Method for resource allocation in synergetic OFDM system
A technology of resource allocation and orthogonal frequency division, applied in the field of OFDM cooperative communication, can solve the problems of not considering various information feedback and interaction of resource allocation, not considering the acquisition of channel state information, unable to apply the actual system, etc., to reduce the complexity of implementation. The effect of high degree, wide application range and low complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
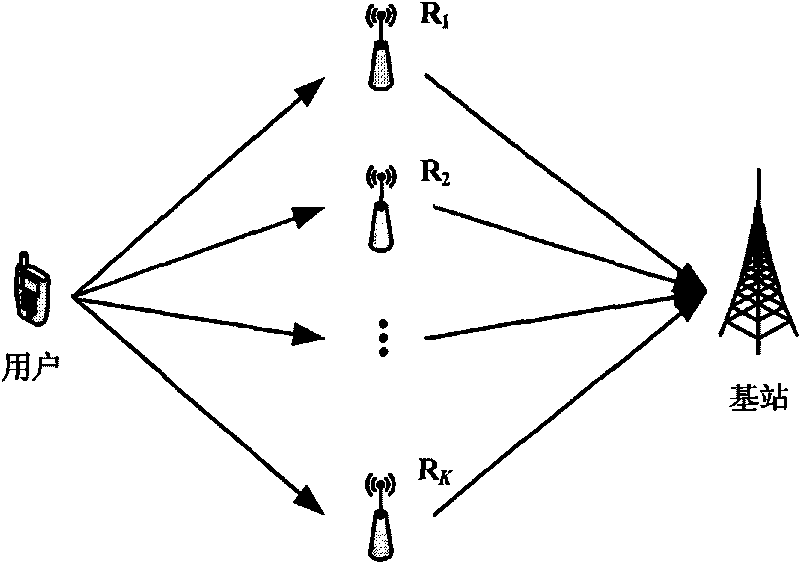
[0053] see figure 1 , the method system of the present invention is provided with a user and a base station, and a positive integer number of relays (R 1 , R 2 ,...,R K ), each relay has the same number of subcarriers.
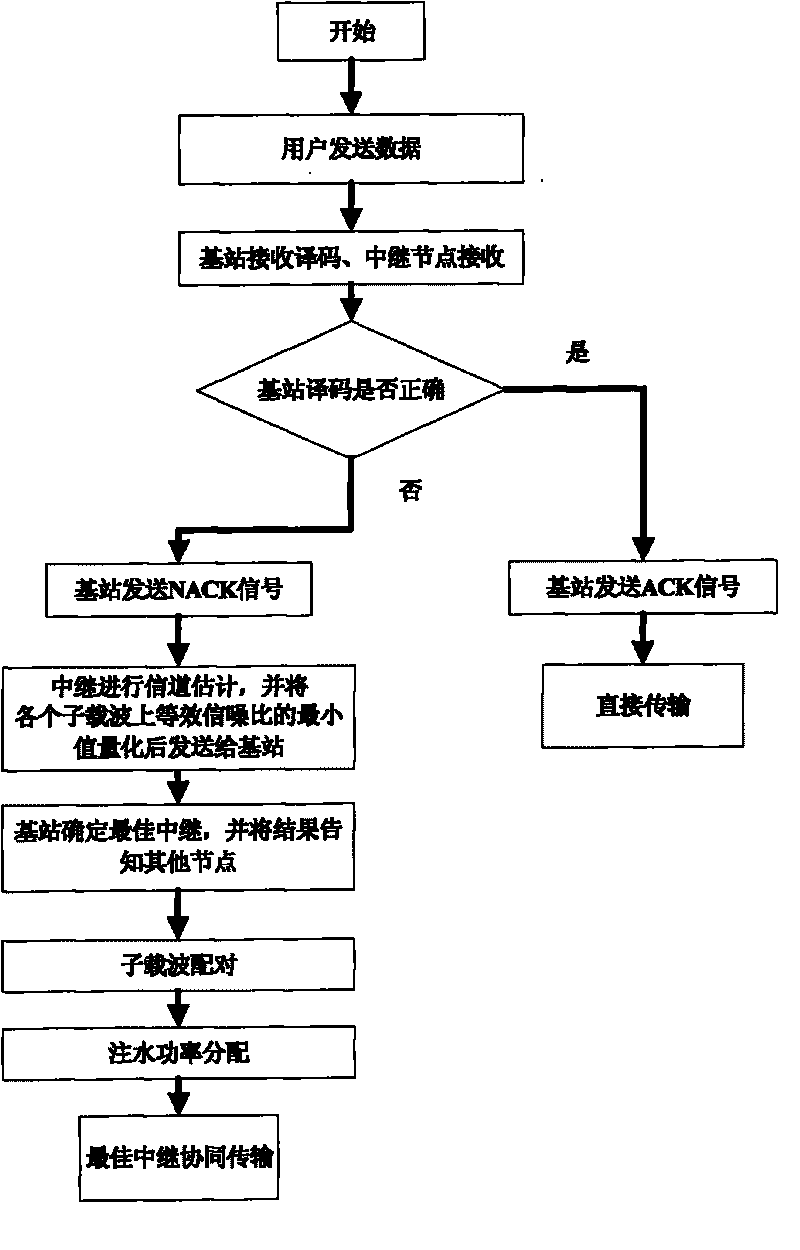
[0054] see figure 2 , taking a coordinated OFDM network with a single user, 10 relays, and a single base station as an example for illustration. It is assumed that the number of sub-carriers of the OFDM system is N=1024, and 10 relays are randomly distributed between the user and the base station. The implementation process is as follows:
[0055] Step 1: Trunk Selection
[0056] a. The user sends data, and the cyclic redundancy check information needs to be added to the user's sent data, so that the base station can judge whether it is correctly decoded;
[0057] b. After receiving the transmitted data, each relay stores the data, and uses the LS (least squares) algorithm to estimate the channel coefficient h between the user and each subcarrier s,k ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com