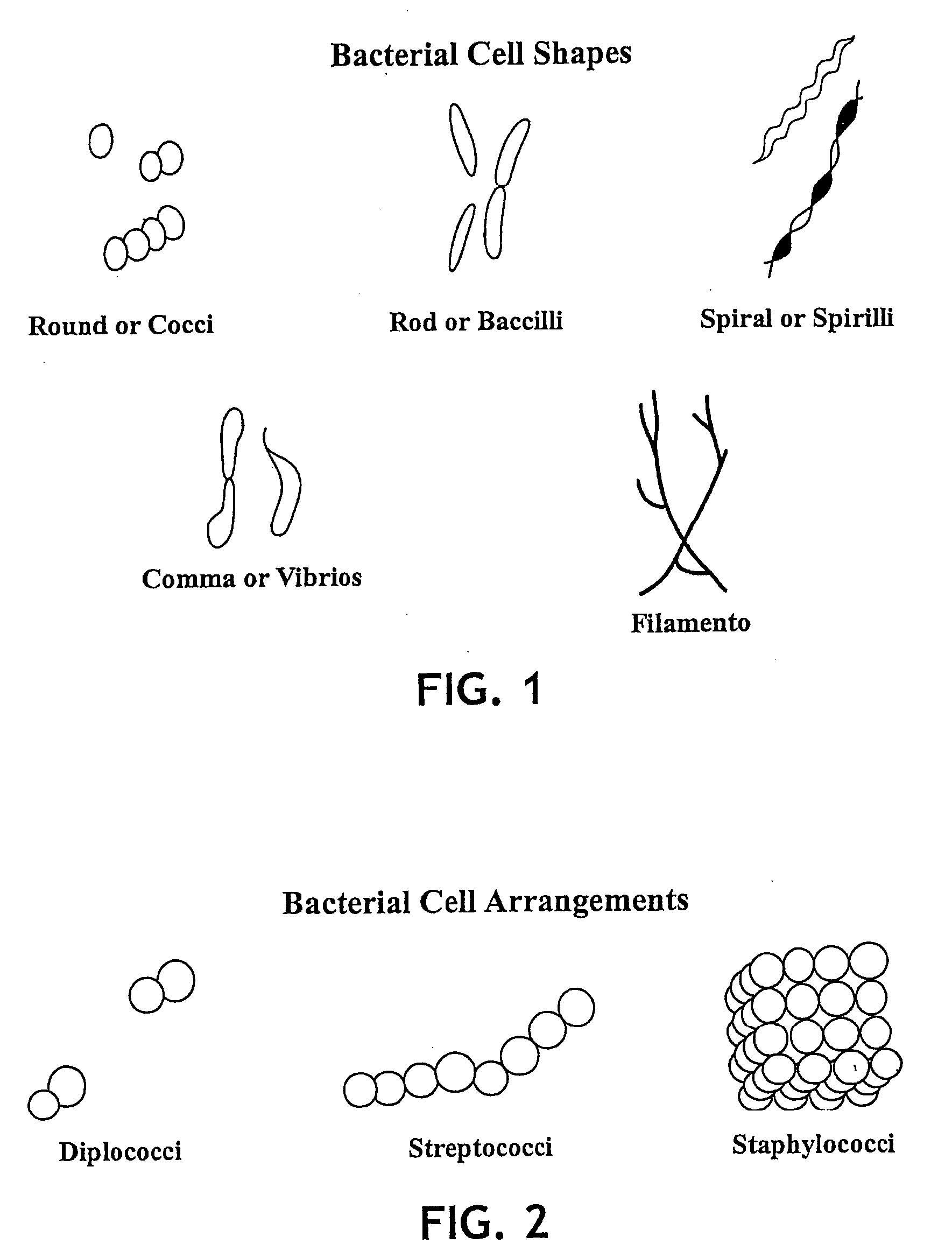
A method for semi-quantitatively or quantitatively detecting the presence of a microbe in a sample is provided. The method utilizes a test dye that undergoes a detectable color change in the presence of one or more microbes. For example, in one embodiment, the test dye is a solvatochromic dye (e.g., Reichardt's dye) that responds to differences in polarity between microbe components (e.g., cell membrane, cytoplasm, etc.) and the environment outside the cell. Alternatively, other mechanisms may be wholly or partially responsible for the interaction between the dye and the microbe, such as acid-base reactions, redox reactions, and so forth. Regardless, the color of the test dye may be compared to the color of a control dye, wherein the color of the control dye corresponds to a known microbe concentration.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Phosphate film-coated powder and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101045828AUniform particlesParticle size distribution andNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesOther chemical processesDepolymerizationDouble decker
This invention relates to a method of preparing envelope powder. The shattering, depolymerization and coating processed at same time, and solid phase acid-base reaction participate the method. This envelope powder possess double-decker or three-layer structure, inner core is composed by oxide or hydrate or inorganic oxysalt, crust composed by inorganic oxysalt, envelope by aluminum phosphate or boron phosphate. This low cost powder be able to used as fortifier, power stuff, colorant and so on, applied to plastic, rubber, ceramics, dope, binder and paper, set foundation for popularization of ultramicro and nanometer powder.
Owner:张义纲 +1
Detection of microbe contamination on elastomeric articles
ActiveUS20060134613A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismOxidation-Reduction Agent
An elastomeric article that contains a chromogen that undergoes a detectable change in color in the presence of one or more microbes is provided. For example, in one embodiment, the chromogen is a solvatochromic dye (e.g., Reichardt's dye) that undergoes a color change in the presence of bacteria or other microbes. More specifically, such dyes may respond to differences in polarity between microbe components (e.g., cell membrane, cytoplasm, etc.) and the environment outside the cell. Alternatively, other mechanisms may be wholly or partially responsible for the interaction between the dye and the microbe, such as acid-base reactions, redox reactions, and so forth.
Owner:O&M HALYARD INC
Urban kitchen waste recycling utilization and harmless treatment technology
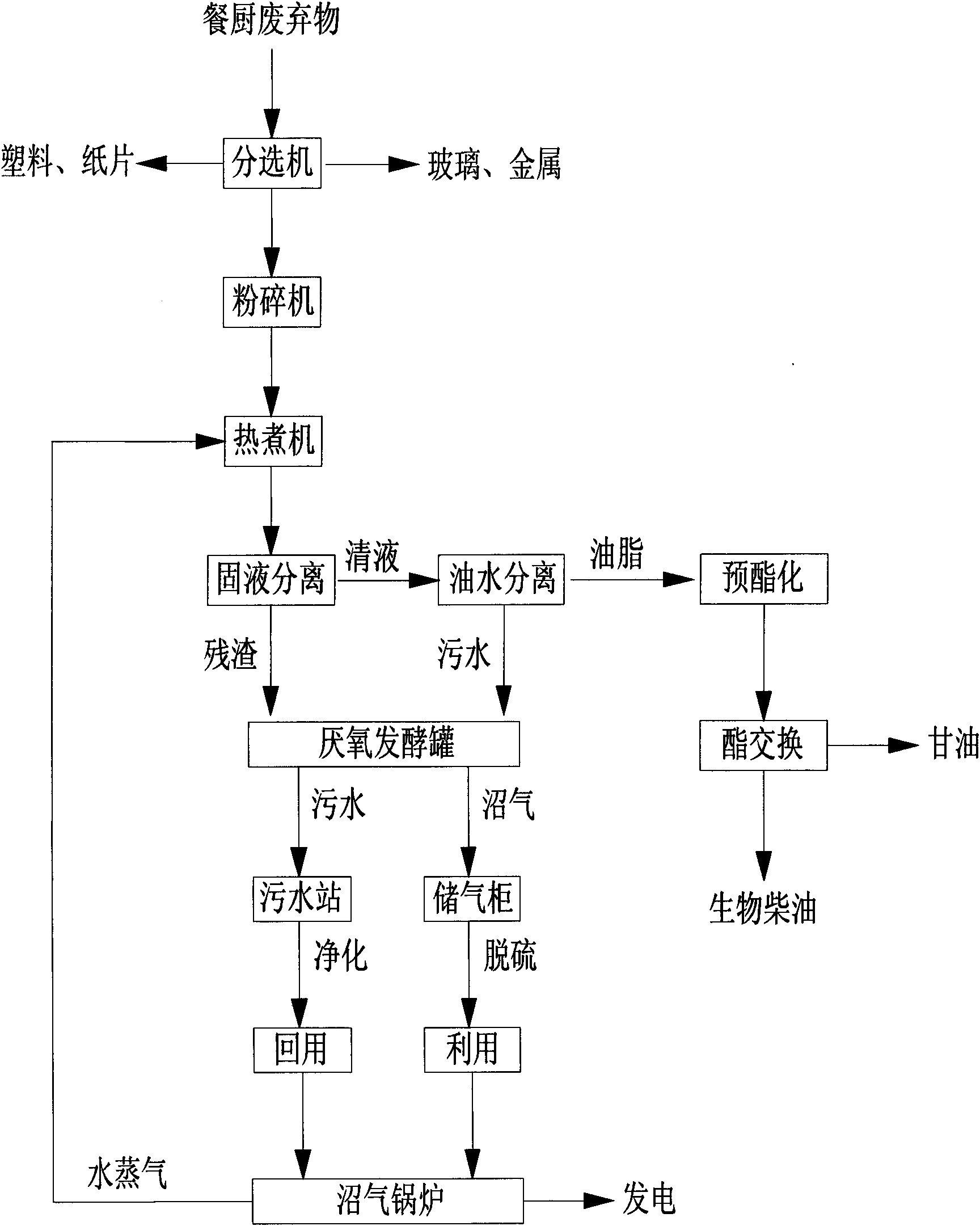
ActiveCN102688881AReasonable process designSimple processBiological substance pretreatmentsFatty acid esterificationBiodieselWater vapor
The invention relates to an urban kitchen waste recycling utilization and harmless treatment technology. The urban kitchen waste recycling utilization and harmless treatment technology is characterized by grinding and sorting kitchen waste by a crushing sorting machine, separating out inorganic substances, carrying out high-temperature steam pyrolysis of organic matter slurry, and carrying out solid-liquid and oil-water separation, wherein separated residues and sewage are fed into a biogas fermentation tank and are subjected to anaerobic fermentation to produce biogas for power generation or civil heating; and separated waste oil undergoes an acid-base reaction to produce glycerin and biodiesel. The urban kitchen waste recycling utilization and harmless treatment technology realizes maximum recycle of active resources of kitchen waste, reduces the pollution and the damage on the environment, and has environmental, economic and social benefits.
Owner:SHANGHAI ONEDEAR ENVIRONMENT TECH
High purity fasudil hydrochloride compound
The invention relates to high purity fasudil hydrochloride compound; the method can obtain high purity fasudil hydrochloride finished goods and belongs to the technical field of medicine. The purity of the fasudil hydrochloride is greatly increased by acid-base reaction, silicagel column elution and activated carbon adsorption. The method has simple technique, low cost and high yield and is suitable for industrialization production.
Owner:HAINAN MEILAN SMITH KLINE PHARMA
High-efficiency and novel biological carrier for sewage biological treatment and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101538083AHigh mechanical strengthAvoid deformationBiological water/sewage treatmentWastewaterWaste rubber
The invention relates to a high-efficiency and novel biological carrier for a sewage biological treatment and a preparation method thereof. The biological carrier is prepared by comprising the following steps of: blending, extruding or injection-molding the following components: PP, PE, and ethylene-propylene copolymer, compatilizer, inorganic materials, plant materials, magnetic particles, and waste rubber according to a certain proportion, thus providing a biological carrier with large specific surface area, high hydrophilicity and easy hanged membrane on surfaces. The shapes of the biological carriers can be spherical, fibrous and polyhedral or powdery with various forms. The chemical or physical methods such as grinding, acid base reaction, coating on surface and the like can also be carried out to prepare the biological carrier, thus further improving the specific surface area, strengthening the adhesive ability of the biological membrane on the carrier, and improving the microorganism concentration. The preparation method of the biological carrier provided by the invention is simple, has wide adjusting range of the carrier density, easy obtaining materials, low cost, high efficiency of eliminating COD and variety shapes, can be lighter or heavier than water, and is applicable to all biological wastewater treatments.
