Thermoelectric module
A technology of thermoelectric components and thermoelectric components, which is applied in the direction of thermoelectric devices that only use the Peltier or Seebeck effect. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
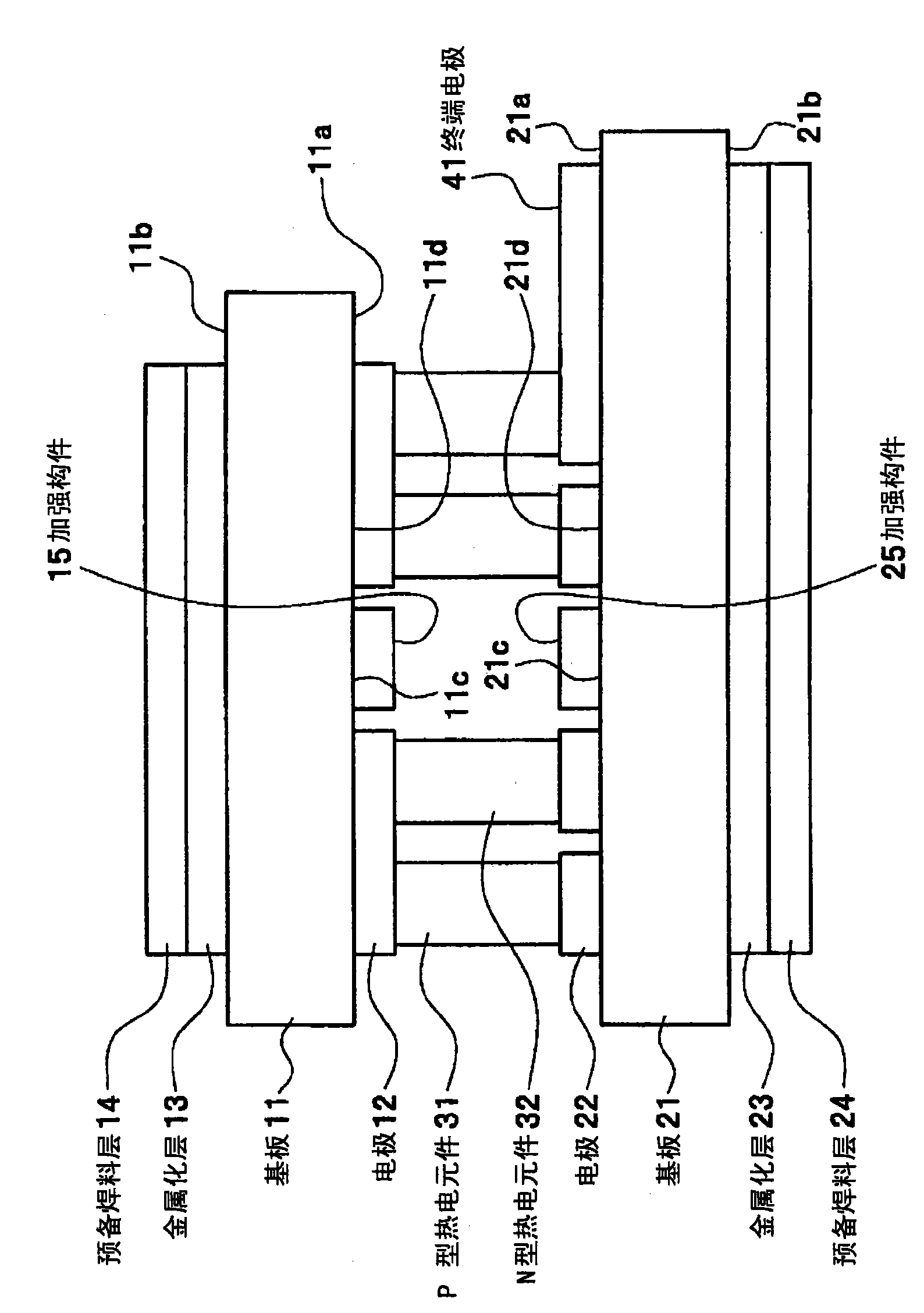
[0065] figure 1 The basic structure of the thermoelectric module of the first embodiment is shown.
