Driving component and using method thereof
A technology of driving components and linear motion, which is applied in the direction of engine components, transmission devices, fluid transmission devices, etc., can solve the problems of inability to output counterclockwise torque, inconvenient use of the drive device, and inability to output different pistons, etc., to achieve light weight, The effect of compact structure and balanced structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
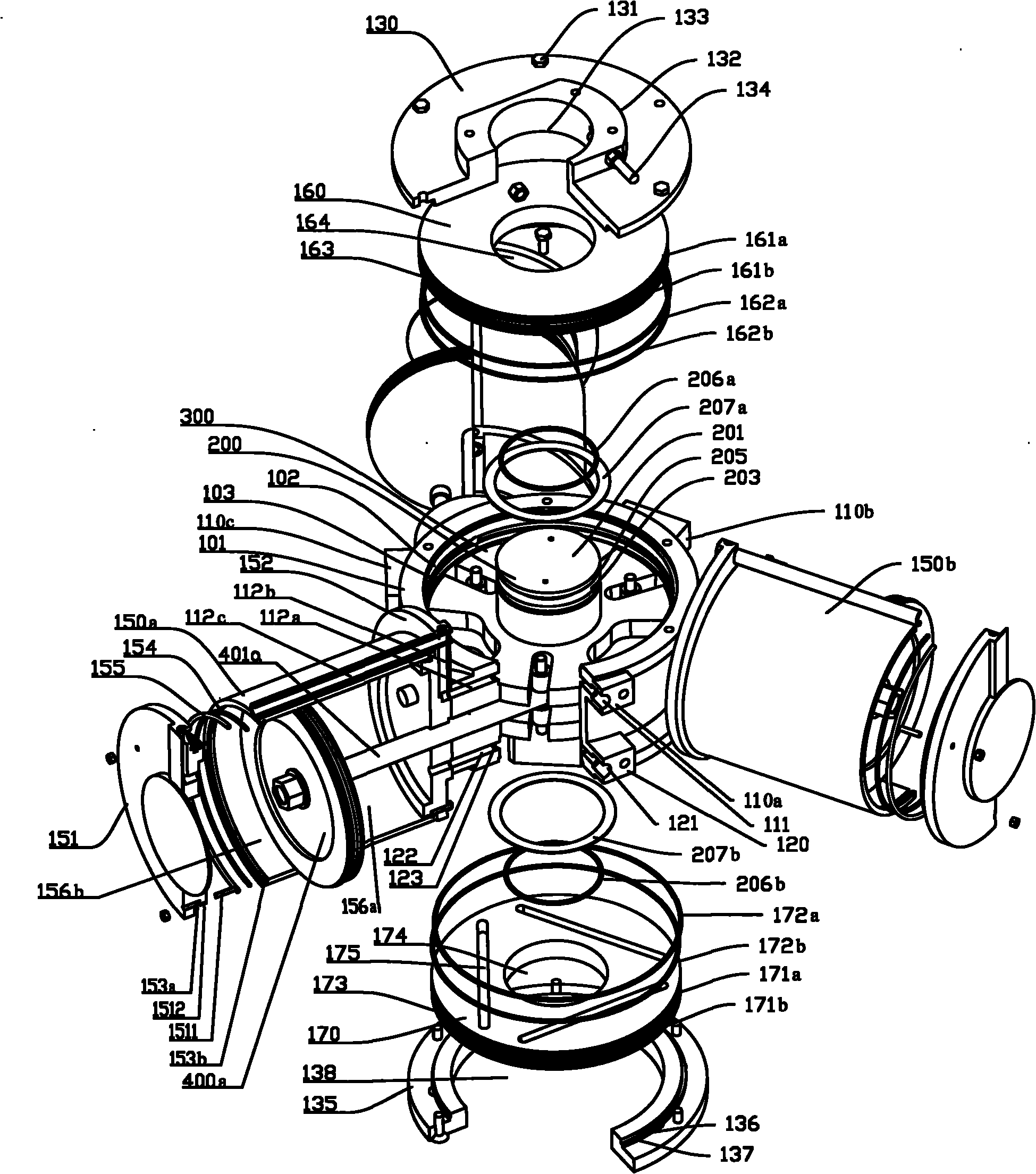
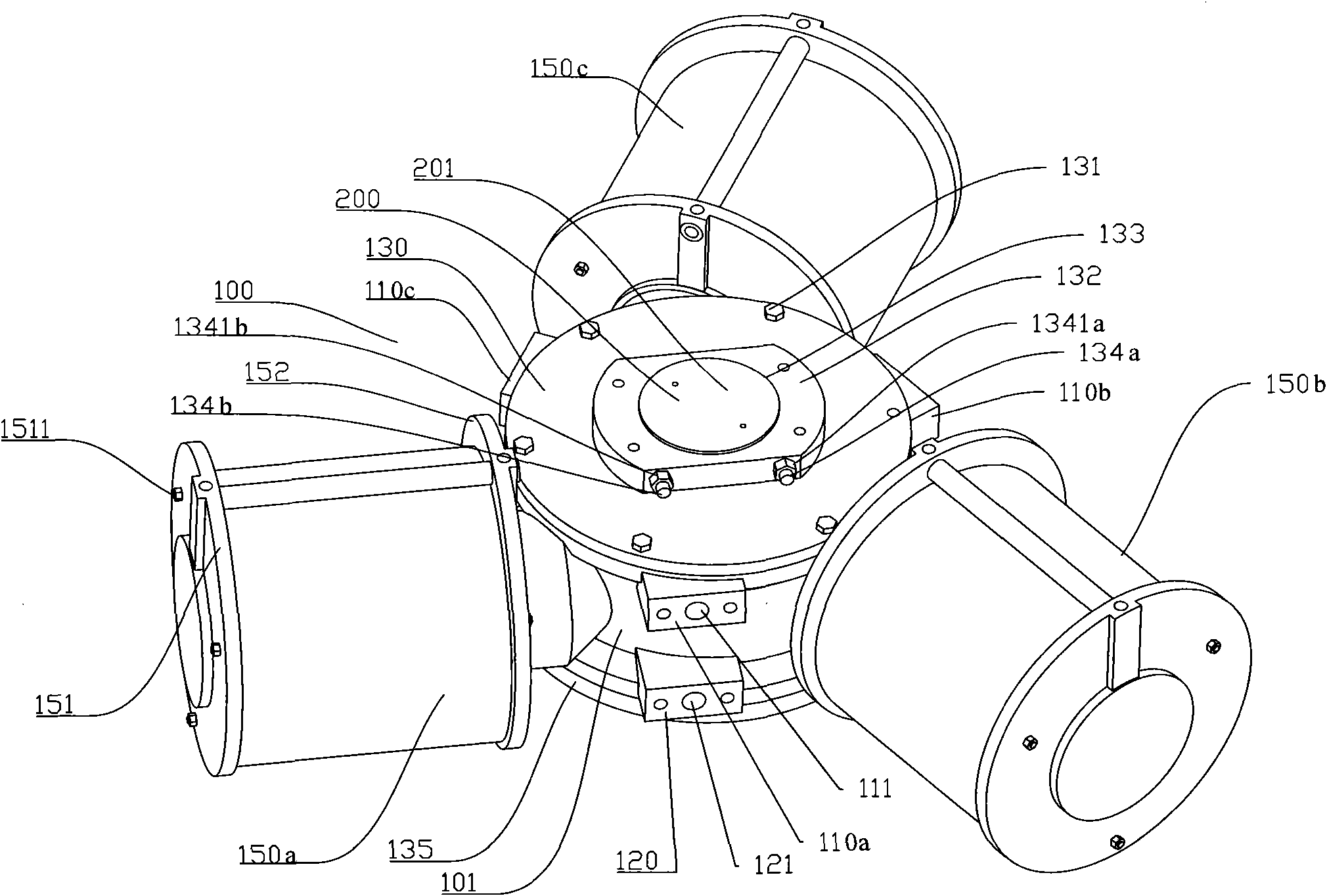
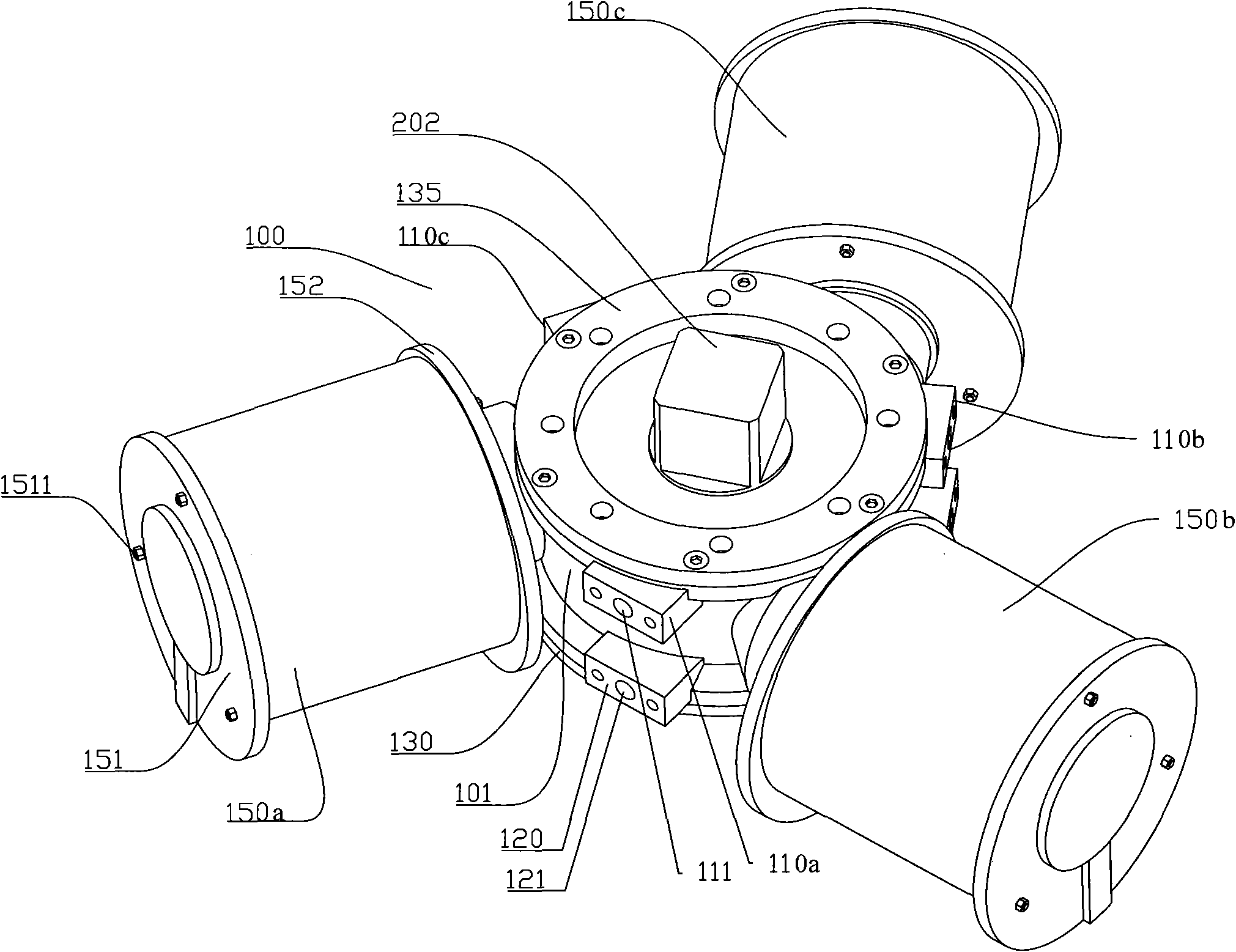
[0111] Fig. 1 is a schematic diagram of the appearance structure of the present invention, and Fig. 2 is a schematic diagram of Fig. 1 turned over 180 degrees. As shown in FIG. 1 and FIG. 2 , the drive assembly includes a casing 100, and the casing 100 includes a first cylinder 101 and three second cylinders (150a, 150b, 150c) with horizontal holes. The three second cylinders (150a, 150b, 150c) have the same structure, and the three second cylinders (150a, 150b, 150c) are equicircumferentially distributed on the outer wall of the first cylinder 101 .