Owner:常州华钛化学有限公司
Addition product, production and use thereof as corrosion inhibitor
InactiveUS20040168748A1Rapid and lasting inhibitionOrganic chemistrySolid state diffusion coatingHexafluorotitanic acidHexafluorosilicic acid
The invention relates to an addition product that can be produced from hexafluorosilicic acid, hexafluorotitanic acid, and / or hexafluorozirconic acid by an acid-base reaction with one or several organic bases and a method for production and use thereof. The addition products according to the invention guarantee a rapid and lasting inhibition of corrosion processes; they are in particular suitable for inhibiting the corrosion of light metals.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Dissociating agents, formulations and methods providing enhanced solubility of fluorides
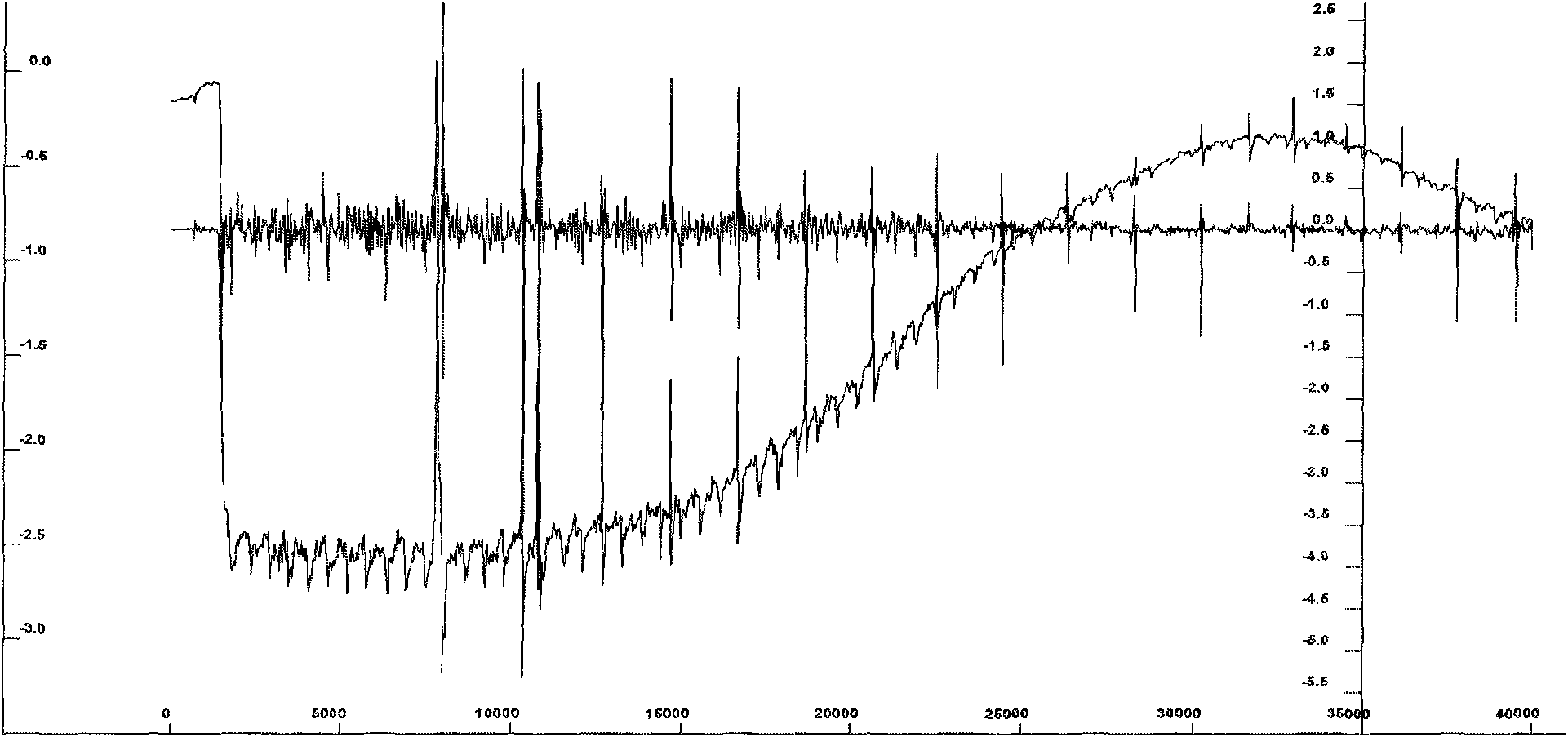
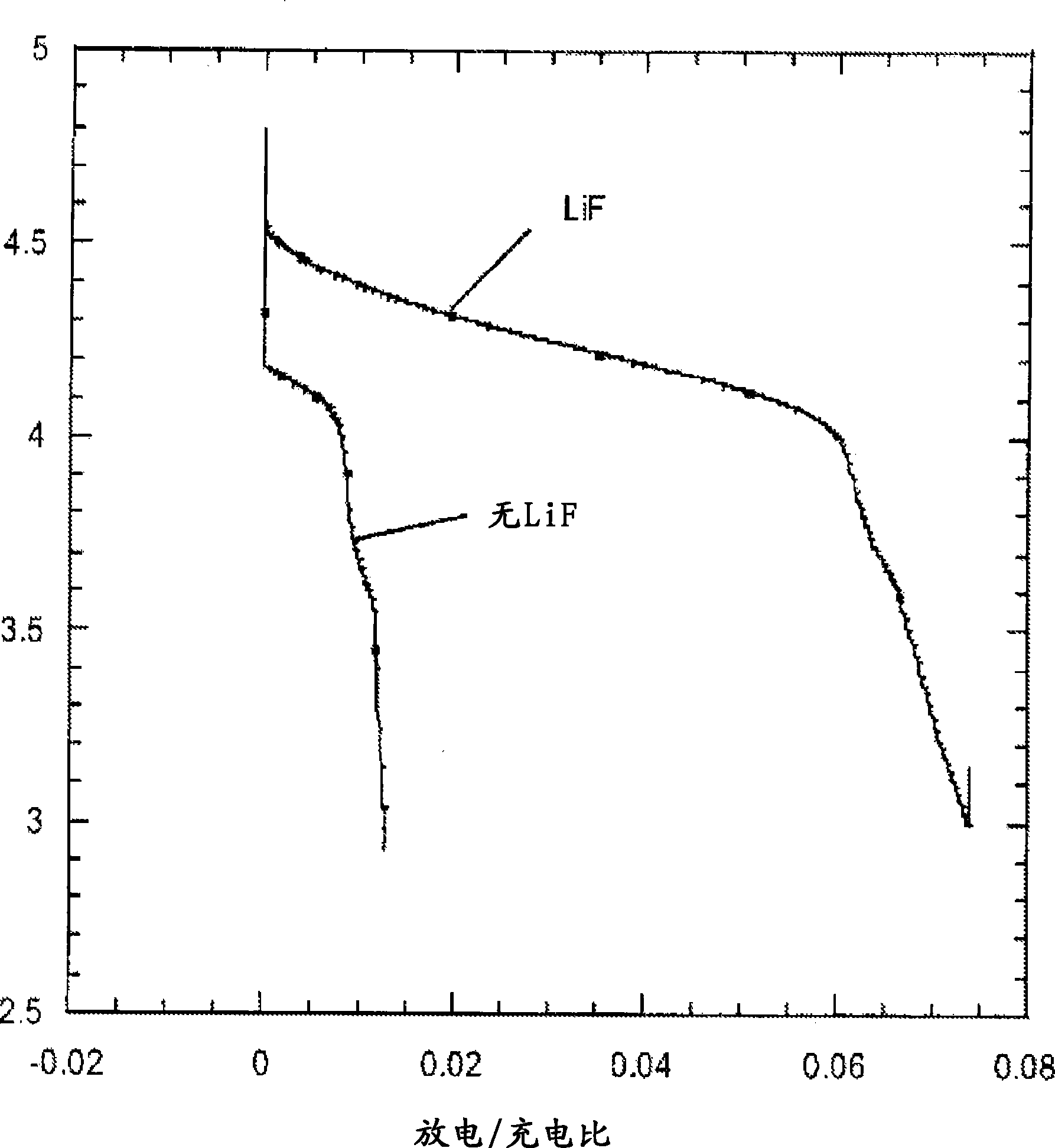
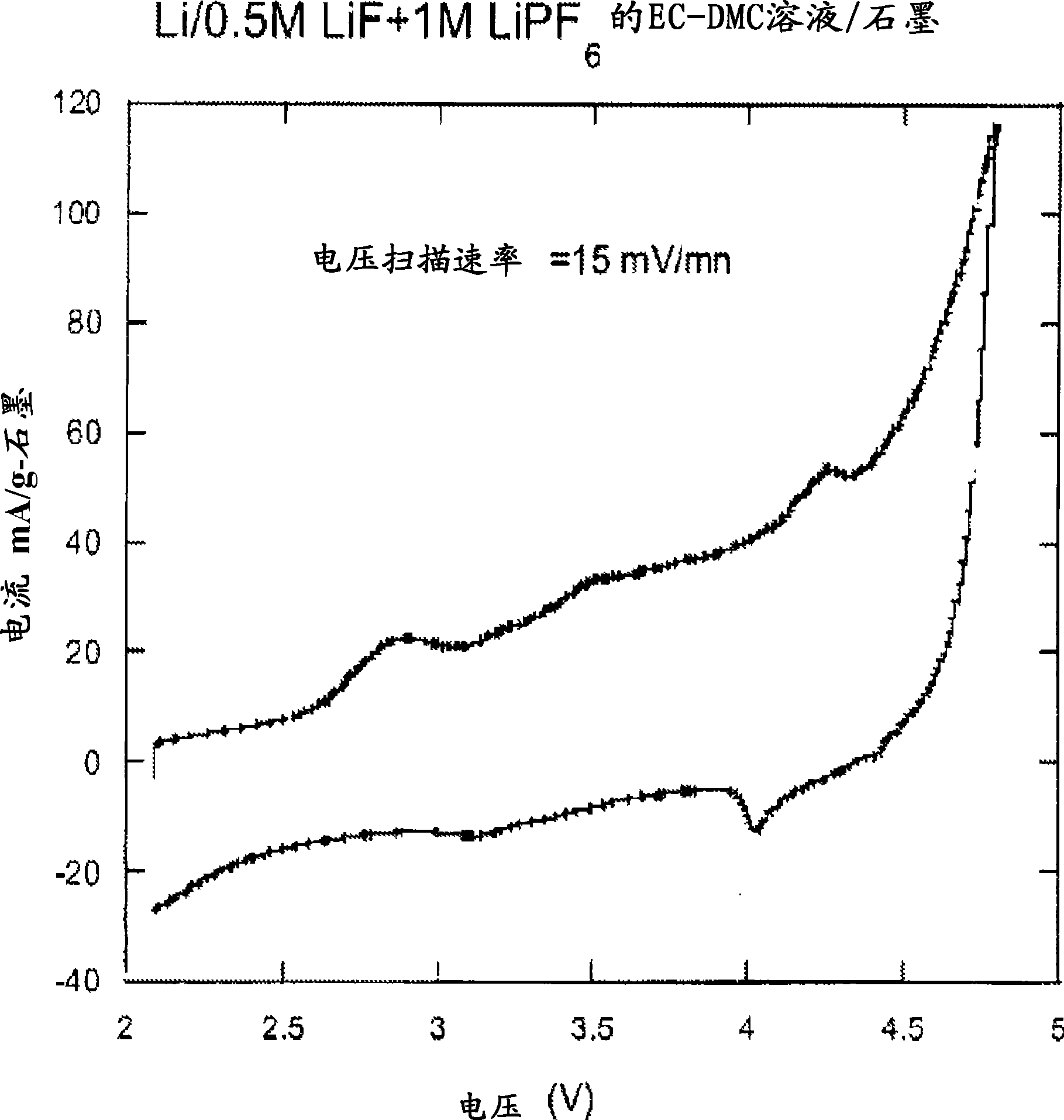
ActiveUS20080171268A1Improve solubilityEnhanced solubility of fluorideCell electrodesOrganic electrolyte cellsSolubilityChemical reaction
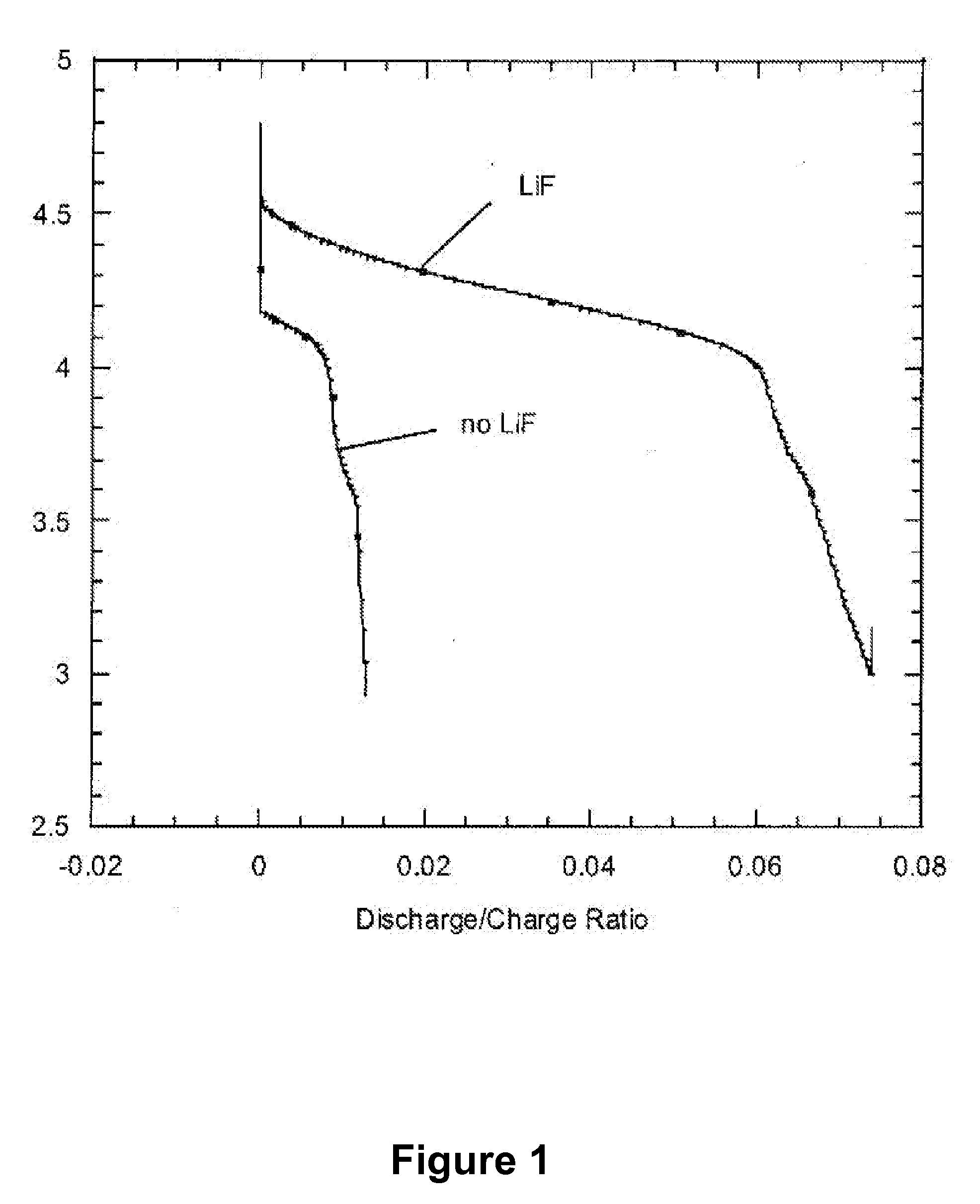
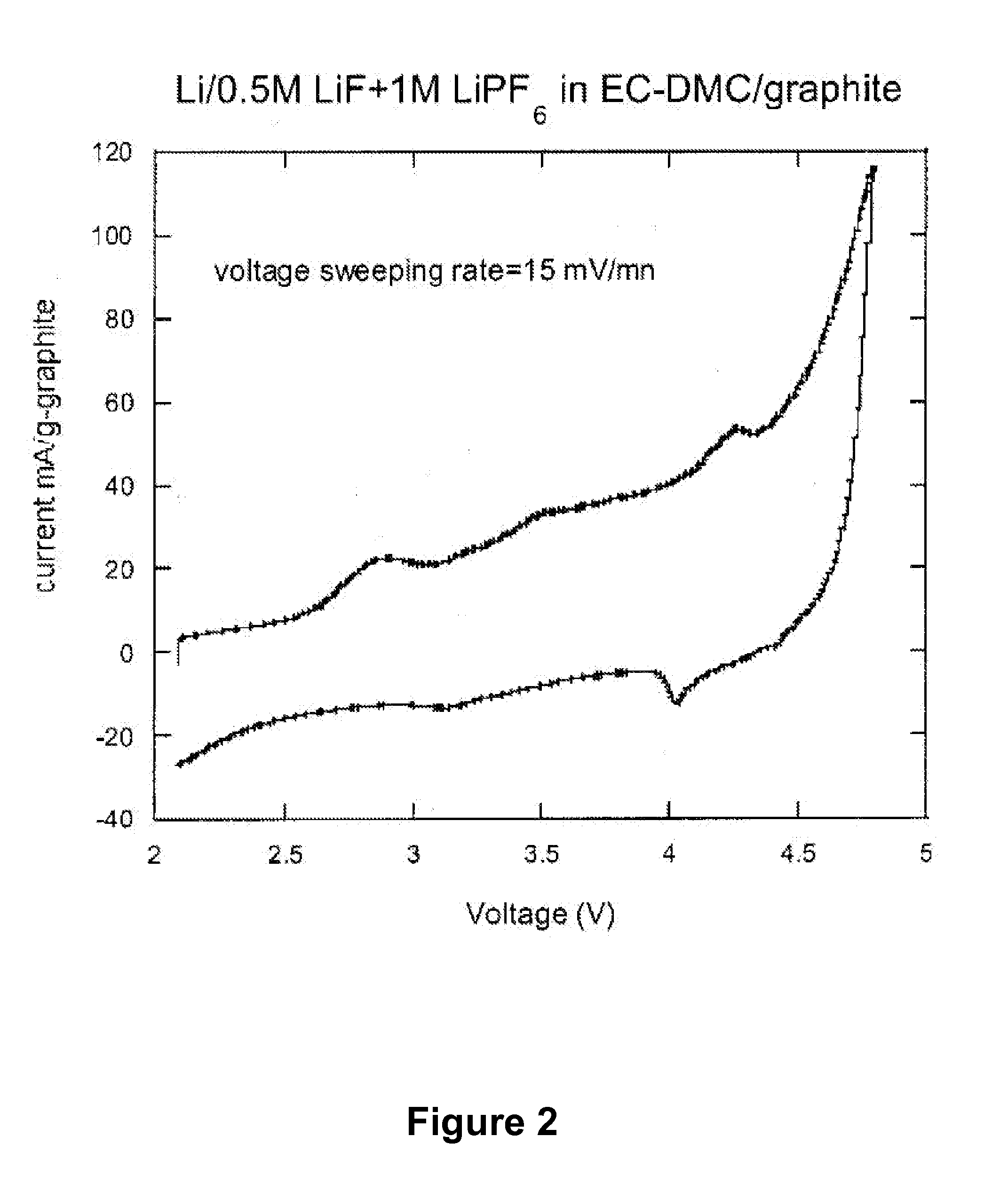
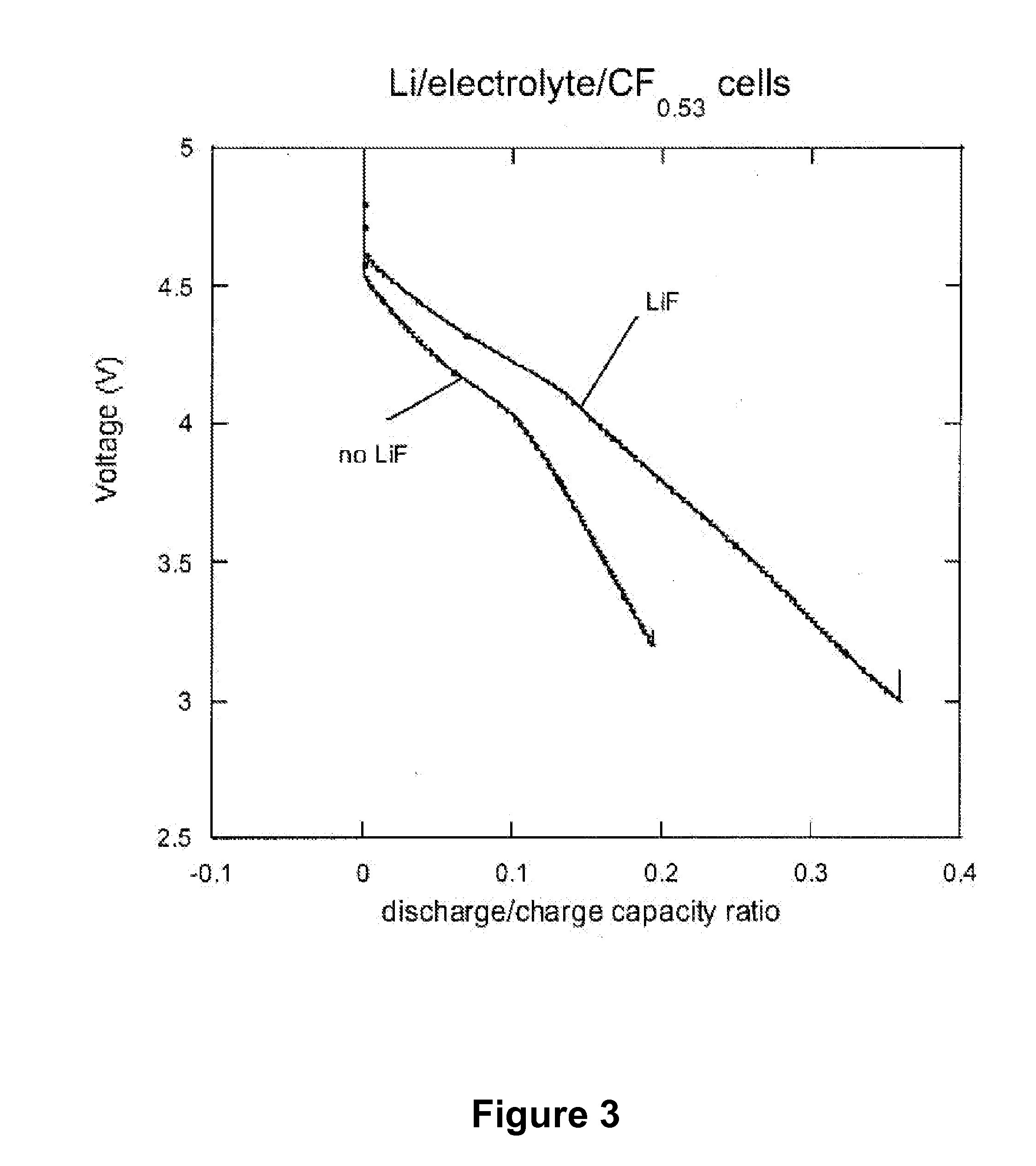
The present invention provides compositions, formulations and methods providing for the effective dissolution of inorganic fluorides in solvents via incorporation of a dissociating agent component. Dissociating agents of the present invention participate in chemical reactions in solution, such as complex formation, acid-base reactions, and adduct formation reactions, that result in enhancement in the dissolution of inorganic fluorides in a range of solvent environments. Dissociating agents comprising Lewis acids, Lewis bases, anion receptors, cation receptors or combinations thereof are provided that significantly increase the extent of dissolution of a range of inorganic fluorides, particularly inorganic fluorides, such as LiF, that are highly insoluble in many solvents in the absence of the dissociating agents of the present invention.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
High strength cement, mortar and concrete including industrial by-products
Cementitious compositions in which the cementitious properties of fly-ash are carefully controlled. The cementitious compositions may be substantially free harsh acids and bases such as citric acids (≈pH 2.2) and alkali metal activators including alkali hydroxides (≈pH 12-14) and metal carbonates (≈pH 11.6). The use of these harsh chemicals creates acid base reactions during use of the products. Instead of these harsh chemicals, a citric salt, for example potassium citrate, may be used as a reaction accelerator. Boric compounds may be used as a retarder in the compositions.
Owner:SECURED NOTEHOLDERS LLC
