Smart under-actuated bionic robot finger device with parallel-connected tendon ropes
A bionic robot and underactuated technology, which is applied in the field of humanoid robots, can solve problems such as few joint degrees of freedom, inability to adapt to the grasping requirements of objects of different sizes, and affect the grasping effect, so as to achieve improved stability, compact structure, anthropomorphic and The effect of stability improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0046] The specific structure and working principle of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
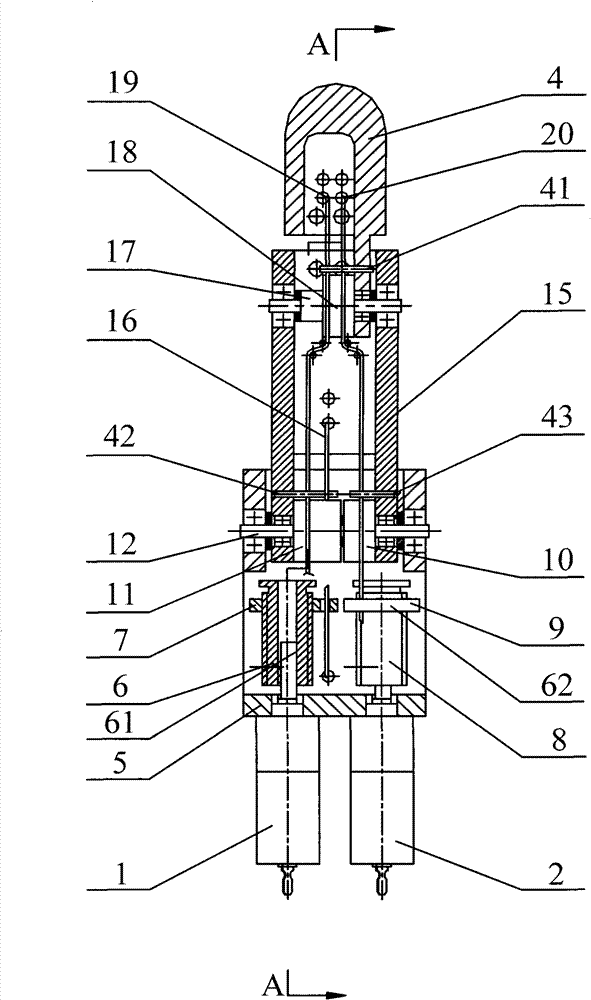
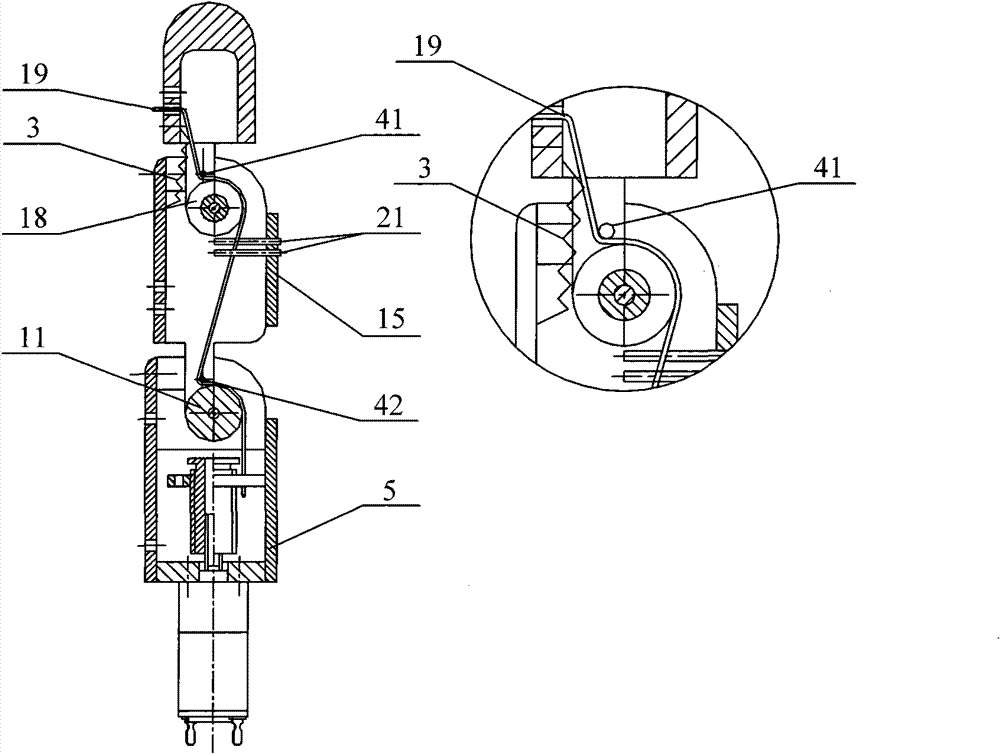
[0047] An embodiment of the tendon rope parallel smart underactuated two-joint bionic robot finger device designed by the present invention, as figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 , Figure 4 , Figure 5 , Image 6 As shown, it includes the first motor 1, the second motor 2, the base 5, the proximal joint shaft 12, the first finger segment 15, the first finger segment joint shaft 17, the terminal finger segment 4, the first transmission mechanism 61, the second The transmission mechanism 62 and the return spring 3; the first motor 2 is fixedly connected to the base 5, and the output shaft of the first motor 1 is connected to the input end of the first transmission mechanism 61; the second motor 2 is connected to the base 5 fixed connection, the output shaft of the second motor 2 is connected to the inpu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com