Patents
Literature
108results about "Proportional-integral-differentail algorithms" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
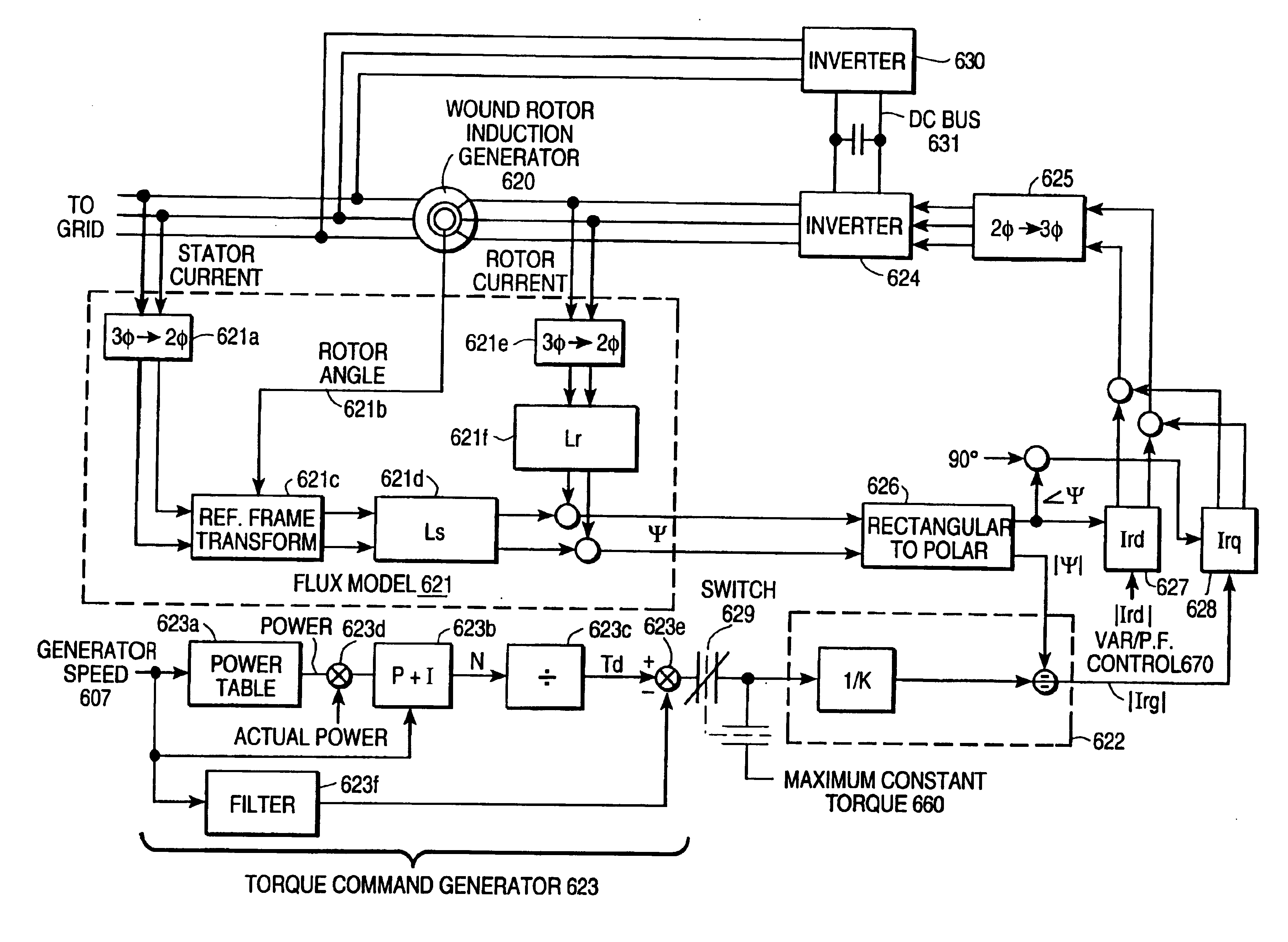
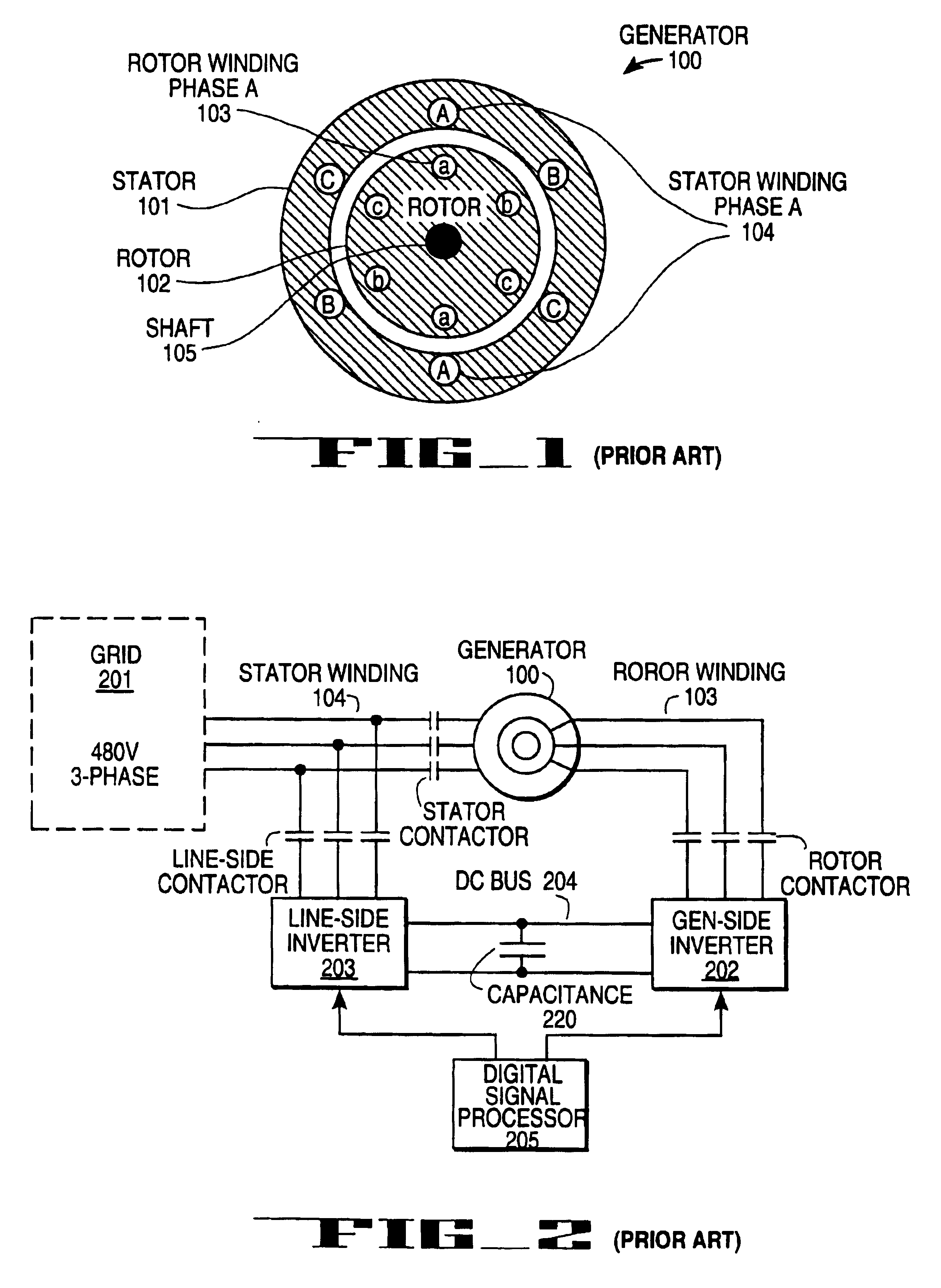
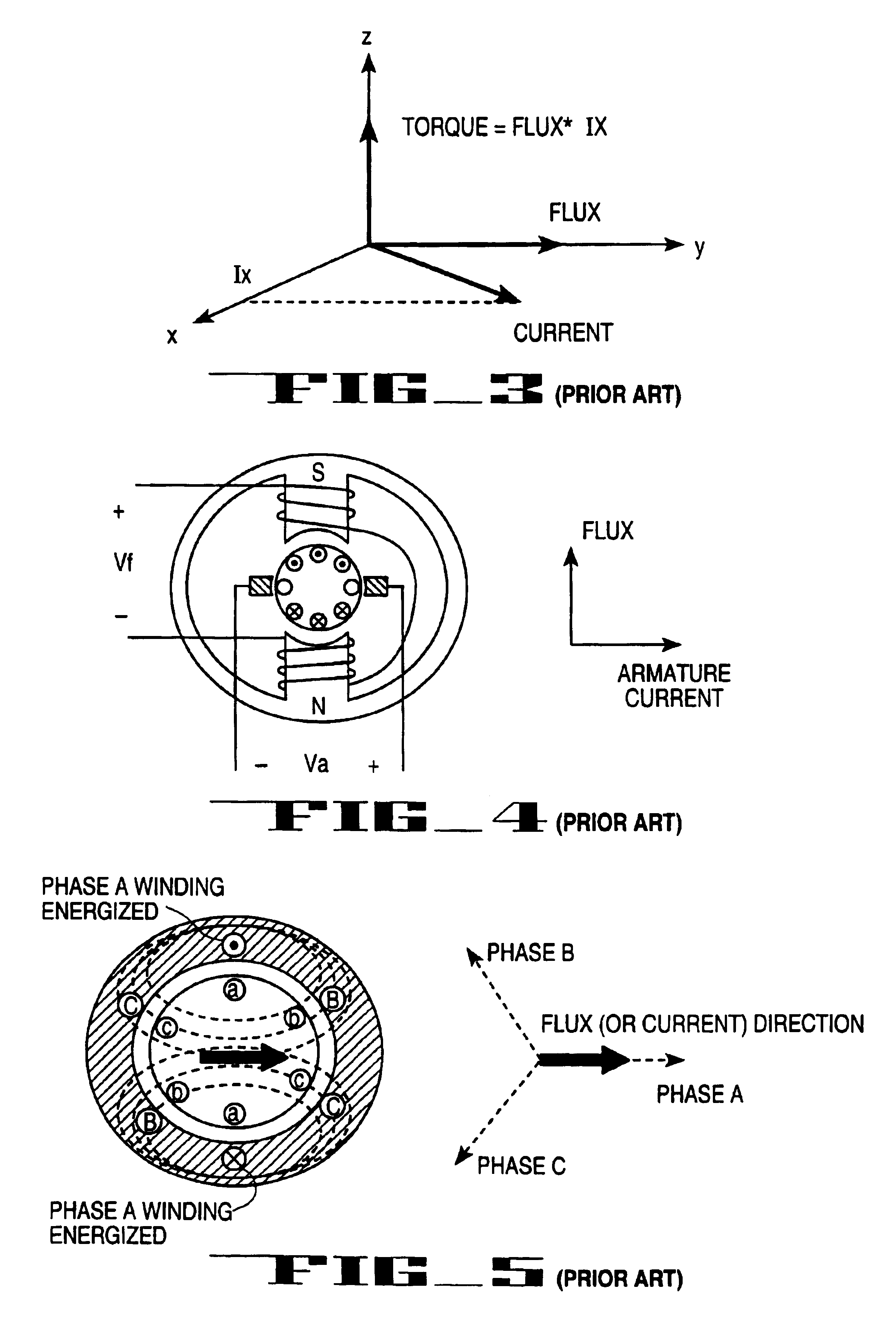
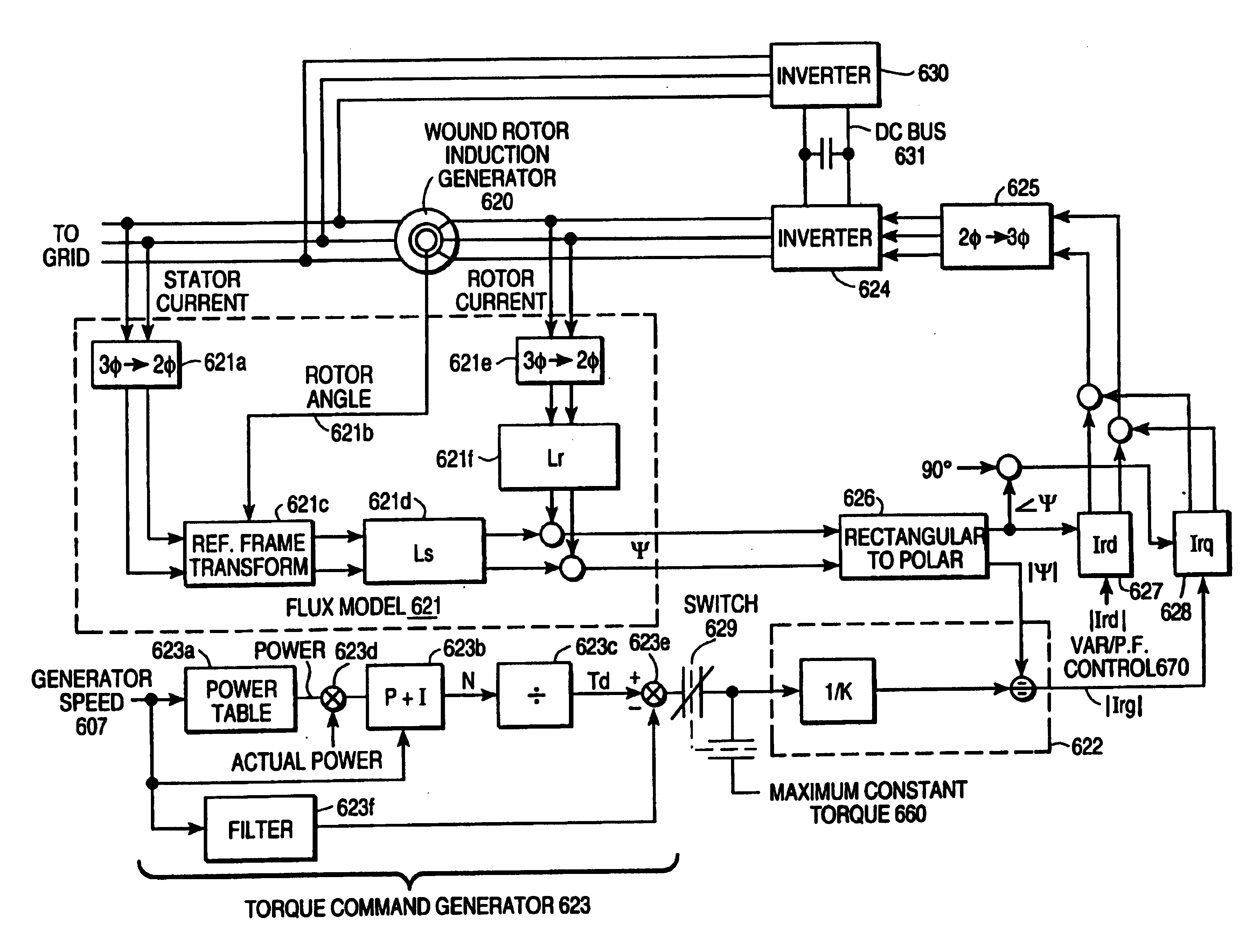
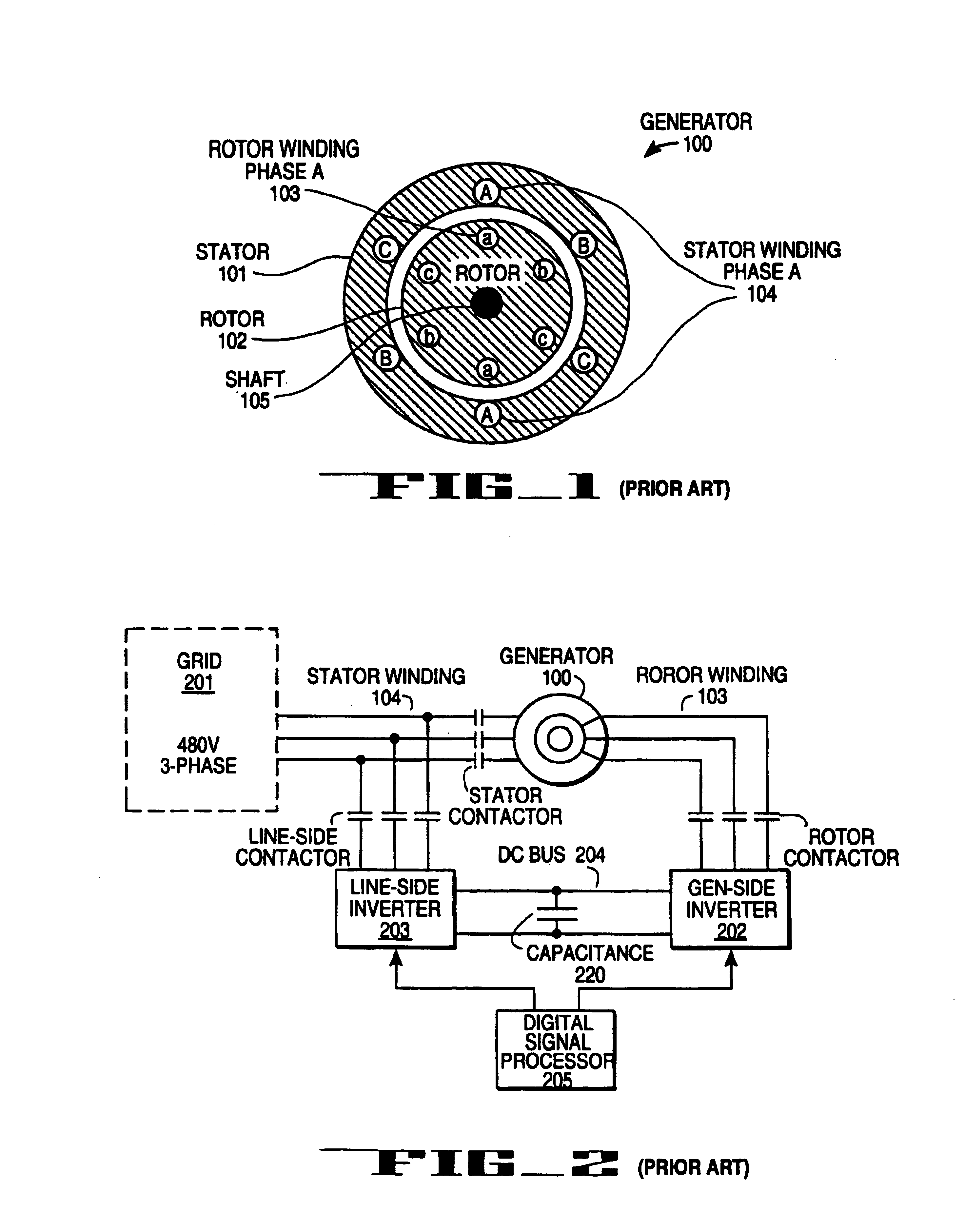
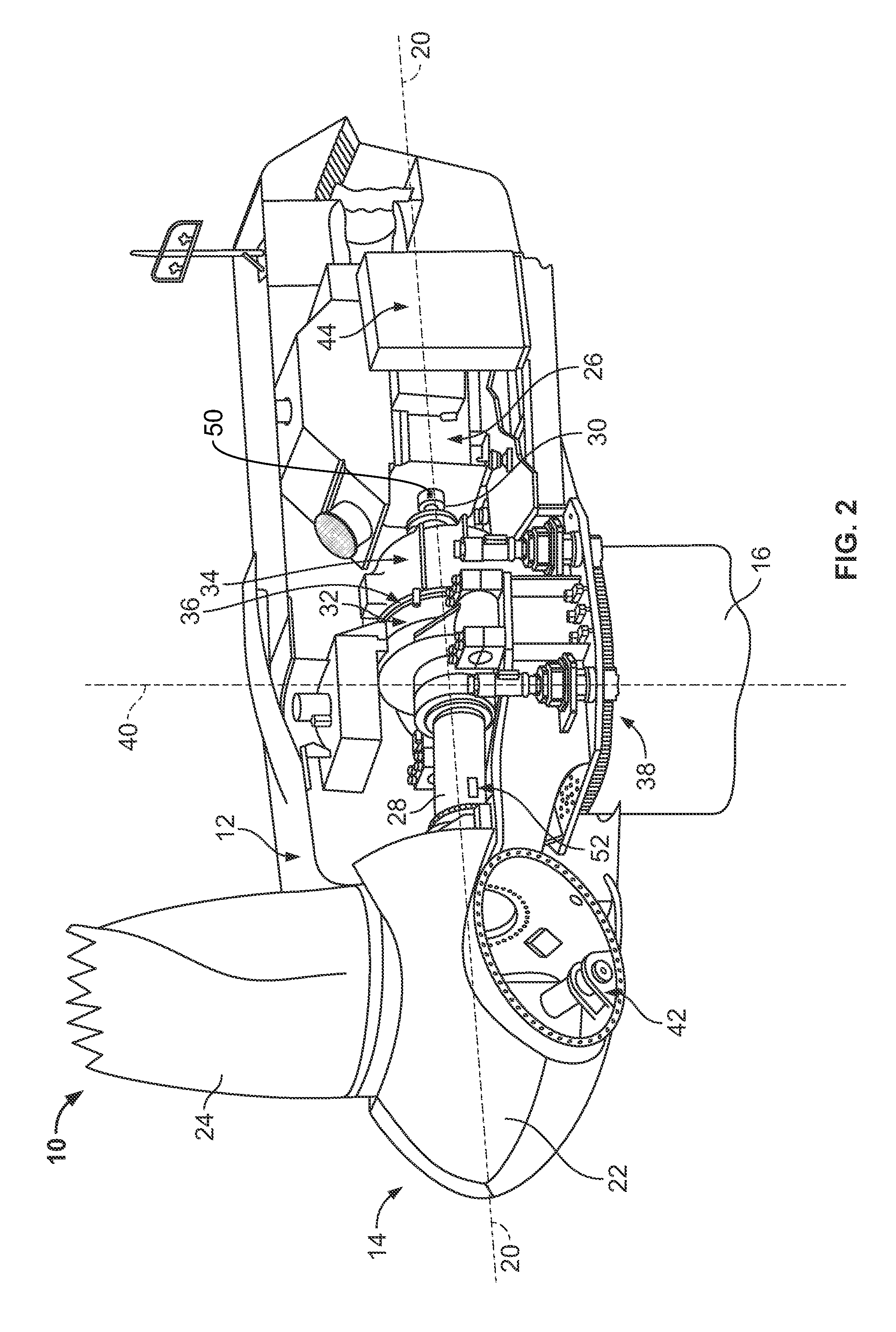
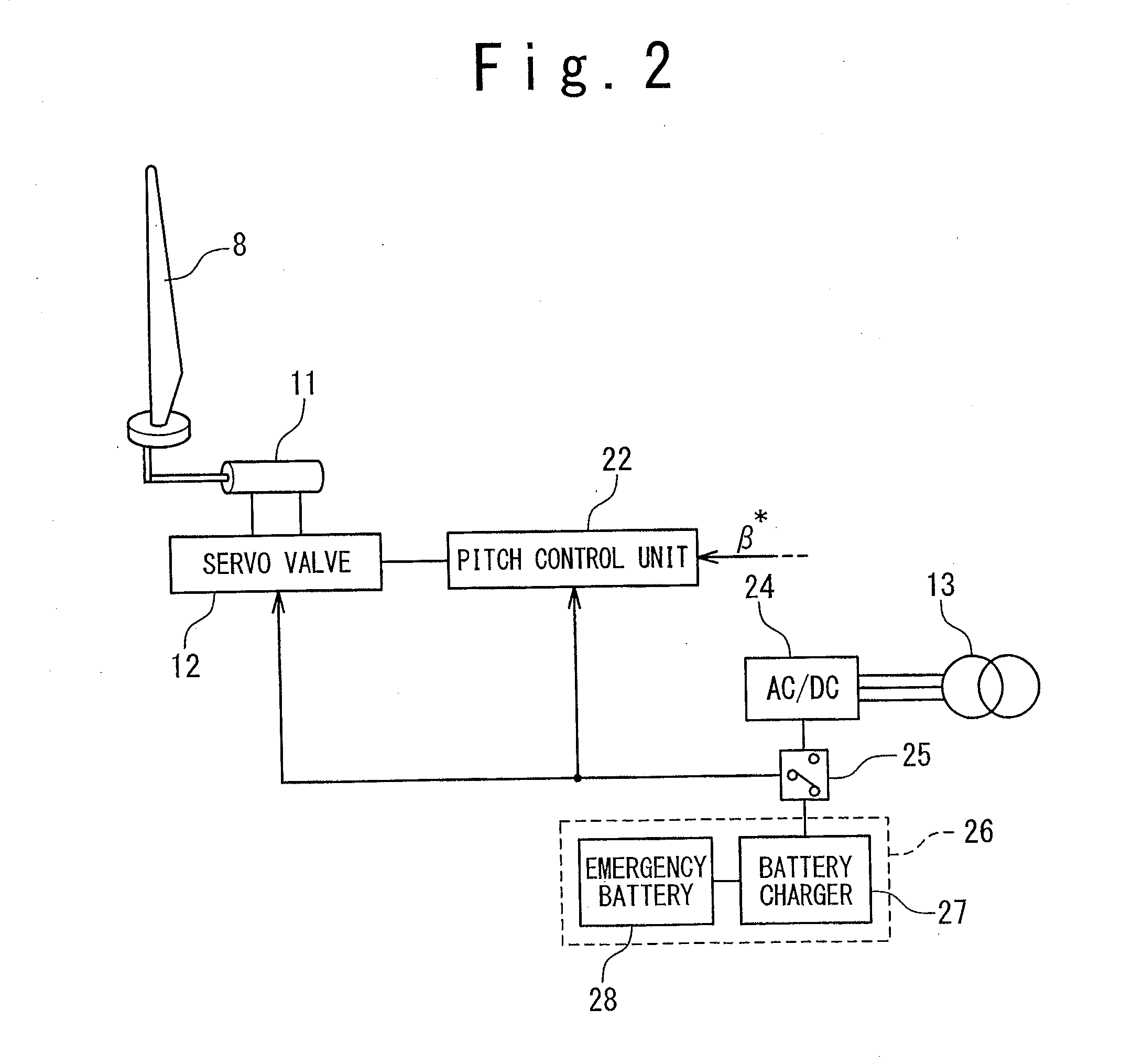
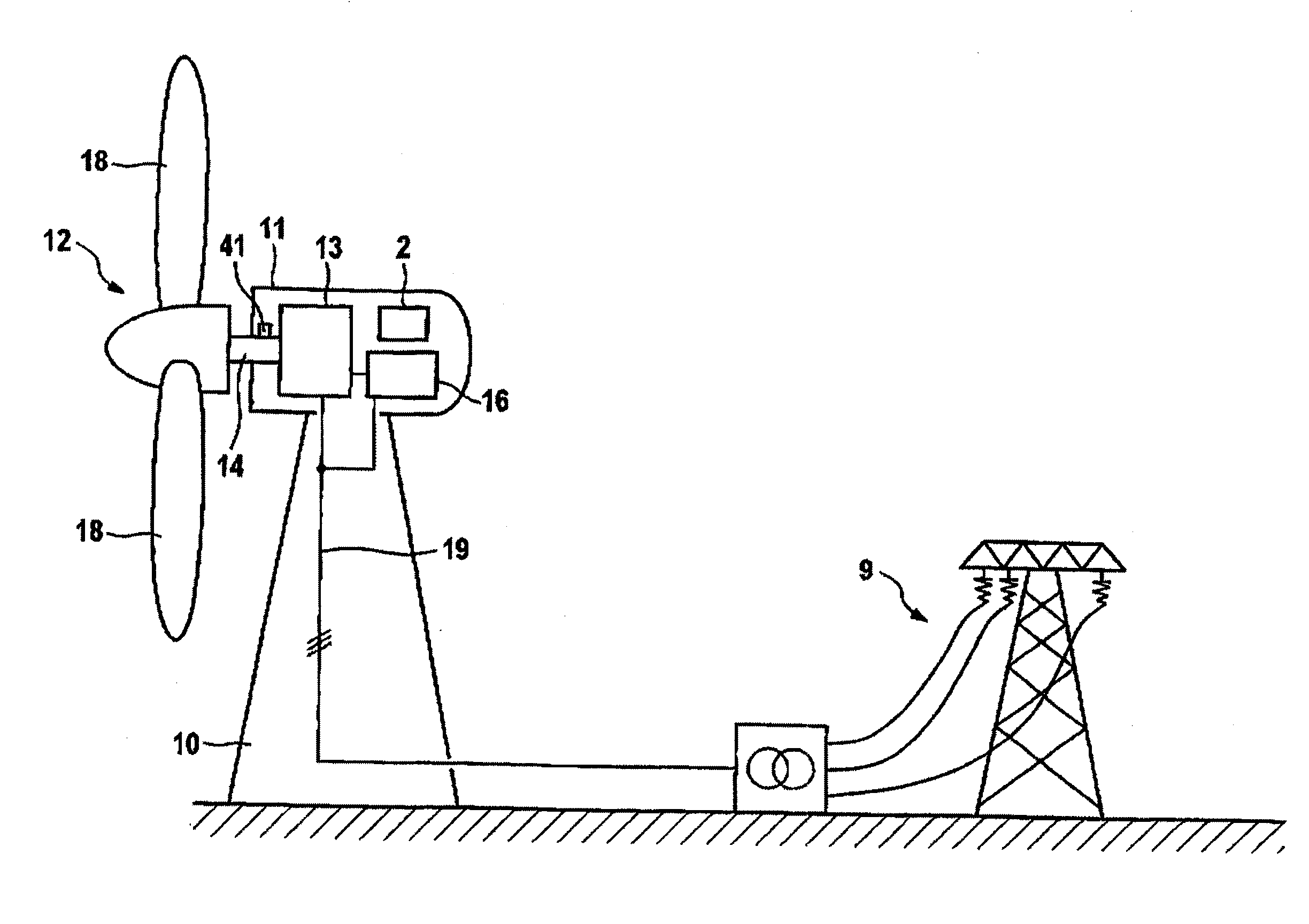
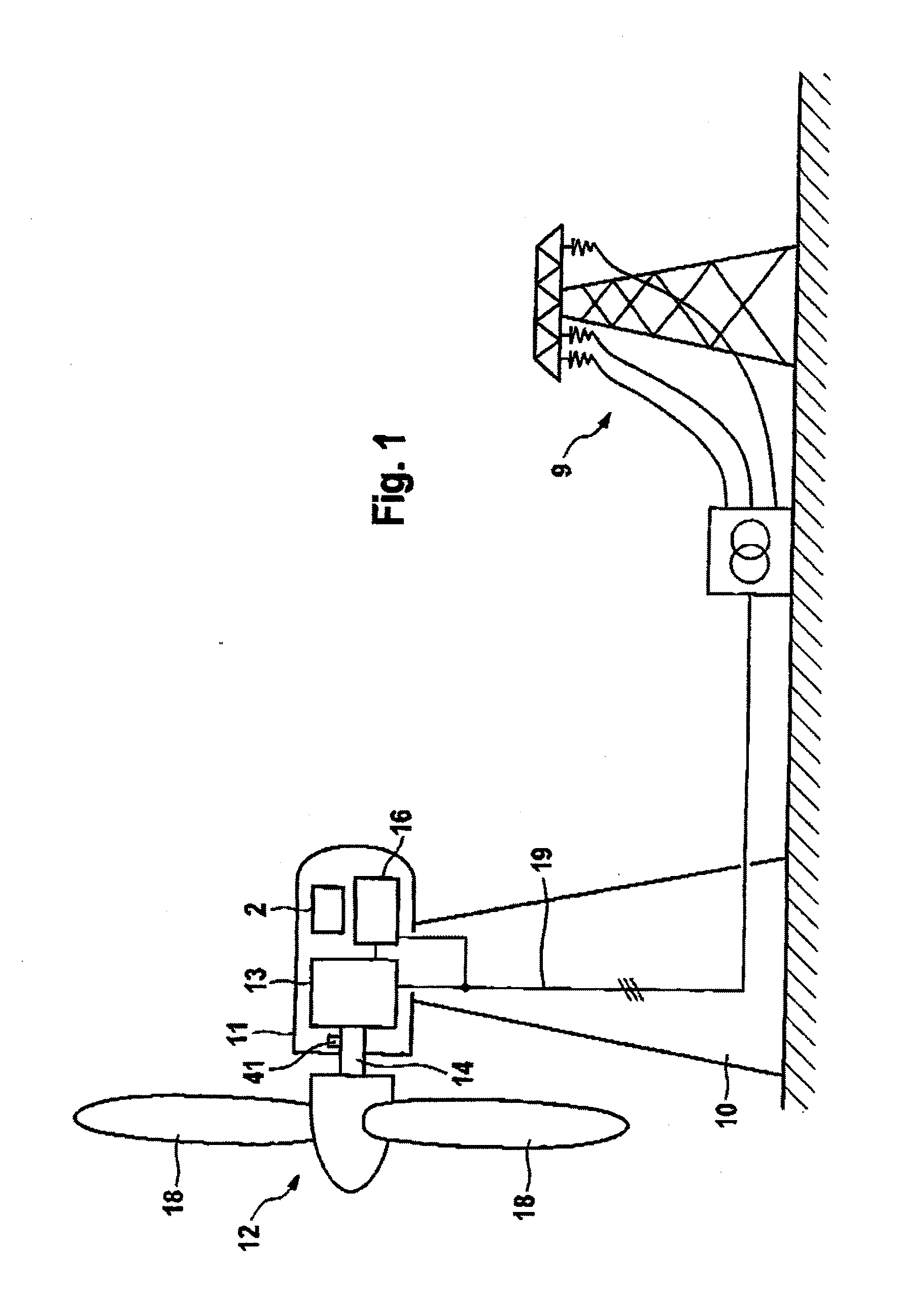
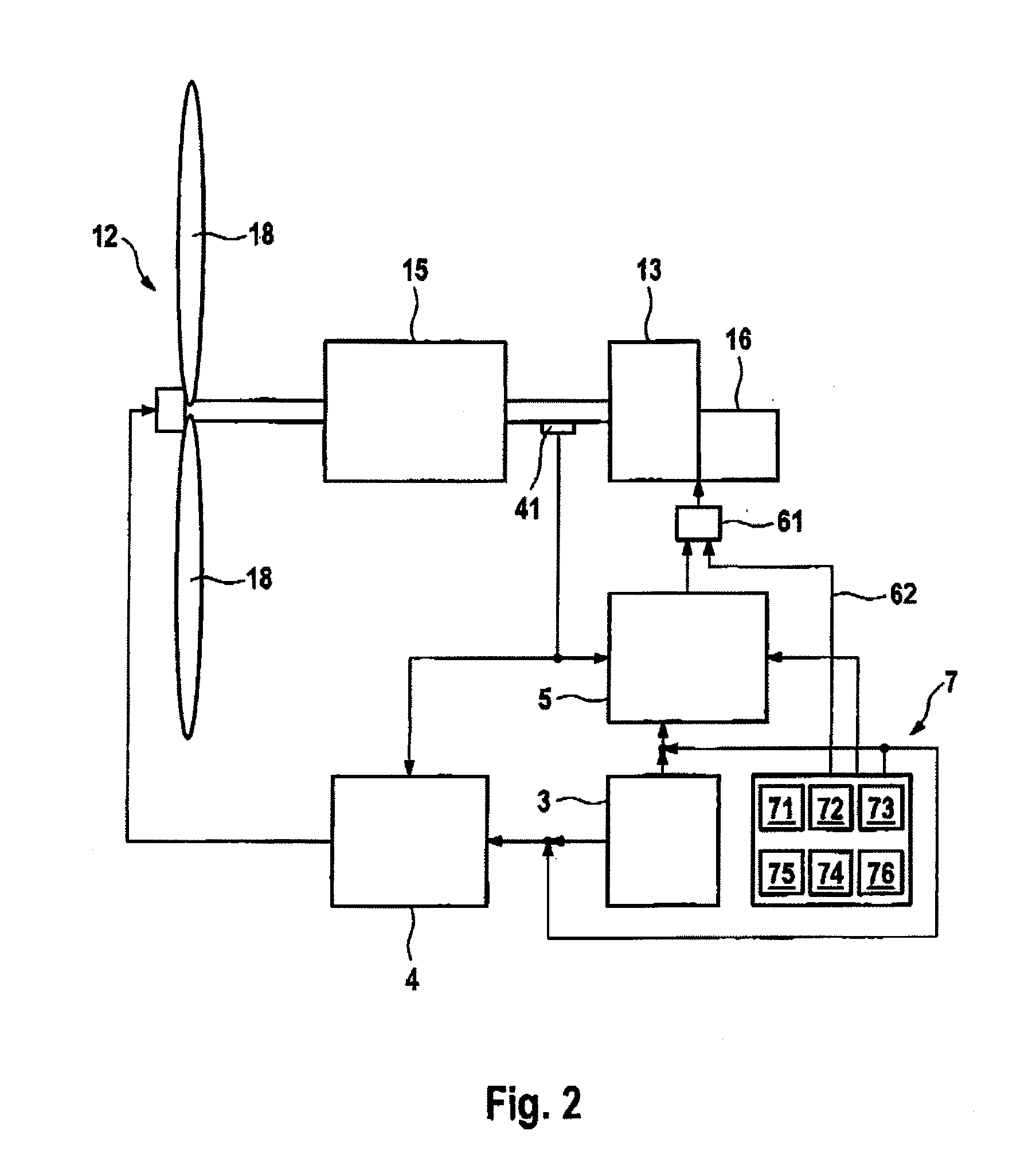
Variable speed wind turbine generator
InactiveUS6856039B2Generator control circuitsWind motor controlVariable speed wind turbineControl theory
A variable speed system for use in systems, such as, for example, wind turbines, is described. The system comprises a wound rotor induction generator, a torque controller and a proportional, integral derivative (PID) pitch controller. The torque controller controls generator torque using field oriented control, and the PID controller performs pitch regulation based on generator rotor speed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Variable speed wind turbine generator
InactiveUS6847128B2Generator control circuitsWind motor controlVariable speed wind turbineControl theory
A variable speed system for use in systems, such as, for example, wind turbines, is described. The system comprises a wound rotor induction generator, a torque controller and a proportional integral derivative (PID) pitch controller. The torque controller controls generator torque using field oriented control, and the PID controller performs pitch regulation based on generator rotor speed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and apparatuses for wind turbine fatigue load measurement and assessment
Techniques and apparatuses for wind turbine component fatigue load measurement and assessment are disclosed. In one embodiment the component is a tower, fore-aft and side-to-side signals from a two-axis accelerometer attached to a bedplate of a wind turbine are used to measure tower fatigue loads. A yaw axis azimuth position signal can also be used for tower fatigue load measurement and assessment.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and methods for controlling a wind turbine