Microbial detection and quantification
InactiveUS7399608B2Increase brightnessGood colorBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismOxidation-Reduction Agent
A method for semi-quantitatively or quantitatively detecting the presence of a microbe in a sample is provided. The method utilizes a test dye that undergoes a detectable color change in the presence of one or more microbes. For example, in one embodiment, the test dye is a solvatochromic dye (e.g., Reichardt's dye) that responds to differences in polarity between microbe components (e.g., cell membrane, cytoplasm, etc.) and the environment outside the cell. Alternatively, other mechanisms may be wholly or partially responsible for the interaction between the dye and the microbe, such as acid-base reactions, redox reactions, and so forth. Regardless, the color of the test dye may be compared to the color of a control dye, wherein the color of the control dye corresponds to a known microbe concentration.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Method for preparing silica aerogel under atmospheric pressure and prepared silica aerogel
The invention provides a method for preparing silica aerogel under atmospheric pressure and the prepared silica aerogel. The method comprises the following steps: (1) diluting an inorganic silicon source with water, and then mixing the diluted inorganic silicon source with an acid to carry out an acid-base reaction to obtain silicic acid sol; (2) gelling the silicic acid sol, and conducting aging treatment on the formed gel to obtain a wet gel; (3) adding modifier base fluid to the wet gel to completely infiltrate the wet gel; then adding a concentrated acid or concentrated alkali solution to the system; and conducting surface modification treatment under an airtight condition or in an installation with a condensing reflux device until the gel is completely modified from hydrophilicity to hydrophobicity; and (4) conducting drying treatment on the modified aerogel obtained in the step (3) to obtain the silica aerogel. The method also comprises a step of adding a polar organic solvent or a polar organic solvent aqueous solution to the silicic acid sol obtained in the step (1), and / or to the system before addition of the concentrated acid or concentrated alkali solution in the step (3).
Owner:ECONANO TECH LTD BEIJING
High-purified cefmetazole sodium compound
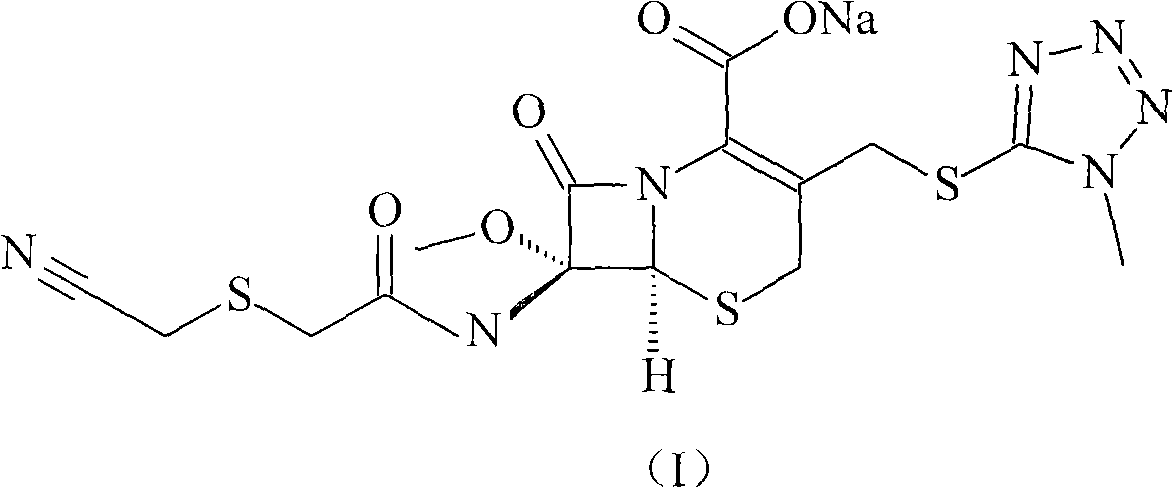
The invention provides a cefmetazole sodium compound, which is highly purified and finally obtained by the way of achieving the purification purpose through acid-base reaction, macroporous absorption resin and activated carbon adsorption, thus optimizing the quality of preparation products and the safety of clinical medication.
