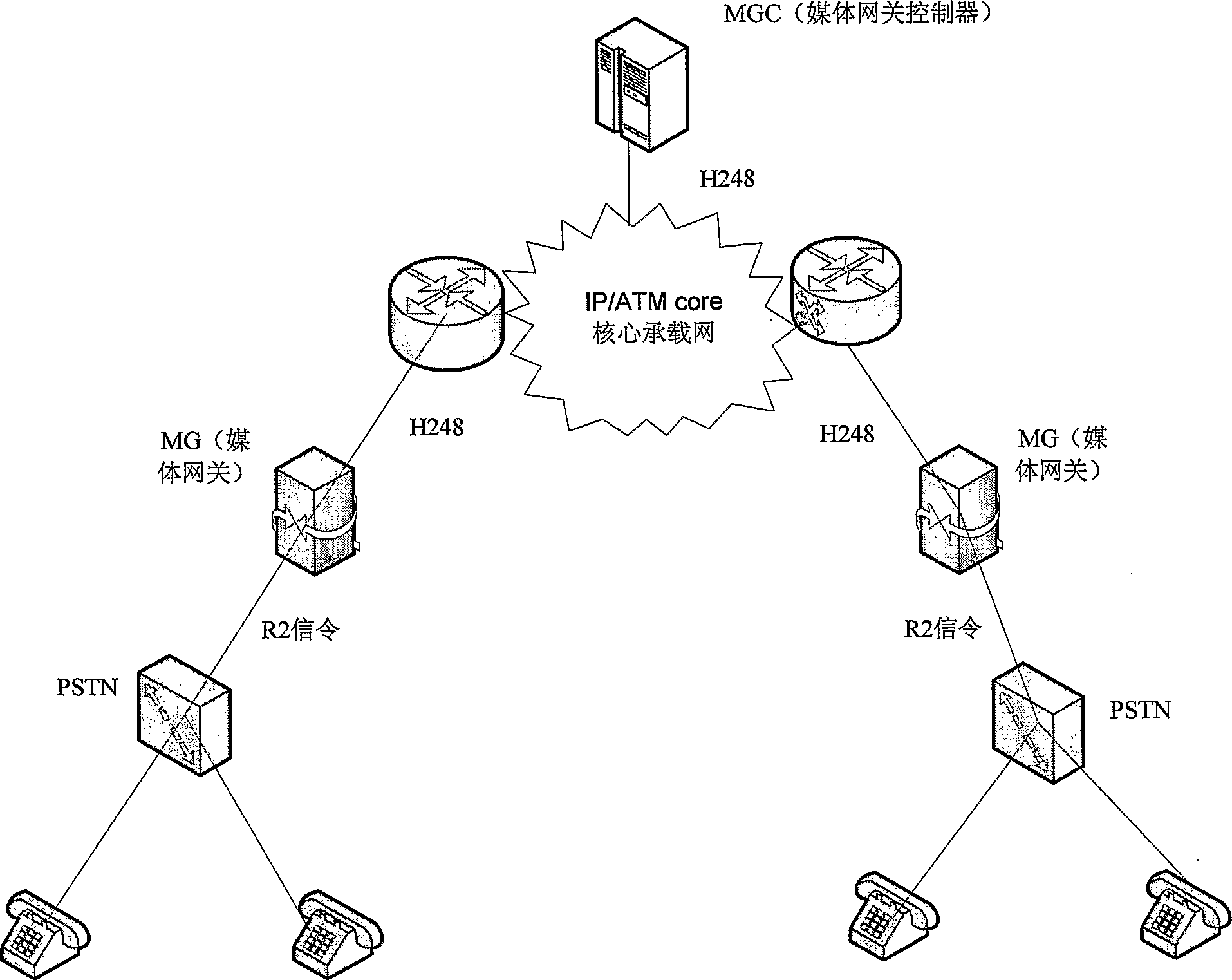
Method for media gateway obtaining calling information
A technology of media gateway and calling number, which is applied in branch offices to provide special service devices, telephone communication, data exchange details, etc. It can solve problems such as call failure and unreasonable caller information processing, and achieve the effect of improving flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Embodiment 1: The MG on the outgoing side actively asks the MGC for calling information
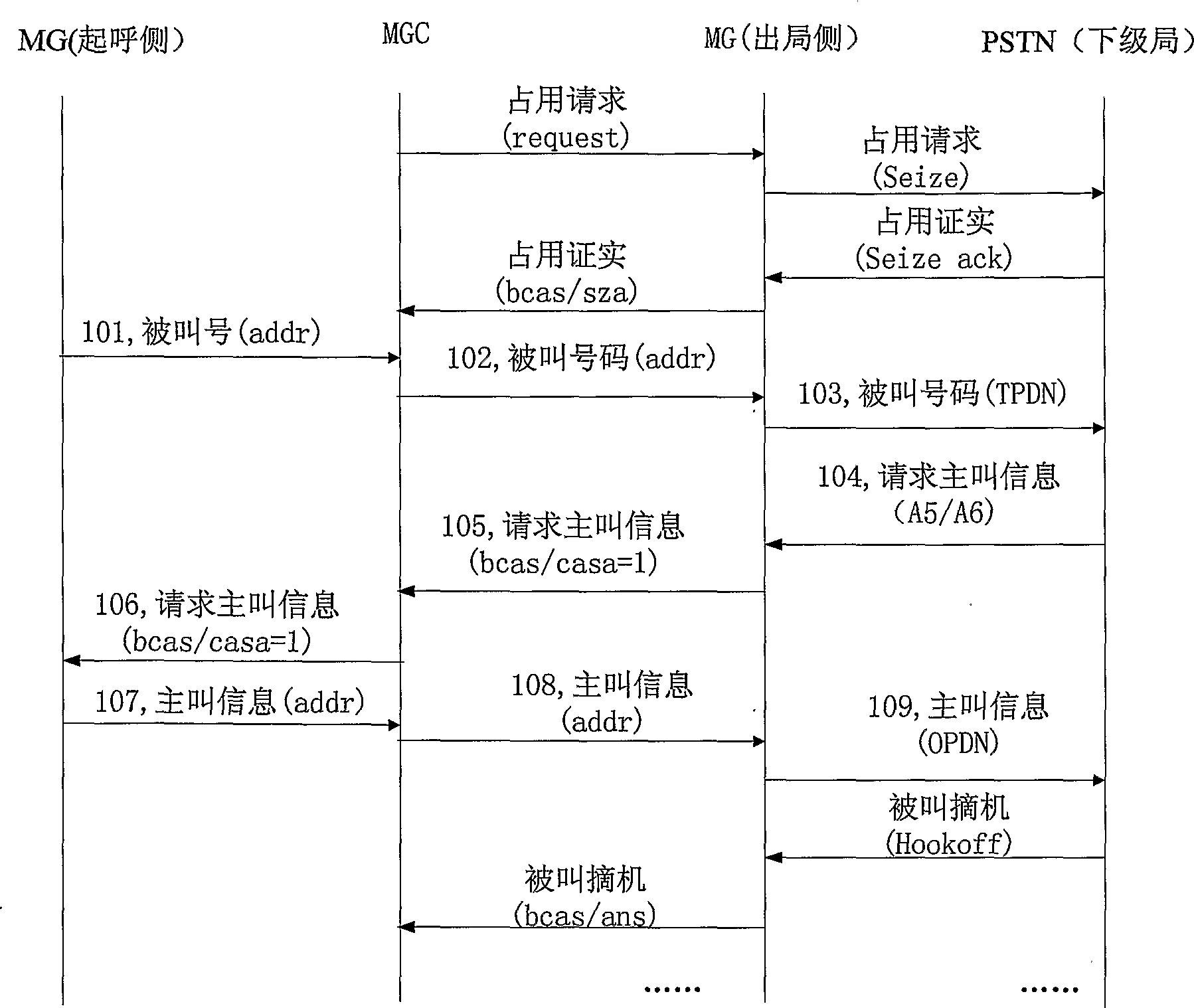
[0038] Such as figure 2 As shown, when the outgoing side PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) asks the outgoing side MG for calling information, but when the MG does not have this information, the MG asks the MGC for the calling information event from the MG defined in the present invention (such as the extended bcas attribute casa=1) to request the caller information from the MGC to complete the call, including the following steps:
[0039] Step 101, the MG at the originating side under the control of the MGC reports the called number to the MGC;
[0040] Step 102, the MGC issues the called number to the MG at the origin side;