A method for controlling operation of a wind turbine is described. The wind turbine includes a rotor having a plurality of rotor blades and an upwind wind condition measurement device. The method includes measuring a wind condition upwind from the rotor using the upwind wind condition measurement device and providing the measured wind condition to a processor. The method also includes determining a control algorithm parameter, based at least partially on the measured wind condition, that controls at least one of a wind turbine response bandwidth, a wind turbine response speed, and a wind turbine control error range. The method also includes determining a wind turbine operating command based at least partially on the control algorithm parameter and applying the wind turbine operating command to operation of the wind turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for controlling a wind power plant and corresponding wind power plant
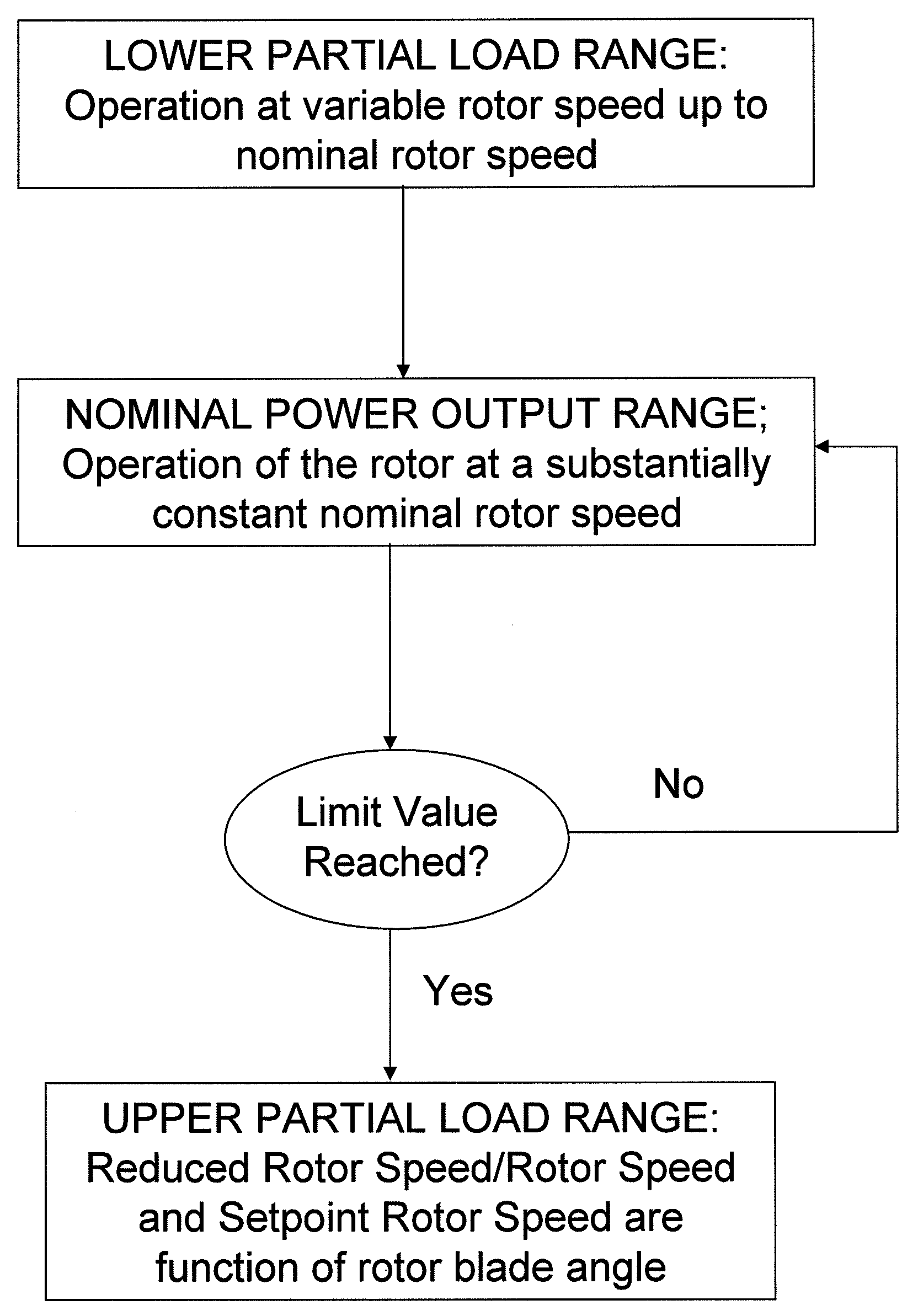
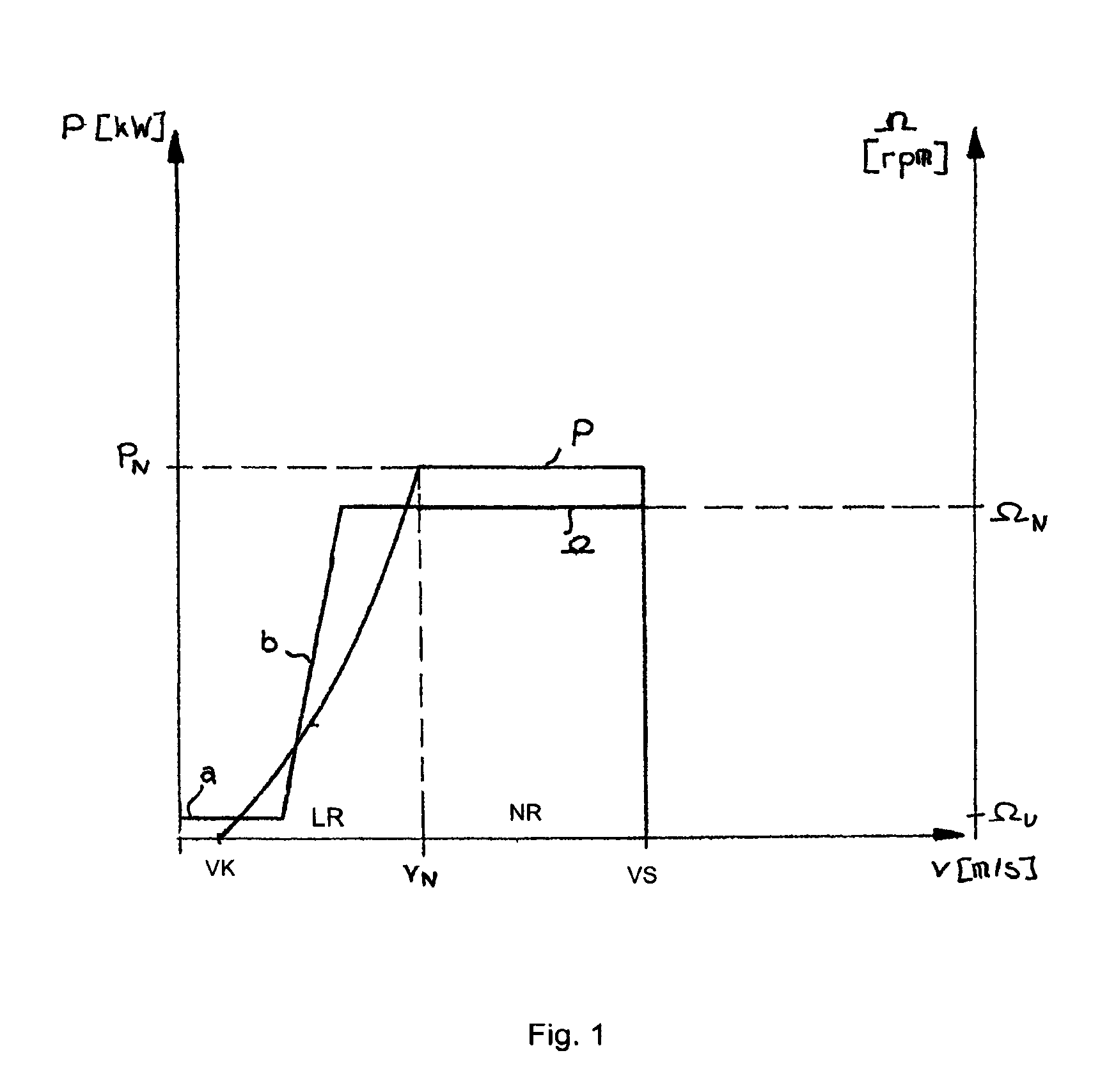
InactiveUS20070216166A1Improved and reliableImprove compatibilityWind motor controlComparison table algorithmsPower stationEngineering
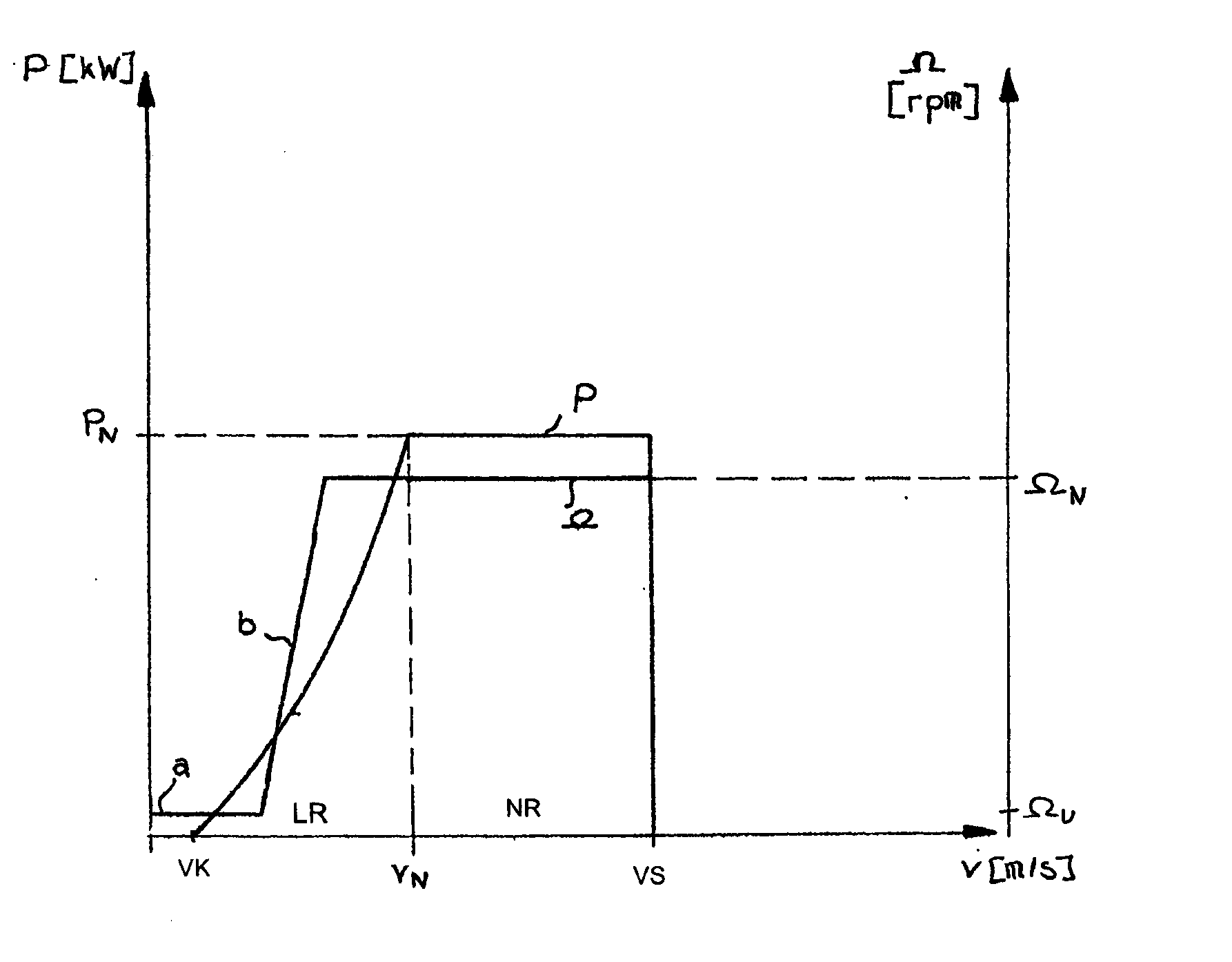
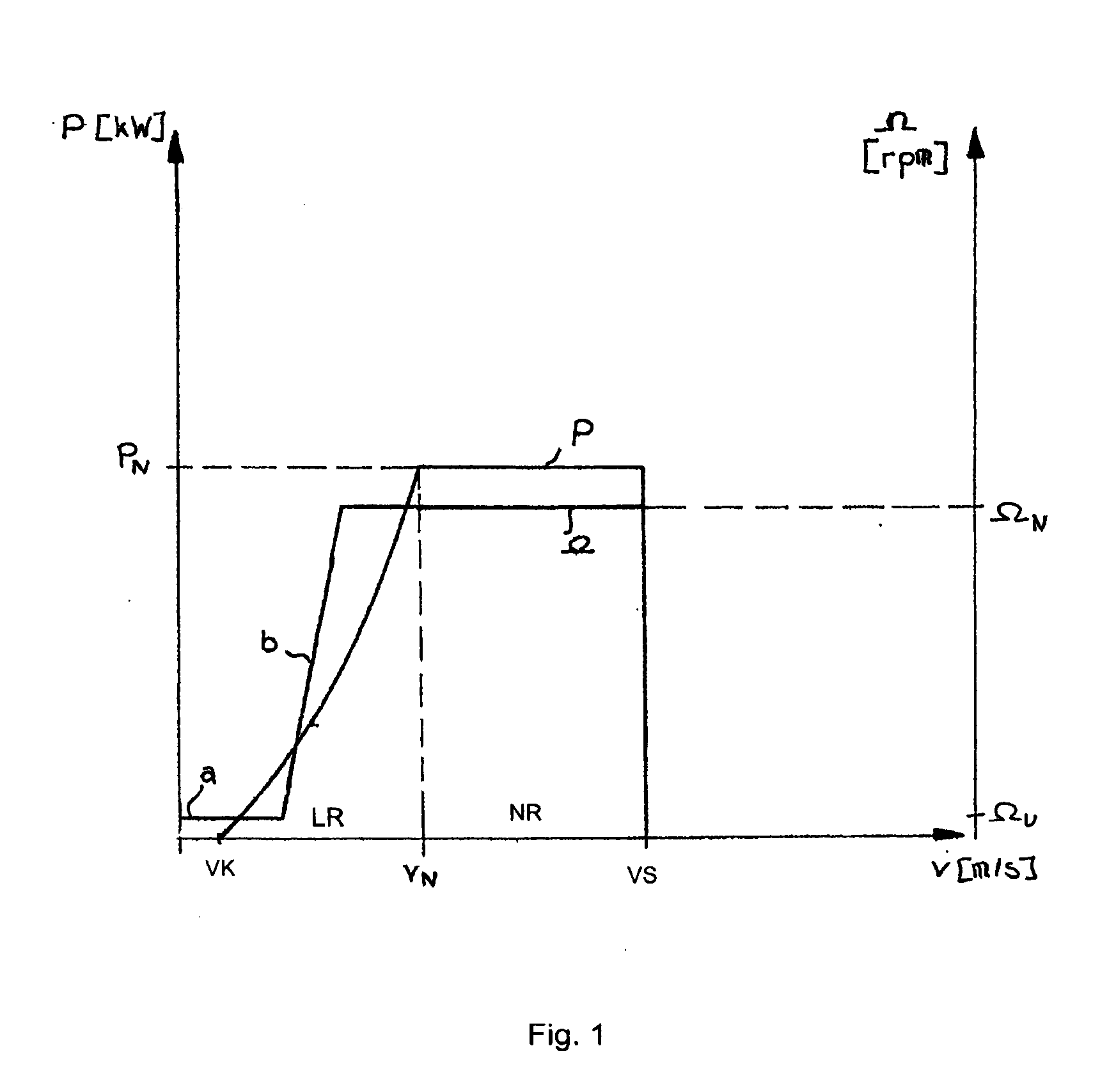
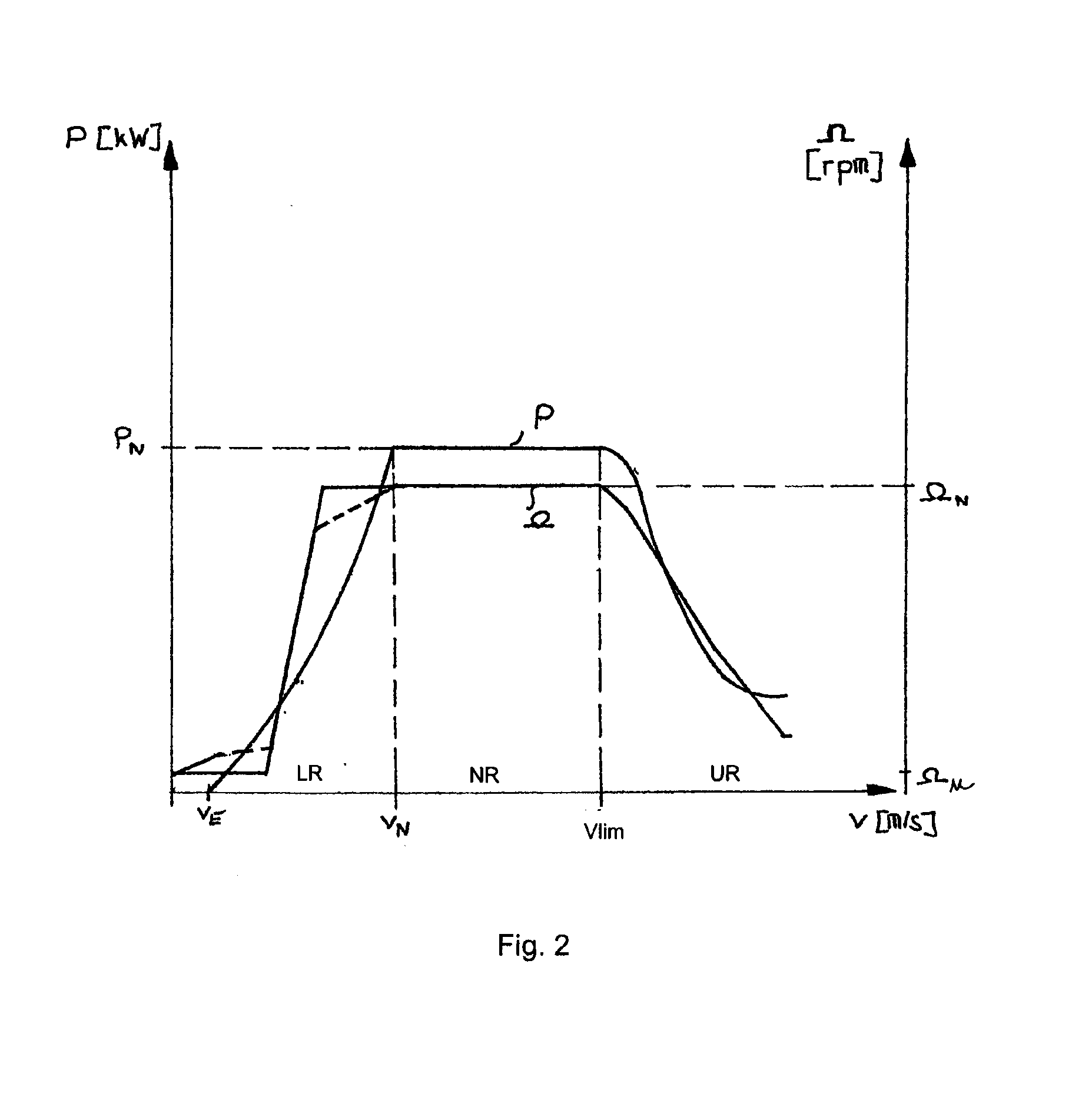
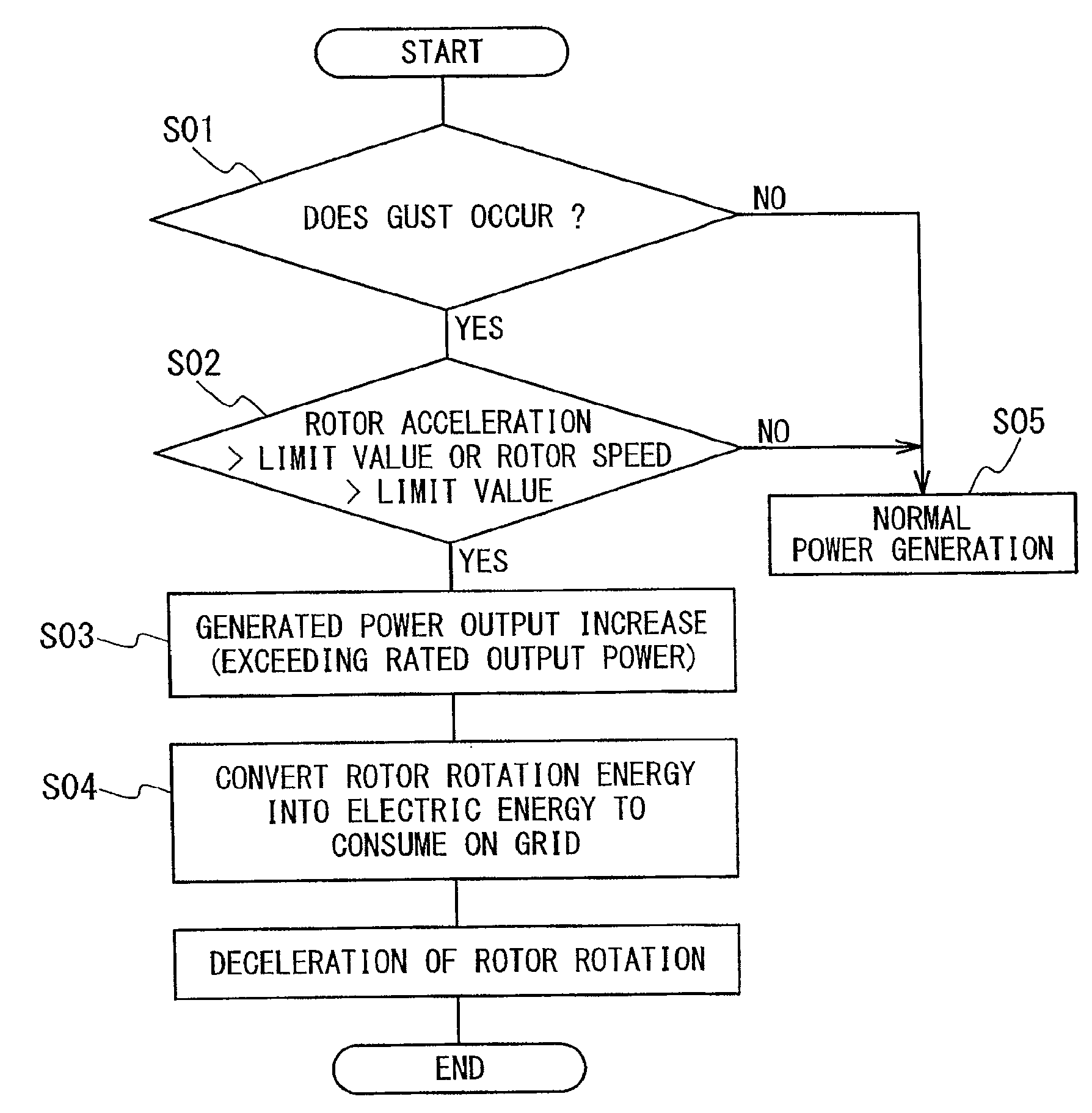
Reduction in power output or rotor speed of a wind turbine above a defined limit value, the reduction not being implemented based on the measured wind speed, but on an input value which on one hand is easily detected physically and by control technology and on the other hand is a good indicator of mechanical stresses on the wind turbine. The invention uses the rotor-blade angle as the input value in a manner that starting at the limit value, the reduction in power output or in rotor speed is adjusted as a function of the rotor-blade angle.