Owner:HAINAN LINGKANG PHARMA CO LTD
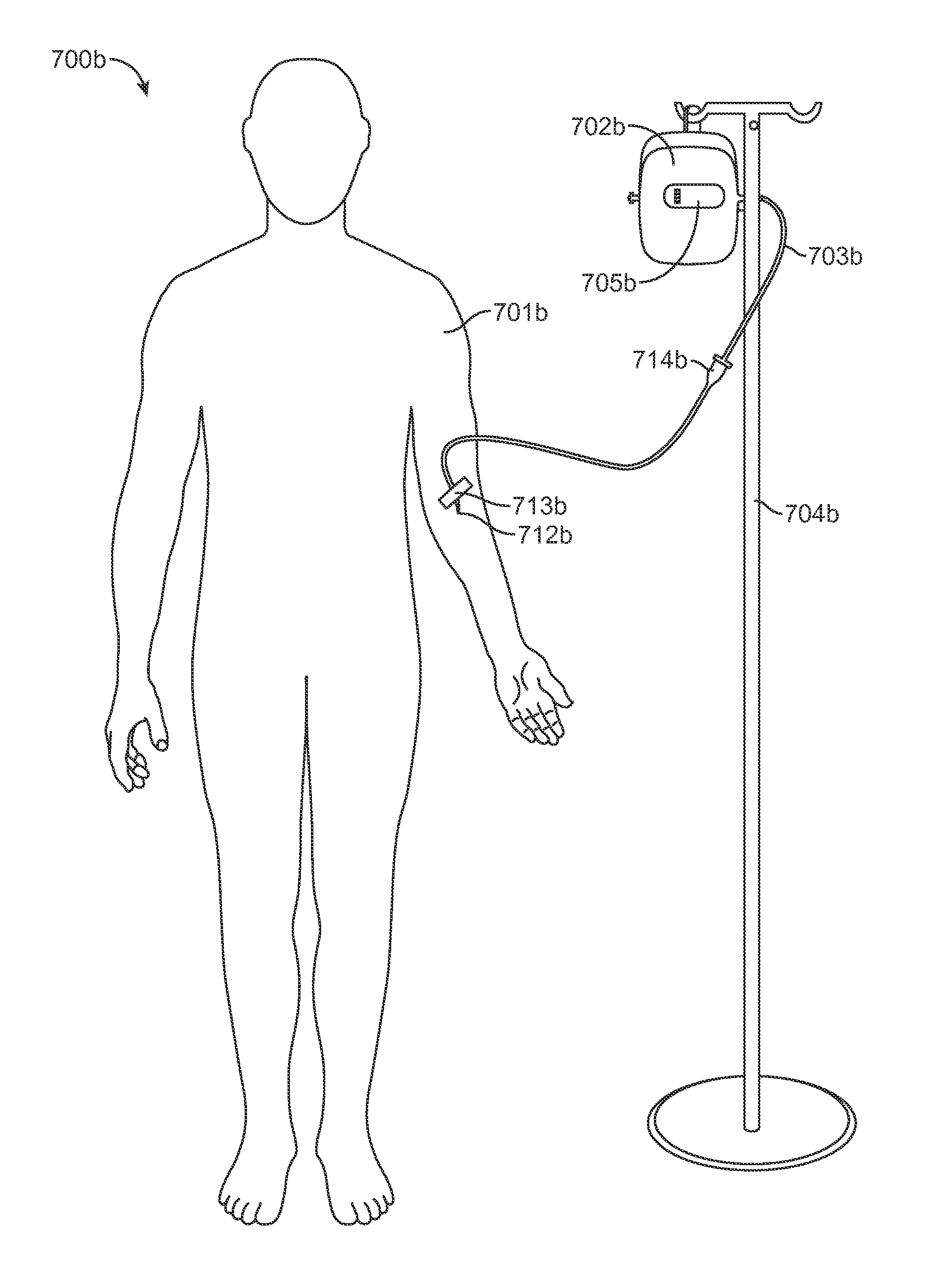
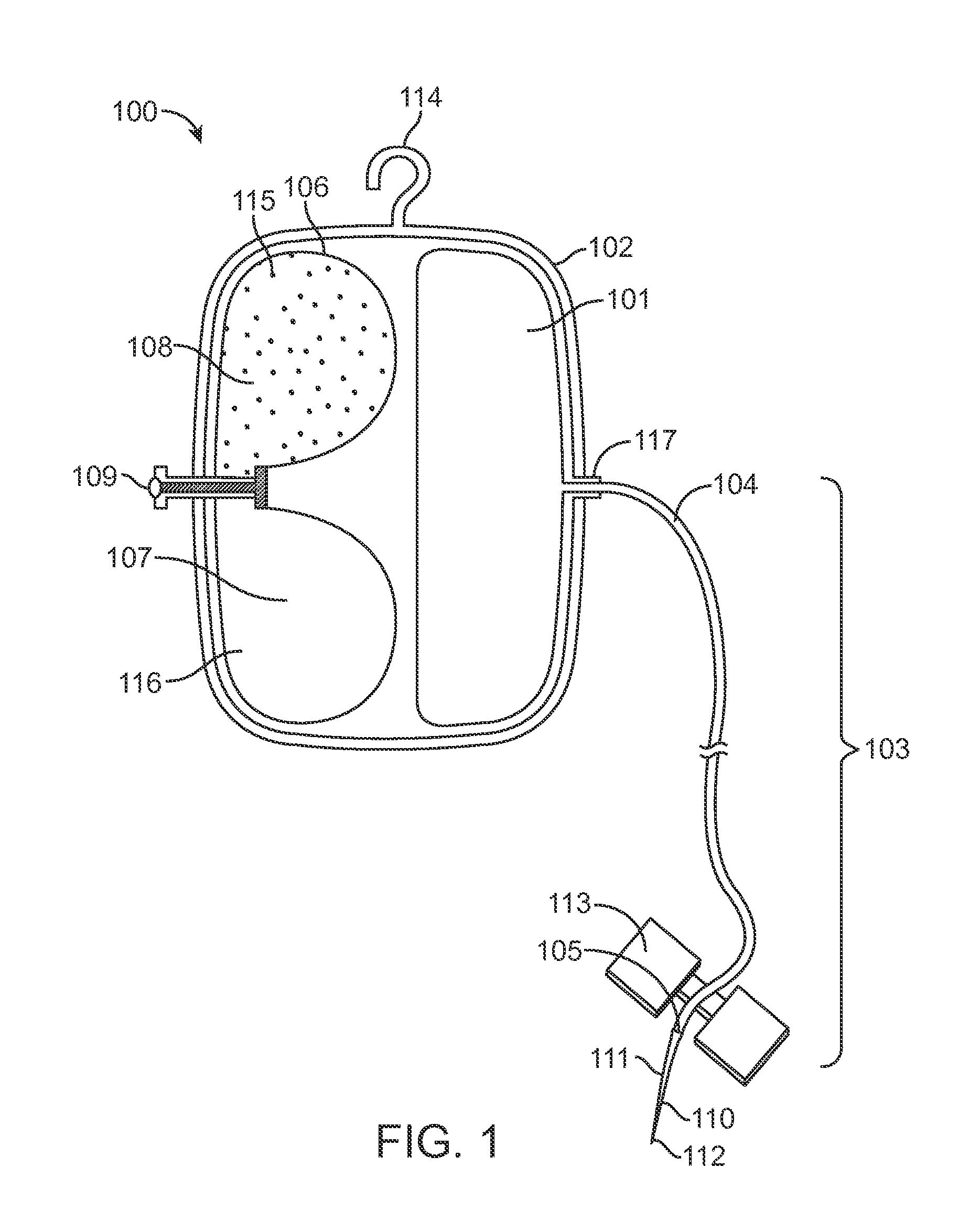
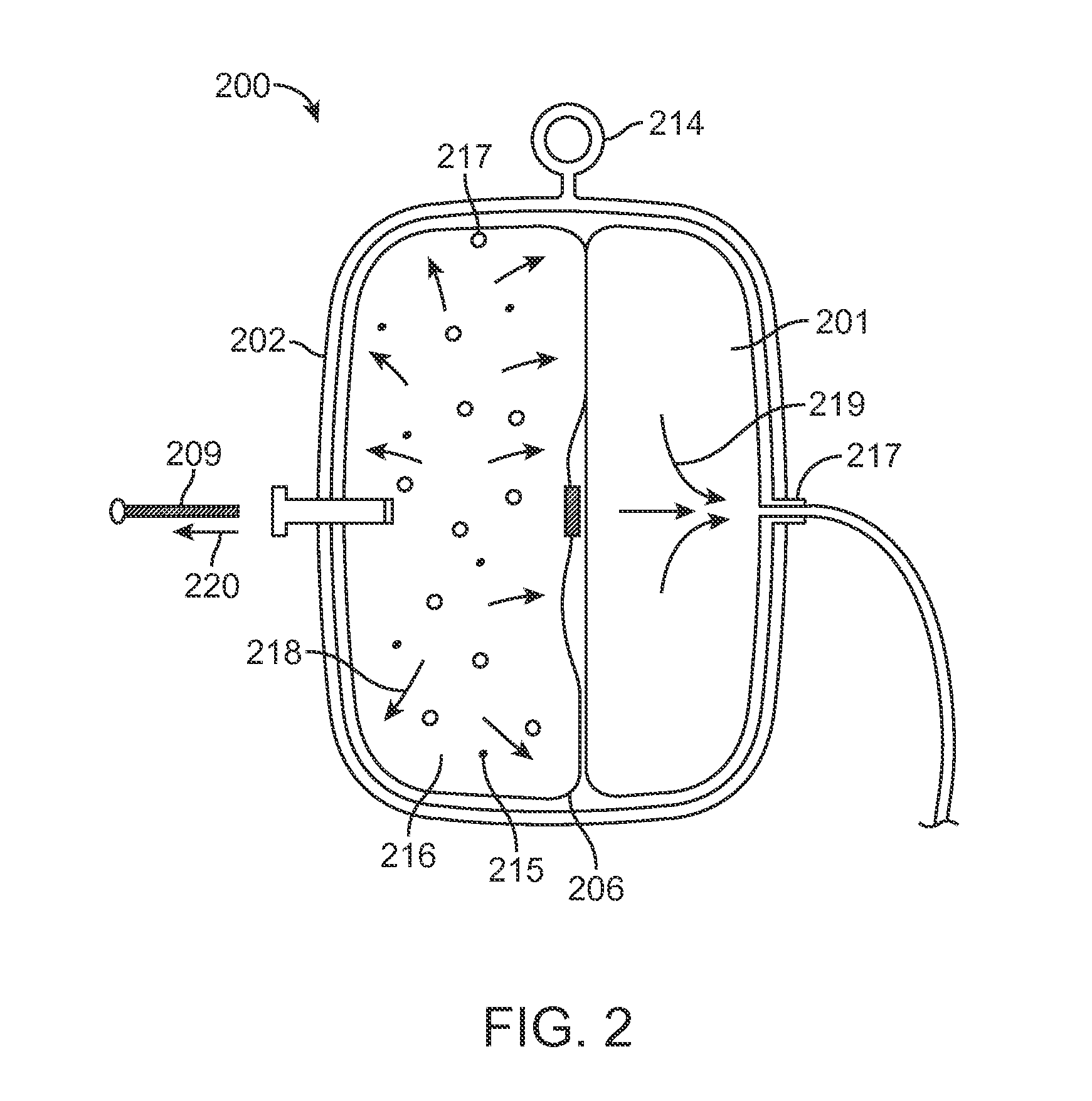
Infusion System for the Controlled Delivery of Therapeutic Agents
ActiveUS20140276587A1Extended shelf lifeKeep sterileMedical devicesPressure infusionDrug reservoirChemical reaction
Embodiments of the invention provide infusion systems for the intravenous or other delivery of drugs and other therapeutic agents to a patient including a human or mammal. The therapeutic agents may be dissolved in solution or comprise the solution itself. Embodiments of the systems can utilize a chemical reaction to predictably drive a flow of drug(s) through a catheter or other flow path and into the patient. More specifically, the reaction may include an acid-base reaction or any other reaction that produces a gaseous substance. The gas is produced and contained in an expandable drive balloon when the acid-base reactants are combined with a liquid. As the gas is produced, the drive balloon expands to exert pressure on a separately-contained drug reservoir which, in turn, pushes drug(s) from the reservoir into the flow path where the drug is ultimately delivered to the patient in a controlled and predetermined manner.
