Wind turbine damping of tower resonant motion and symmetric blade motion using estimation methods
A technology of resonant motion and wind turbine, which is applied in the direction of wind turbines, wind turbines, and wind turbine components in the same direction as the wind. It can solve the problems of increased phase and gain errors and difficult control, and achieve the effect of reducing 3P motion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
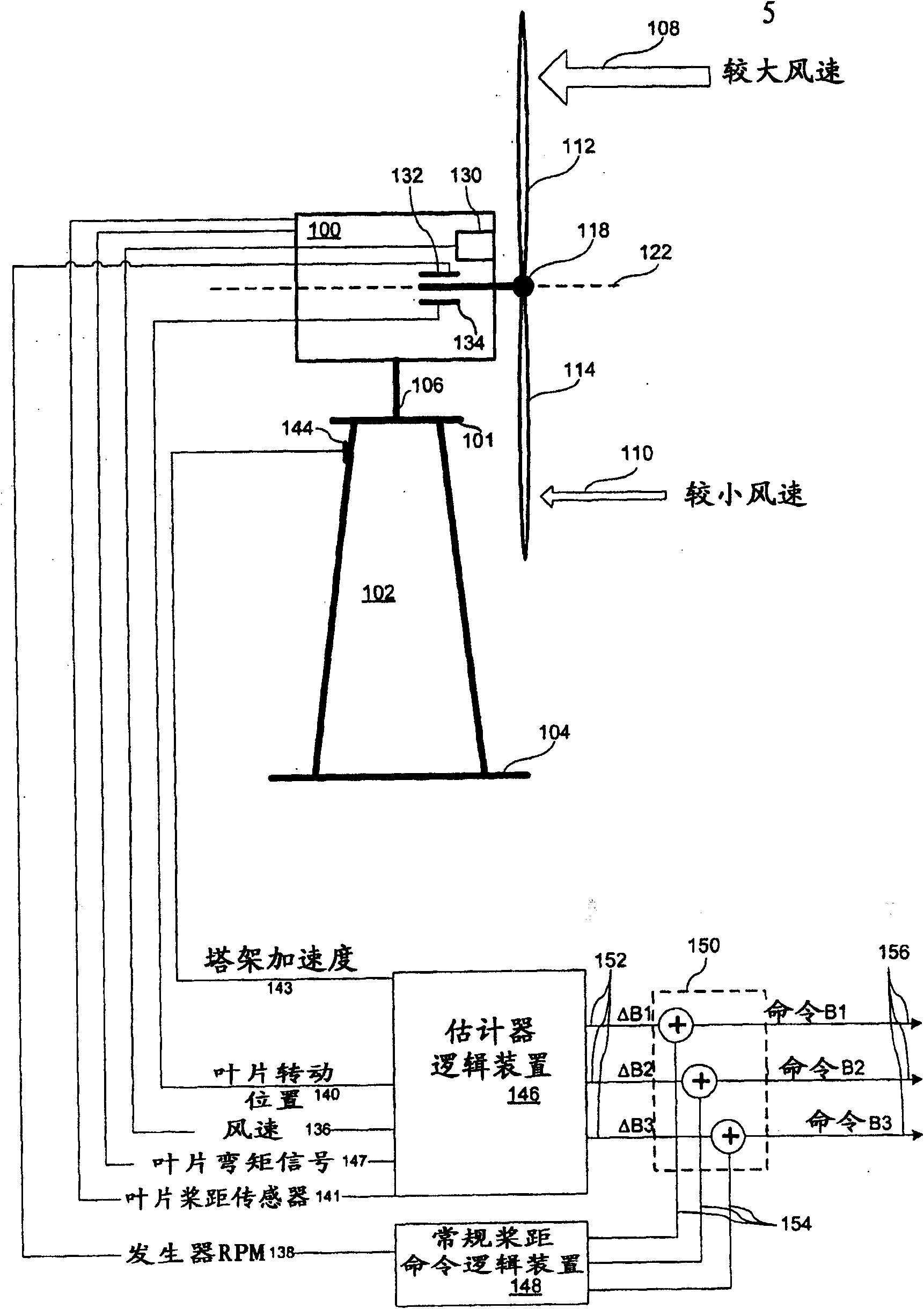
[0037] refer to figure 1 , which is a block diagram of a variable speed wind turbine plant according to the invention. A wind power plant includes a turbine with one or more generators housed in a pod 100 mounted on top of a tall tower structure 102 anchored to the ground 104 . The pod 100 rests on the angle of attack platform 101 and is free to rotate about the angle of attack pivot 106 in the horizontal plane and remains in the path of the prevailing wind flow.
[0038] The turbine has a rotor with pitched blades 112 , 114 connected to a rotor hub 118 . These blades turn in response to wind currents. Each of the blades may have a root section and a blade extension section such that the length of the rotor is variable to provide a variable diameter rotor. As described in US Pat. No. 6,726,439, the rotor diameter can be controlled to fully extend the rotor at low flow rates and to retract the rotor as flow rates increase such that the loads transmitted by or placed on the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com