Owner:SENVION GMBH
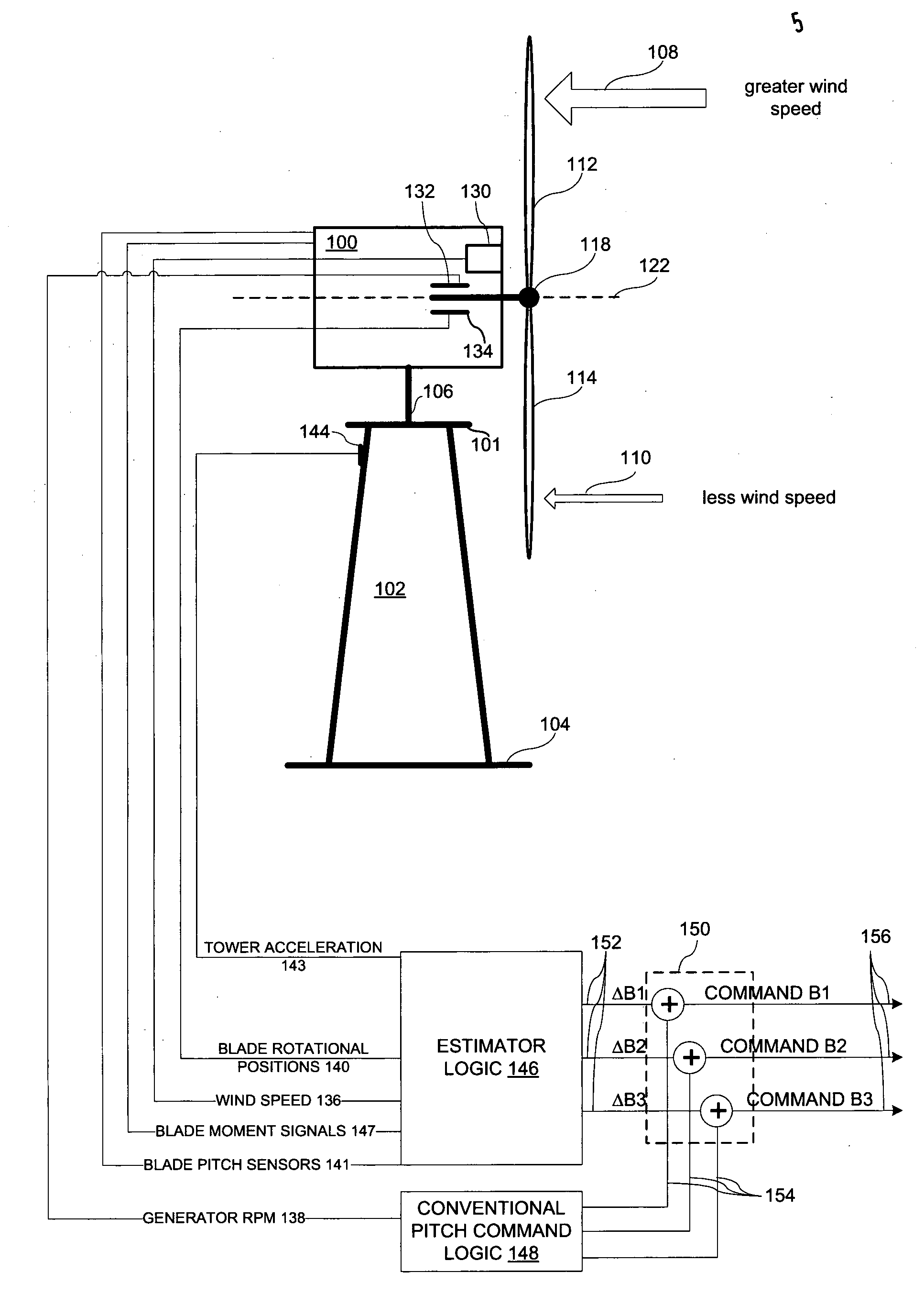
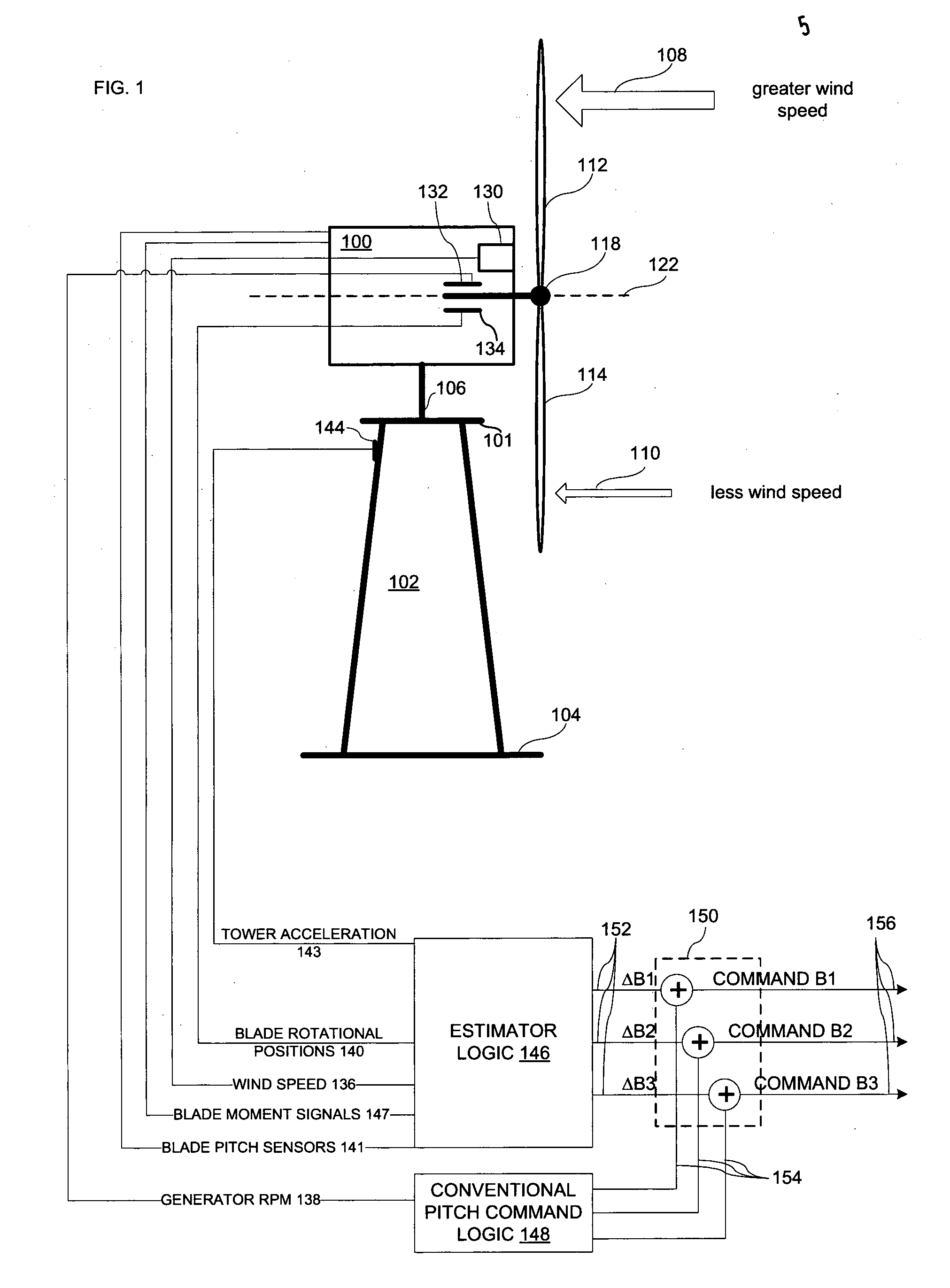
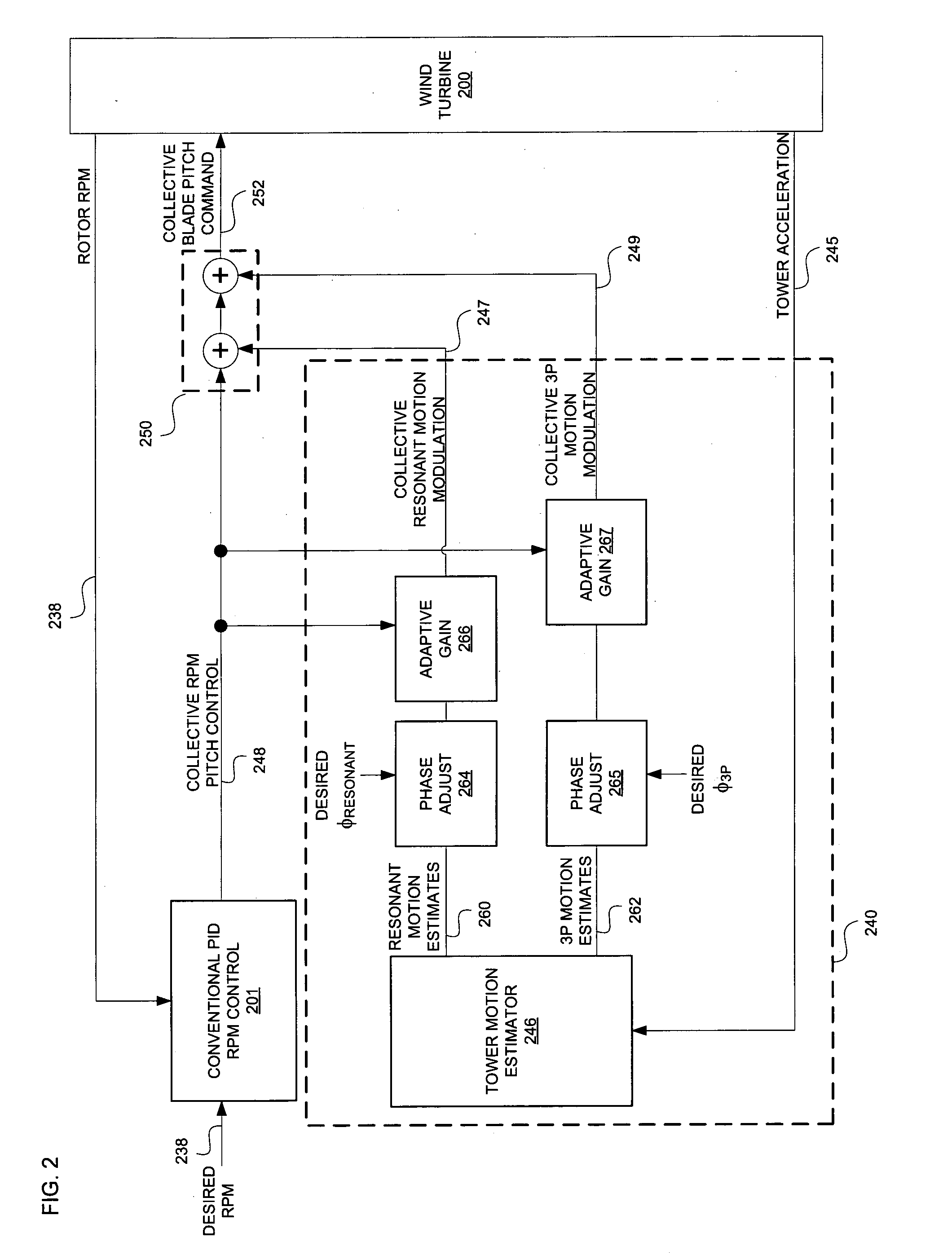
Wind turbine damping of tower resonant motion and symmetric blade motion using estimation methods
InactiveUS20100111693A1Reduce relative motionSolution to short lifePropellersWind motor controlEstimation methodsEngineering
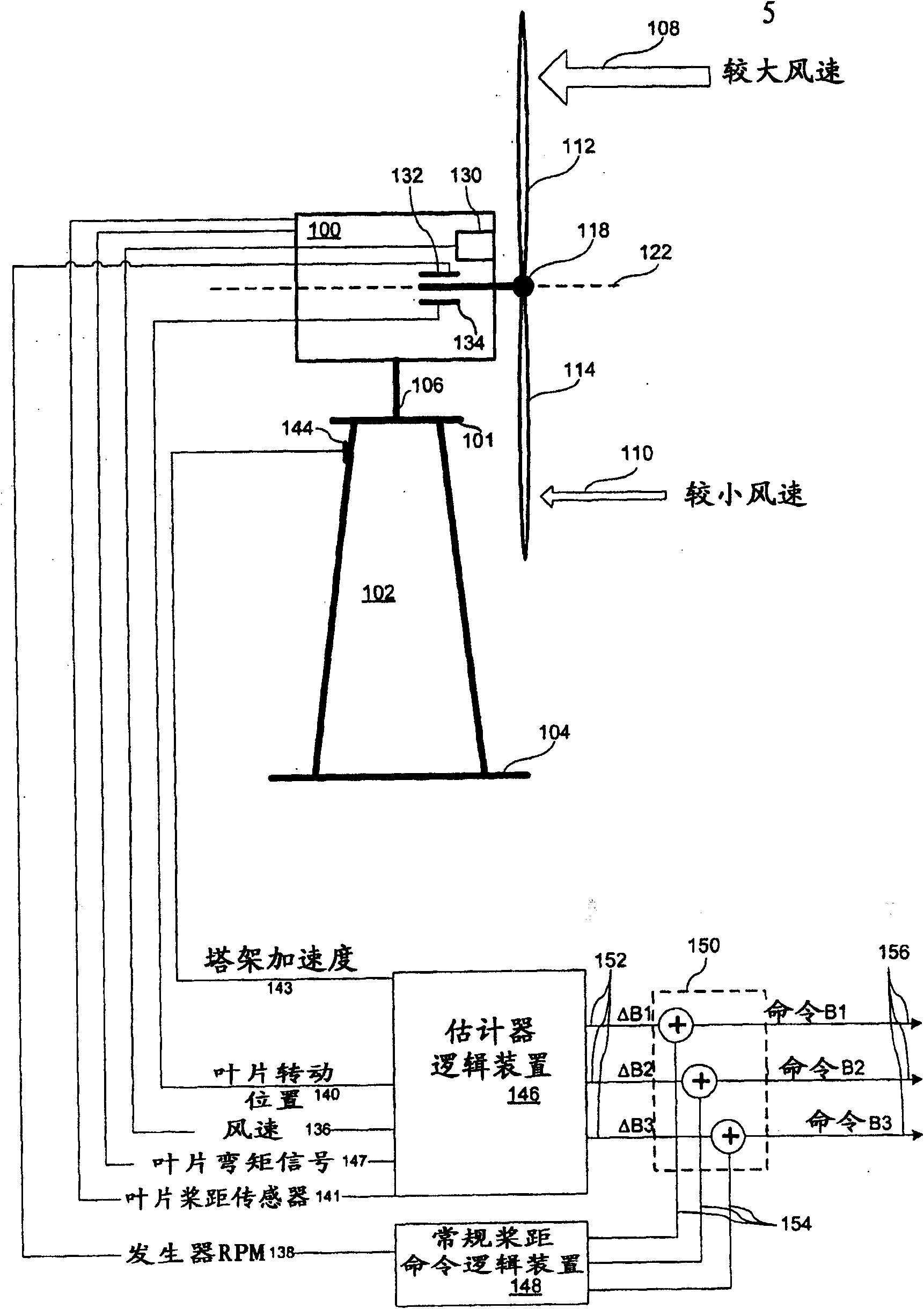
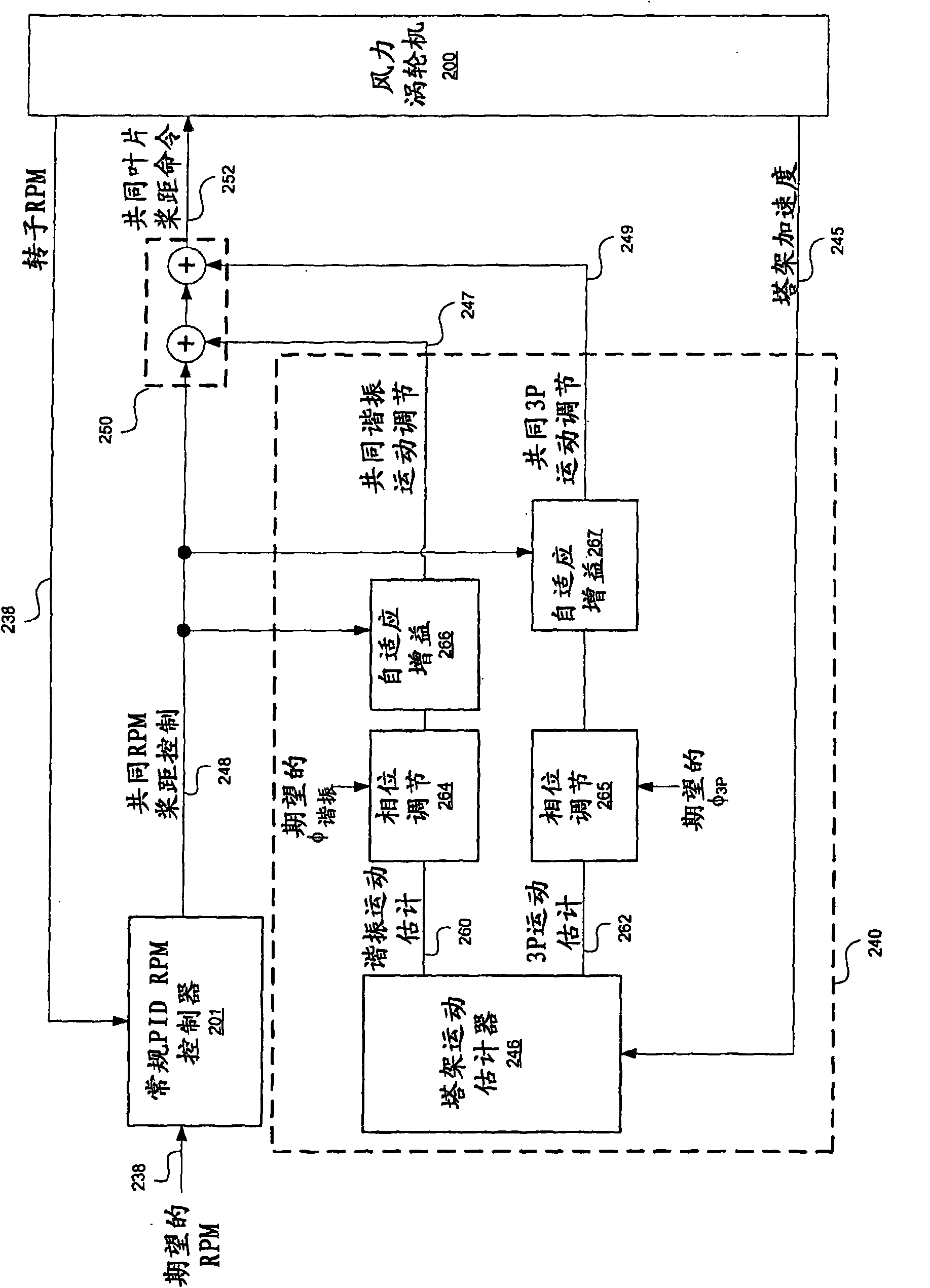
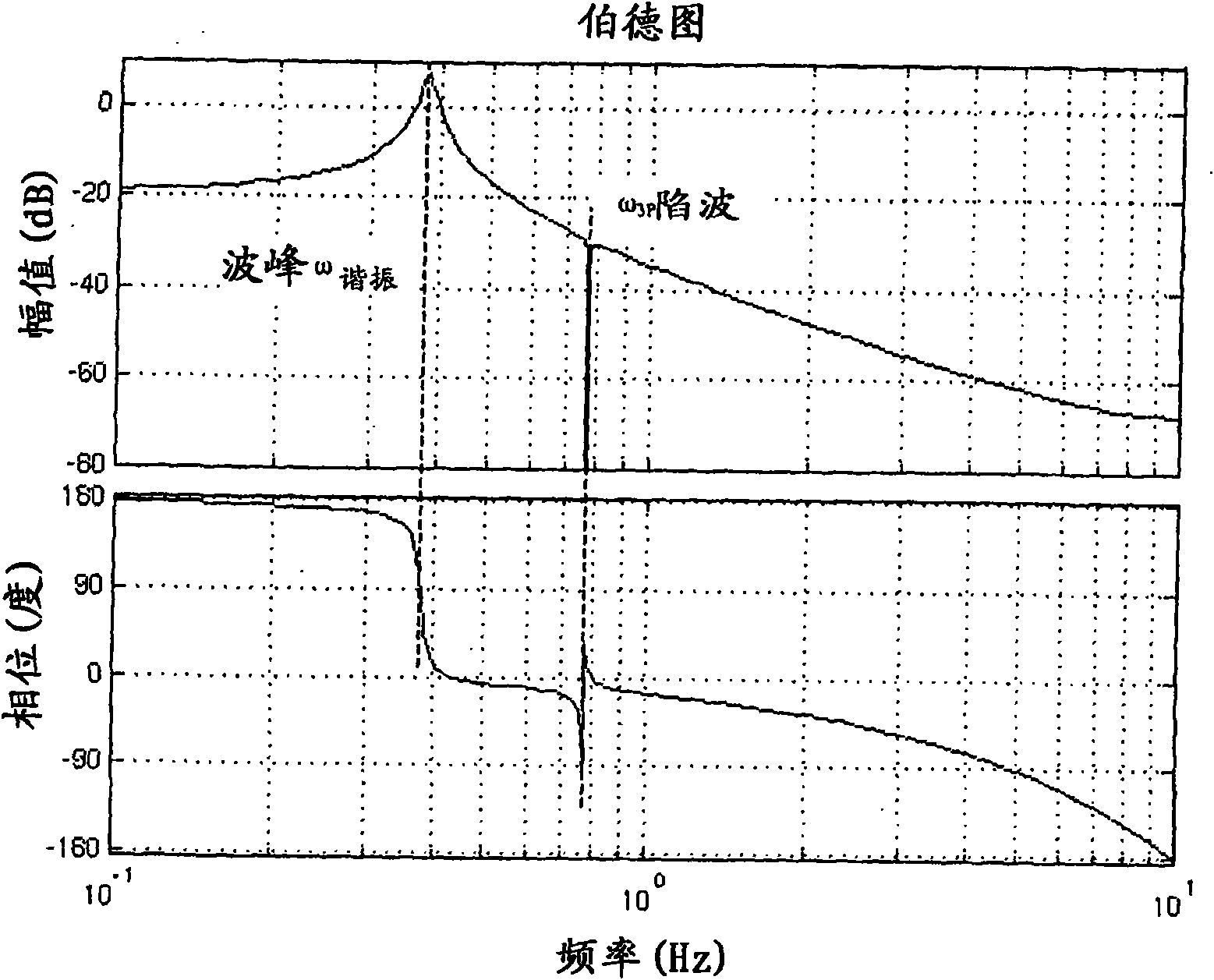
A method for wind turbine tower load control includes controlling the pitch of the rotor blades in a conventional manner by a collective command component. An estimator estimates the tower resonant acceleration and the thrice-per-revolution blade imbalance acceleration. Combining logic, connected to the estimated resonant acceleration and to the estimated thrice-per-revolution (3P) acceleration provides a combined pitch modulation to damp the tower resonant motion and the thrice-per-revolution motion using collective modulation. The pitch modulation is combined with the collective command component to drive the pitch actuators.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
System and methods for controlling a wind turbine
A method for controlling operation of a wind turbine is described. The wind turbine includes a rotor having a plurality of rotor blades and an upwind wind condition measurement device. The method includes measuring a wind condition upwind from the rotor using the upwind wind condition measurement device and providing the measured wind condition to a processor. The method also includes determining a control algorithm parameter, based at least partially on the measured wind condition, that controls at least one of a wind turbine response bandwidth, a wind turbine response speed, and a wind turbine control error range. The method also includes determining a wind turbine operating command based at least partially on the control algorithm parameter and applying the wind turbine operating command to operation of the wind turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for controlling a wind turbine and corresponding wind turbine
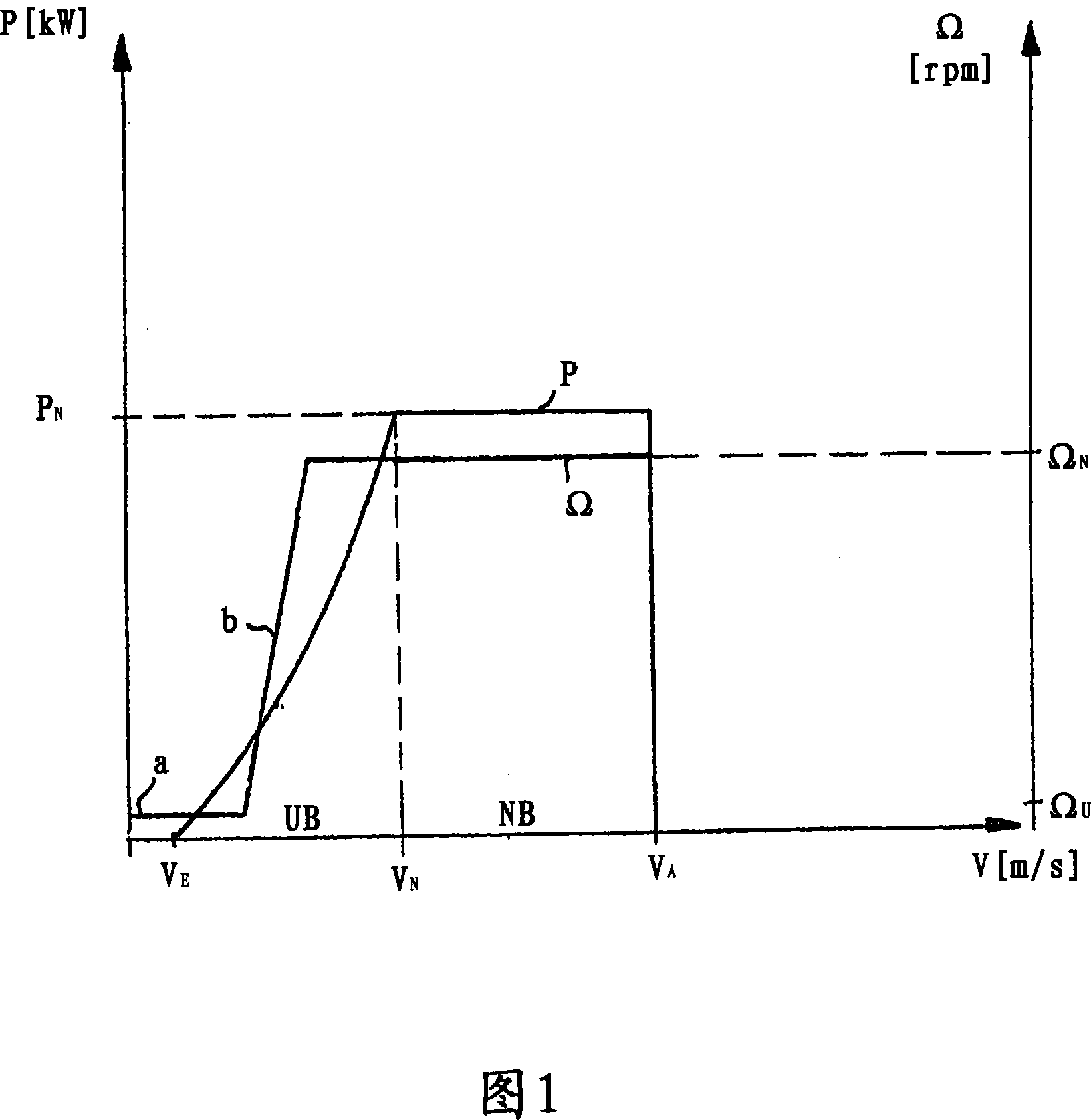
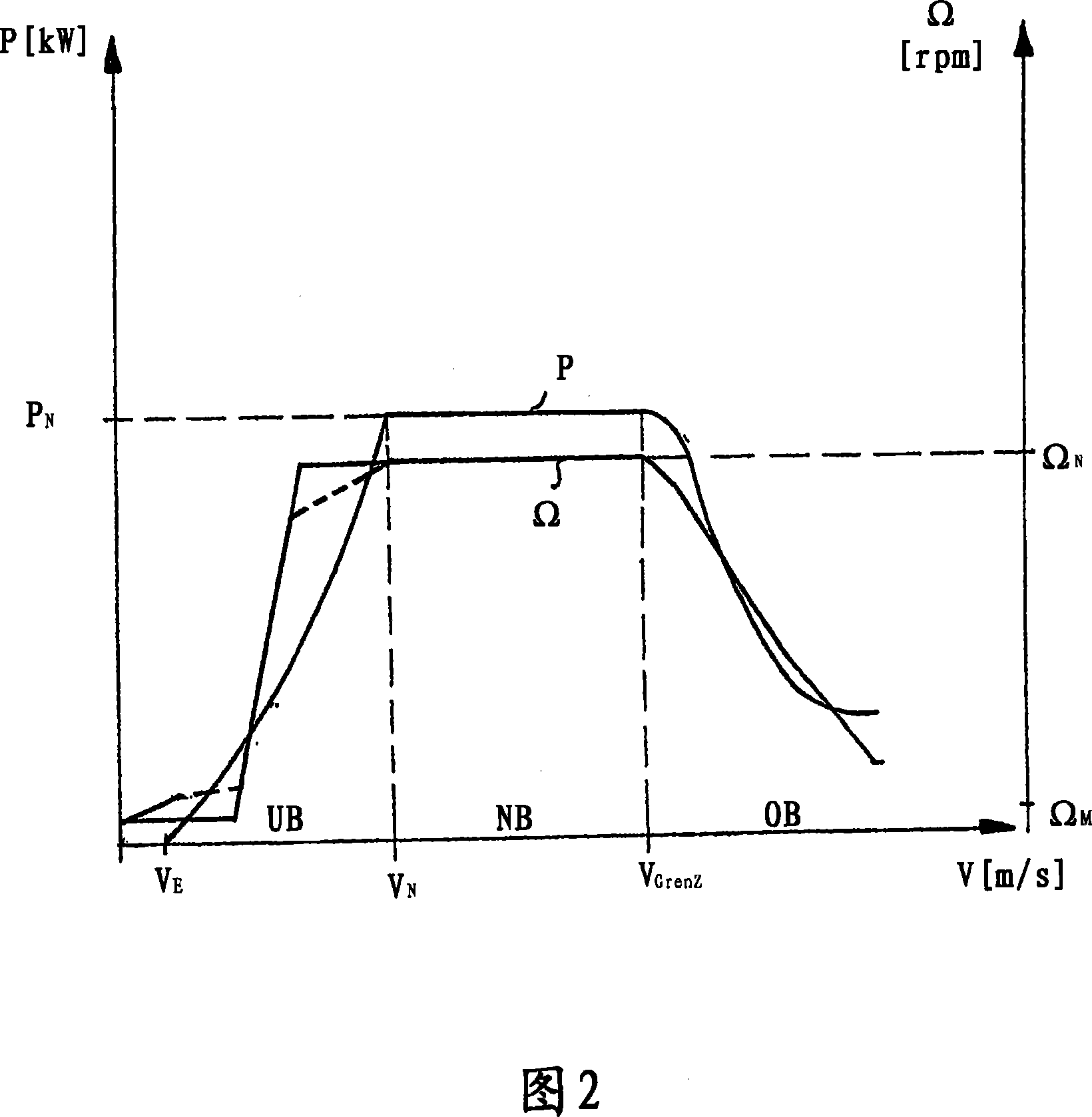
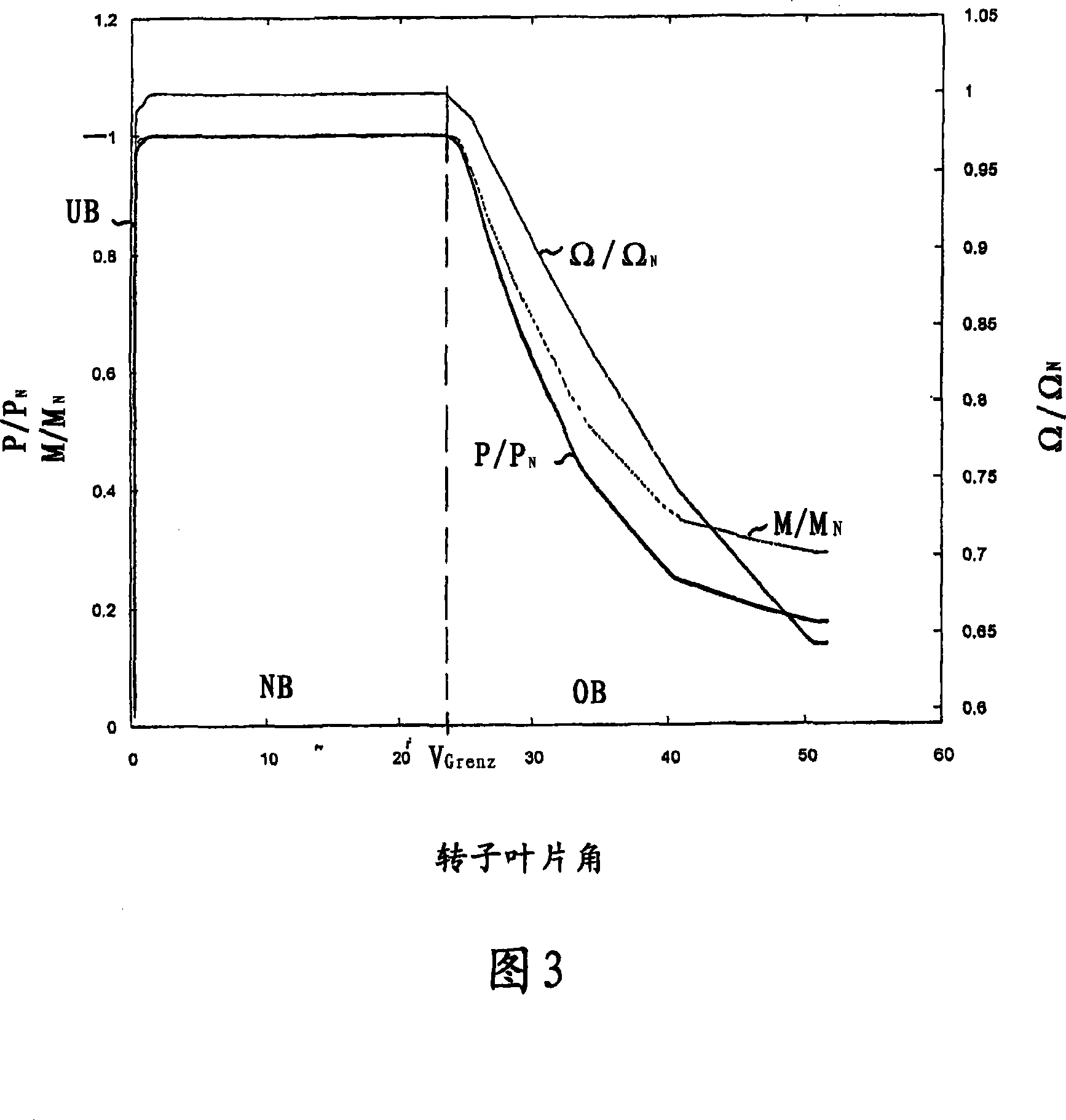
InactiveUS7629702B2Improved and reliableImprove compatibilityWind motor controlComparison table algorithmsEngineeringLimit value
Reduction in power output or rotor speed of a wind turbine above a defined limit value, the reduction not being implemented based on the measured wind speed, but on an input value which on one hand is easily detected physically and by control technology and on the other hand is a good indicator of mechanical stresses on the wind turbine. The invention uses the rotor-blade angle as the input value in a manner that starting at the limit value, the reduction in power output or in rotor speed is adjusted as a function of the rotor-blade angle.