Owner:INCUBE LABS
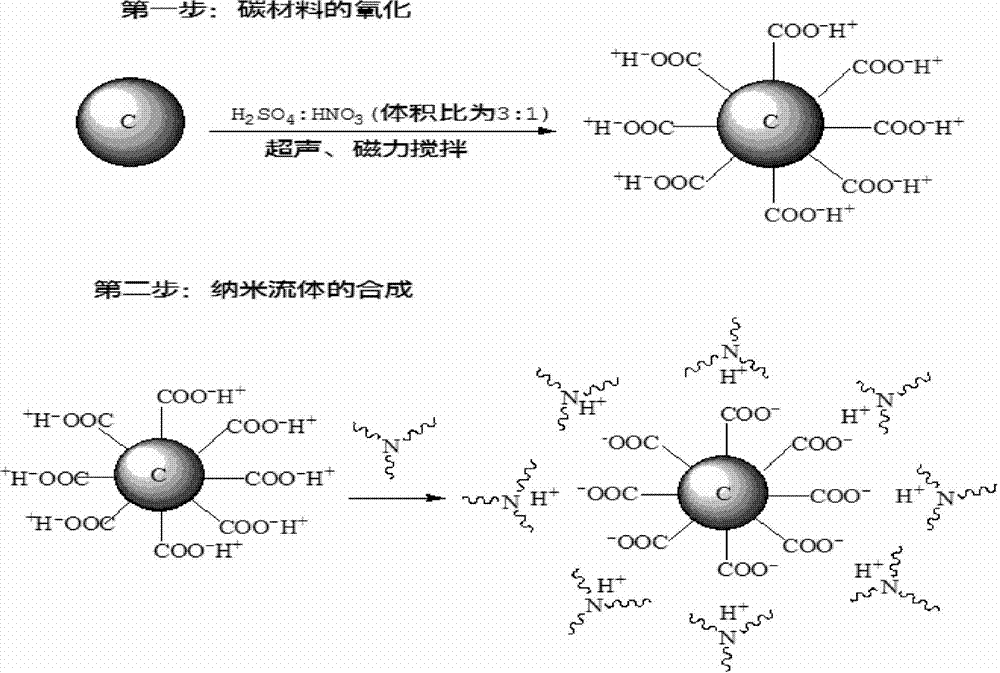
Preparation method for nanocarbon fluid
InactiveCN102924751AIncrease -COOH contentHigh grafting rateFibre treatmentCoatingsCarbon oxideAcid–base reaction
The invention relates to a preparation method for a novel nanocarbon fluid. The method comprises the following steps: adding the original nanocarbon material into strongly acidic oxidation liquid (the volume ratio of concentrated sulfuric acid to concentrated nitric acid is 3:1) to obtain an active carbon oxide material with the surface containing -COOH; adding amino-containing polyether amine serving as a modifier into the suspension liquid of the active carbon oxide material under the conditions of ultrasonic and magnetic stirring, performing acid-base reaction on the amino and carboxyl on the interface of the polyether amine and the carbon oxide material and grafting the polyether amine and the carbon oxide; and adjusting the type and the using amount of the polyether amine to obtain the nanocarbon fluid. The method is simple, effectively controls and increases the grafting ratio of the polyether amine on the surface of the nanocarbon material and is applicable to synthesis of various carbon material fluids. The nanocarbon fluid material prepared by the method has hydrophilicity, lipophilicity and good application prospect in aspects of coating, plastic, rubber, functional materials and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
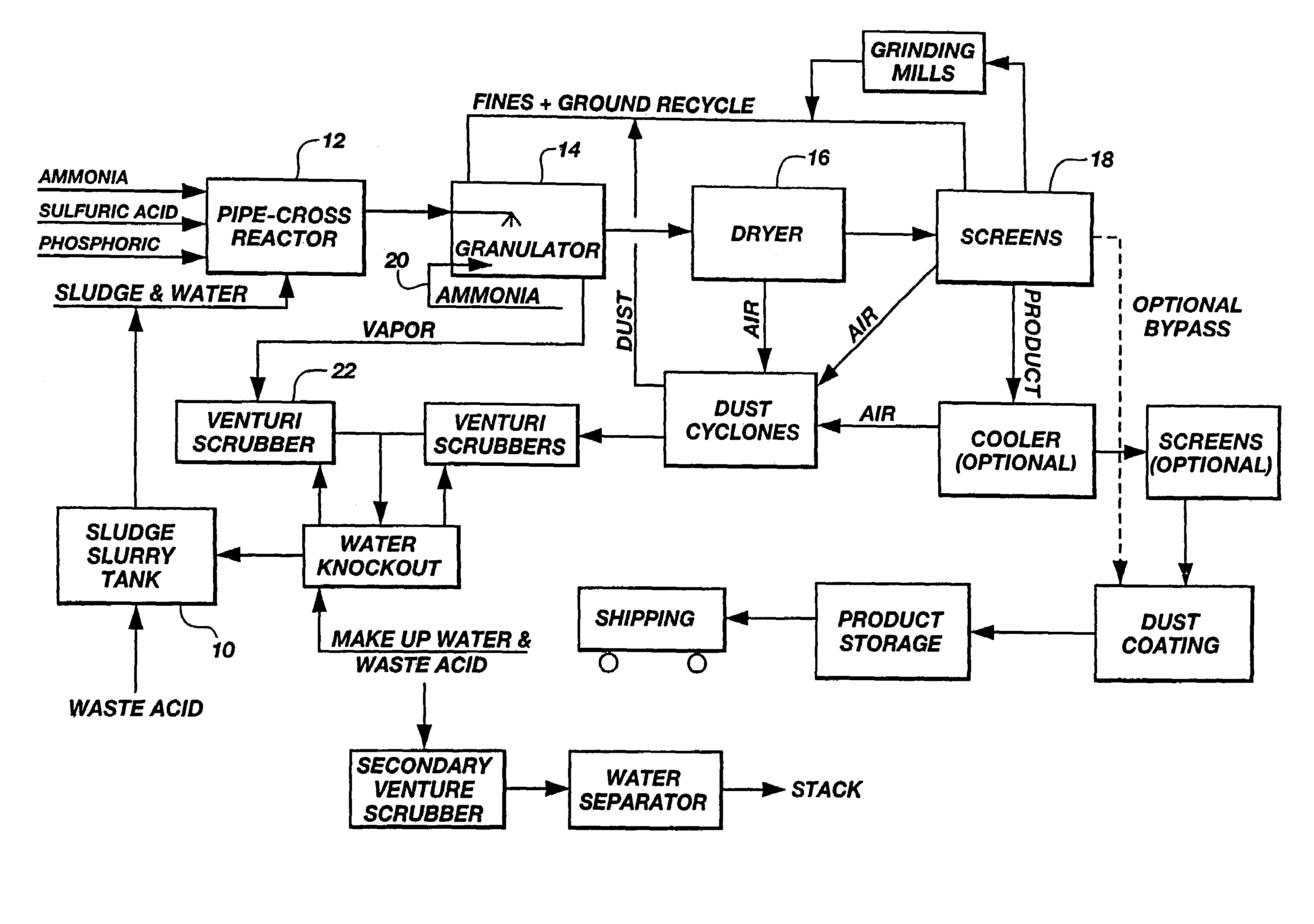
Sewage sludge recycling with a pipe cross-reactor
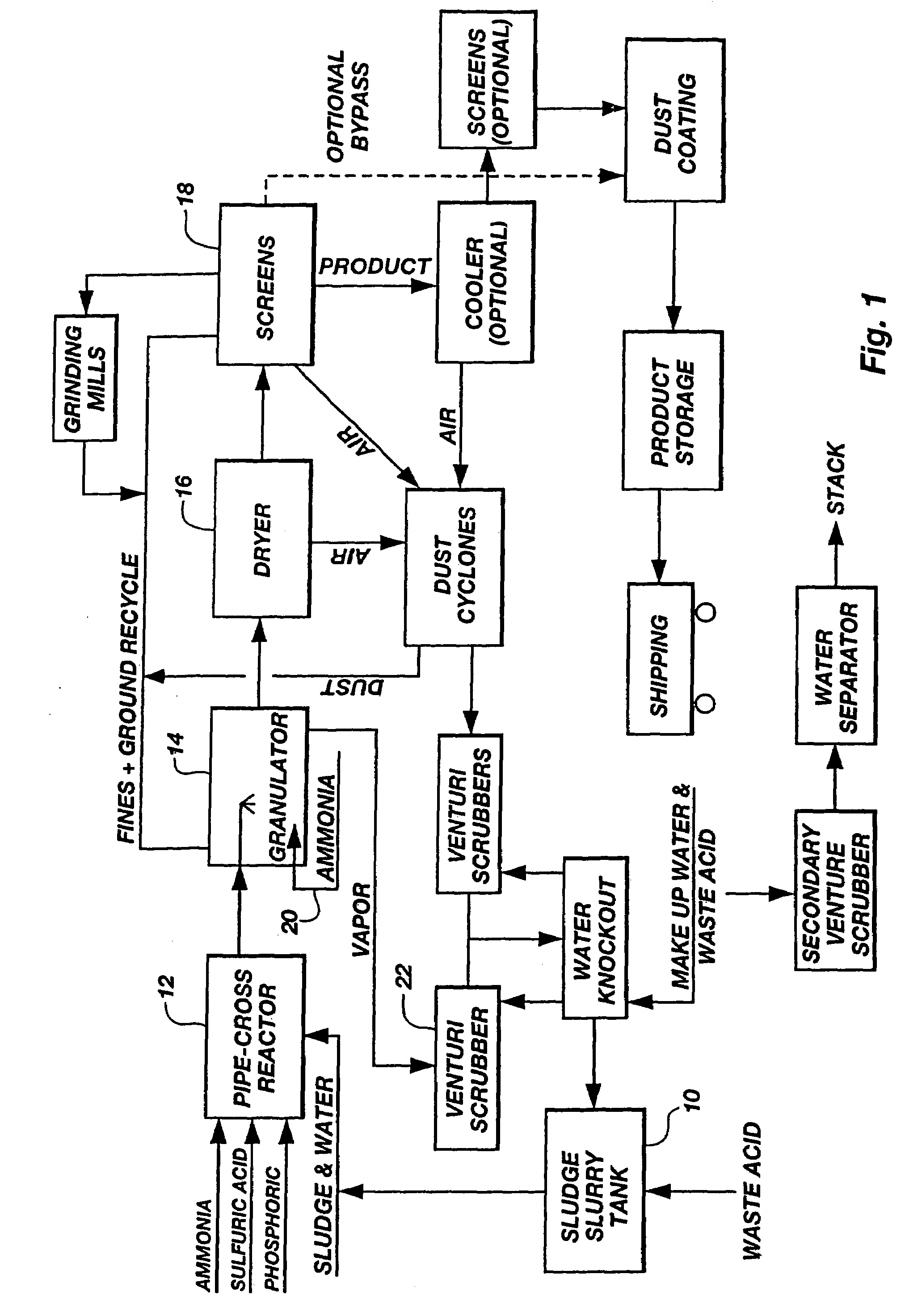
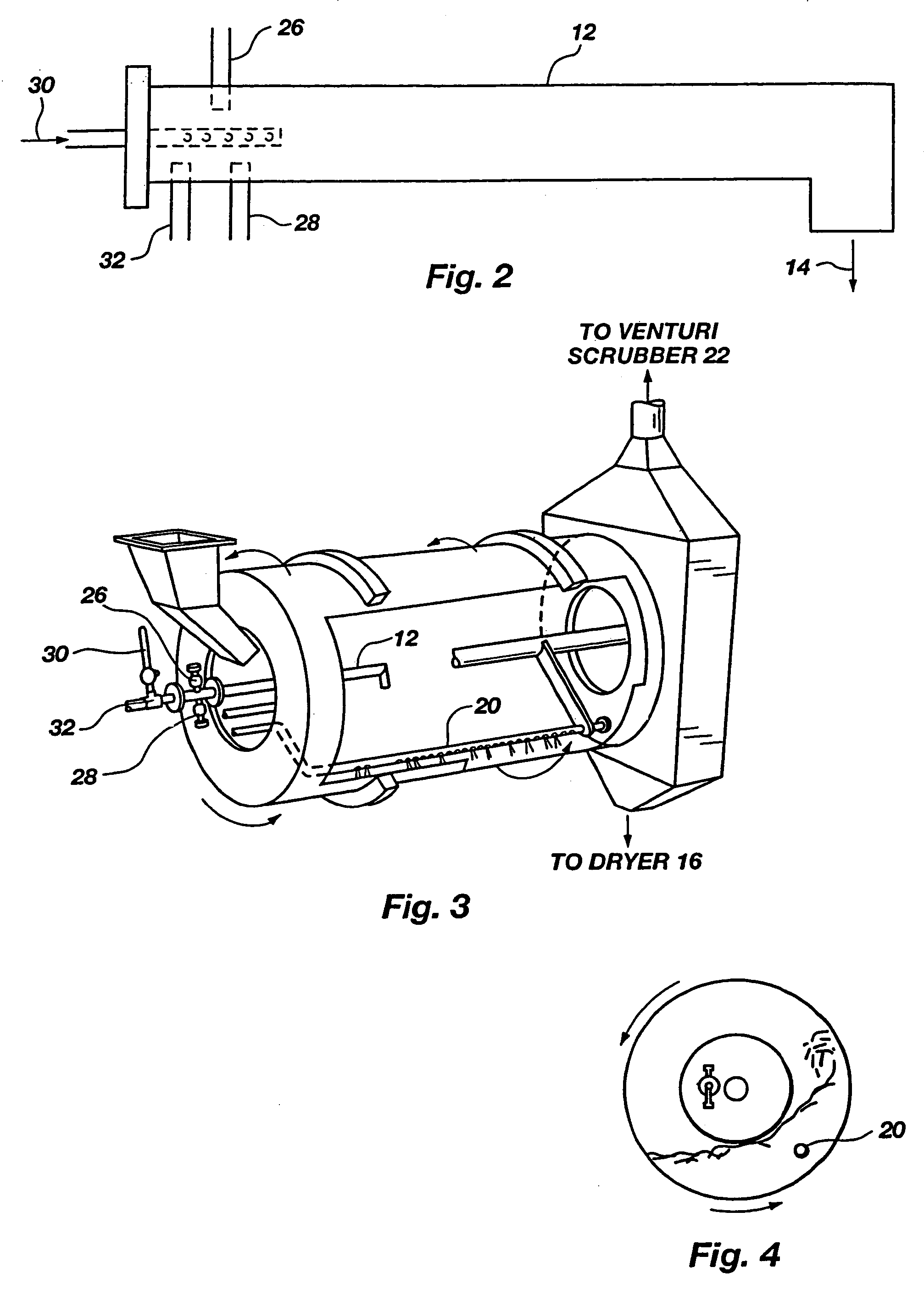
InactiveUS7169204B2Increase valueReduce moisture contentBio-organic fraction processingSludge treatmentSludgeVolumetric Mass Density
An improved process for enhancing the plant nutrient value of relatively low analysis organic waste material (e.g., sewage sludge) involves treating the waste material with an acid and base in a pipe-cross reactor. The process more particularly involves mixing the waste material with water to form a slurry (or initially taking the waste material as a slurry); pumping the slurry to a pipe-cross reactor for reaction with a base, acid, and water to form a melt; spraying the melt onto a recycling bed of fines in a granulator, and flashing off the water contained in the melt as steam; rolling the melt onto recycled fine particles in a granulator to form granulated particles; and drying these granulated particles to form an enhanced plant nutrient value composition (e.g., a fertilizer or soil conditioner having a greater “NPK” value than the original relatively low analysis organic waste material). The invention also includes fertilizers produced according to the improved process, which fertilizers are of the same size and shape and density of commonly used fertilizers. The method advantageously utilizes the heat generated by the exothermic acid-base reaction in the pipe-cross reactor to remove the approximately 80% water from sludge, thus saving large amounts of energy normally used in conventional drying or burning methods, while, at the same time, conserving the intrinsic values of the nutrients and humates contained in the sludge. In one embodiment, the process includes a method of disposing of spent acid from a hot dip galvanizing process or a steel pickling process involving incorporating the spent acid to maintain the low pH of a venturi scrubber used in the improved process.