[0066] figure 1 The thermoelectric assembly shown in 1 with Figure 18 The structural components of the conventional thermoelectric module 9 shown are the same, and the connection relationship of each structural component is also the same. The difference is the arrangement of the thermoelectric elements 31 , 32 or the electrodes 12 , 22 on the opposing surfaces 11 a , 21 a of the substrates 11 , 21 . Thus, in figure 1 In each structural part of the shown thermoelectric assembly 1 and Figure 18 In the shown thermoelectric module 9, the same components are assigned the same symbols, and the description of the structural components and connection relationship is omitted.
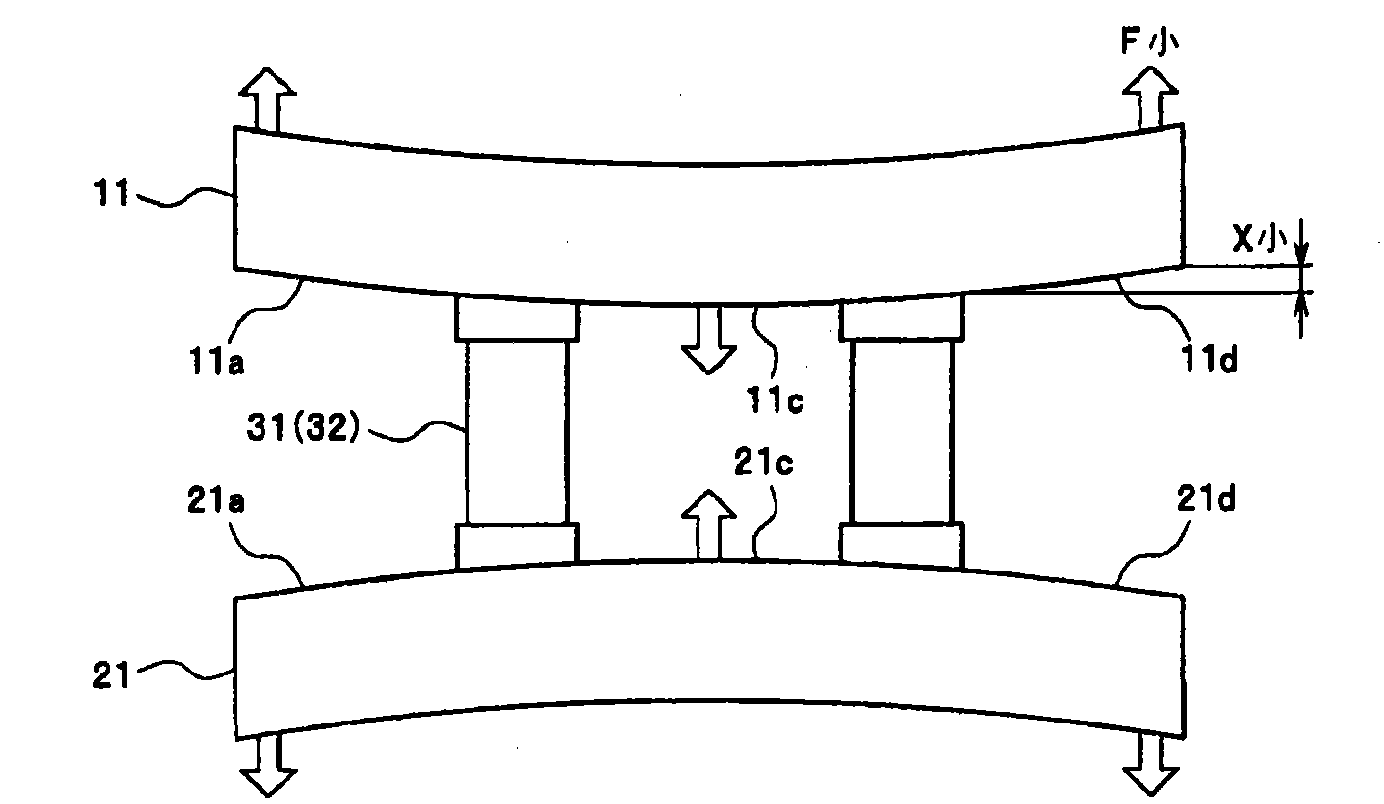
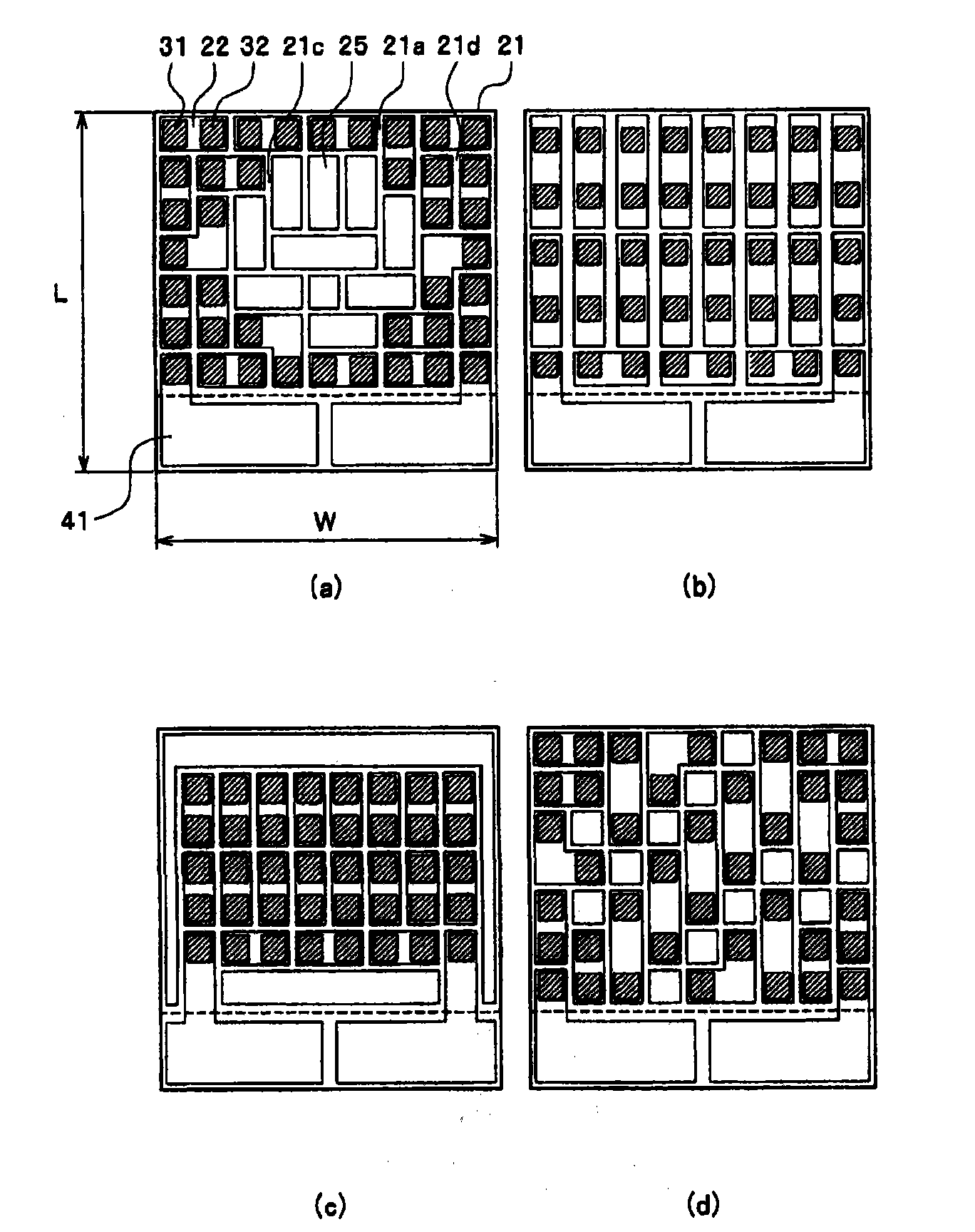
[0067] The thermoelectric elements 31 , 32 are arranged in areas 11 d , 21 d of the opposing surfaces 11 a , 21 a of the substrates 11 , 21 except for the central areas 11 c , 21 c. In the thermoelectric...
no. 2 approach
[0094] Figure 11 The basic structure of the thermoelectric module of the second embodiment is shown.
[0095] Figure 11 Thermoelectric assembly 2 shown with Figure 18 Most of the structural components of the conventional thermoelectric module 9 shown are the same, and the connection relationship and arrangement of each structural component are also the same. The difference is the thickness difference between the electrode and the metallization layer. Thus, in Figure 11 In each structural part of the shown thermoelectric assembly 2 and Figure 18 In the shown thermoelectric module 9, the same components are assigned the same symbols, and the description of the structural components and connection relationship is omitted.
[0096] Figure 11In the shown thermoelectric module 2 , the thickness of each electrode 12 , 22 is formed to be thicker than the thickness of the metallization layer 13 , 23 . The difference in thickness is such that the rate of change in resistance ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com