Owner:SENVION GMBH
Method of damping tower vibrations of a wind turbine and control system for wind turbines
InactiveUS20090250932A1Easy to distinguishRapidly damp oscillation in rotor speedWind motor controlEngine fuctionsControl systemEngineering
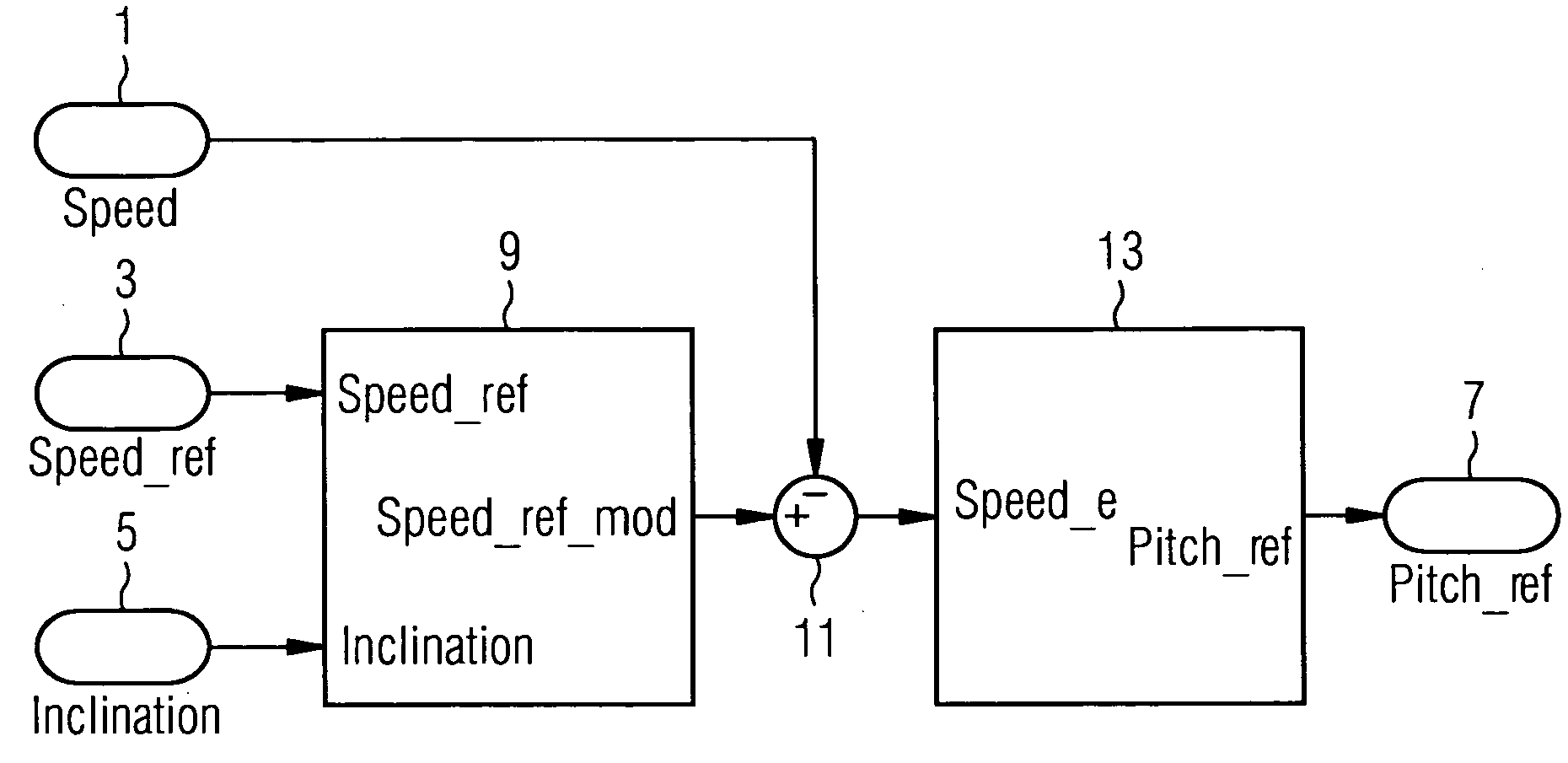
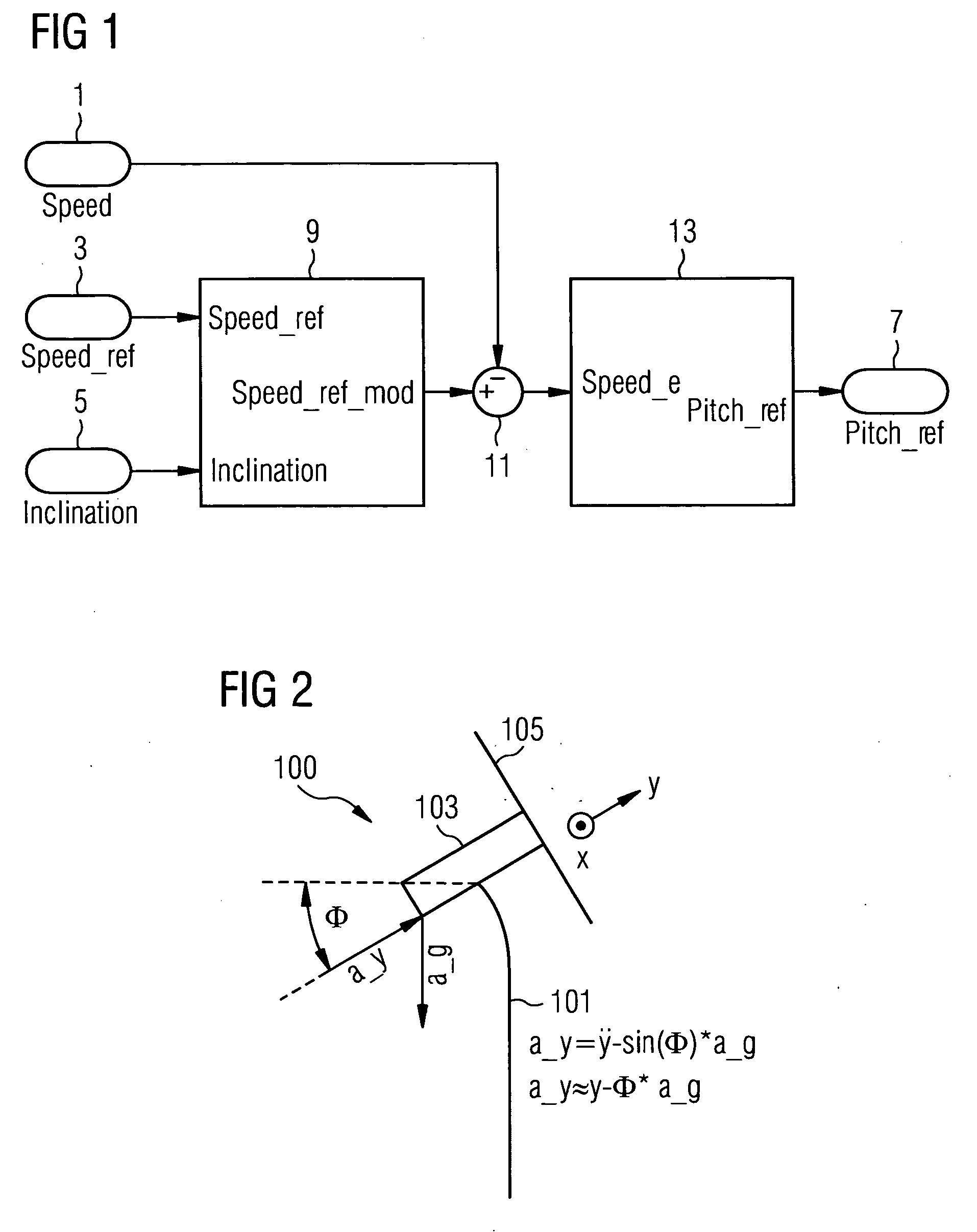
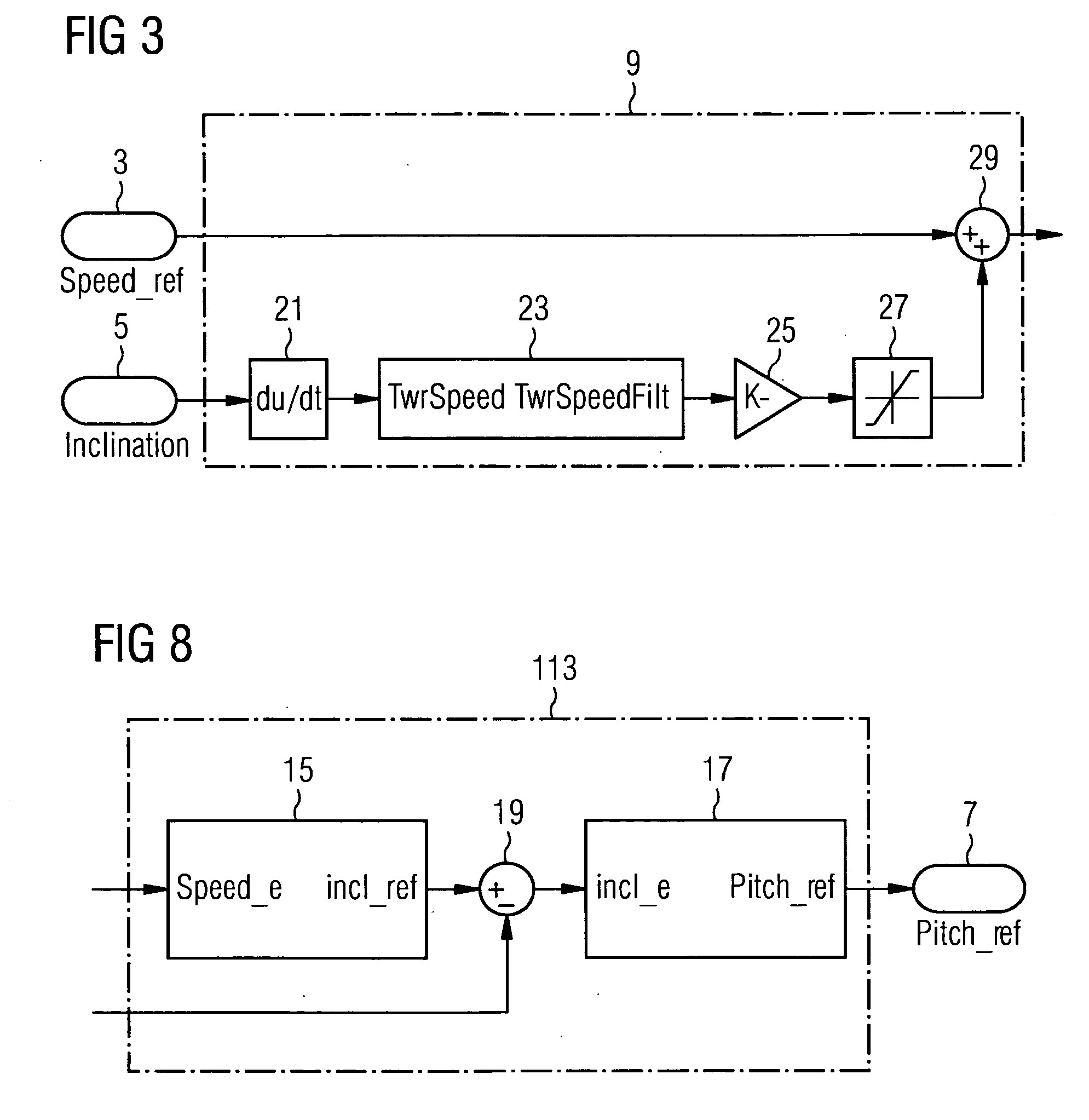
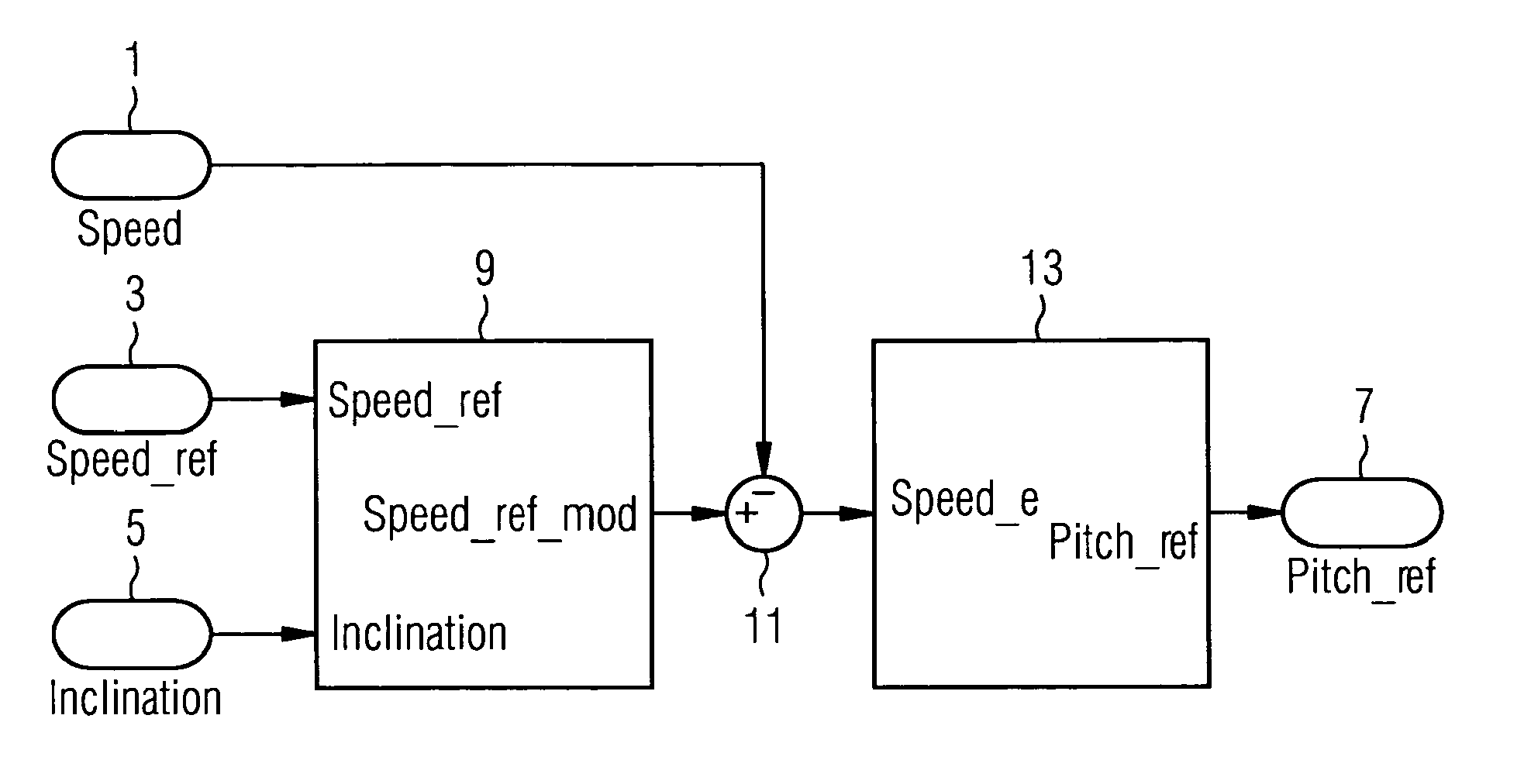
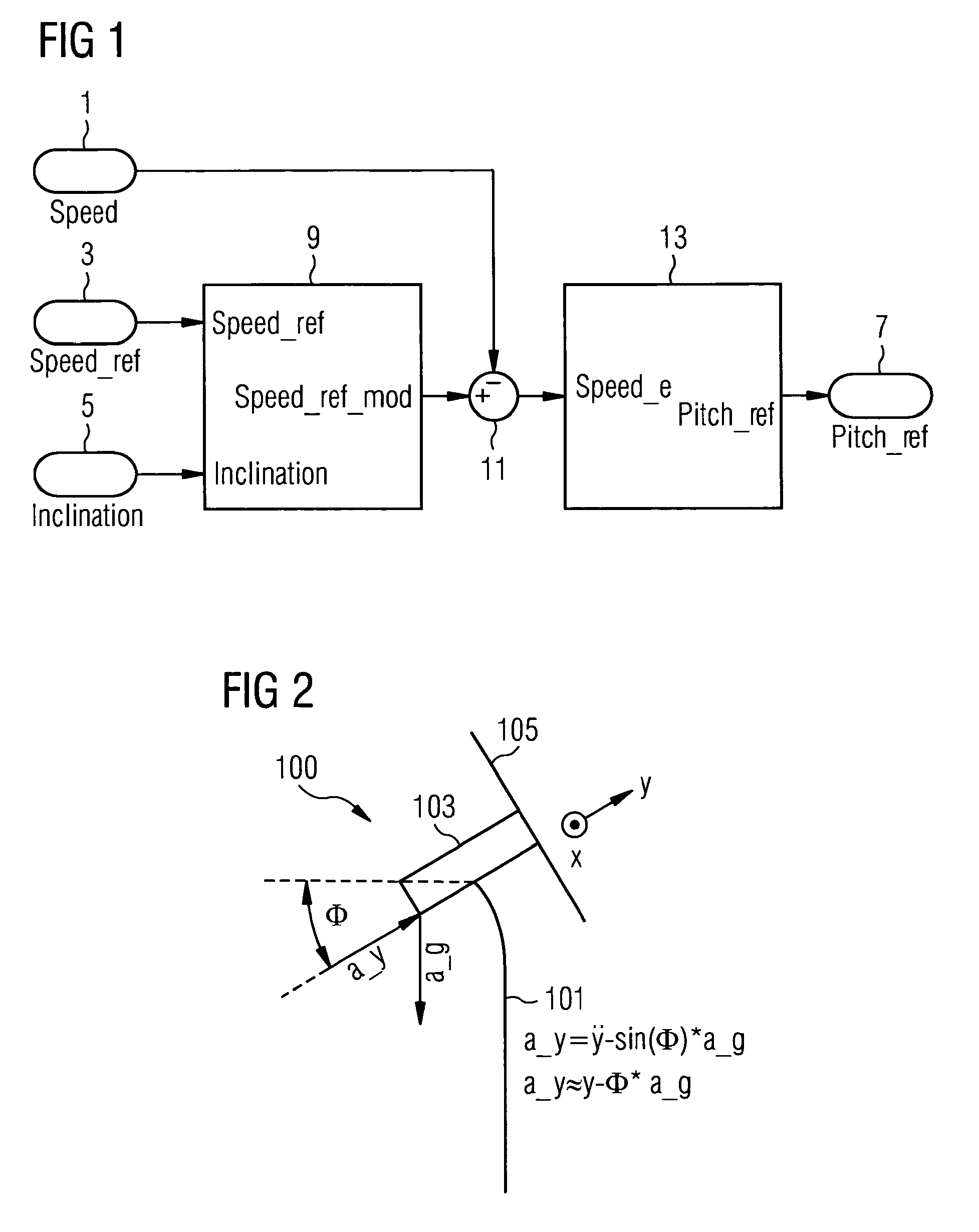
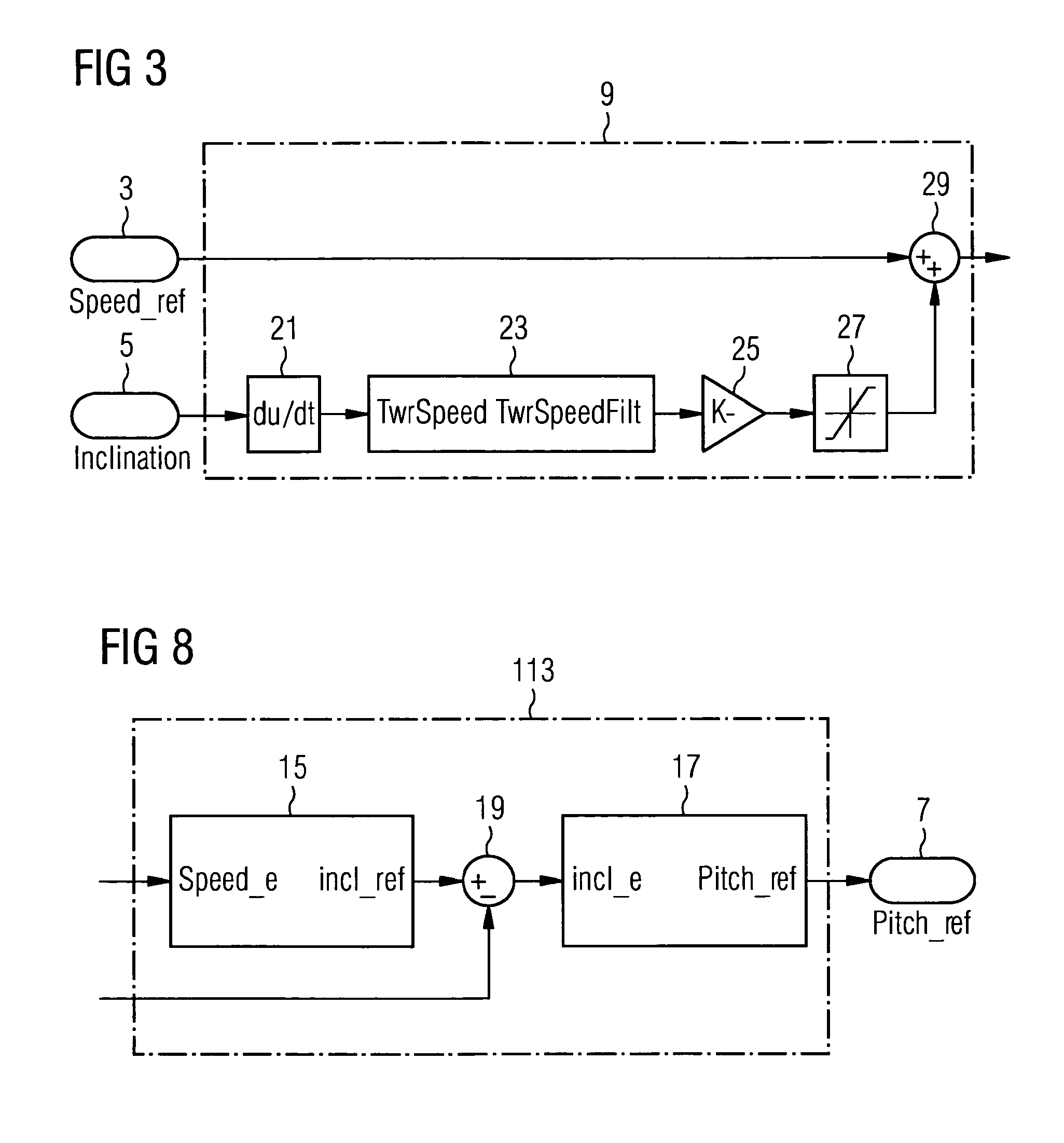
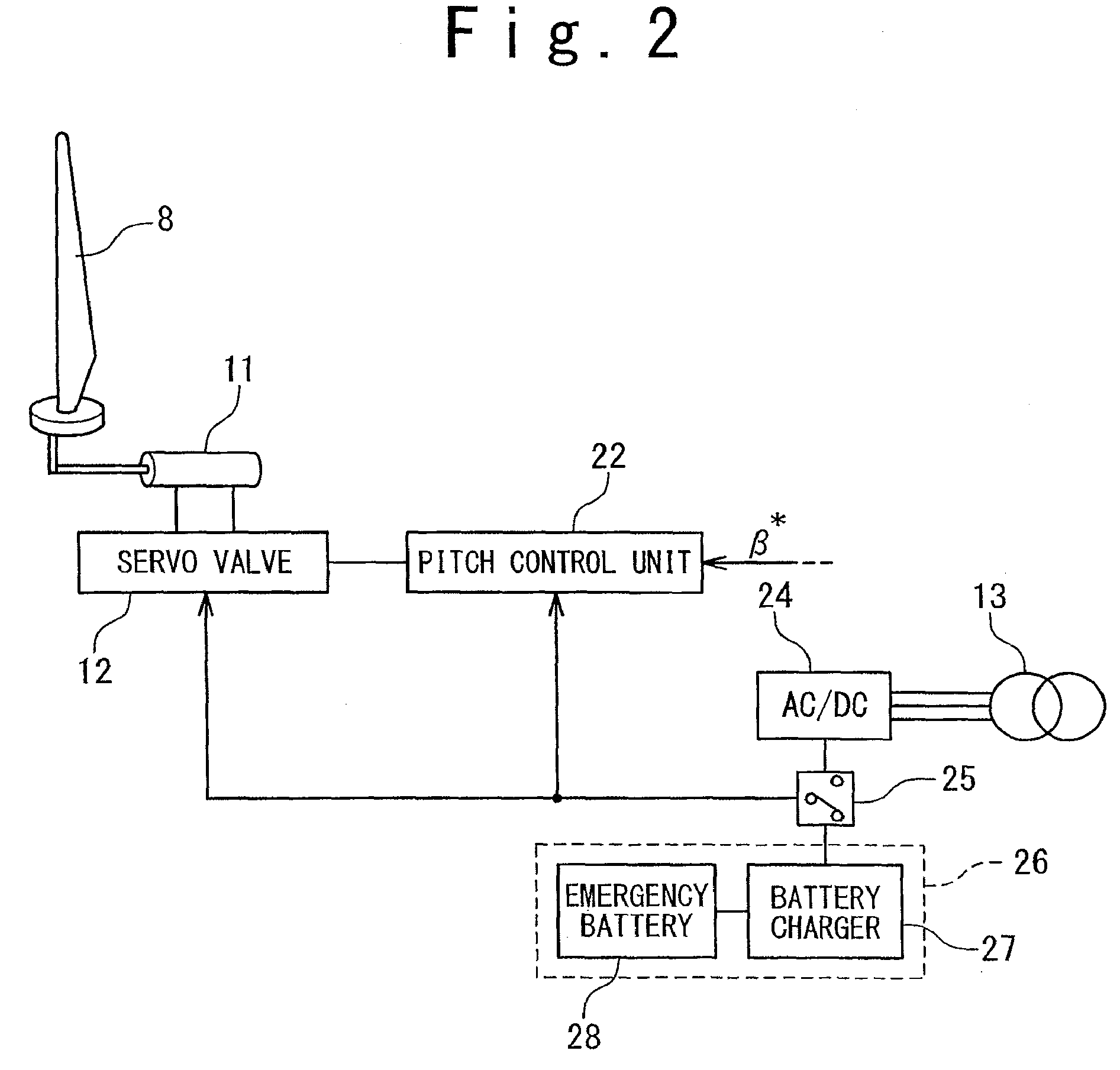
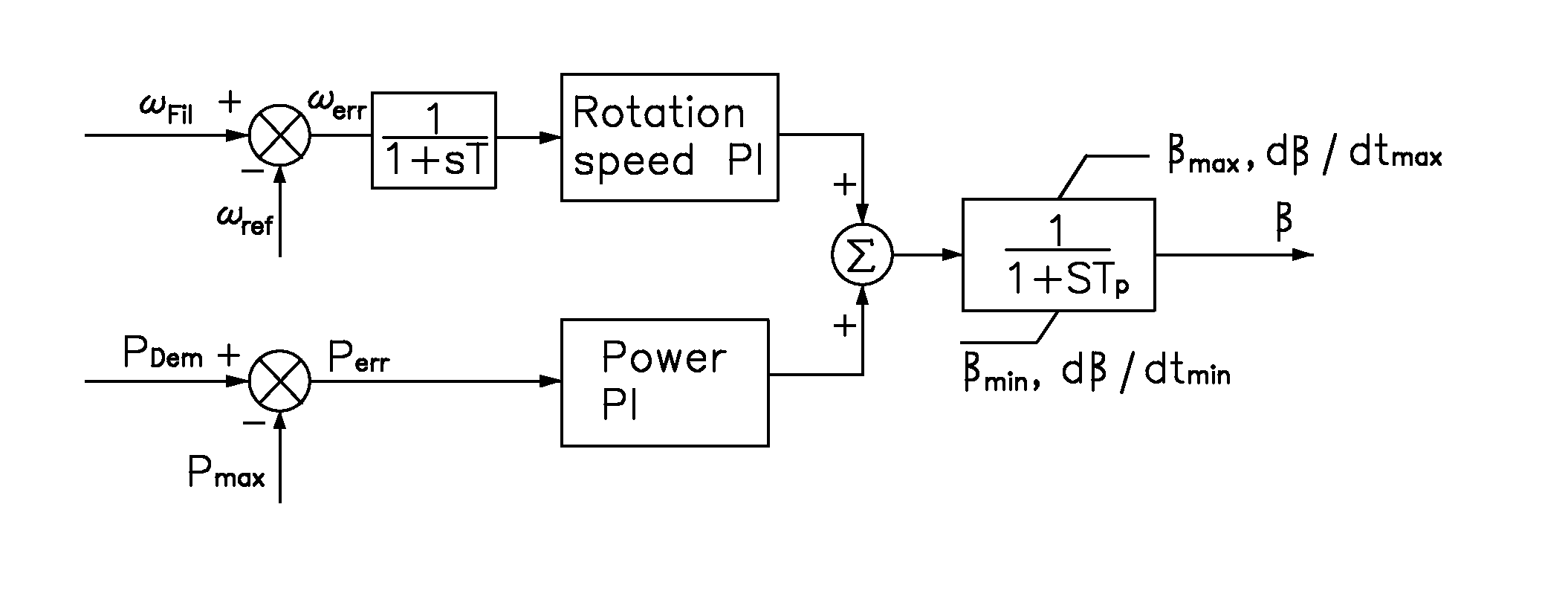
A control system for a wind turbine is provided. A pitch-control unit establishes a pitch-reference signal representing a pitch to be set by the pitch-actuator system. A rotor-speed input receives a signal representing a speed of the rotor. A speed-reference input receives a speed-reference signal for the rotor speed. An inclination-signal input receives a signal representing a tower inclination. A pitch-reference output outputs the pitch reference signal. A modification unit is connected to the speed-reference input to receive the speed-reference signal and connected to the inclination-signal input to receive the inclination signal. The modification unit establishes a modification signal based on the inclination signal, to modify the speed-reference signal via the modification signal, and to output a modified-speed-reference signal. The pitch-control unit connected to the modification unit to receive the modified-speed-reference signal and establish the pitch-reference value at least based on the difference between the modified-speed-reference and the rotor-speed signals.