Owner:UNITY FERTILIZER LLC
Micro-calorimetric method suitable for quickly detecting total amount of microorganisms in food
InactiveCN101592624AEasy to detectDetection is practicalMaterial heat developmentMicroorganismChemical reaction
The invention relates to a micro-calorimetric method suitable for quickly detecting total amount of microorganisms in food, which changes microorganism growth heat release into acid-base reaction heat release, and comprises the following steps: 1) detecting CO2 released by thalli growth instead of detecting thalli growth heat, and using the CO2 to perform acid-base chemical reaction with alkali liquor to release heat; and 2) neutralizing the residual alkali liquor in a Micro DSCIII sample cell and a reference cell with acid, wherein the alkali liquor in the reference cell is not neutralized by the CO2 so that the released heat is bound to be more than the heat of the sample cell, and the difference of the two heat values is the amount of the consumed alkali, thus the amount of the CO2 consumed by the consumed alkali can be calculated, and the amount of the microorganisms contained in a sample can be calculated according to a standard curve for measuring the total amount of bacteria. The micro-calorimetric method used for detecting the total amount of the microorganisms greatly improves the detection sensibility, shortens the detection time, and is applicable to detecting the total number of the microorganism through a calorimetric method.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Dissociating agents, formulations and methods providing enhanced solubility of fluorides
The present invention provides compositions, formulations and methods providing for the effective dissolution of inorganic fluorides in solvents via incorporation of a dissociating agent component. Dissociating agents of the present invention participate in chemical reactions in solution, such as complex formation, acid-base reactions, and adduct formation reactions, that result in enhancement in the dissolution of inorganic fluorides in a range of solvent environments. Dissociating agents comprising Lewis acids, Lewis bases, anion receptors, cation receptors or combinations thereof are provided that significantly increase the extent of dissolution of a range of inorganic fluorides, particularly inorganic fluorides, such as LiF, that are highly insoluble in many solvents in the absence of the dissociating agents of the present invention.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Lactobacillus effervescent tablet and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101496821AIncrease the effective contact rangeReduce usageBacteria material medical ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismSodium bicarbonateIn vivo
The invention discloses a lactobacillus effervescent tablet, which is prepared from 1 to 15 portions of lactobacillus powder, 20 to 50 portions of auxiliary materials, 10 to 30 portions of acid sources, 11 to 30 portions of sodium bicarbonate, 2 to 35 portions of disintegrating agent and 0.2 to 2.5 portions of lubricant. The effervescent tablet transmits lactobacillus to various parts of the uterus after effervescence through an acid-base reaction, increases the effective contact range of the lactobacillus and the uterus, makes a larger area of the lactobacillus adsorbed and set by a mucous membrane of the uterus, avoids the use of ointment, a suppository and a liquid preparation, overcomes the defect that the medicine can be only sent to the bottom and the side wall of the uterus, and not only achieves the aims of treatment and prevention but also reduces in vivo antibiotic residue.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
High-purity cefmenoxime hydrochloride compound
InactiveCN101798314AHigh purityImprove product qualityOrganic chemistryActivated carbonChromatographic separation
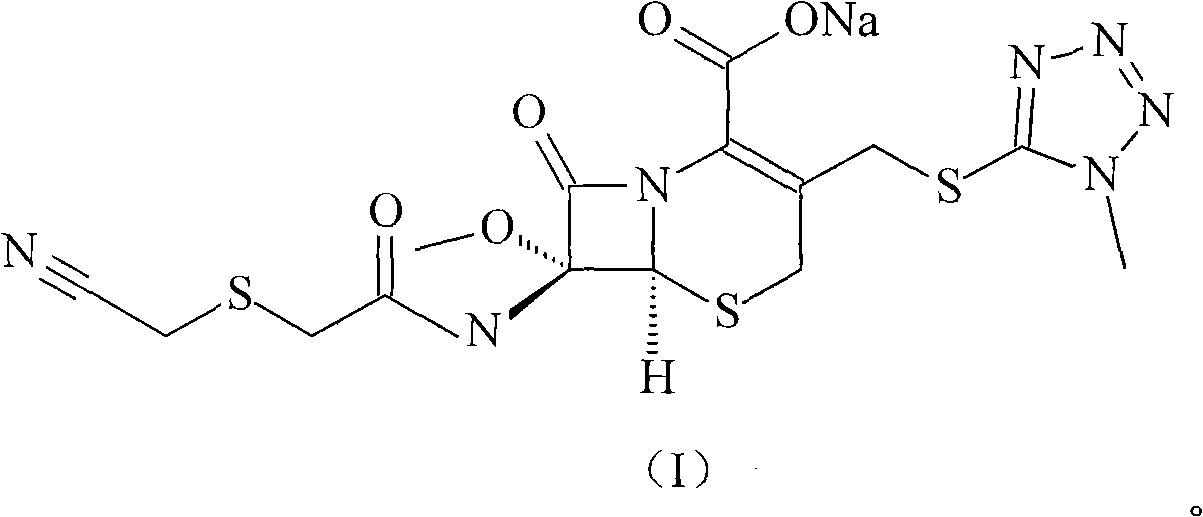
The invention relates to a cefmenoxime hydrochloride compound, which is prepared through acid-base reaction, activated carbon adsorption, separation and purification of prepared chromatography so as to achieve the aim of purification and obtain the high-purity cefmenoxime hydrochloride compound finally. The invention optimizes the product quality, and guarantees safety of clinical medication.
Owner:HAINAN LINGKANG PHARMA CO LTD
Detection of microbe contamination on elastomeric articles
ActiveUS7300770B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismOxidation-Reduction Agent
