Method for accessing NAND gate flash memory by application protocol data unit
A technology that uses protocol data and flash memory. It is applied to record carriers used in machines, instruments, and inductive record carriers. It can solve the problem of not being able to read the length of the smart card and achieve the effect of fast access and enhanced compatibility.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
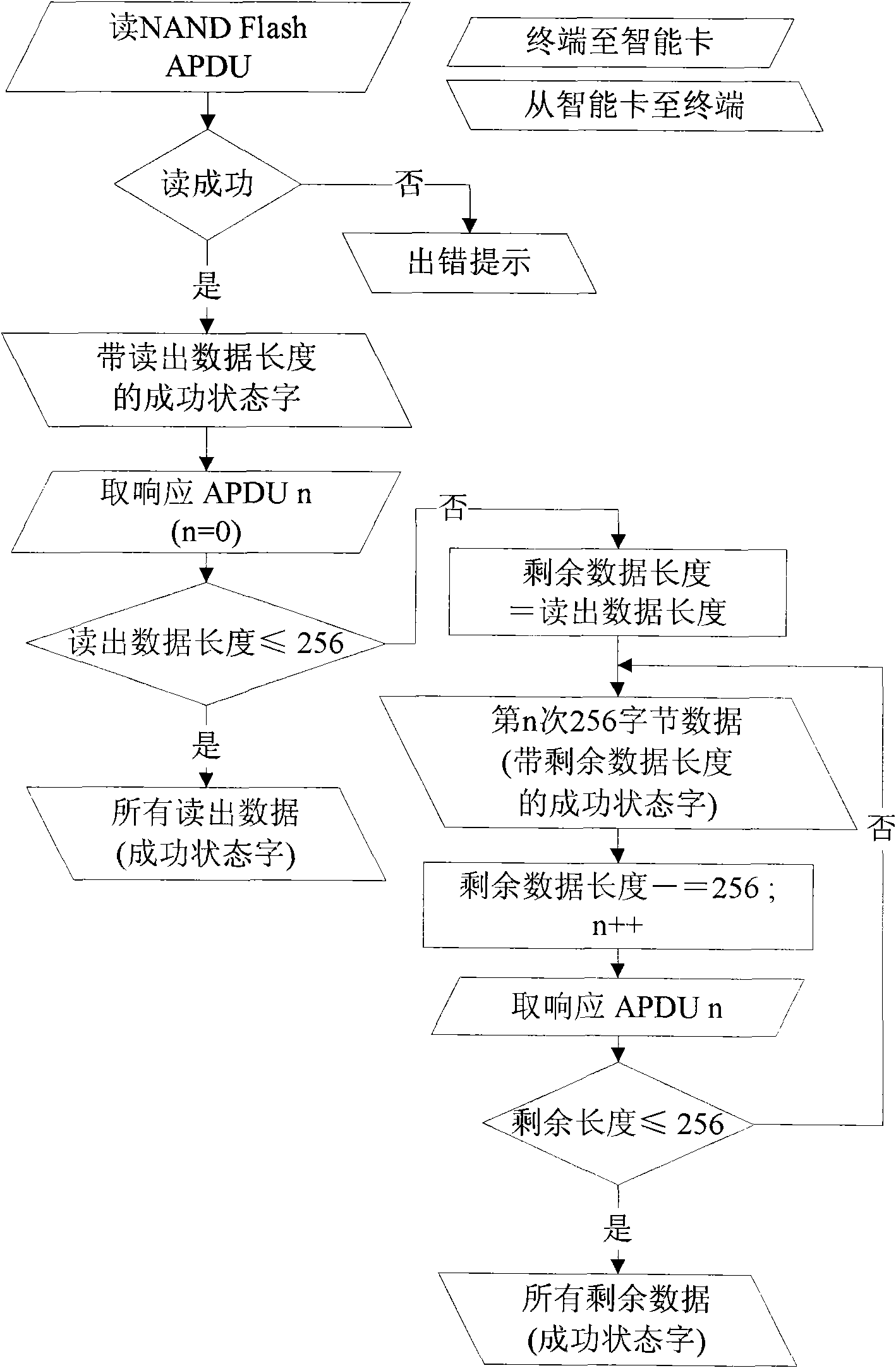
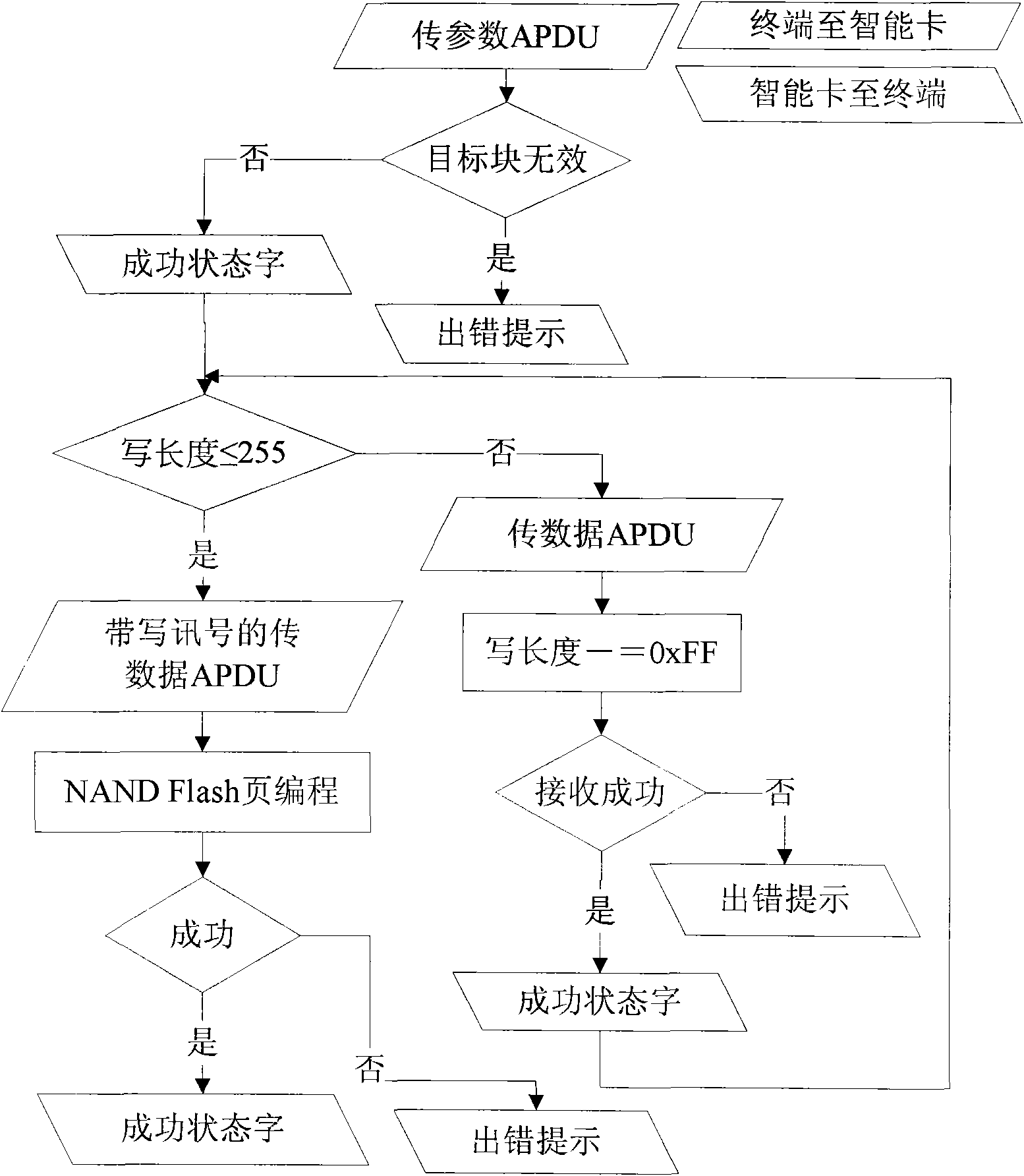