[0041] Step 103, the MG at the outgoing side sends the called number to the lower-level office (ie, the PSTN at the outgoing side) through channel-associated signaling;
[0042] Step 104, after receiving the called number, the lower office requests t...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Embodiment 2, the MG on the incoming side is controlled by the MGC device to process the caller information (whether the attribute rqsi of the calling number is required, and this flag is configured on the MGC)
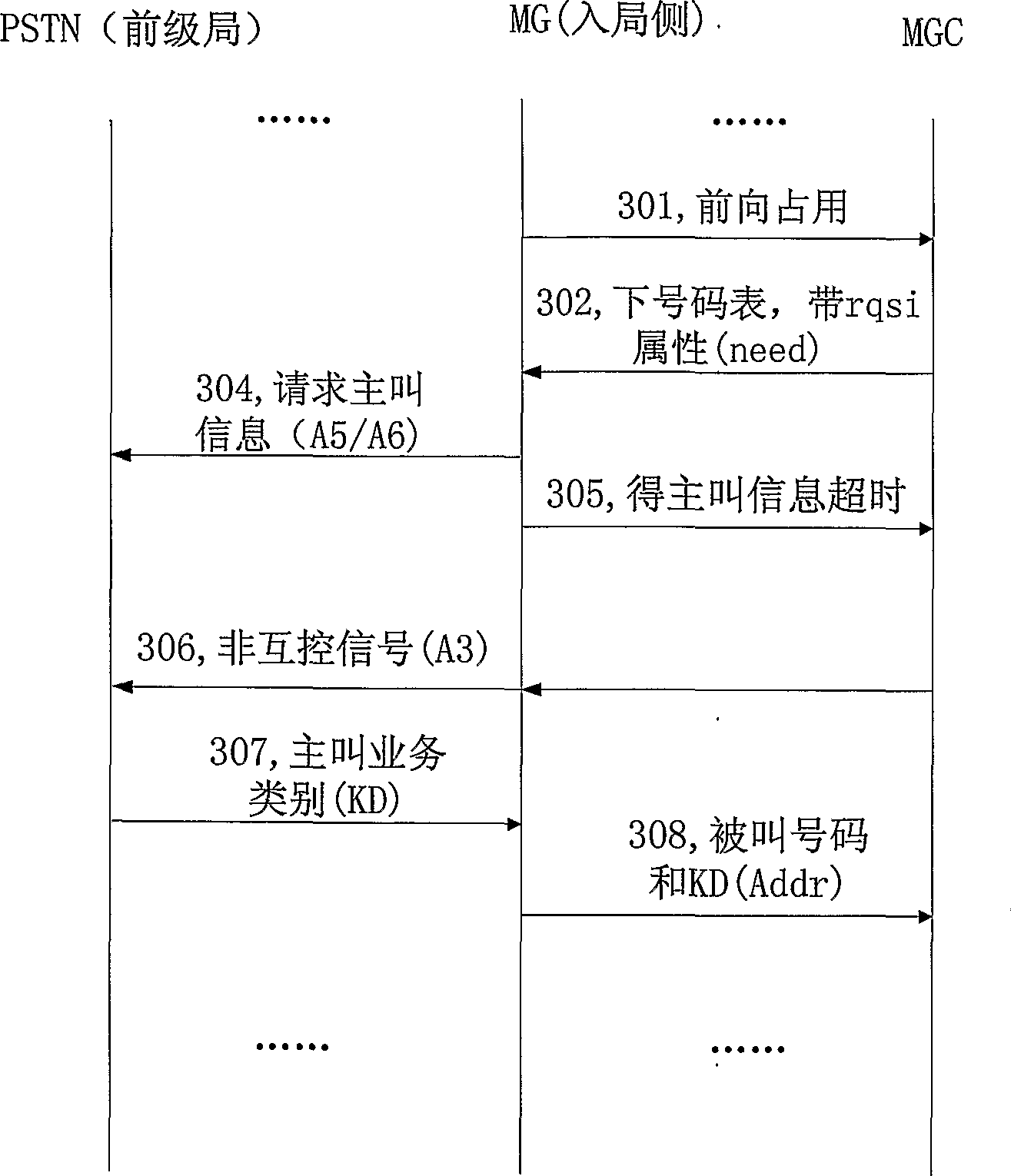
[0068] Such as image 3 As shown, when the MG requests the calling number from the PSTN side after timeout, it sends a non-mutual control signal A3 to the PSTN to request KD (the non-mutual control signal is sent because the MG’s mutual control signal requesting the calling number has not yet been received. When the response is reached, that is, the mutual control process is not over yet, at this time, the MG cannot send another mutual control signal, the same below), after receiving the KD, the MG sends the called number and the KD to the MGC to complete the connection, if the KD times out Report a timeout error to the MGC, including the following steps:
[0069] Step 304, the MG at the incoming side asks for the calling number from the upper-level office;
...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Embodiment 3, the incoming MG is controlled by the MGC device to process the calling information (whether the attribute rqsi of the calling number is required, this flag is configured on the MGC)
[0077] Such as Figure 4 As shown, when the MG requests the calling number from the PSTN side for a timeout, it directly reports a timeout error to the MGC, and the MGC releases the call this time.
[0078] Step 404, the MG at the incoming side requests the calling number from the upper-level office,
[0079] Step 405, the MG fails to obtain the calling number after timeout;
[0080] Step 406, the MG at the incoming side reports an error to the MGC
[0081] In the above step 405, if the MG can obtain the calling number, then its subsequent steps are the same as steps 306-308 in the second embodiment. The incoming side MG sends a mutual control signal A3 to the front-level office to request KD, and after obtaining the calling number and KD Report to the MGC, and report an e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com