An elastomeric article that contains a chromogen that undergoes a detectable change in color in the presence of one or more microbes is provided. For example, in one embodiment, the chromogen is a solvatochromic dye (e.g., Reichardt's dye) that undergoes a color change in the presence of bacteria or other microbes. More specifically, such dyes may respond to differences in polarity between microbe components (e.g., cell membrane, cytoplasm, etc.) and the environment outside the cell. Alternatively, other mechanisms may be wholly or partially responsible for the interaction between the dye and the microbe, such as acid-base reactions, redox reactions, and so forth.
Owner:O&M HALYARD INC
Preparation method of onium hydroxide
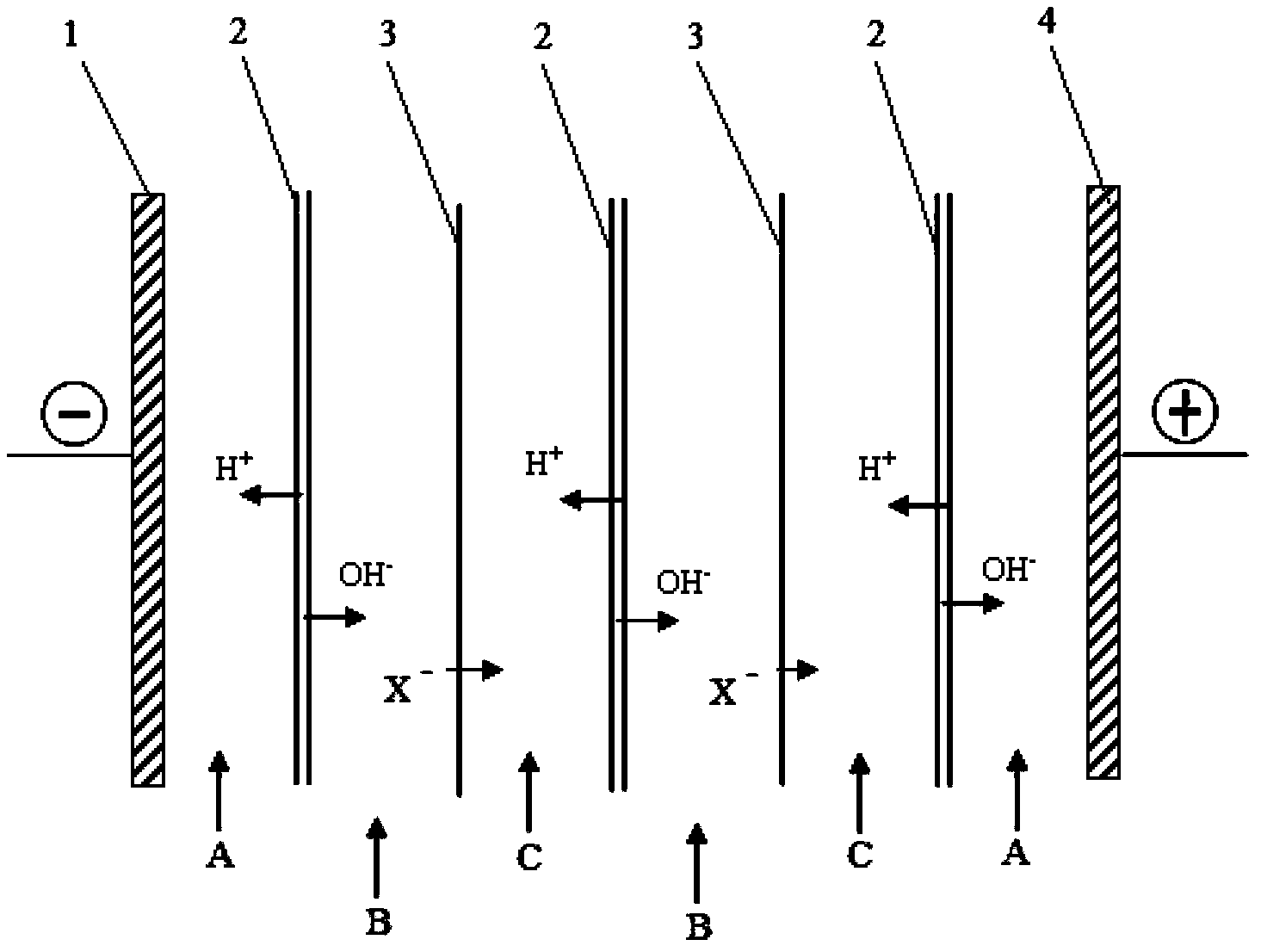
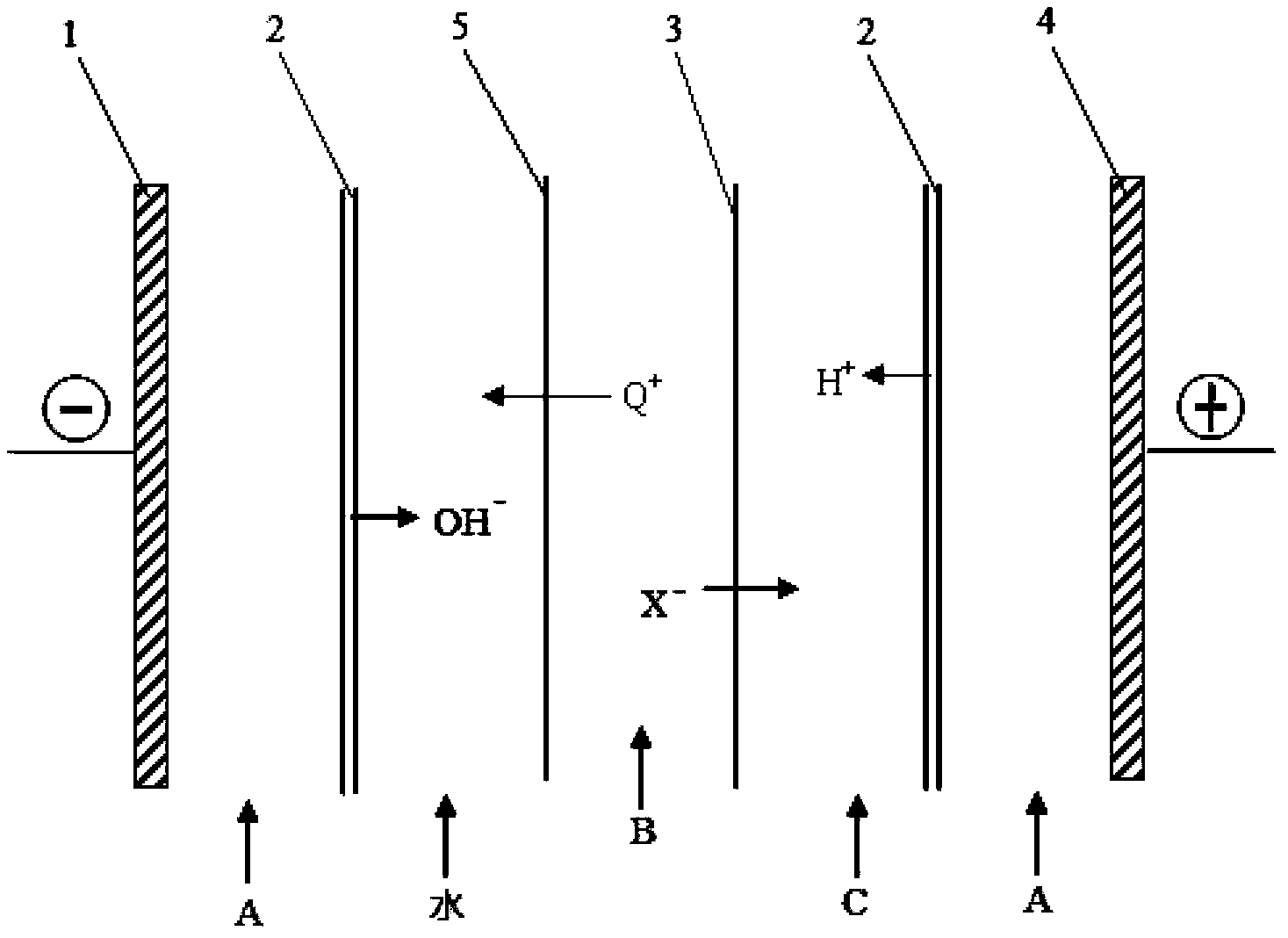
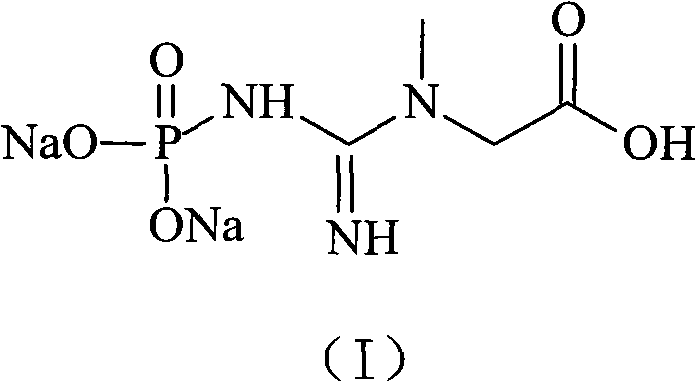
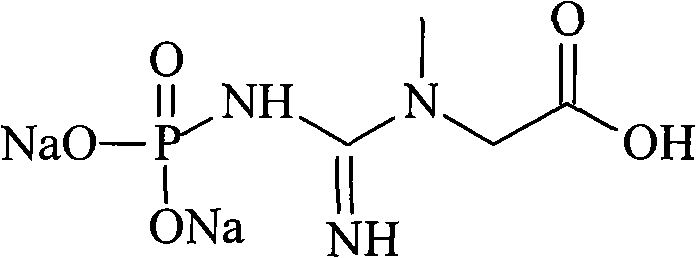
ActiveCN104292114ALong continuous running timeHigh puritySemi-permeable membranesAmino preparation from aminesAcid–base reactionAqueous solution
The invention provides a preparation method of an onium hydroxide represented by formula I. The method comprises the following steps: sending an aqueous solution of onium salt represented by formula II into a bipolar membrane electrodialysis apparatus, and carrying out bipolar membrane electrodialysis to obtain an aqueous solution of the onium hydroxide represented by formula I, wherein a neutralizing liquid is sent into the acid chamber of the bipolar membrane electrodialysis apparatus, and contains a substance, and the substance and HX undergo an acid-base reaction. The preparation method of the onium hydroxide has the advantages of long continuous running time of the bipolar membrane electrodialysis apparatus, production cost reduction and production efficiency increase. The onium hydroxide prepared through the method has purity and good quality.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DAYOU FINE CHEM PLANT
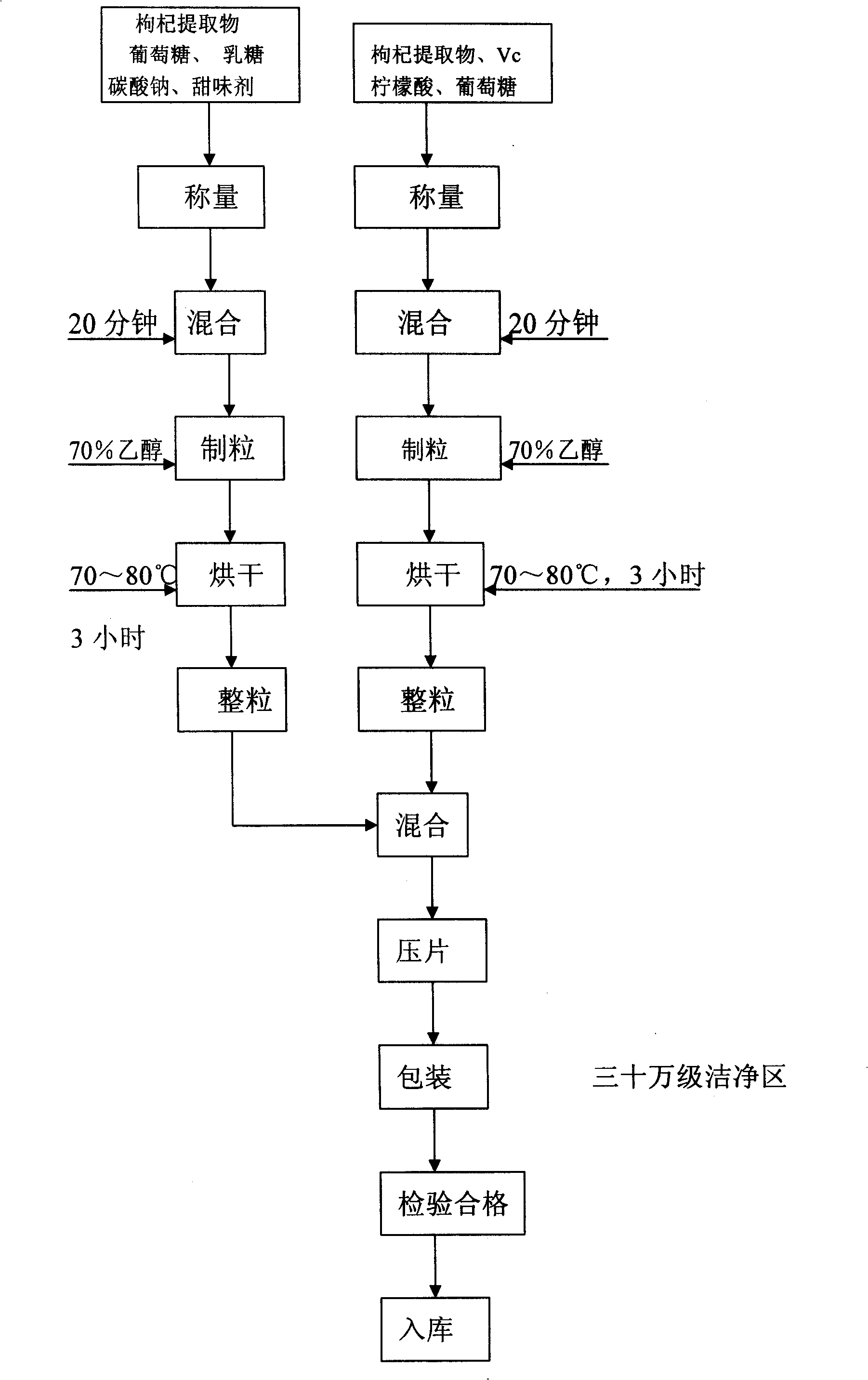
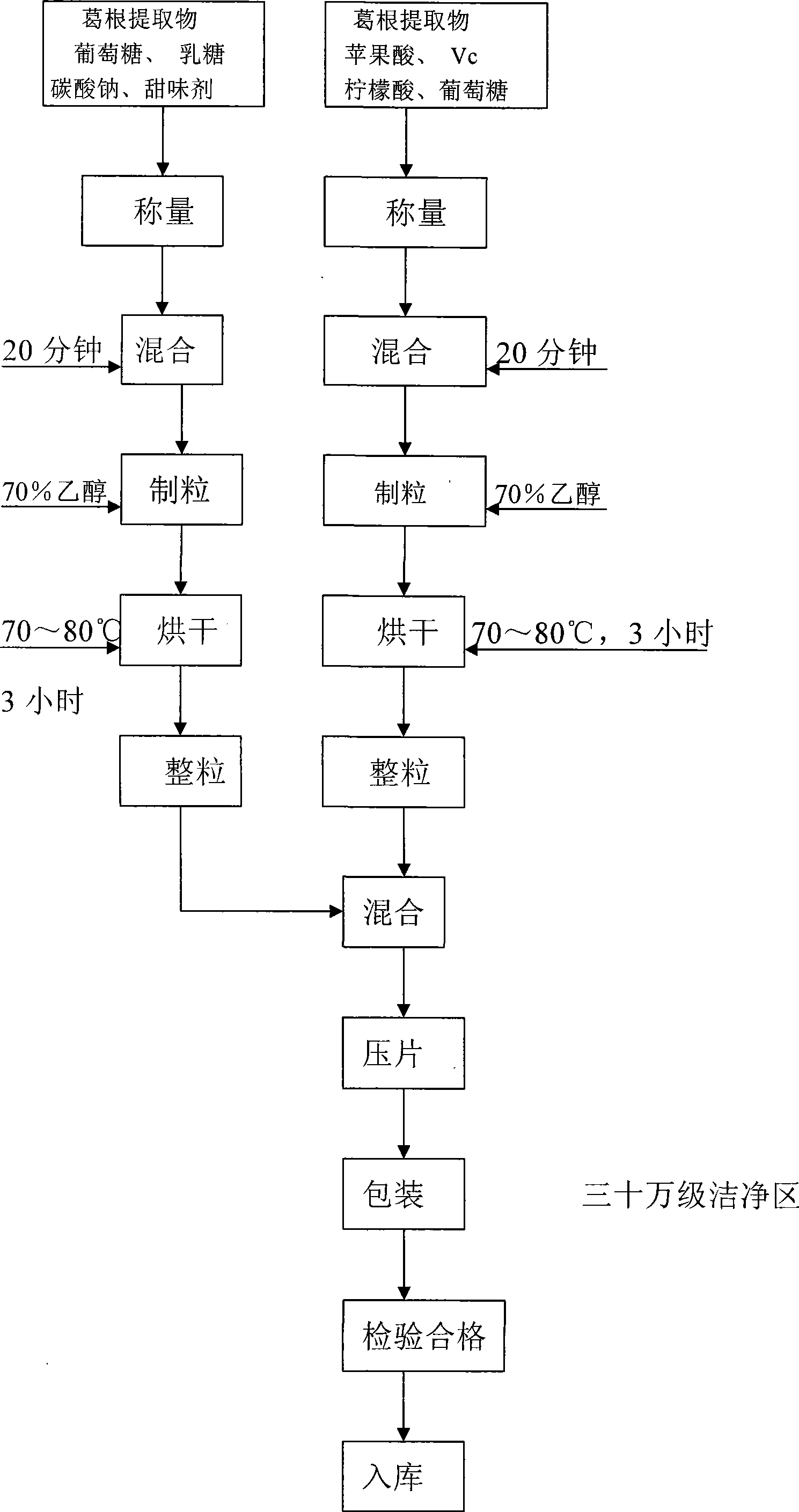
Medlar nutrient effervescence decoction pieces and process for producing the same
InactiveCN101352255AChange hard to swallowPromote absorptionFood preparationVitamin CAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a medlar product and a production process of a medlar nutritious effervescent tablet thereof. A medlar extract is taken as a main component of the medlar nutritious effervescent tablet. The effervescing agent is made by mixing and tabletting alkaline particles and acid particles. The alkaline particles are made from the medlar extract, sodium carbonate, lactose, glucose and a sweetener. The acid particles are of the medlar extract, vitamin C, citric acid and glucose. The medlar nutritious effervescent tablet of the invention is immediately disintegrated into water solution by an acid-base reaction, therefore, people can easily take the tablet with good taste, and the people can enjoy drinking as well as can absorb more nutritious components.
Owner:刘洪生 +1
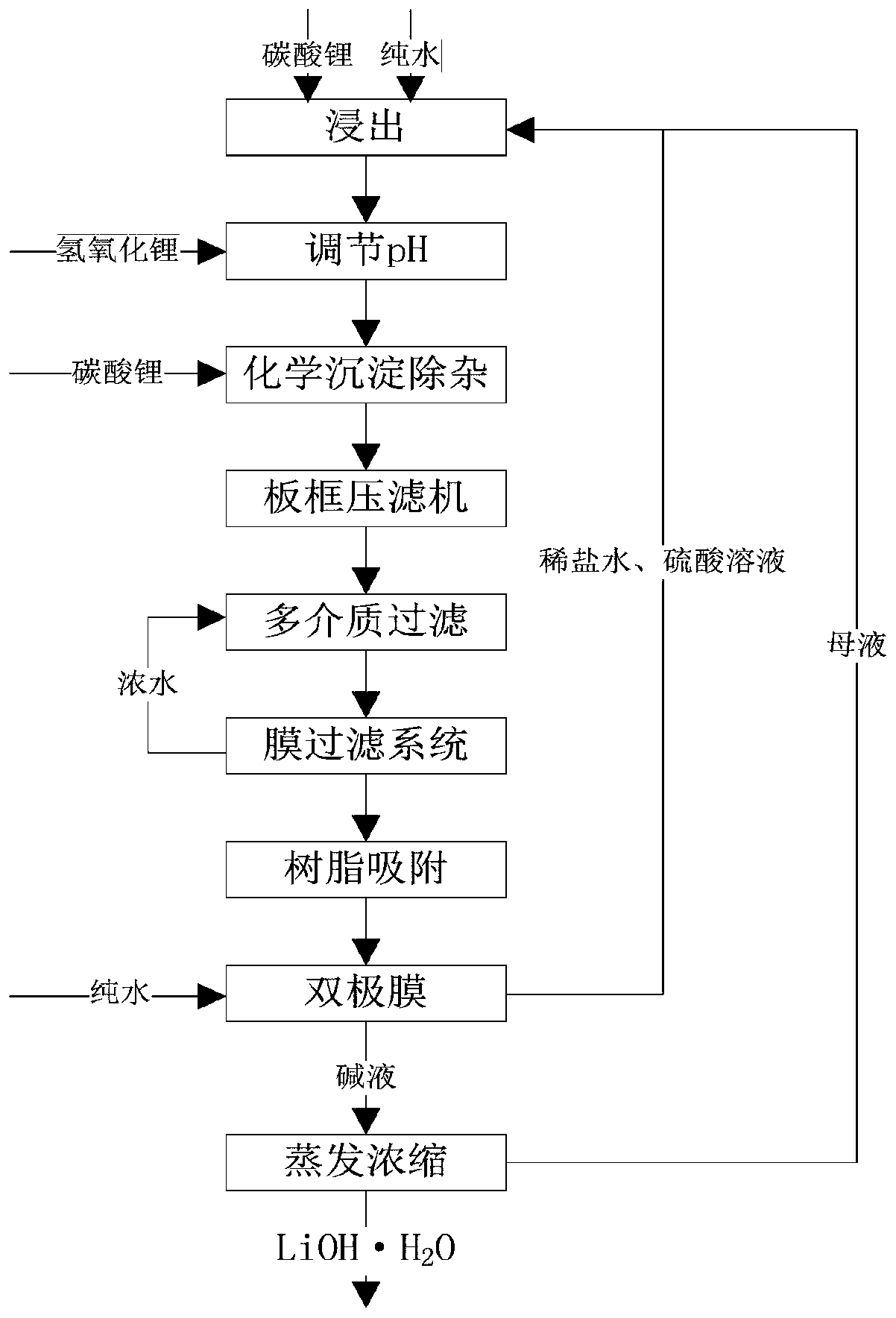
Method for preparing high-purity lithium hydroxide
ActiveCN109850927AHigh purityNo pollution in the processLithium oxides/hydroxidesFiltrationEvaporation
The invention discloses a method for preparing lithium hydroxide, which comprises the following steps: S1, dissolving raw lithium carbonate with sulfuric acid to obtain lithium sulfate solution; S2, using lithium hydroxide to regulate that pH of the solution to be 6.6-8.5; adding lithium carbonate to precipitate and filtering to obtain a first filtrate; S3, filtering by adopting a membrane filterdevice to obtain a second filtrate; S4, adopting resin adsorption to obtain resin adsorbed liquid; S5, adding water to dilute, and passing through a bipolar membrane to obtain dilute brine, acid waterand alkali water; the alkali water being a lithium hydroxide solution; S6, after evaporating and concentrating alkali water and crystallizing, obtaining the crystal being lithium hydroxide monohydrate, and the purity being more than 99wt%. A material liquid with extremely low impurity content is obtained by acid-base reaction precipitation impurity and multi-stage filtration treatment, membrane filtration and resin adsorption treatment using crude lithium carbonate as raw material, alkali water is obtained by bipolar membrane separation, and high-quality and high-purity lithium hydroxide is obtained by evaporation and concentration crystallization.