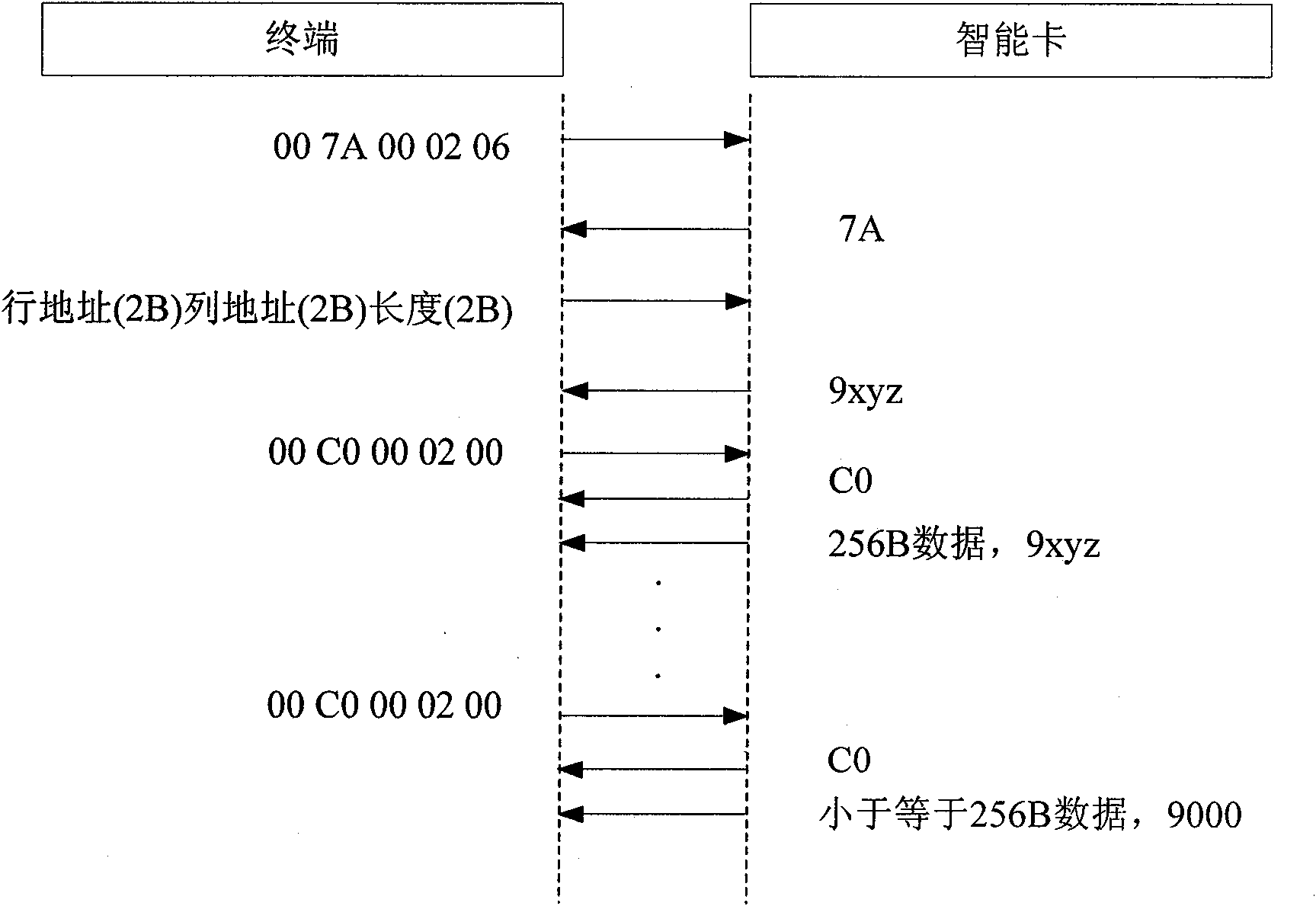
[0028] see Figure 1 to Figure 4 , use a terminal containing APDU to realize access to NAND Flash with a total capacity of 128MB (megabytes) in the smart card, a page size of 2112 bytes (main storage area 2048 bytes, redundant area 64 bytes), and a block size of 64 pages Methods:
[0029] 1) To read the NAND Flash identification number, use the APDU in the second case defined by the ISO / IEC 7816 specification. The APDU format is 00 7A 00 01 P3, where the parameter P3 of the APDU specifies the number of bytes of the identification number to be read. .
[0030] APDU: 00 7A 00 01 xx
[0031] Card response: xx byte NAND Flash identification number
[0032] Success status word: 9000
[0033] Error definition:
[0034] Parameter P3 error, status word 6C00;
[0035] Failed to read NAND Flash identification number, status word 6504.
[0036]2) To read NAND Flash data, use the APDU of the fourth case defined by the ISO / IEC 7816 specification. The format of the read APDU is 00 7A...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com