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Apparatus and system for pitch angle control of wind turbine
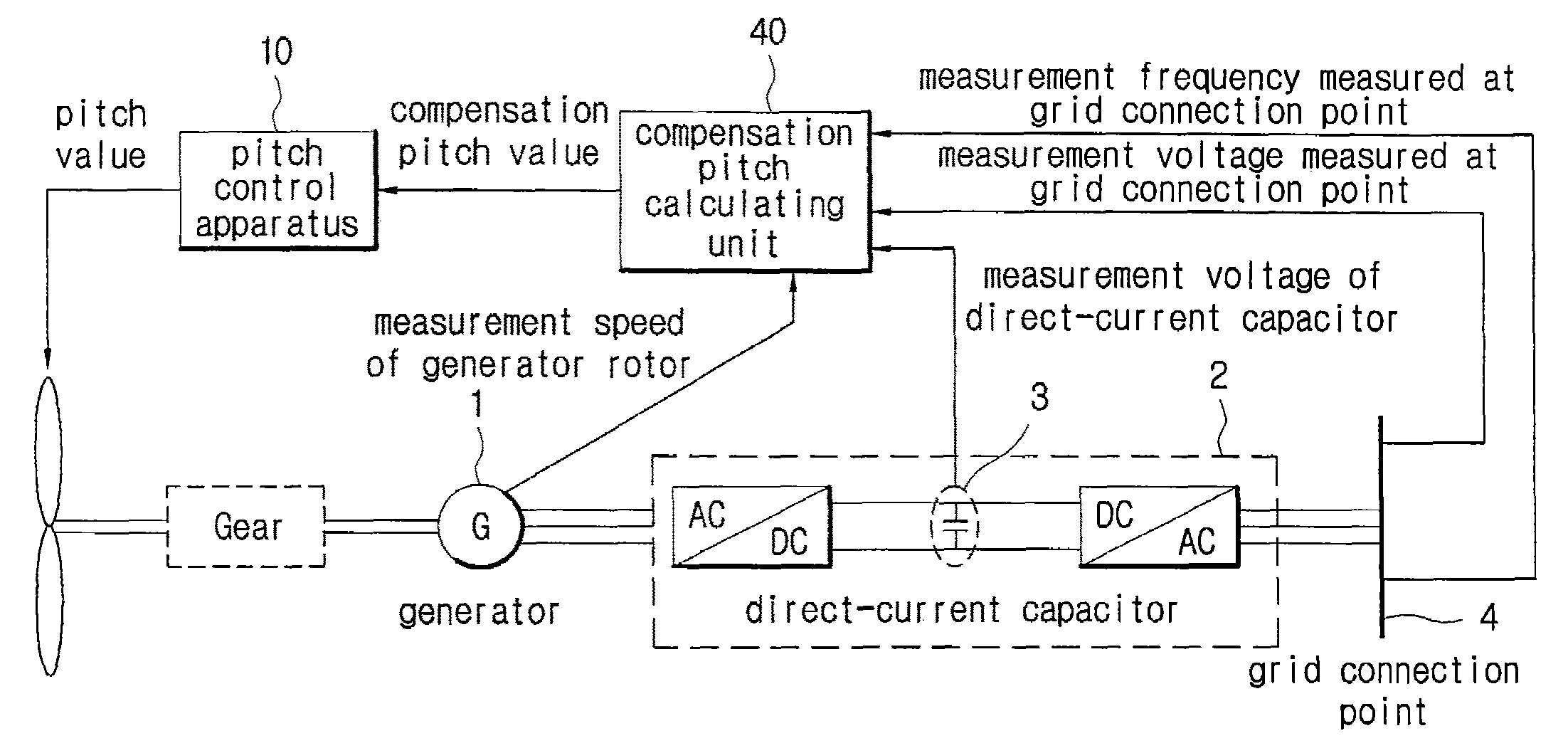
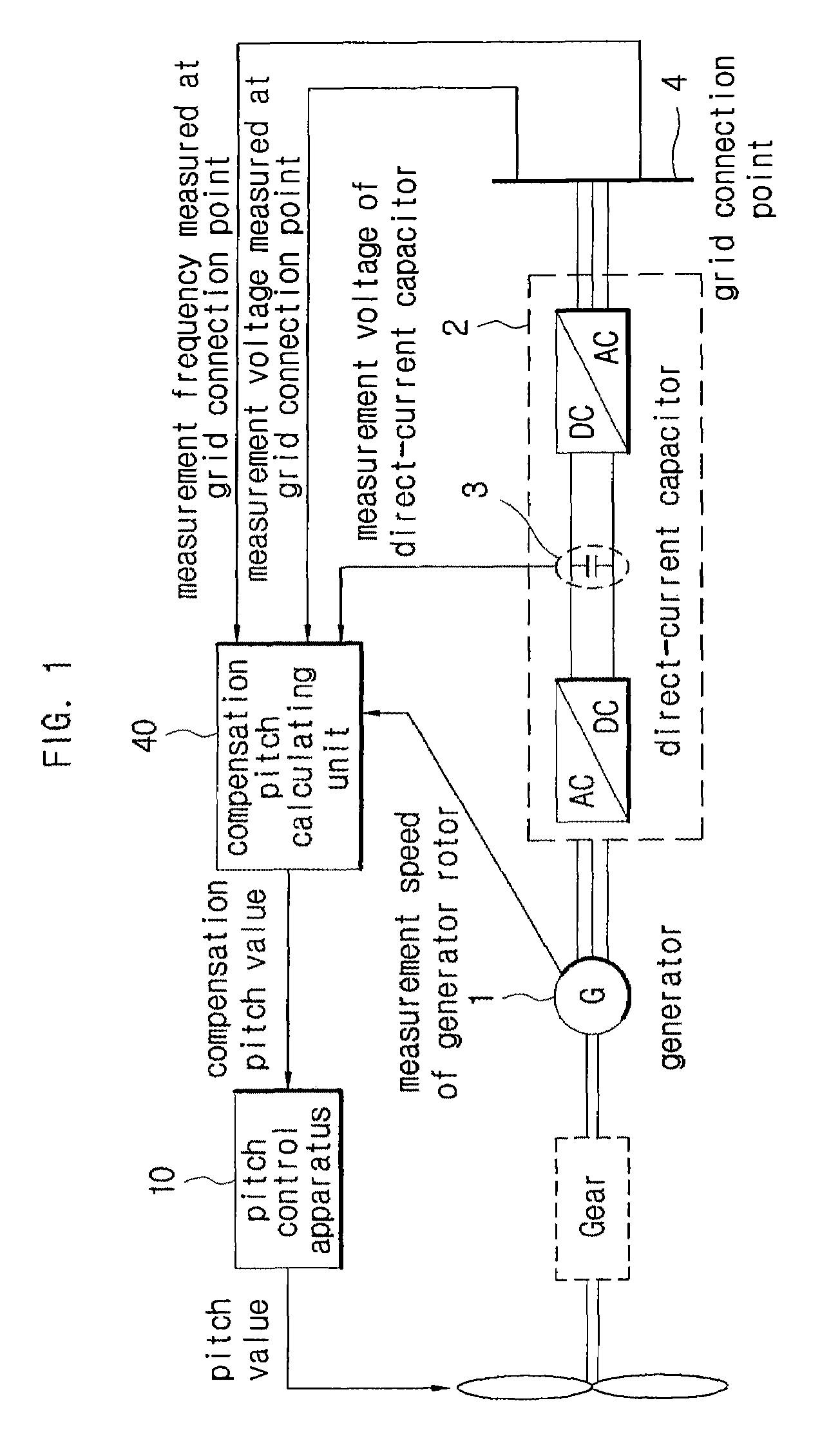
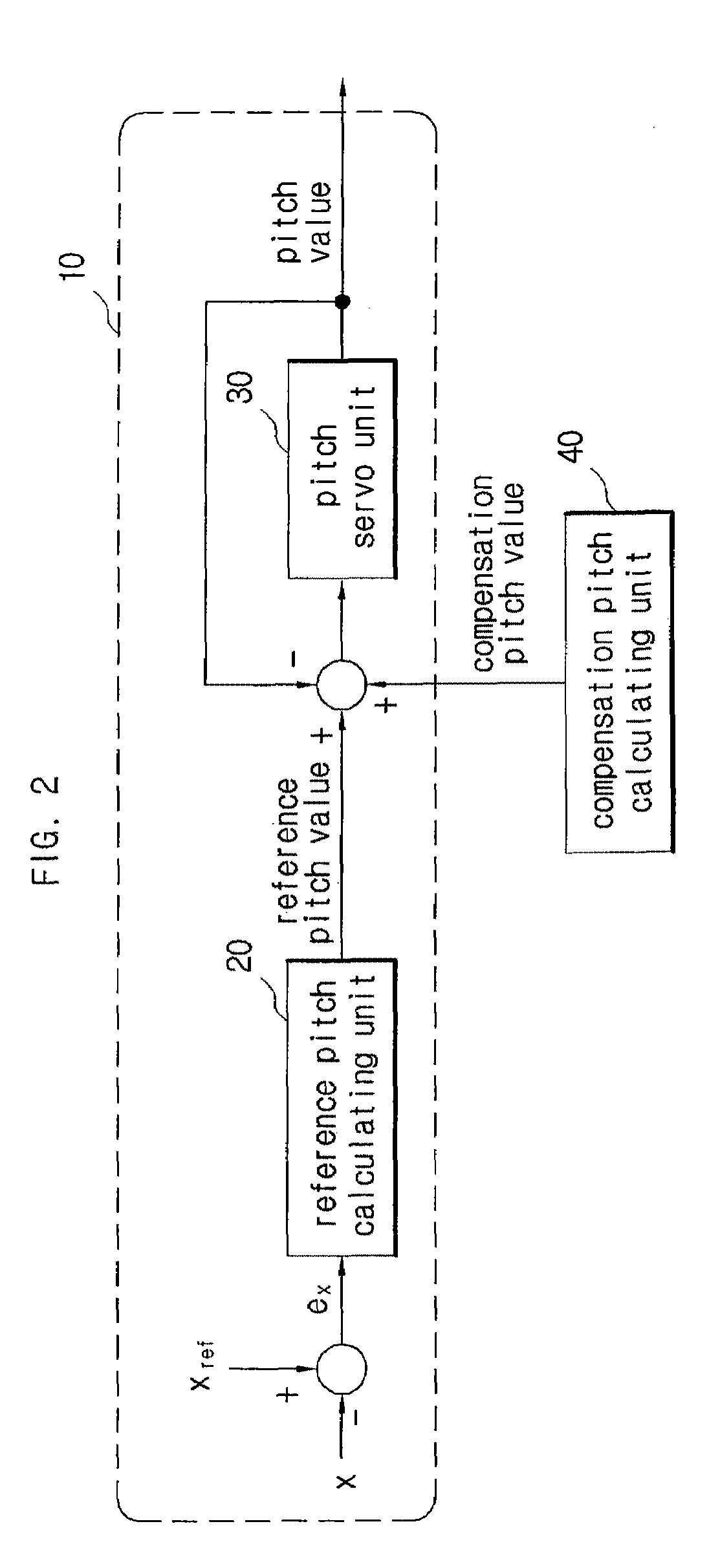
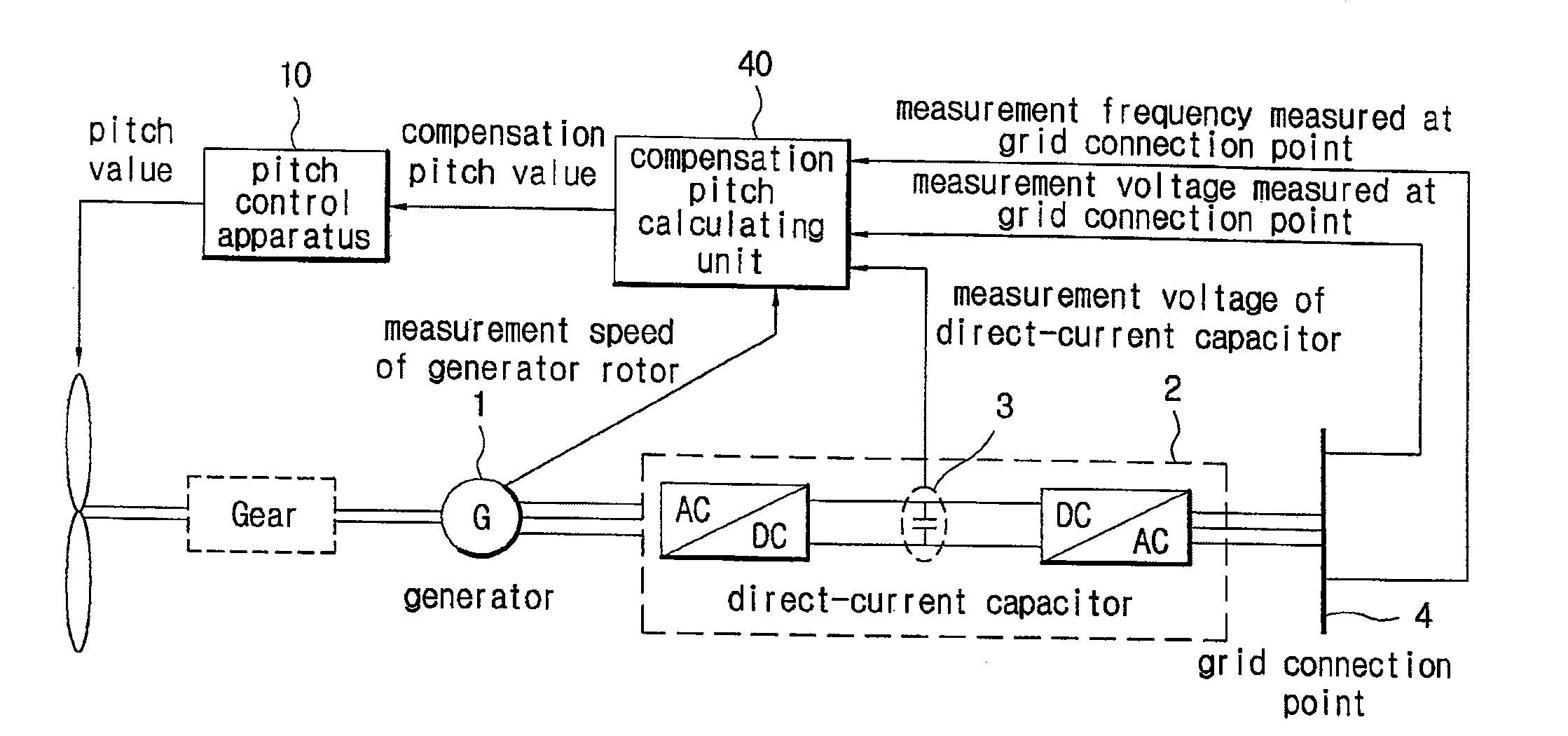
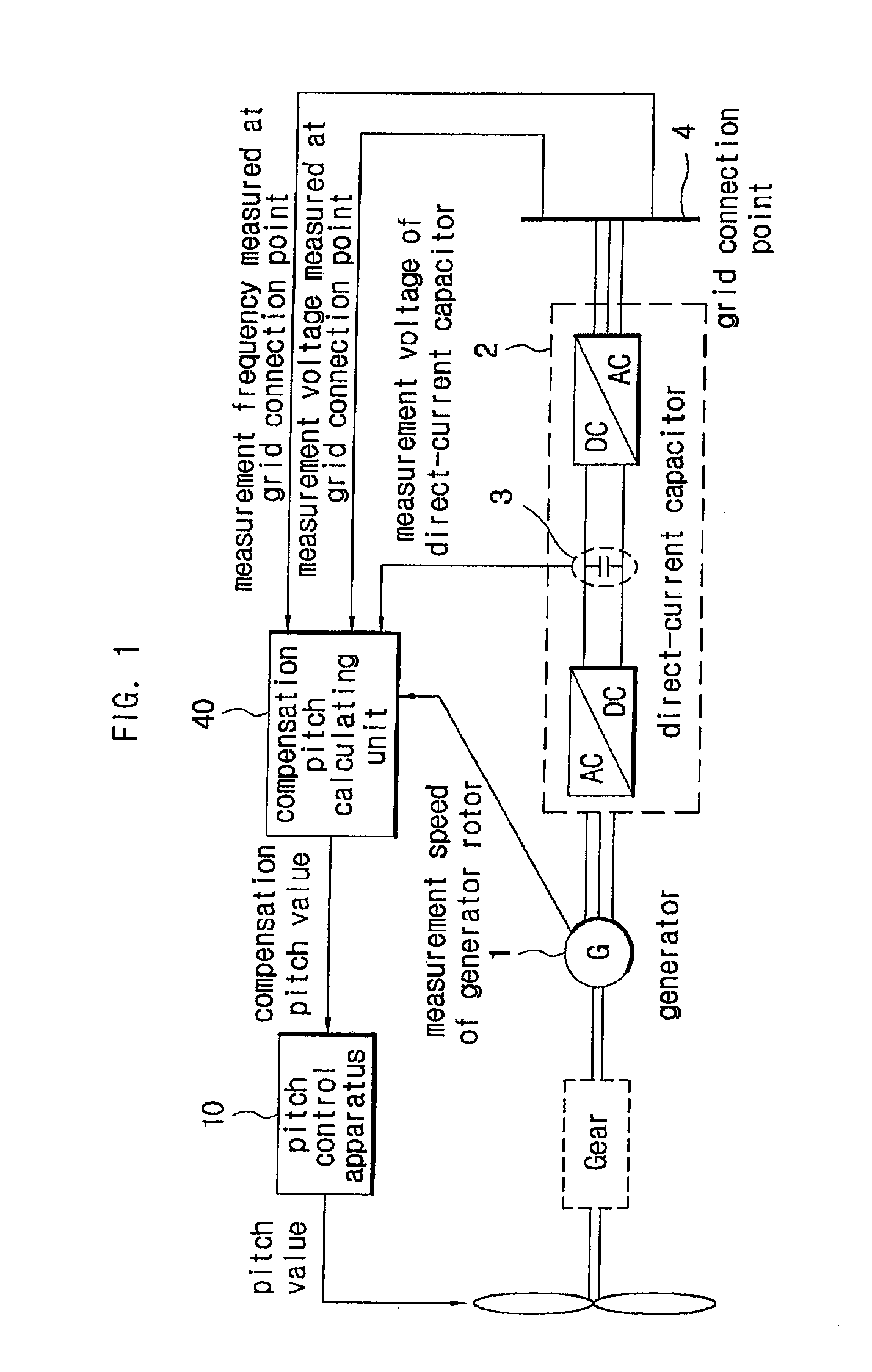
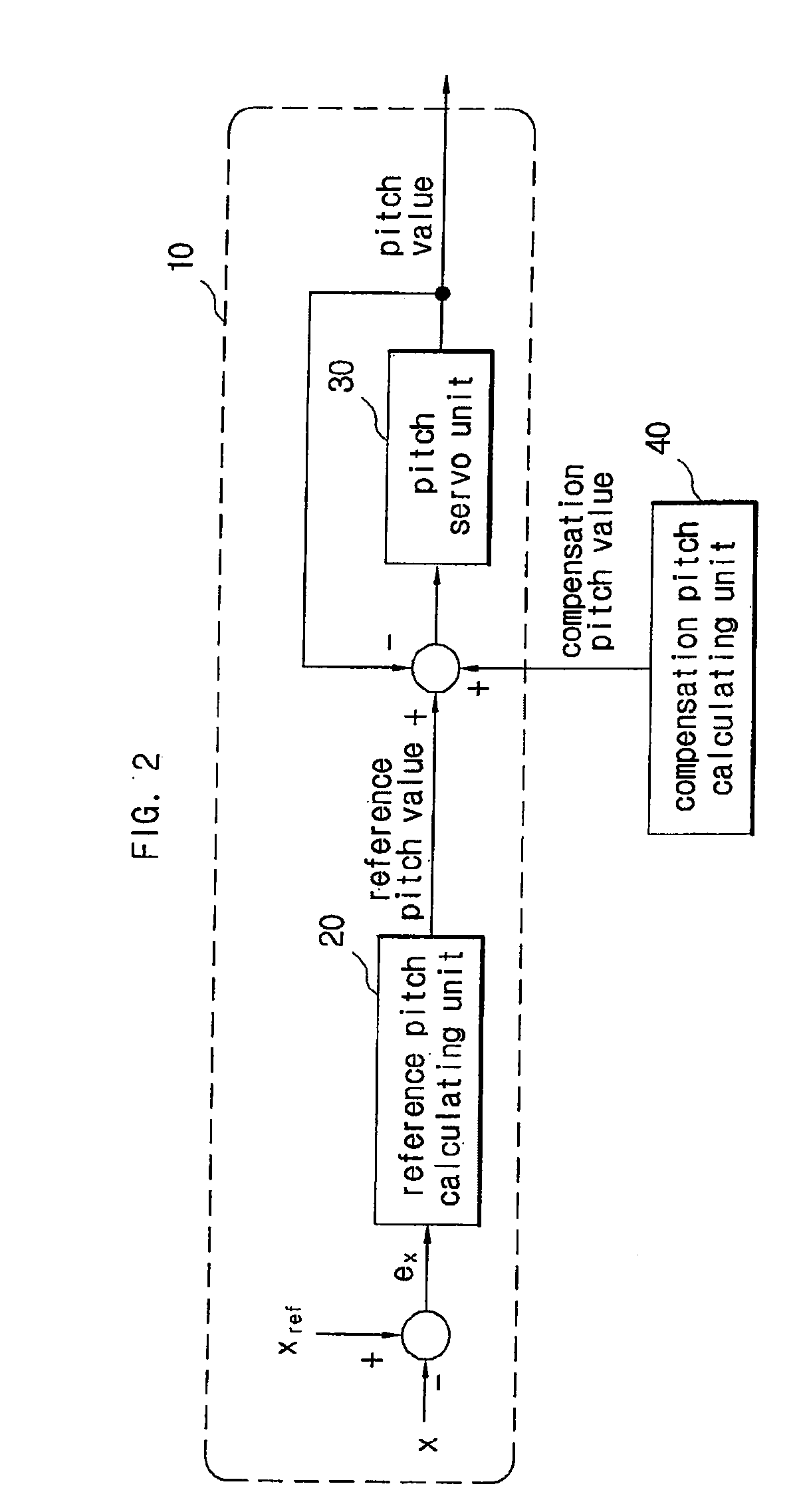
A pitch control apparatus for controlling the pitch value for a wind power generation system includes a generator comparing unit that calculates an error signal based on a difference between a generator measurement signal corresponding with an operation of the power generation system and a generator reference signal, and a reference pitch calculating unit that calculates a reference pitch value using the error signal. The pitch control apparatus further includes a compensation pitch calculating unit that calculates a compensation pitch value using an error value from the wind power generation system and a pitch calculating unit that calculates a pitch value using the reference pitch value and the compensation pitch value. The error value may be any one of a voltage error value from a direct-current capacitor, a voltage error value from a grid connection point, a speed error value from a rotor, and a frequency error value from a grid connection point.