Owner:MEISHAN SHUNYING POWER BATTERY MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for producing single crystalline zinc oxide nanoparticles
ActiveUS20170130358A1Suitable for mass productionMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthAlcoholZinc nanoparticles
A method for producing single crystalline zinc oxide nanoparticles that is capable of mass production includes mixing, between processing surfaces which are disposed in a position facing each other so as to be able to approach and separate from each other and rotate relative to each other, a zinc oxide separating solvent prepared by homogeneously mixing an acidic substance with a solvent containing at least alcohol and a raw material solution obtained by mixing a zinc oxide nanoparticle raw material with a basic solvent or a raw material solution that is basic as a result of mixing and dissolving a zinc oxide nanoparticle raw material with and into a solvent, and discharging a mixed fluid in which zinc oxide nanoparticles have separated out from between the processing surfaces. The zinc oxide separating solvent and the raw material solution are mixed between the processing surfaces so that the mixed fluid becomes basic, and zinc oxide nanoparticles are generated by an acid-base reaction due to mixing of the acidic substance and the basic solvent.
Owner:M TECHN
Kudzu root nutrient effervescent tablets and manufacture technique thereof
InactiveCN101422271AChange hard to swallowPromote absorptionAntipyreticAnalgesicsVitamin CAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a kudzuvine root extract, in particular to a kudzuvine root nutrient effervescent tablet made by taking the kudzuvine root extract as a main raw material and a production technique thereof. The kudzuvine root nutrient effervescent tablet takes the kudzuvine root extract as a main component. The effervescent is made by mixing alkaline granule with acid granule for tablet making, wherein, the alkaline granule is made from the kudzuvine root extract, sodium carbonate, milk sugar, glucose and an edulcorator, and the acid granule is made from the kudzuvine root extract, vitamin C, malic acid, citric acid and glucose. The kudzuvine root nutrient effervescent tablet can quickly disintegrate into aqueous solution by taking use of acid-base reaction and therefore, when taking the tablet, the difficulty for swallowing the tablet by people is solved and the taste thereof is improved and the absorption of nutrient components is enhanced when people enjoy beverage.
Owner:刘洪生 +1
High-purity creatine phosphate sodium compound
InactiveCN101812088AHigh purityIncrease contentGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsActivated carbonChromatographic separation
The invention relates to a high-purity creatine phosphate sodium compound; by the acid-base reaction, the activated carbon adsorption and the preparation of chromatographic separation and purification, the purity and content of the creatine phosphate sodium is greatly increased, the product quality of the preparation is optimized and the safety of the clinical medication is guaranteed; and the method has simple technique, low cost and high yield and is suitable for industrialization production.
Owner:HAINAN MEIDA PHARMA
High-purified tropisetron hydrochloride compound
InactiveCN101787021AHigh purityImprove product qualityOrganic chemistryActivated carbonAcid–base reaction
The invention relates to a tropisetron hydrochloride compound. The purity of the tropisetron hydrochloride is greatly improved by acid-base reaction, activated carbon adsorption and separation and purification prepared chromatographic columns, thus optimizing the quality of preparation products and the safety of clinical medication. The method has simple process, low cost and high yield, and is applicable to industrial production.
Owner:HAINAN LINGKANG PHARMA CO LTD
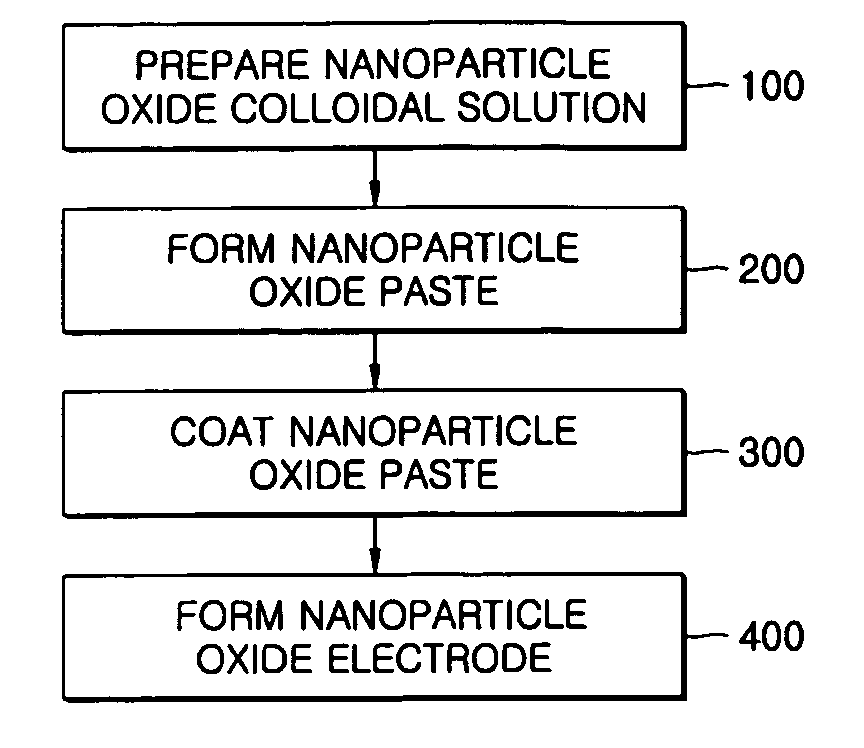
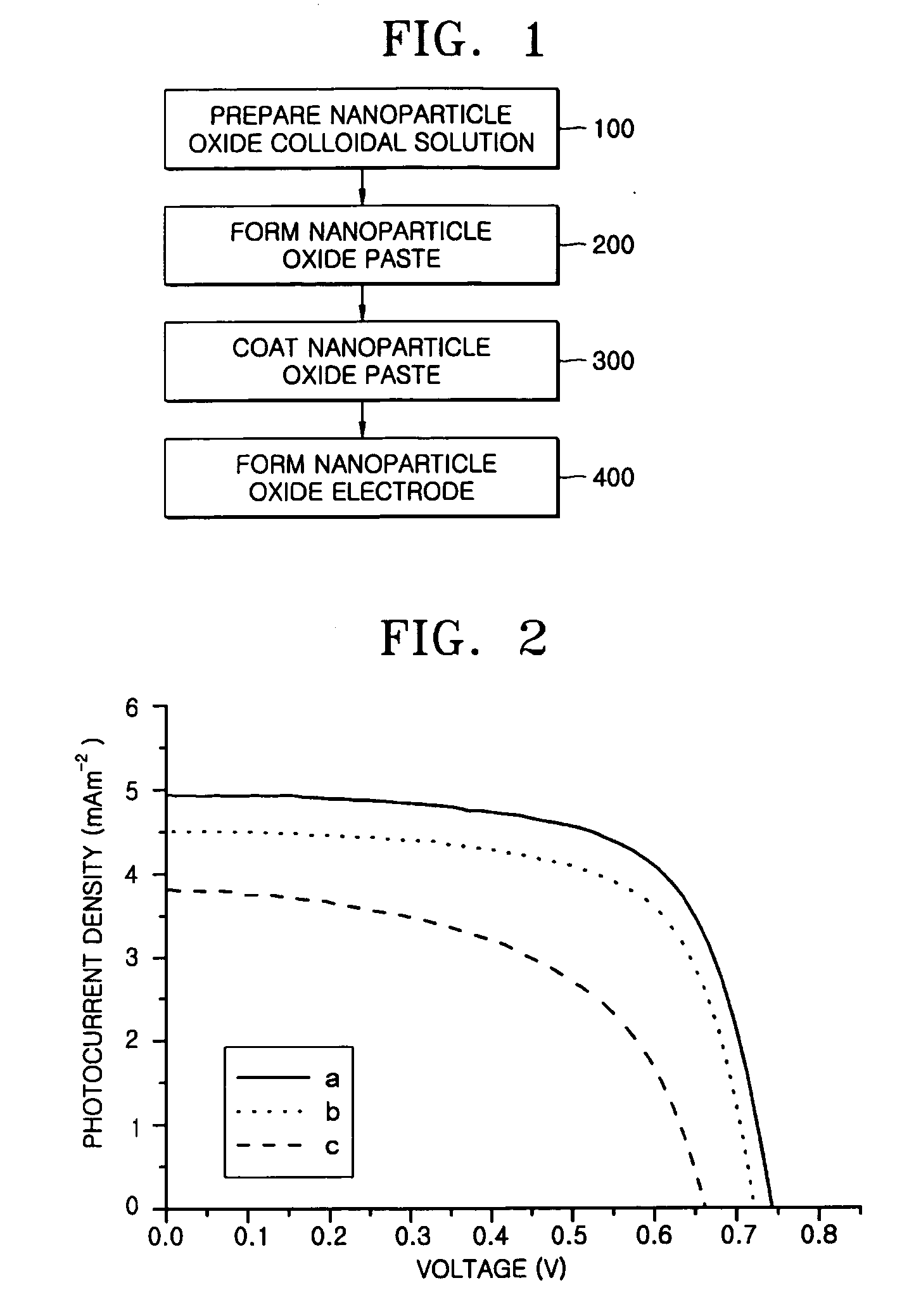
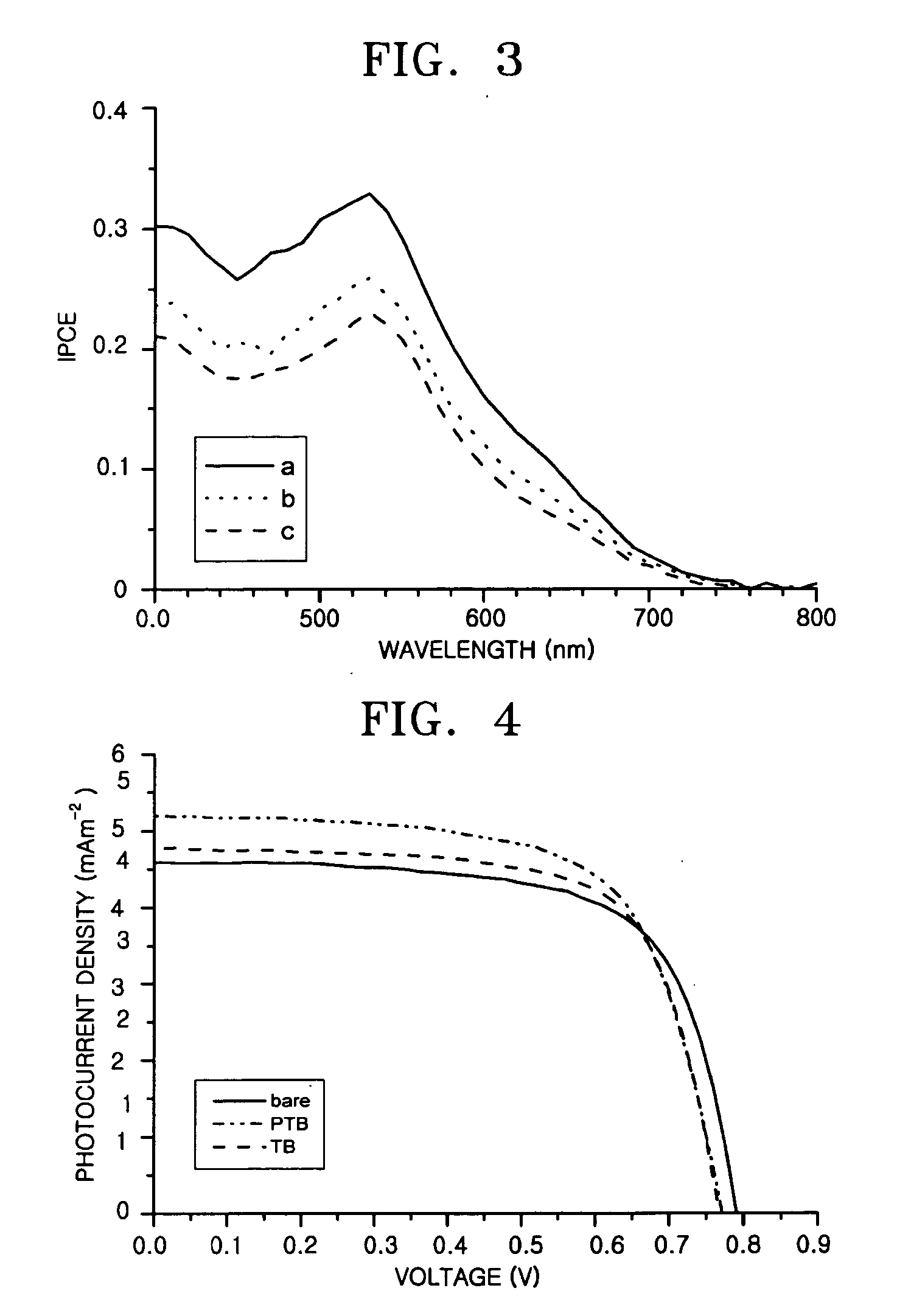
Method of forming nanoparticle oxide electrode of plastic-type dye-sensitized solar cell using high viscosity nanoparticle oxide paste without binder
InactiveUS20060063296A1High viscosityGreat interconnectionElectrolytic capacitorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoparticleAcid–base reaction
A method for forming a nanoparticle oxide electrode of a dye-sensitized solar cell is provided. In the method, a basic aqueous solution or an acidic aqueous solution is respectively added to a nanoparticle oxide colloidal solution having a good acidic or basic dispersion, to form a basic nanoparticle oxide paste by an acid-base reaction. Next, after the nanoparticle oxide paste is coated on a substrate, the coated nanoparticle oxide paste is dried at a low temperature of 150° C. or lower. Accordingly, the low-temperature coating nanoparticle oxide paste with high viscosity can be manufactured on the basis of the acid-base reaction, even without the addition of polymer, and accordingly, the nanoparticle oxide electrode can be formed even at a low temperature.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com