[0112]A top cover 130 and a bottom cover 135 are respectively mounted on two ends of the first cylinder 101 . The top cover 130 is mounted on the top of the first cylinder 101 via bolts 131 . A positioning block 132 is disposed on the top cover 130 , and the positioning block 132 protrudes from the top cover 130 . The positioning block 132 is provided with a first through hole 133 . One end of the output shaft 200 is located ...
Embodiment 2
[0144]Fig. 14 is a schematic structural diagram of Embodiment 2 of the present invention. As shown in FIG. 14 , the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the second end 202 of the output shaft 200 does not have a cube adapter, but adopts an eccentric cylinder 202B and a cylinder 202A connected in sequence as the adapter. The eccentric cylinder 202B is located between the housing 200 and the cylinder 202A. All the other structures are the same as in Example 1. FIG. 15 is a half-sectional view of the output shaft 200 in Embodiment 2 and a schematic view of a method of use. The adapter 500 of the valve in Fig. 15 is also a half-sectional view. As shown in FIG. 15 , the valve adapter 500 is provided with a circular hole 501 matching with the cylinder 202A and an eccentric circular hole 502 matching with the eccentric cylinder 202B. When using the output shaft 200 to drive the valve, the cylinder 202B of the output shaft 200 can be inserted into the circular hole 501 of the adapt...
Embodiment 3
[0148] Fig. 16 is a cross-sectional view of one of the second cylinders 150a of Embodiment 3. As shown in Fig. 16, the difference between it and Embodiment 1 is that a spring 157 is arranged in the second part 156b of the inner chamber of the second cylinder 150a. , both ends of the spring 157 are respectively connected to the end cover 151 and the piston 400a. After the high-pressure fluid enters the first part 150a of the inner cavity of the second cylinder 150a, the piston 400a is pushed to move to the left, that is, when moving away from the roller (not shown), the piston 400a compresses the spring 157, and the spring 157 is compressed. Generate potential energy. If there is always high-pressure fluid in the first part 150a of the inner cavity of the second cylinder 150a, the spring 157 can always be in a compressed state. After the high-pressure fluid in the first part 150a of the inner cavity of the second cylinder 150a is emptied, the potential energy of the spring 157...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com