Owner:SAMSUNG HEAVY IND CO LTD
Wind turbine generator system and control method of the same
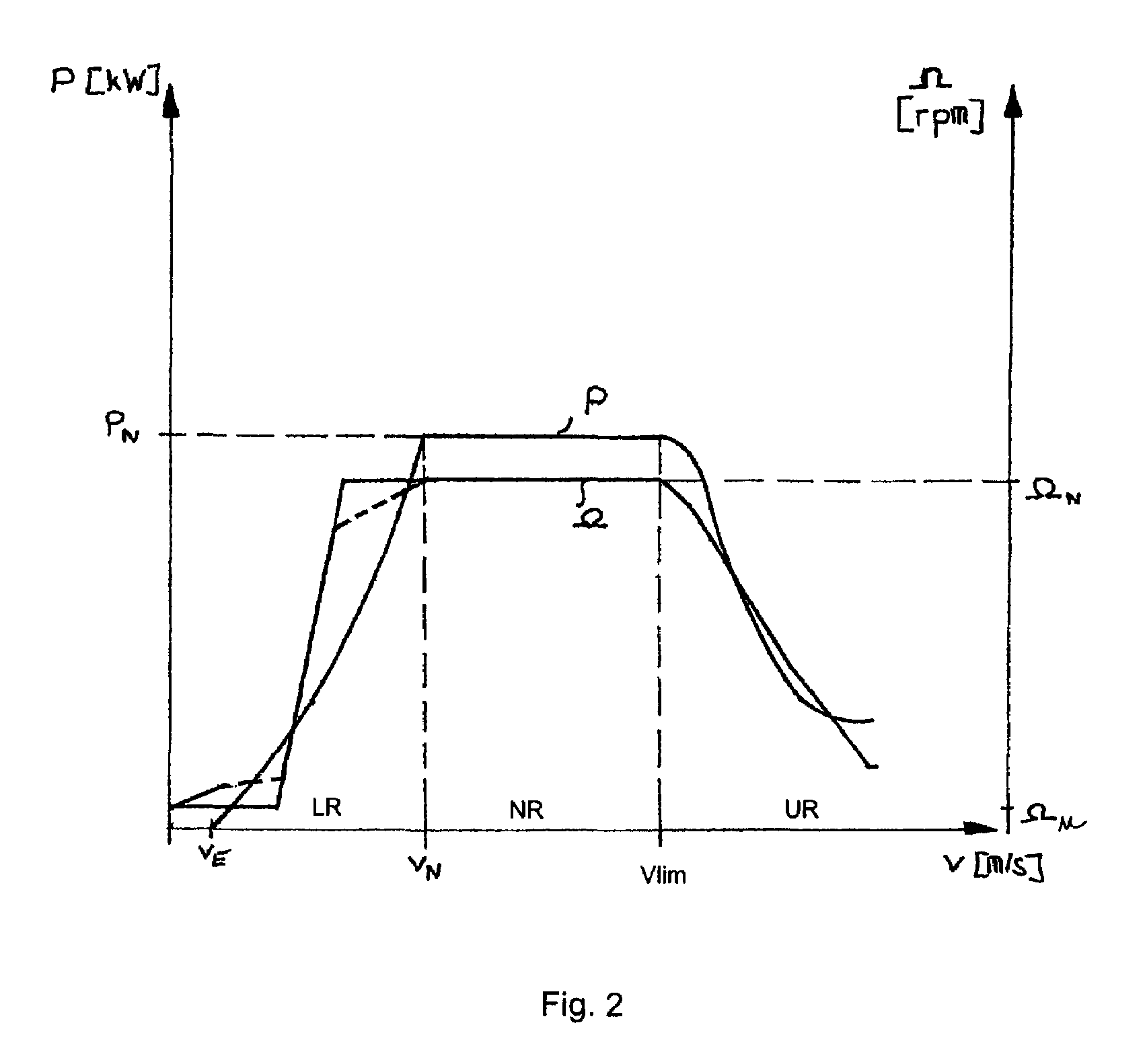
ActiveUS20110089694A1Suppress output power fluctuationsGenerating efficiency is reducedMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlControl theoryFlat rated
A wind turbine generator system includes: a wind turbine rotor including a blade having a variable pitch angle; a generator driven by the wind turbine rotor; and a control unit controlling the output power of the generator and the pitch angle of the blade in response to the rotational speed of the wind turbine rotor or the generator. The control unit performs a first control in which the output power is controlled in accordance with a predetermined power-rotational speed curve until the rotational speed is increased to reach a predetermined rated rotational speed, and performs a second control in which the output power is controlled to a predetermined rated power when the rotational speed exceeds the rated rotational speed; the control unit is responsive to the pitch angle for maintaining a state of performing the second control is or for switching to a state of performing the first control, when the rotational speed is reduced below the rated rotational speed after the control unit is once placed into the state of performing the second control.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
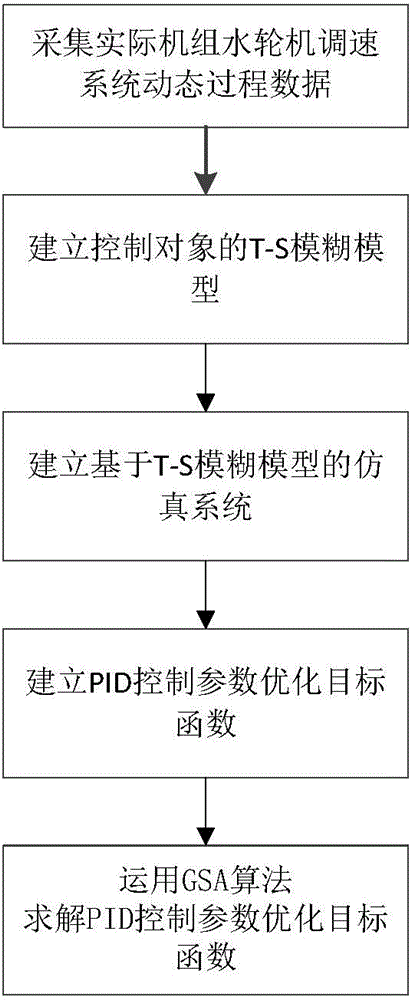
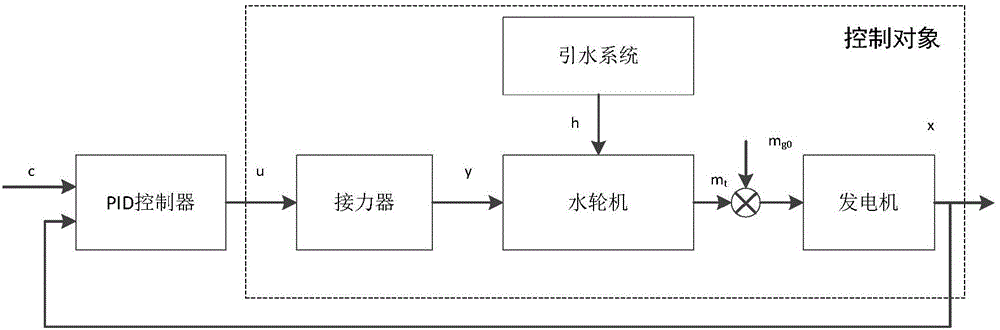
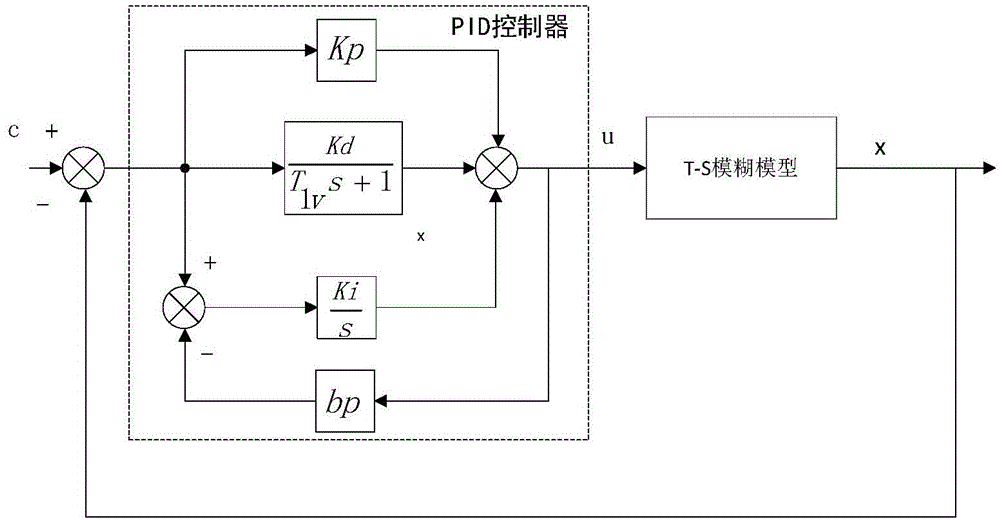
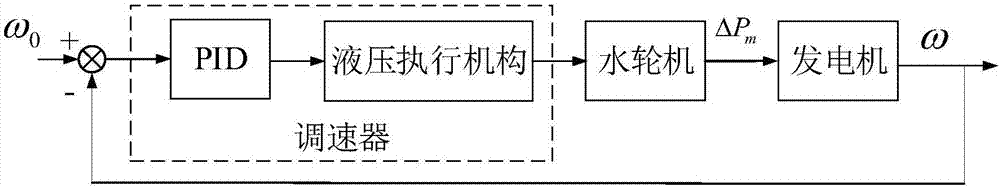
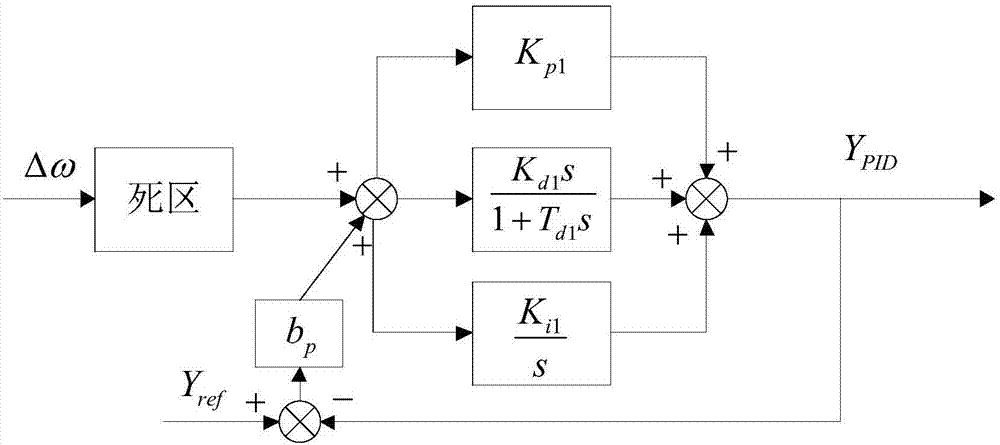
Automatic setting method for control parameters of water turbine speed regulating system
ActiveCN104533701AHigh precisionImprove dynamic qualityHydro energy generationMachines/enginesWater turbineUnit speed
The invention relates to an automatic setting method for control parameters of a water turbine speed regulating system. According to the method, firstly, T-S fuzzy model identification is conducted on a control object of the water turbine speed regulating system of a real unit to obtain a high-precision simulation system of the water turbine speed regulating system; secondly, according to the simulation system, a target function with the PID control parameters as optimization variables is set up, and the target function is worked out through a gravitational search algorithm to obtain the optimal PID control parameters. Due to the fact that the precision of the set simulation system is high, the characteristics of the real unit can be really reflected, the control parameter optimization result obtained through the simulation system can be directly applied to the real unit, and the dynamic quality of the unit speed regulating system is effectively improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Water turbine speed regulator PID parameter optimizing method and system
The invention discloses a water turbine speed regulator PID parameter optimizing method and system. The method comprises the steps that the speed regulator PID parameter optimizing overall objective function J restraining ultra-low frequency oscillation is obtained, optimization is conducted through the optimization algorithm, the optimal PID parameter is sought, and the overall objective function is minimal. According to the method, the value obtained after weighting of the frequency step response deviation absolute value integral and speed regulating system damping at the focused ultra-low frequency band integral serves as the optimization objective, the obtained speed regulator parameter integrates the speed regulator adjusting performance and damping level at the same time, accordingly, the problem of ultra-low frequency oscillation caused by speed regulator negative damping is solved, and the speed regulator adjusting dynamic quality is combined.
Owner:STATE GRID SICHUAN ELECTRIC POWER CORP ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +3
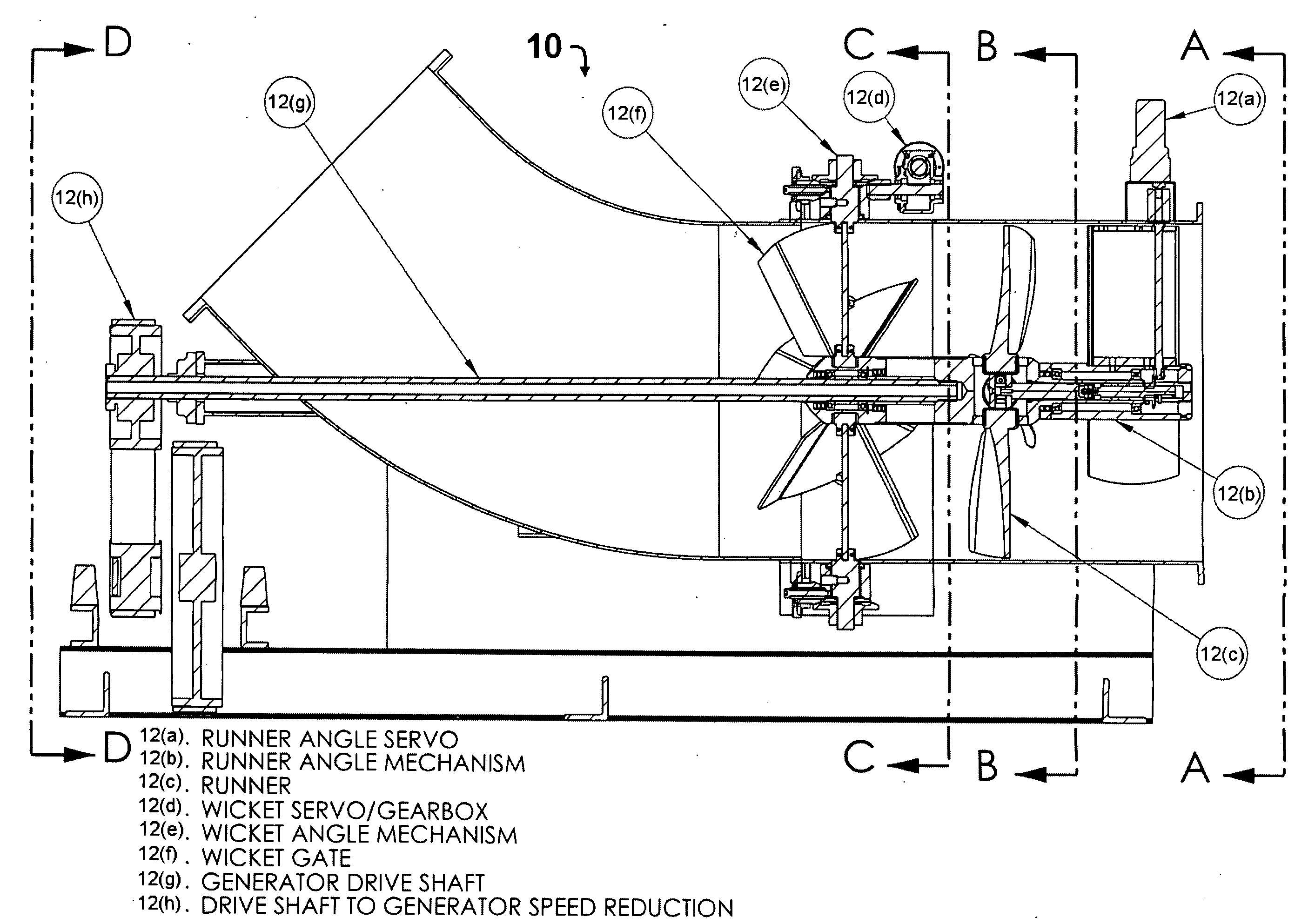
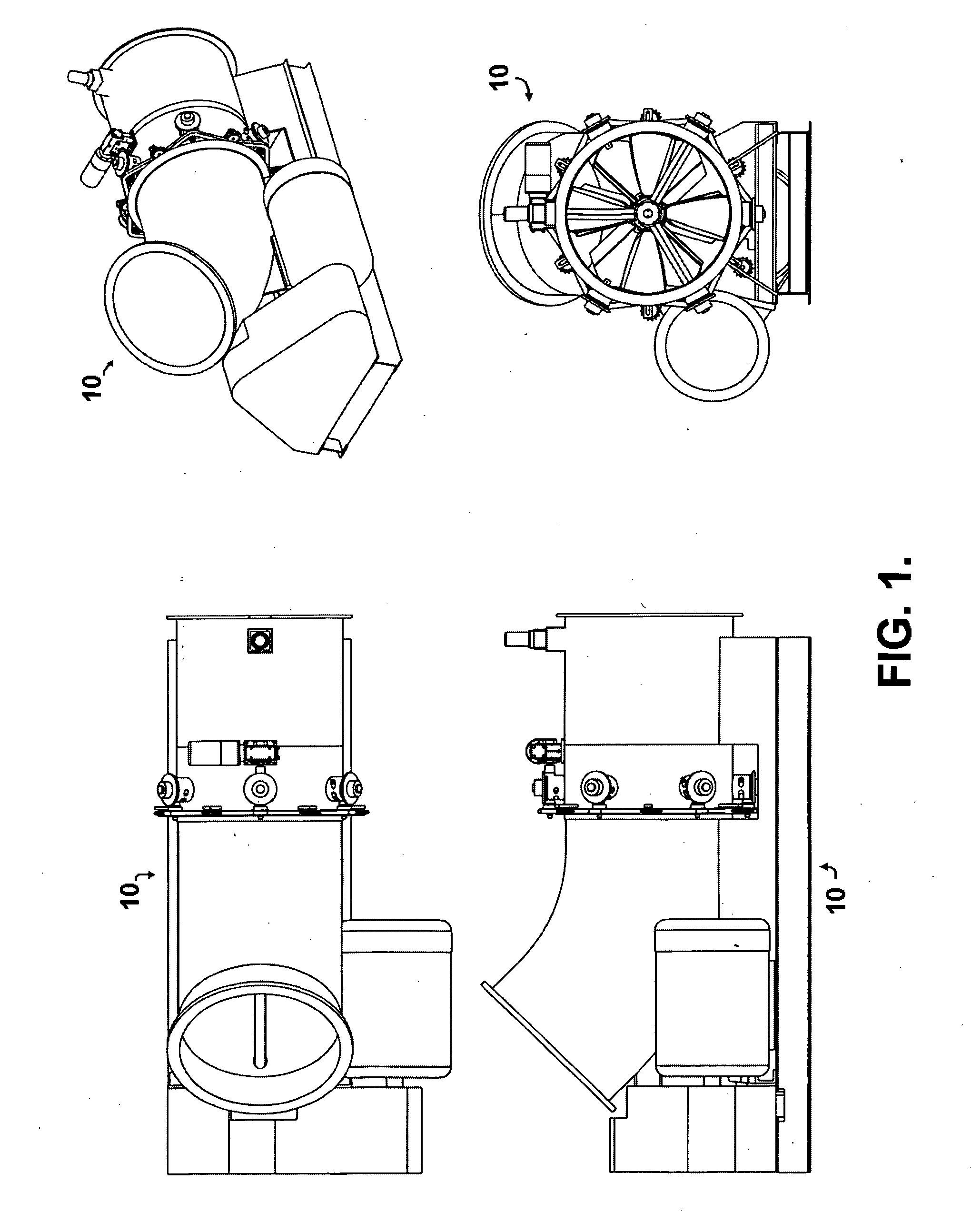
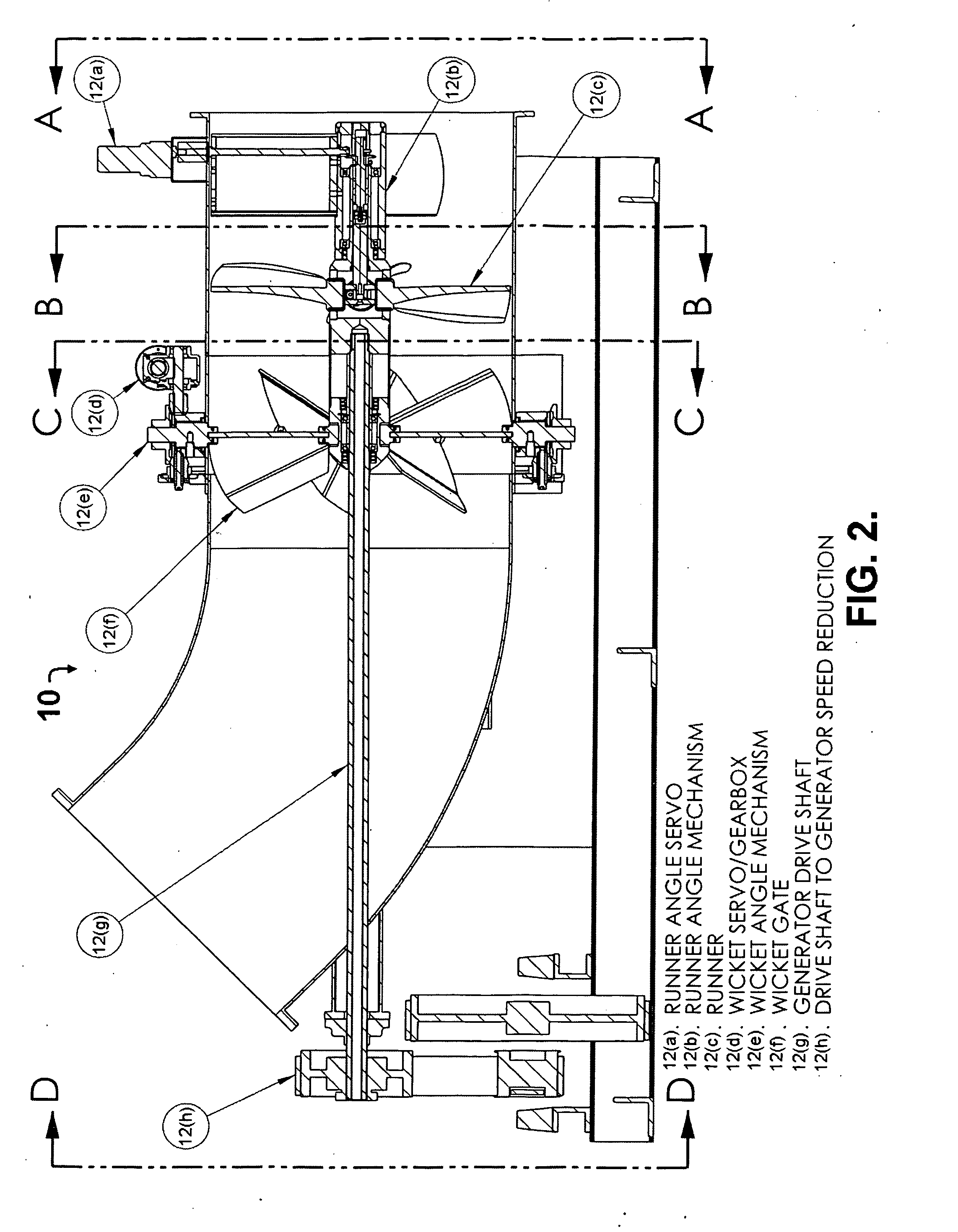
Hydro turbine generator
ActiveUS20090021011A1Reduce speedEasy maintenanceWind motor controlGas turbine plantsPre-conditionControl system
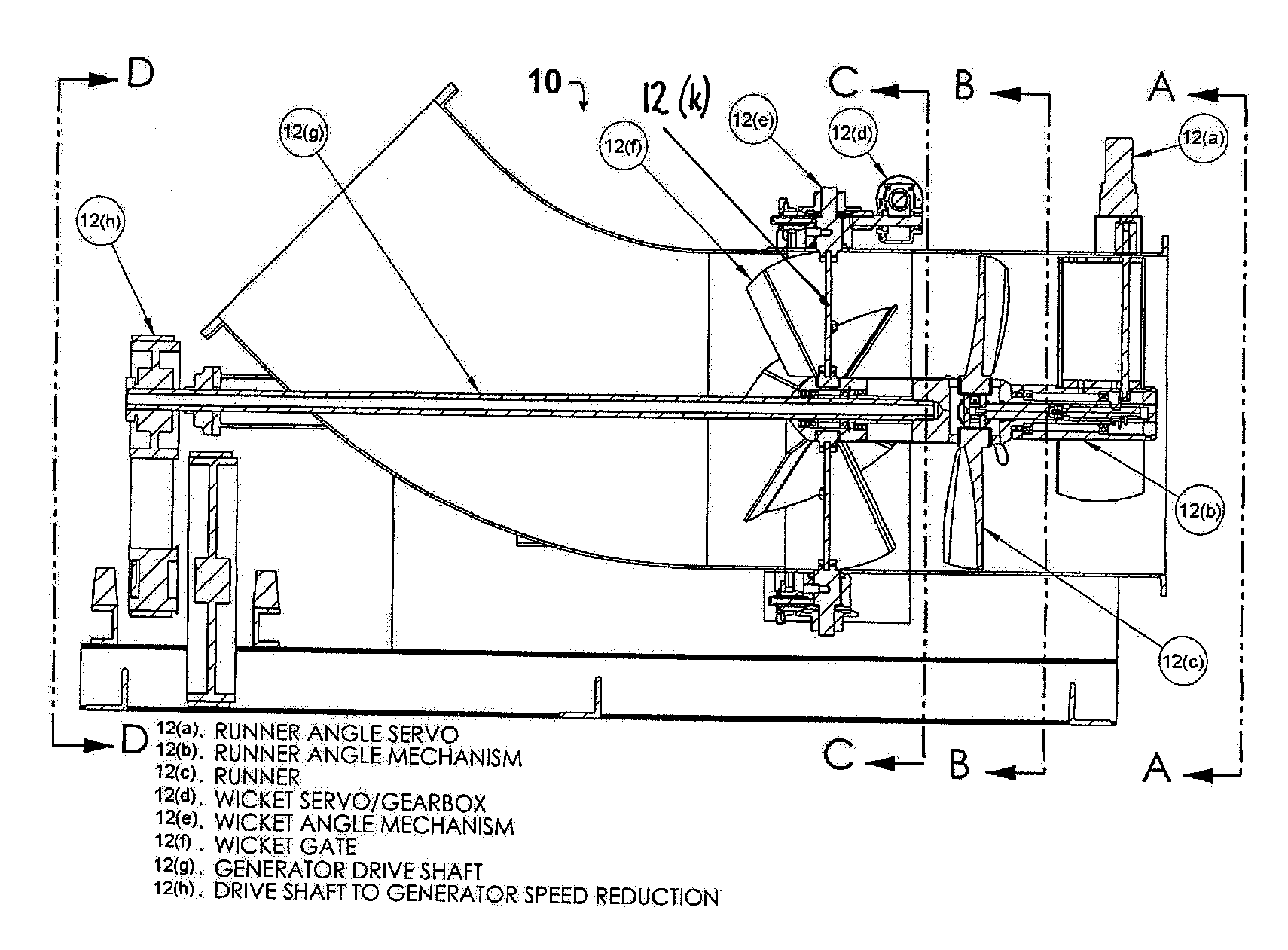
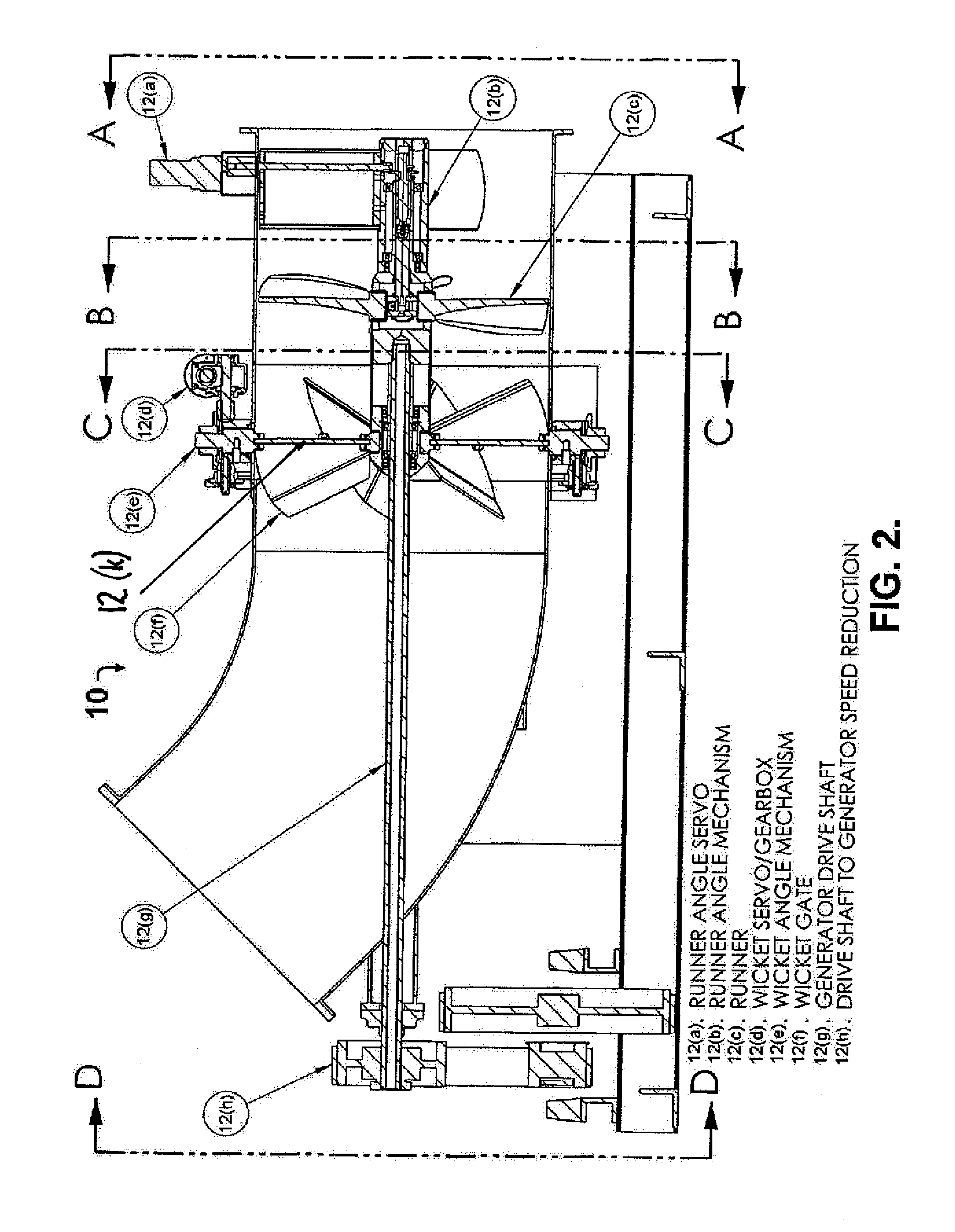
A hydroelectric turbine generator and control system is provided that optimizes the maximum possible power output at all times by strictly monitoring power output from the generator unit and modulating the wicket gate angle and the runner blade pitch independently of one another. The hydroelectric turbine generator includes a means for separately controlling wicket gate angle and runner blade pitch. The wicket gate angle control mechanism controls the flow into the system, pre conditions flow for maximum power and maintains reservoir level. The runner blade pitch control mechanism continuously monitors the system power output based on actual power produced, and adjusts system parameters in order to achieve maximum power output.
Owner:SHIFRIN SALVATORE +1
Control device for wind power systems having power failure detection
ActiveUS20100283247A1Improve regulator dynamicGood dynamic responseLevel controlWind motor controlElectricityWind system
A wind energy installation control device includes a wind rotor, a generator driven by the wind rotor, a torque control unit configured to control a torque of the generator, and a control system. The control system includes a detector configured to identify a grid dip and an end of the grid dip, a residual torque transmitter configured to provide a preset value for a torque of the generator after identification of the grid dip, and an initializer configured to initialize a component of the torque control unit at the preset value. Accordingly, upon return of grid power after a grid dip, the vibration behaviour of a wind power system can be significantly improved. Overload of a drive train upon return of grid voltage can thus be reduced.
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY SERVICE GMBH
Method for controlling a wind power plant and corresponding wind power plant
InactiveCN101031720AWind motor controlComparison table algorithmsPeaking power plantMachine utilization
The power of wind energy or the revolution rate drive down to the prescribed limit value has been carried based on easily measured in physical and control technique aspect and reflect the input variable of machine utilization but not based on the metrical wind speed. For the assume of this invention, use rotor blade angle as input variable, then when arrive in the limit value adjust power and the drive down of revolution rate based on the rotor blade angle.
Owner:SENVION GMBH
Hydro turbine generator
ActiveUS20120146330A1Reduce speedEasy maintenanceGas turbine plantsReaction enginesPre-conditionControl system
A hydroelectric turbine generator and control system is provided that optimizes the maximum possible power output at all times by strictly monitoring power output from the generator unit and modulating the wicket gate angle and the runner blade pitch independently of one another. The hydroelectric turbine generator includes a means for separately controlling wicket gate angle and runner blade pitch. The wicket gate angle control mechanism controls the flow into the system, pre conditions flow for maximum power and maintains reservoir level. The runner blade pitch control mechanism continuously monitors the system power output based on actual power produced, and adjusts system parameters in order to achieve maximum power output.
Owner:SHIFRIN SALVATORE +1
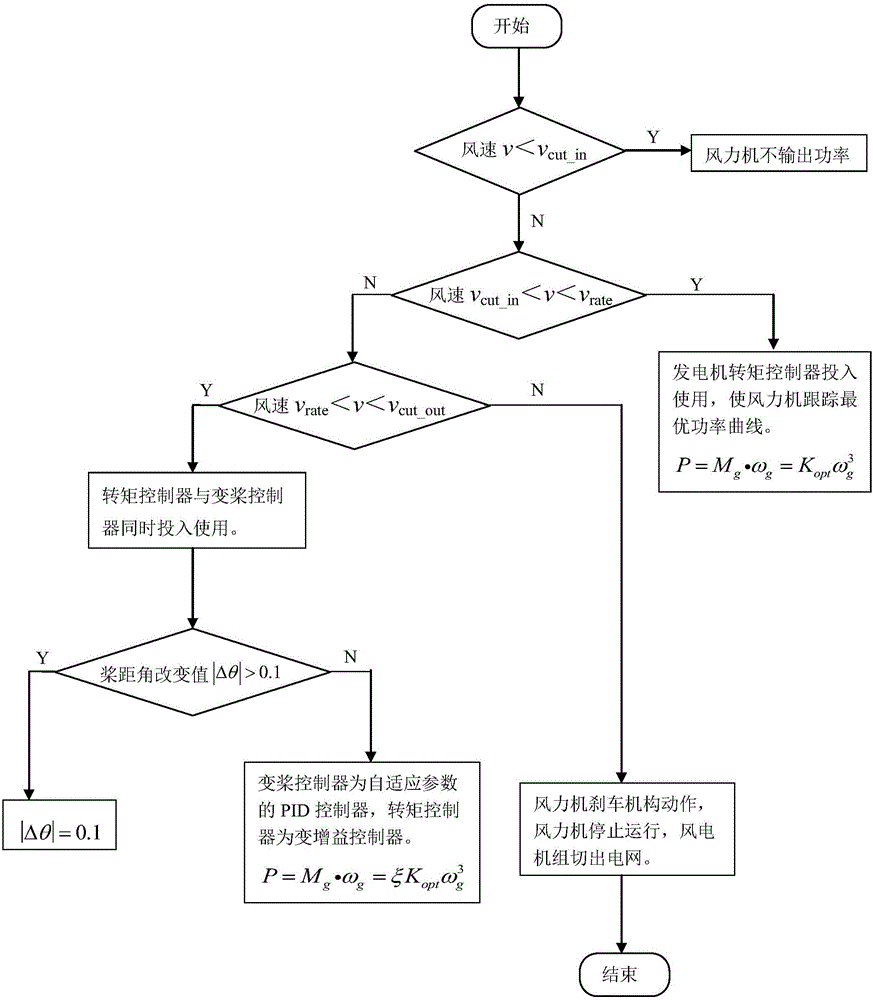
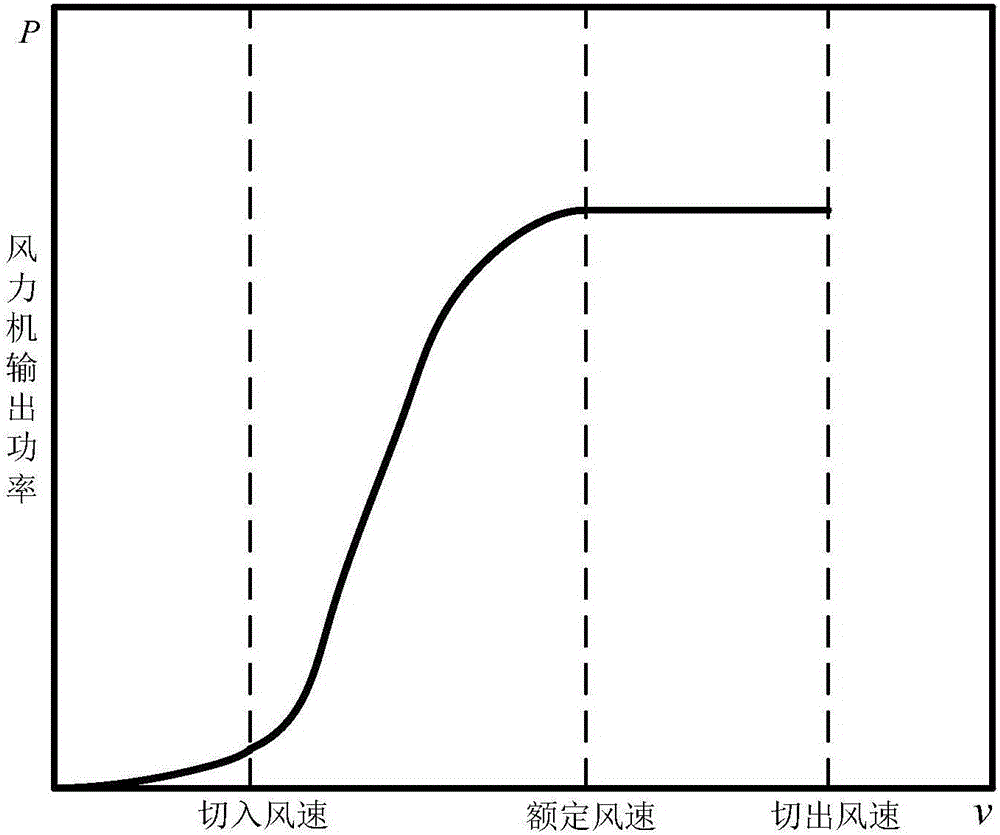
Power optimal control method for variable-speed and variable-pitch wind turbine
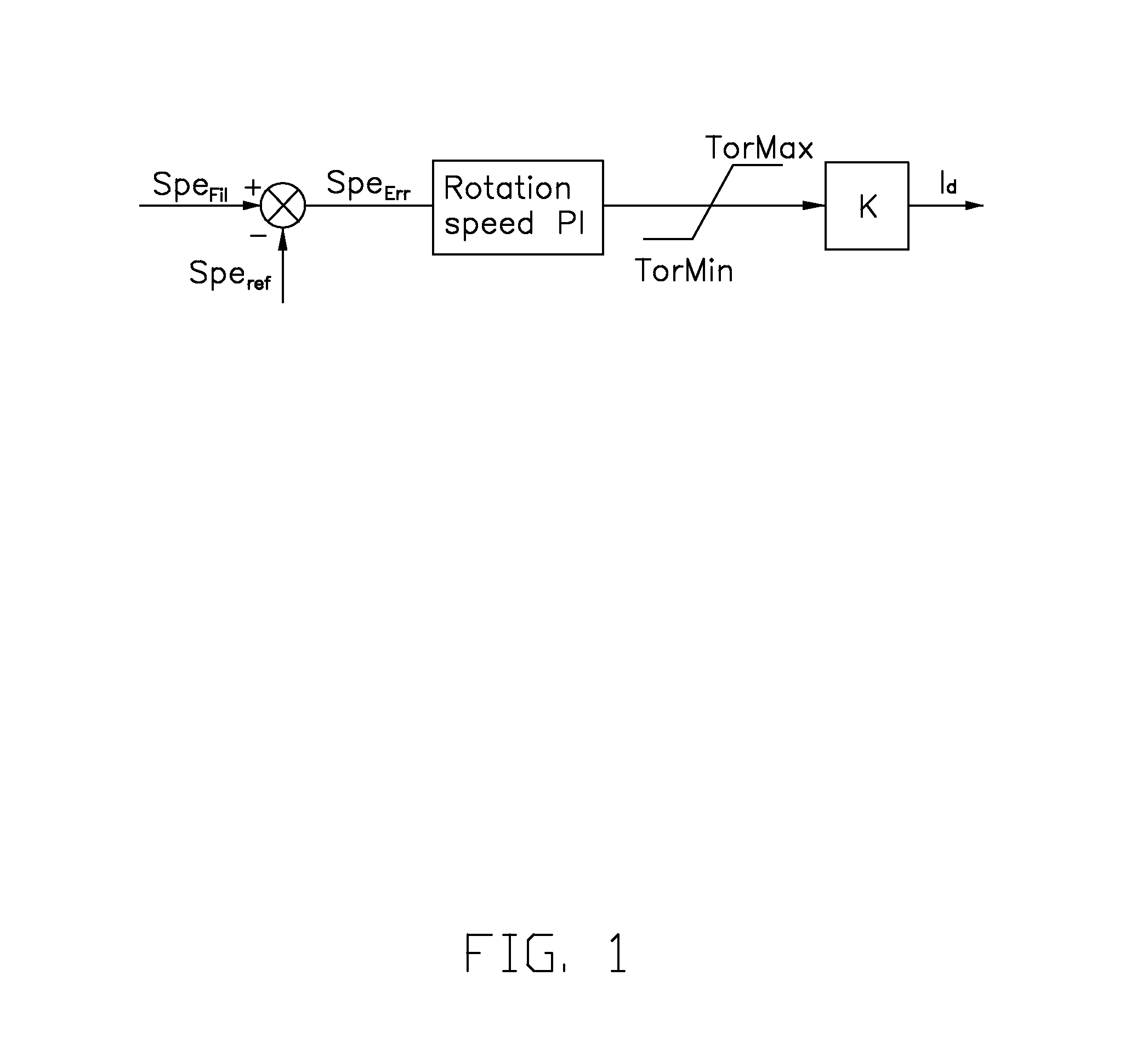
InactiveCN105986961AGuaranteed operationAvoid frequent switchingWind motor controlVariable speed operation controlOptimal controlTorque controller
The invention relates to a power optimal control method for a variable-speed and variable-pitch wind turbine. The variable-speed and variable-pitch wind turbine is controlled within the whole designed wind speed range. When the wind turbine operates between the cut-in wind speed and rated wind speed, a variable-speed control mode is adopted, and at the time, by adjusting the electromagnetic torque of a generator, the wind turbine is made to operate under the optimal efficiency CP max. When the wind turbine operates above the rated wind speed, a variable-pitch controller begins to be used, and by adjusting the pitch angle, the maximum power output is limited at a rated value. At the time, a torque controller is a variable-gain controller, and different gains are set according to the rotation speed values corresponding to different wind conditions. The phenomenon that the wind turbine generates high power output within a short time when affected by gust and the like is greatly relieved. In addition, a switch rule is set for the variable-pitch controller near the rated wind, so that frequent switching of the variable-pitch controller near the rated wind is avoided. By means of the power optimal control method for the variable-speed and variable-pitch wind turbine, the service life of a gearbox is prolonged, and it is guaranteed that the wind turbine operates in a bad environment.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
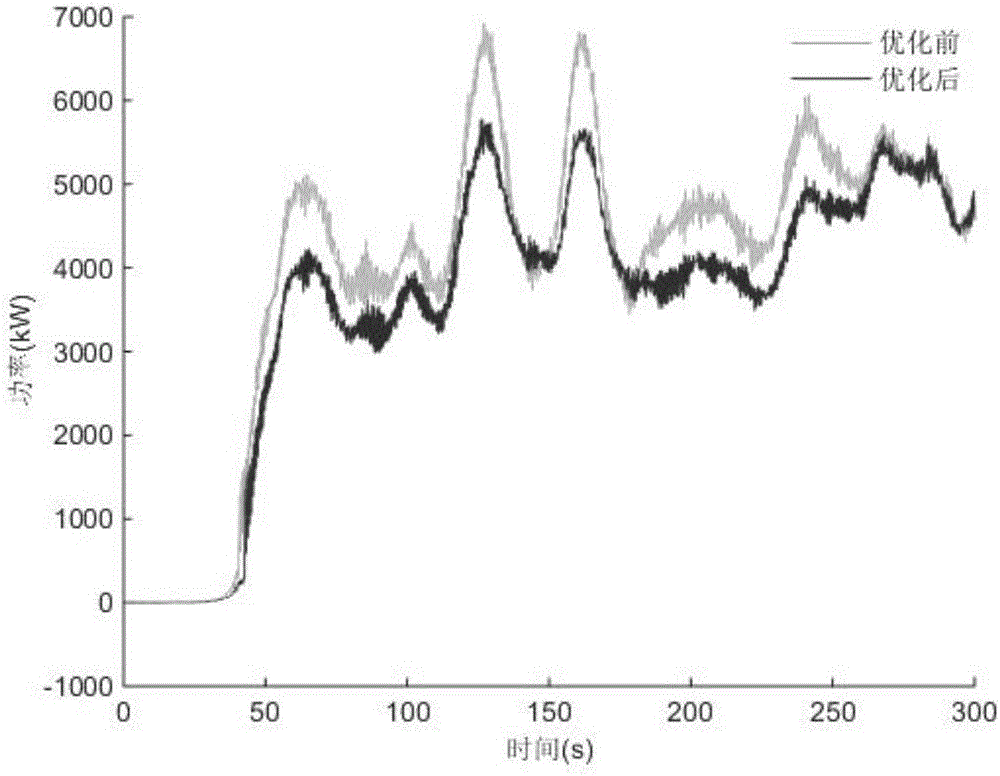
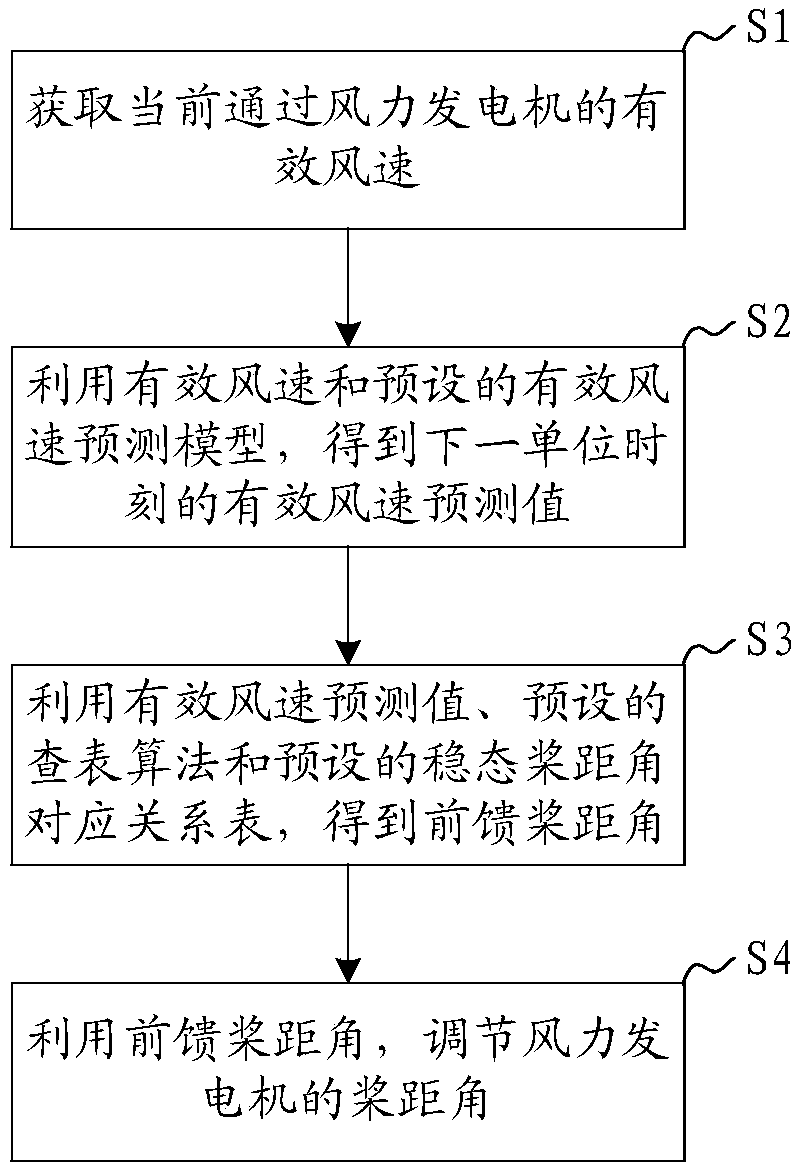
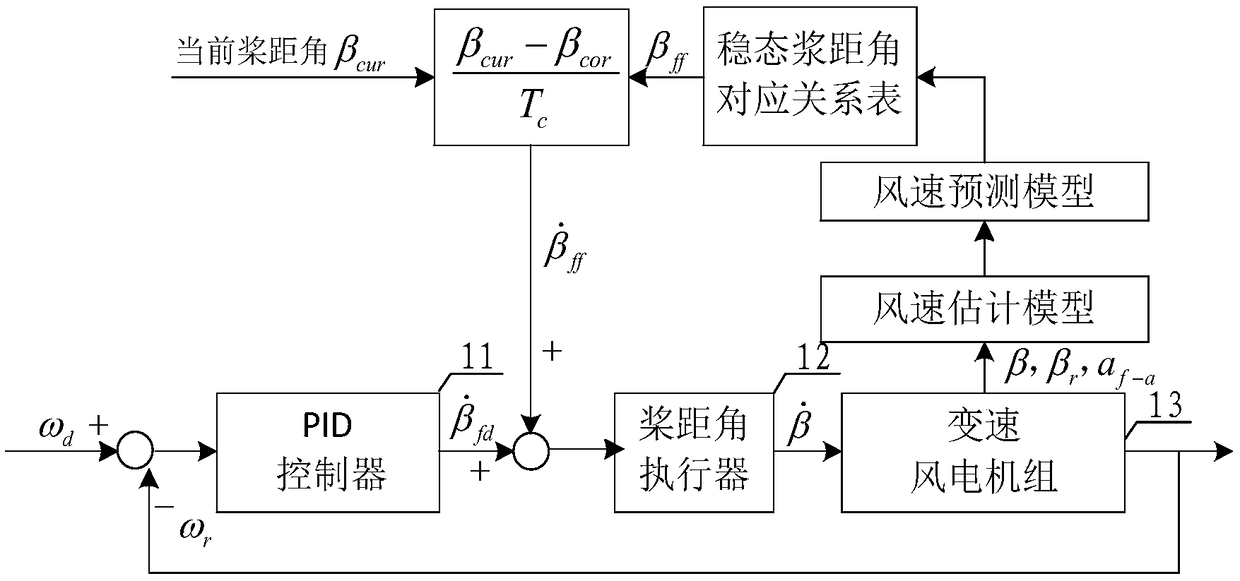
Wind driven generator pitch angle control method, system and device and readable storage medium
ActiveCN109185054AImplement early transformationIncrease transition timeWind motor controlClimate change adaptationEngineeringDynamo
The invention discloses a wind driven generator pitch angle control method, system and device and a computer readable storage medium. The method comprises the steps that the effective wind speed of awind driven generator at present is obtained; the effective wind speed predicted value in the next unit time is obtained through the effective wind speed and a preset effective wind speed prediction model; the feedforward pitch angle is obtained through the effective wind speed predicted value, the preset lookup algorithm and the preset steady pitch angle corresponding relation table; and throughthe feedforward pitch angle, the pitch angle of the wind driven generator is adjusted. According to the method, the effective wind speed predicted value of the current effective wind speed e in the next unit time is predicted in advance, through the effective wind speed predicted value, the feedforward pitch angle is looked up and worked out in the preset steady pitch angle corresponding relationtable, the pitch angle of the wind driven generator is adjusted, the pitch is changed in advance, the pitch change time is prolonged, the change rate is not too large, resistance of wind force to pitch change is reduced, the load of a pitch system is decreased, and the service life of the pitch system is prolonged.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WINDEY +1
Method of damping tower vibrations of a wind turbine and control system for wind turbines
InactiveUS8044529B2Easy to distinguishRapidly damp oscillation in rotor speedWind motor controlEngine fuctionsControl systemEngineering
A control system for a wind turbine is provided. A pitch-control unit establishes a pitch-reference signal representing a pitch to be set by the pitch-actuator system. A rotor-speed input receives a signal representing a speed of the rotor. A speed-reference input receives a speed-reference signal for the rotor speed. An inclination-signal input receives a signal representing a tower inclination. A pitch-reference output outputs the pitch reference signal. A modification unit is connected to the speed-reference input to receive the speed-reference signal and connected to the inclination-signal input to receive the inclination signal. The modification unit establishes a modification signal based on the inclination signal, to modify the speed-reference signal via the modification signal, and to output a modified-speed-reference signal. The pitch-control unit connected to the modification unit to receive the modified-speed-reference signal and establish the pitch-reference value at least based on the difference between the modified-speed-reference and the rotor-speed signals.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Wind turbine damping of tower resonant motion and symmetric blade motion using estimation methods
InactiveCN101627207AMitigate feedback pitch signalWind motor controlEngine fuctionsEstimation methodsEngineering
A wind turbine tower load control method. The pitch of the rotor blades is controlled in a conventional manner by a collective command component. An estimator estimates the tower resonant acceleration and the thrice-per-revolution blade imbalance acceleration. Combining logic, connected to the estimated resonant acceleration and to the estimated thrice-per-revolution (3P) acceleration provides a combined pitch modulation to damp the tower resonant motion and the thrice-per-revolution motion using collective modulation. Said pitch modulation is combined with the collective command component to drive the pitch actuators.
Owner:CLIPPER WINDPOWER INC
Apparatus and system for pitch angle control of wind turbine
A pitch control apparatus for controlling the pitch value for a wind power generation system includes a generator comparing unit that calculates an error signal based on a difference between a generator measurement signal corresponding with an operation of the power generation system and a generator reference signal, and a reference pitch calculating unit that calculates a reference pitch value using the error signal. The pitch control apparatus further includes a compensation pitch calculating unit that calculates a compensation pitch value using an error value from the wind power generation system and a pitch calculating unit that calculates a pitch value using the reference pitch value and the compensation pitch value. The error value may be any one of a voltage error value from a direct-current capacitor, a voltage error value from a grid connection point, a speed error value from a rotor, and a frequency error value from a grid connection point.
Owner:SAMSUNG HEAVY IND CO LTD
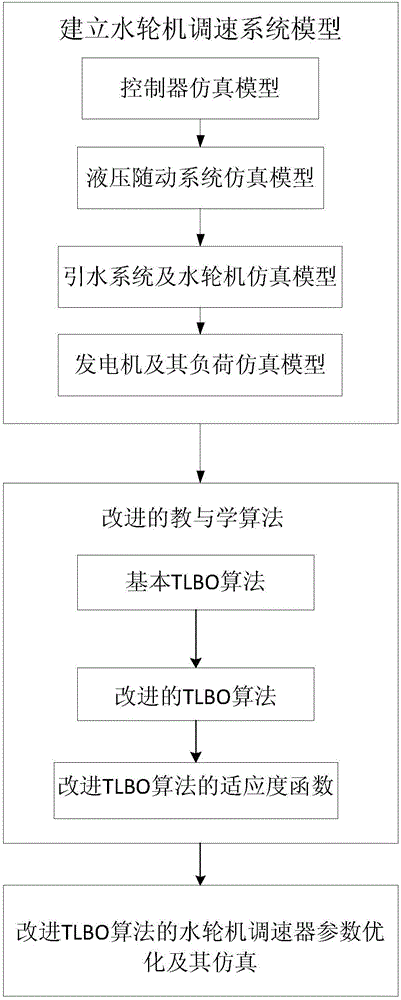
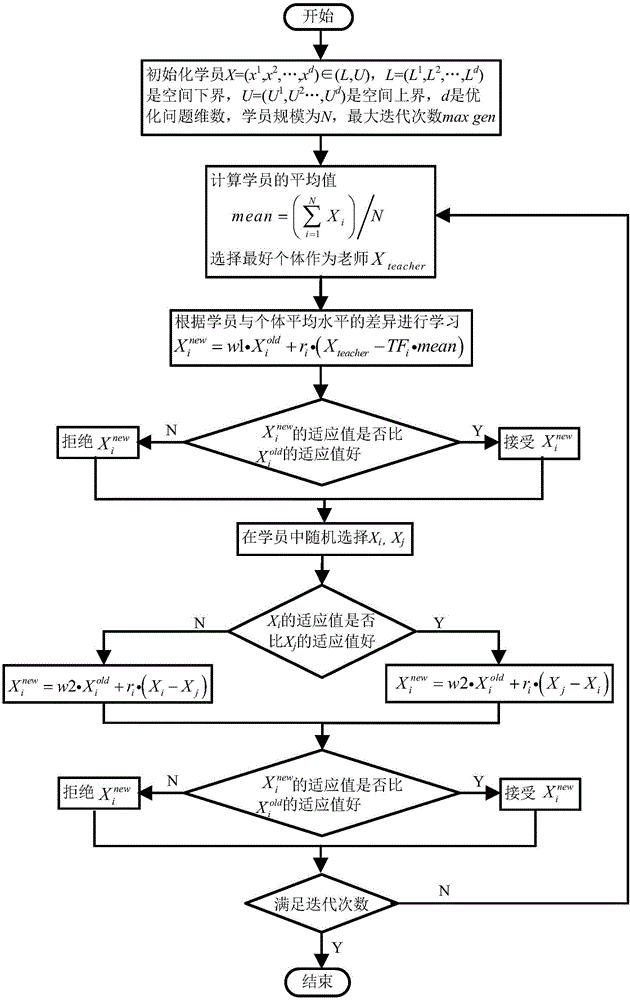
Improved TLBO (teaching-learning-based optimization) algorithm-based hydroelectric generating set PID (proportional-integral-differential) speed regulator parameter optimization
ActiveCN106837678AAvoid premature convergenceEngine fuctionsHydro energy generationProportional integral differentialLocal optimum
The invention belongs to the technical field of hydroelectric generation, and particularly relates to improved TLBO (teaching-learning-based optimization) algorithm-based hydroelectric generating set PID (proportion-integration-differentiation) speed regulator parameter optimization. The optimization comprises the following steps of (1) building a hydroturbine speed regulating system simulation model; (2) improving a basic TLBO algorithm; (3) applying the improved TLBO algorithm to optimizing parameters of the speed regulator of a hydroturbine speed regulating system, and obtaining a simulation result. Self-adaptive teaching factors, i.e., absorption weight of students and the after-school tutoring of teachers are added into the basic TLBO algorithm, while the convergence speed and the convergence precision are guaranteed, the phenomena of early-maturing and early convergence of the algorithm are avoided. An ITAE index of rotation rate deviation of a hydroturbine set serves as a standard fitness function, and the improved TLBO algorithm is used to optimize the parameters of the speed regulator, so that the convergence speed optimization efficiency is obviously improved, and the phenomenon of local optimum is avoided.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
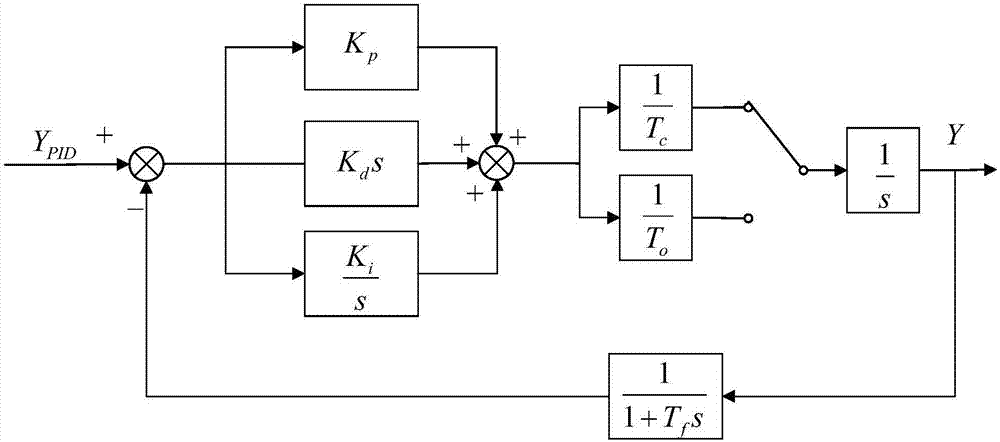
Control method and control device for guide vane opening of water turbine
ActiveCN108443057AImprove accuracyGuaranteed stabilityHydro energy generationMachines/enginesWater turbineServomotor
The invention discloses a control method and control device for the guide vane opening of a water turbine. Integral output amplitude limits (DB1,DB2) are determined through a water turbine speed governor disturbance test; servomotor stroke parameters are collected, and a feedback value H is determined according to the servomotor stroke parameters; a guide vane opening fixed value M is input, and acontrol voltage output value u is determined through a series integral control standard; the feedback value H and the guide vane opening fixed value are substituted into an integral zero clearing control standard for judgment, and whether integral zero clearing is needed or not is determined according to a judgment result; and the control voltage output value u is transmitted to a data transmission control unit, and a servomotor is moved. Thus, effective output of control voltage can be improved, and when the output voltage is too small, the accuracy of guide vane opening control can be improved, the stroke speed of the servomotor is controlled, and the stability of the guide vane opening is ensured.
Owner:YUNNAN POWER GRID CO LTD ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Active load reducing control system and method for large wind turbine blade
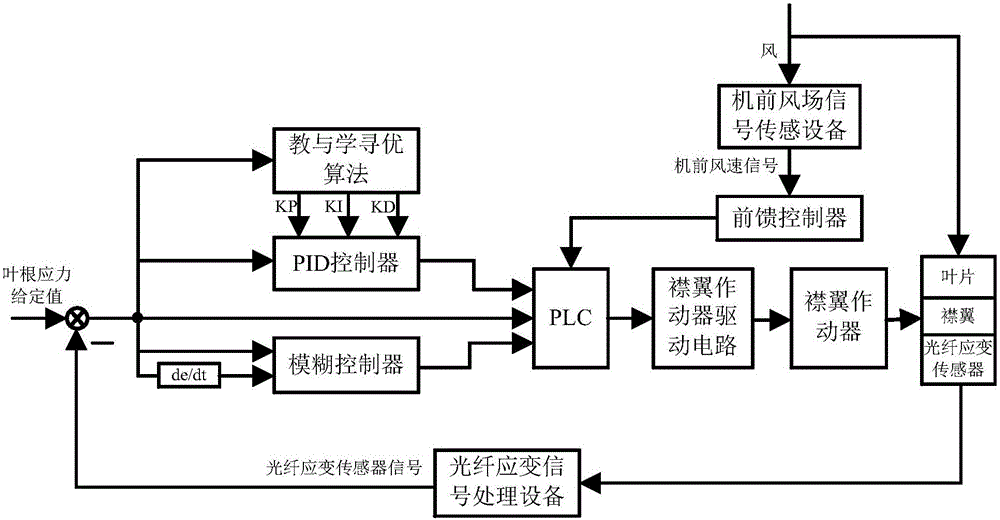
InactiveCN105888971AReduce strainReduce use costWind motor controlMachines/enginesControl systemTurbine blade
The invention relates to an active load reducing control system and method for a large wind turbine blade. An optical fiber strain sensor measures a stress value of the root portion of the blade and transmits the stress value to a control unit; the control unit comprises a PID controller performing parameter optimization through a teaching and learning algorithm and a fuzzy controller for processing a strain force signal of the root portion of the blade; a flap swing angle is subjected to switching control through the fuzzy controller and the PID controller, and beneficial effects of fuzzy control and PID control are synthesized; meanwhile, a machine front wind field signal sensing device measures the front air speed of a wind turbine and transmits the front air speed to the control unit; a feedforward controller in the control unit calculates control quantities needed by uniform loads caused by reducing stochastic wind or turbulent wind by monitoring the change of the machine front air speed in real time; and the control unit couples the two parts of control quantities, and control over the flap swing angle is completed. The active load reducing control system and method for the large wind turbine blade effectively reduce the strain force of the root portion of the blade, the service life of the blade is prolonged, and the using cost of a wind turbine unit is reduced.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
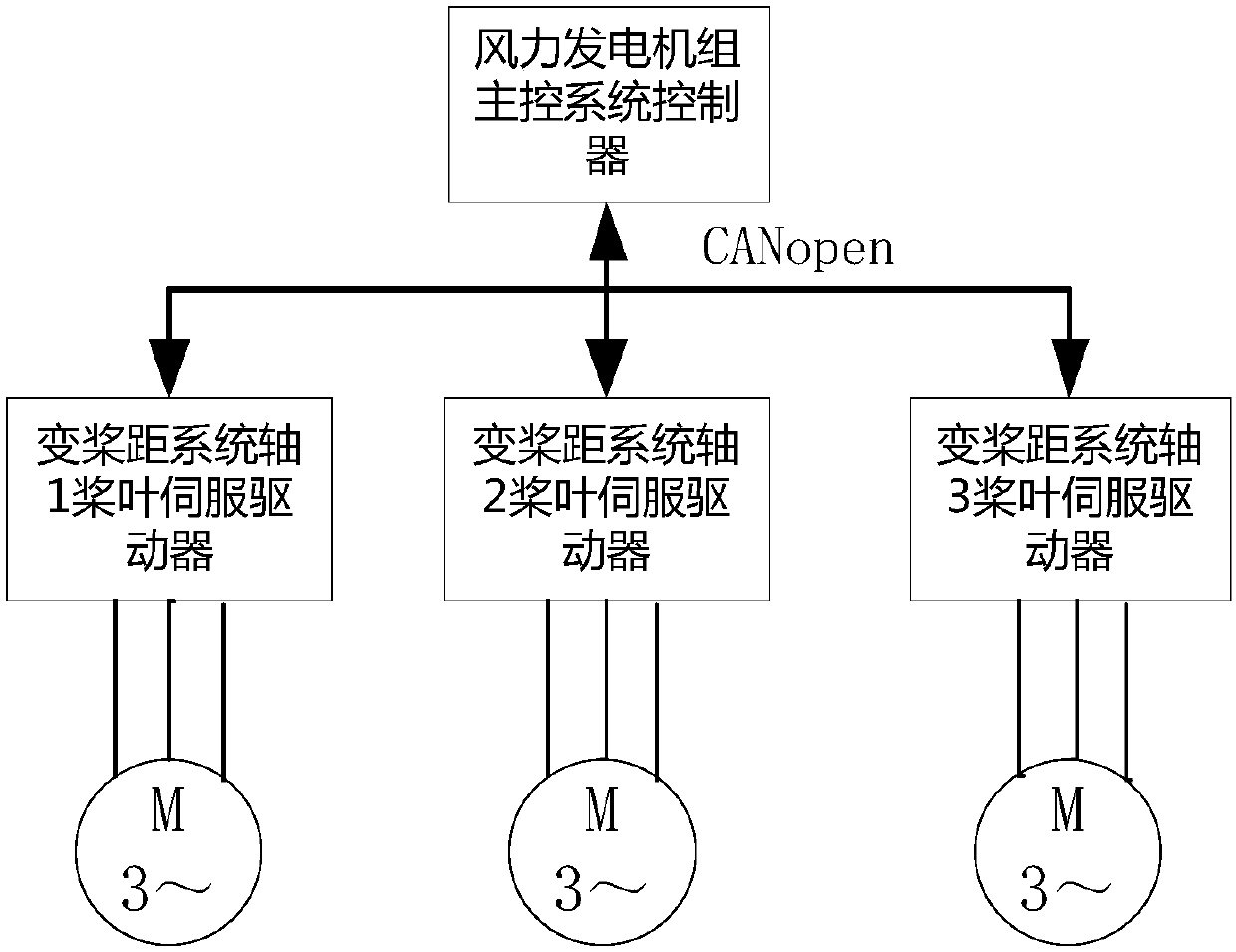
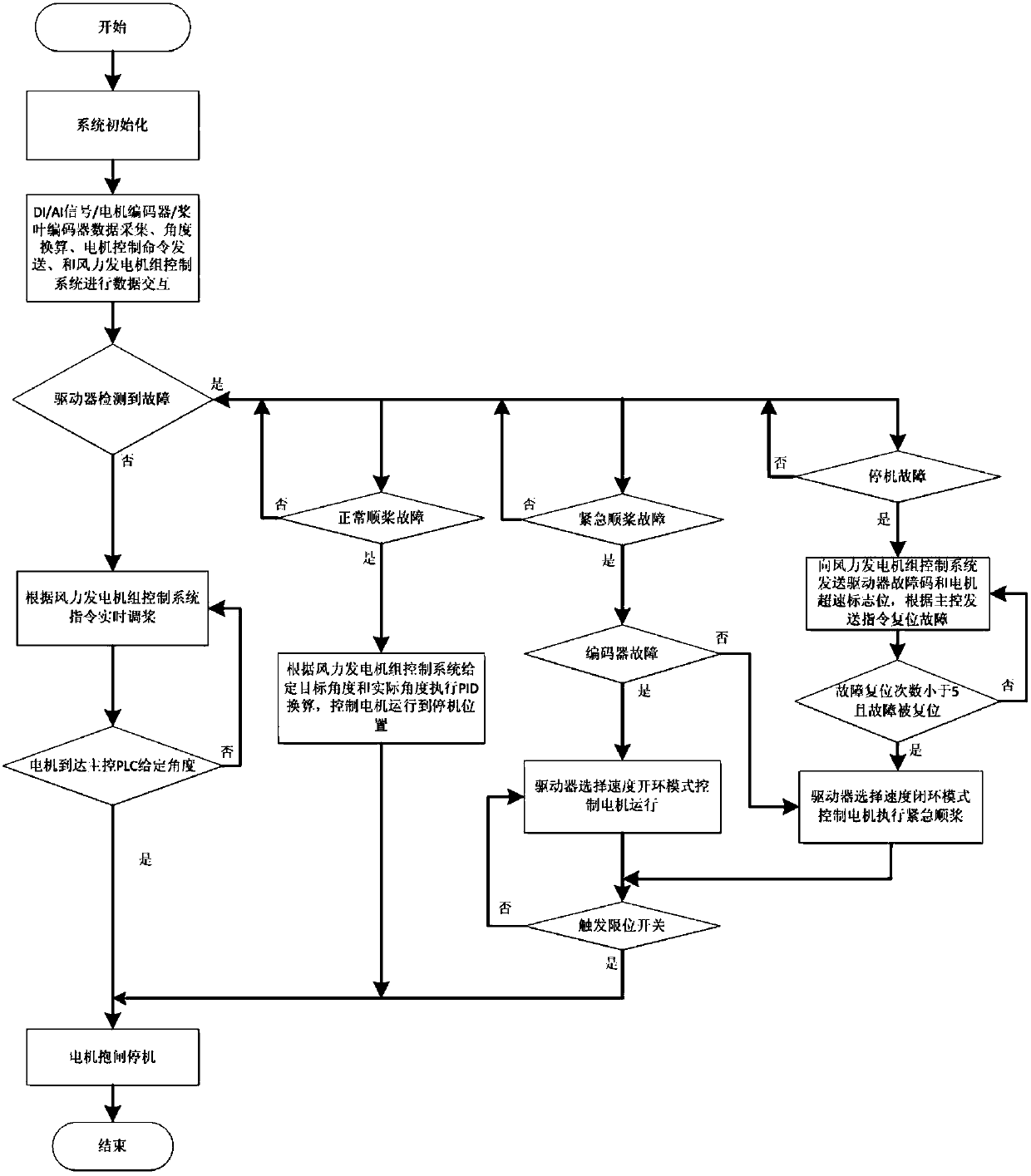
Fault protection method for wind turbine generator variable pitch system without independent controller
InactiveCN107781106ALow failure rateGuaranteed uptimeRotational speed controlWind motor controlControl systemCANopen
Provided is a fault protection method for a wind turbine generator variable pitch system without an independent controller. Three-shaft blades of the wind turbine generator variable pitch system are respectively controlled by independent servo drives. The three-shaft servo drives are communicated with a wind turbine generator main control system by means of a CANopen network to realize a data exchange. The three-shaft blade servo drivers collect a piece of information of each shaft to determine the operating status of a device. When the status of the device is abnormal, the fault is triggeredand the fault flag bit is uploaded to the main control system. The wind turbine generator main control system sends an emergency feathering command so as to control each blade to execute the emergencyfeathering.
Owner:CORONA WIND EQUIP BEIJING CO LTD +1
Wind turbine generator system and control method of the same
ActiveUS7982327B2Suppress power fluctuationsLow efficiencyMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlControl theoryFlat rated
A wind turbine generator system includes: a wind turbine rotor including a blade having a variable pitch angle; a generator driven by the wind turbine rotor; and a control unit controlling the output power of the generator and the pitch angle of the blade in response to the rotational speed of the wind turbine rotor or the generator. The control unit performs a first control in which the output power is controlled in accordance with a predetermined power-rotational speed curve until the rotational speed is increased to reach a predetermined rated rotational speed, and performs a second control in which the output power is controlled to a predetermined rated power when the rotational speed exceeds the rated rotational speed; the control unit is responsive to the pitch angle for maintaining a state of performing the second control is or for switching to a state of performing the first control, when the rotational speed is reduced below the rated rotational speed after the control unit is once placed into the state of performing the second control.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Wind power installation and method of operating it
ActiveCN101483344AWind motor controlSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsHysteresisPower grid
The purpose of the invention is to reduce the contribution of wind power installations to frequency errors on the grid, and preferably to contribute to the elimination of such errors. Thus, the method involves the use of PID control and / or control with hysteresis so as to regulate the active power injected into the grid, in view of the deviation between a measured grid frequency and the nominal grid frequency.
Owner:GAMESA INNOVATION & TECH SA
Static testing and calibrating method for PID link of control system of wind turbine
A static testing and calibrating method for PID link of control system of wind turbine includes following steps. A PID control link of the PID link of the control system of wind turbine is tested. A PID regulator response characteristics is tested. The PID link of control system is calibrated by applying test results of the PID control link and the PID regulation response characteristics.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
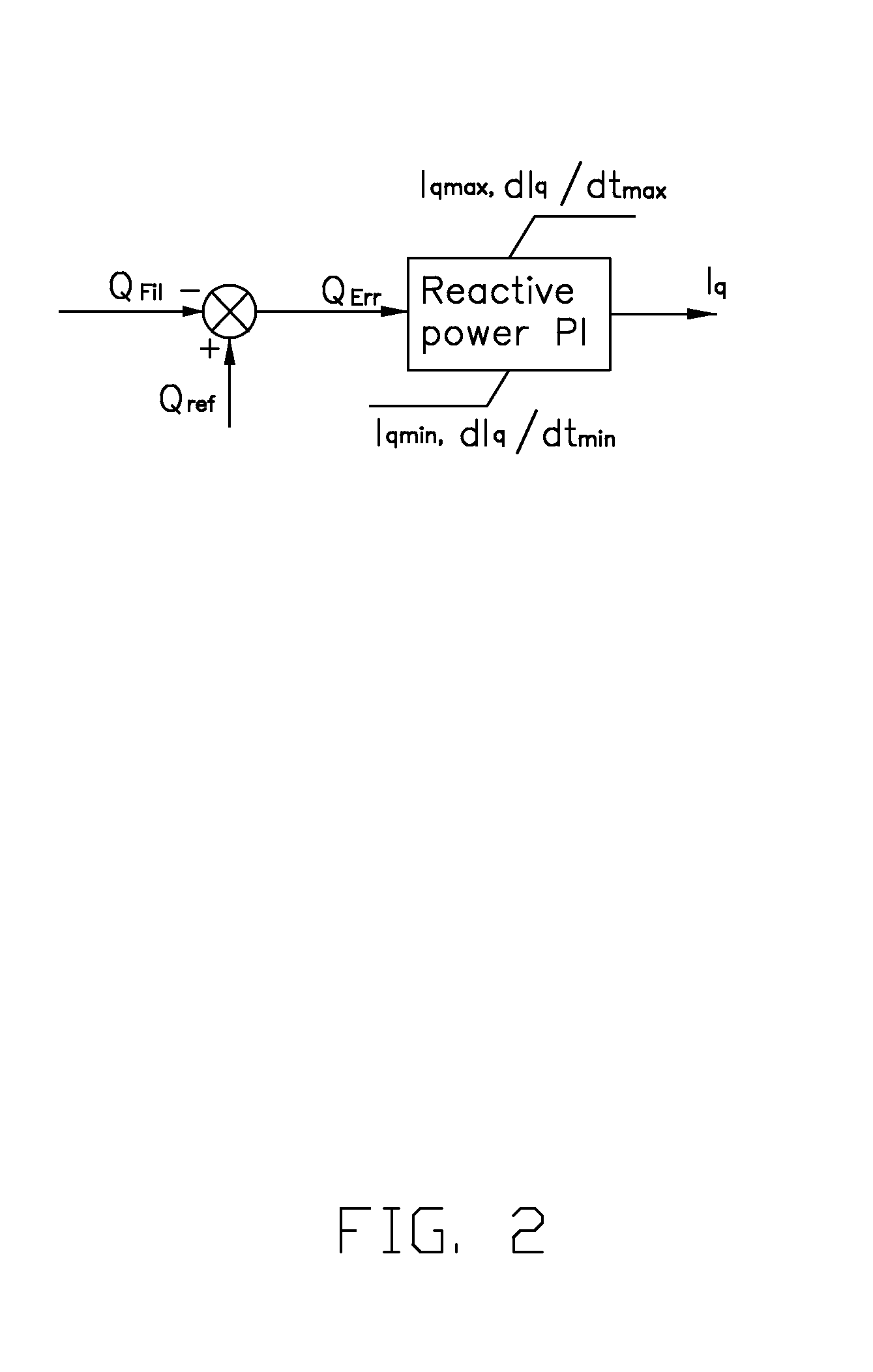
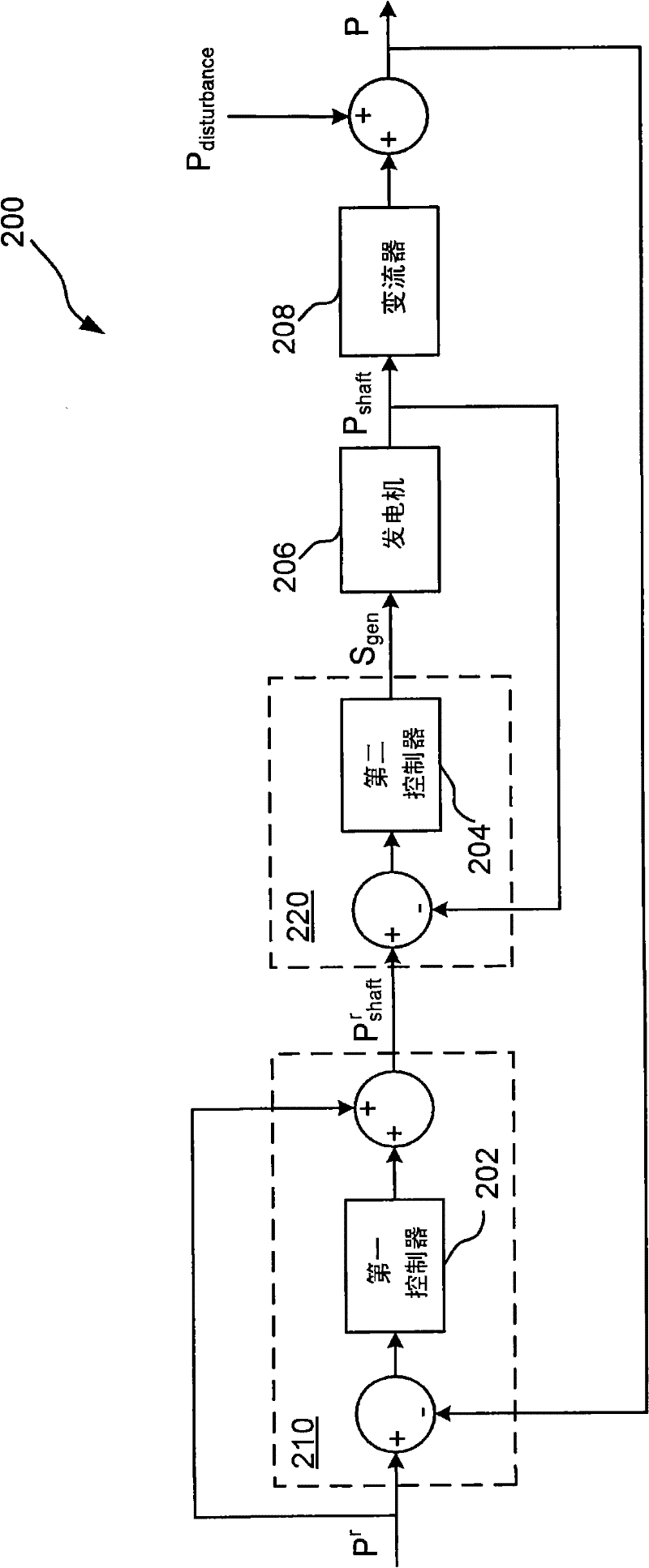
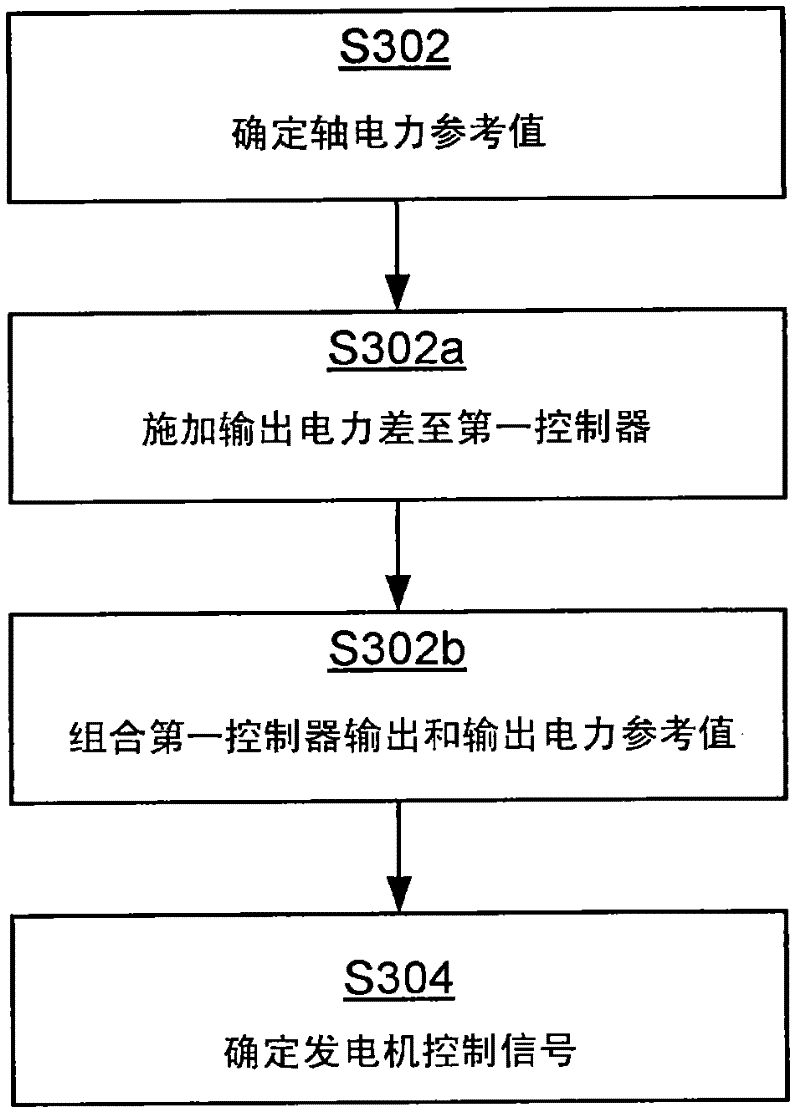
Method of controling a wind turbine generator
ActiveCN102214930AFast control dynamicsSuppression of high frequency interferenceWind motor controlSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsTurbineControl theory
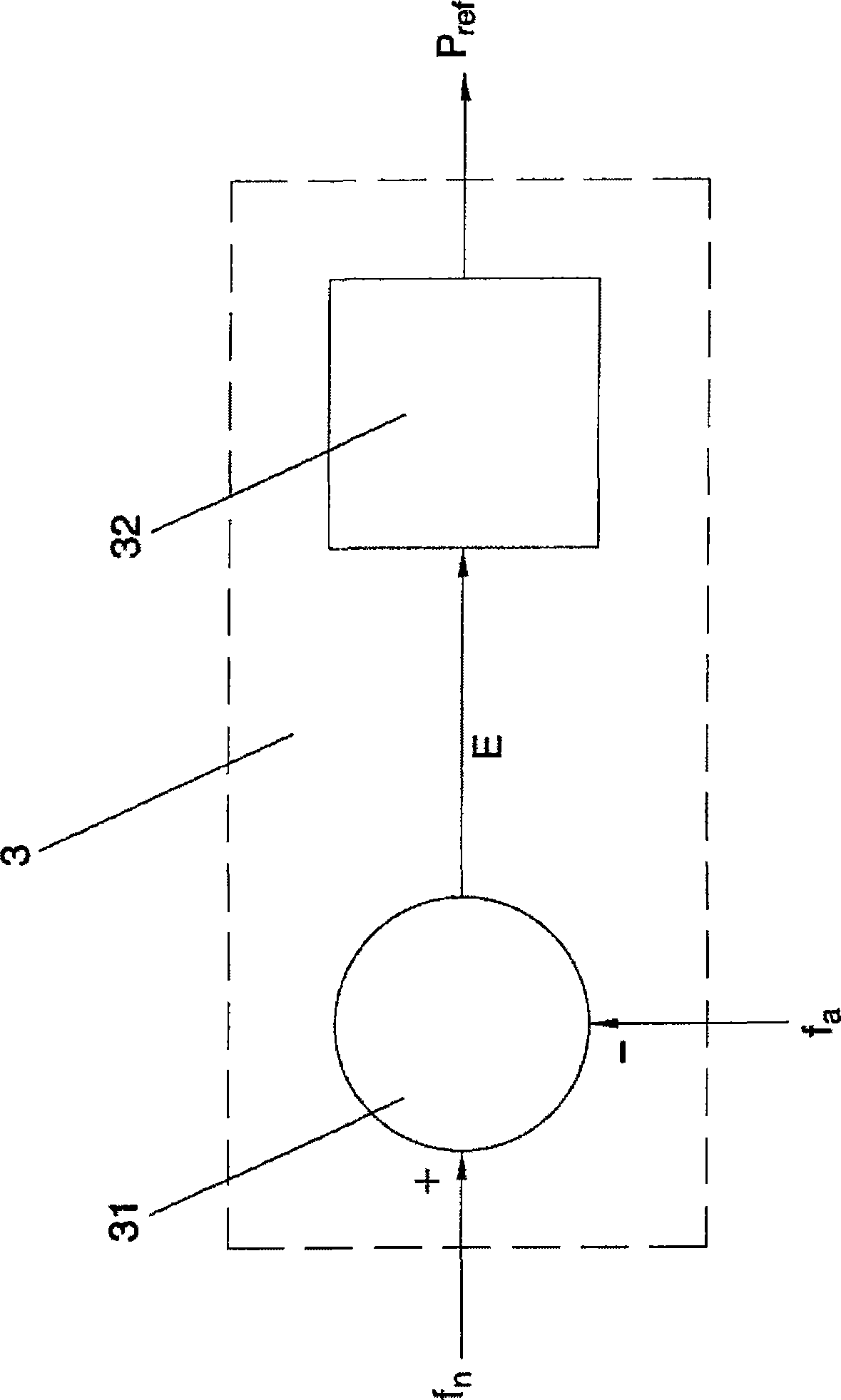
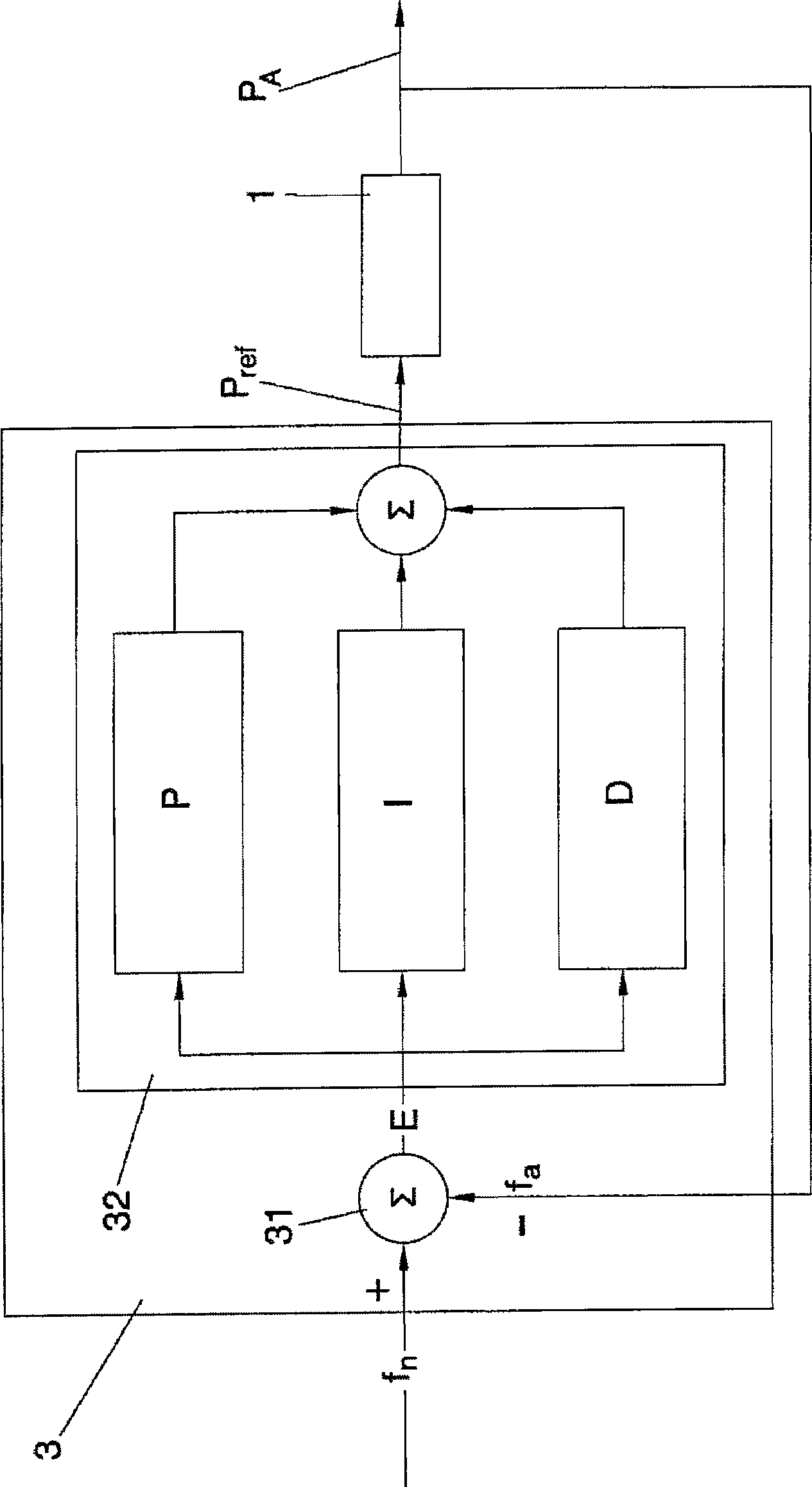
A method for controlling a wind turbine generator is disclosed. The method comprises comparing an output power reference value and an actual output power value in a first control block with a first controller having a first control dynamics, comparing the output from the first control block with an actual generator shaft power value in a second control loop with a second controller having a second control dynamics, to determine a generator control signal, wherein the output power reference value is fed-forward and summed with the output of the first controller in the first control block. The disclosed method allows for fast reactions to changes in the output power reference value by the second controller regardless of the speed of the first controller.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
Popular searches
Emergency protective circuit arrangements Dynamo-electric converter control Wind motor combinations Engine components Wind energy generation Proportional-integral-differentail algorithms Proportional-integral algorithms Generator control by field variation Special data processing applications Measurement gauges
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com