Cooperative data transmission method and system
A technology for collaborative transmission and data, applied in the field of communication
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
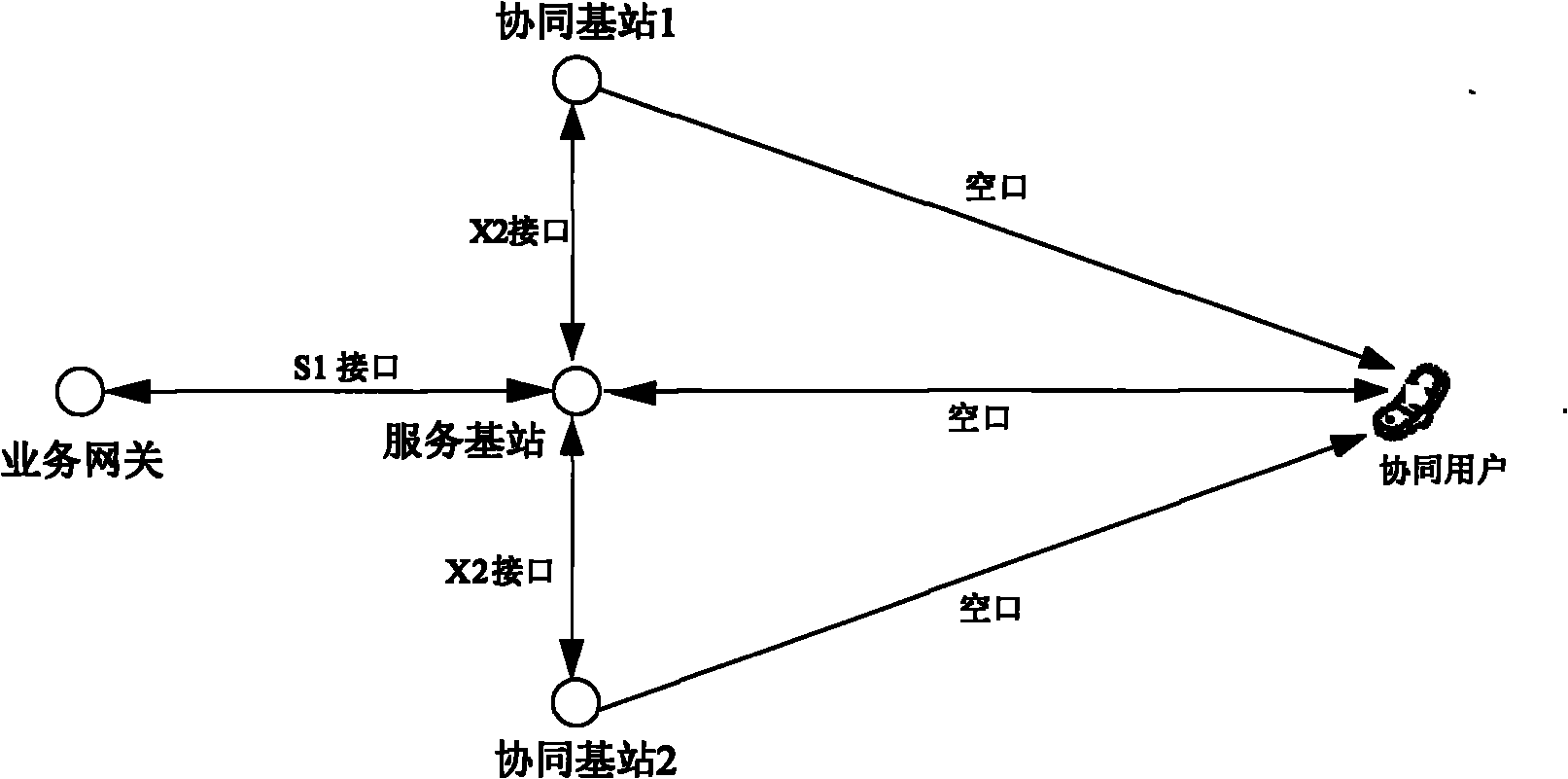
[0059] figure 1 As shown in the figure, it is a schematic diagram of the data distribution of scheme 1. The method of scheme 1 is that the service gateway treats the cooperative user data and the non-cooperative user data in the same way, and does not perform special processing; the service gateway transmits the user data through S1 The interface is delivered to the serving base station of the user, so that the serving base station receives the coordinated user data and non-cooperative user data within its service range; for the non-cooperative user data, the serving base station performs air interface processing and transmits it to the non-cooperative user through the transmitting antenna.
[0060] For cooperative user data, the serving base station first transmits the user data to other cooperative base stations in the cooperative group through the X2 interface according to the cooperative group information of the user. The candidate coordinating base station sends a coordin...
example 2
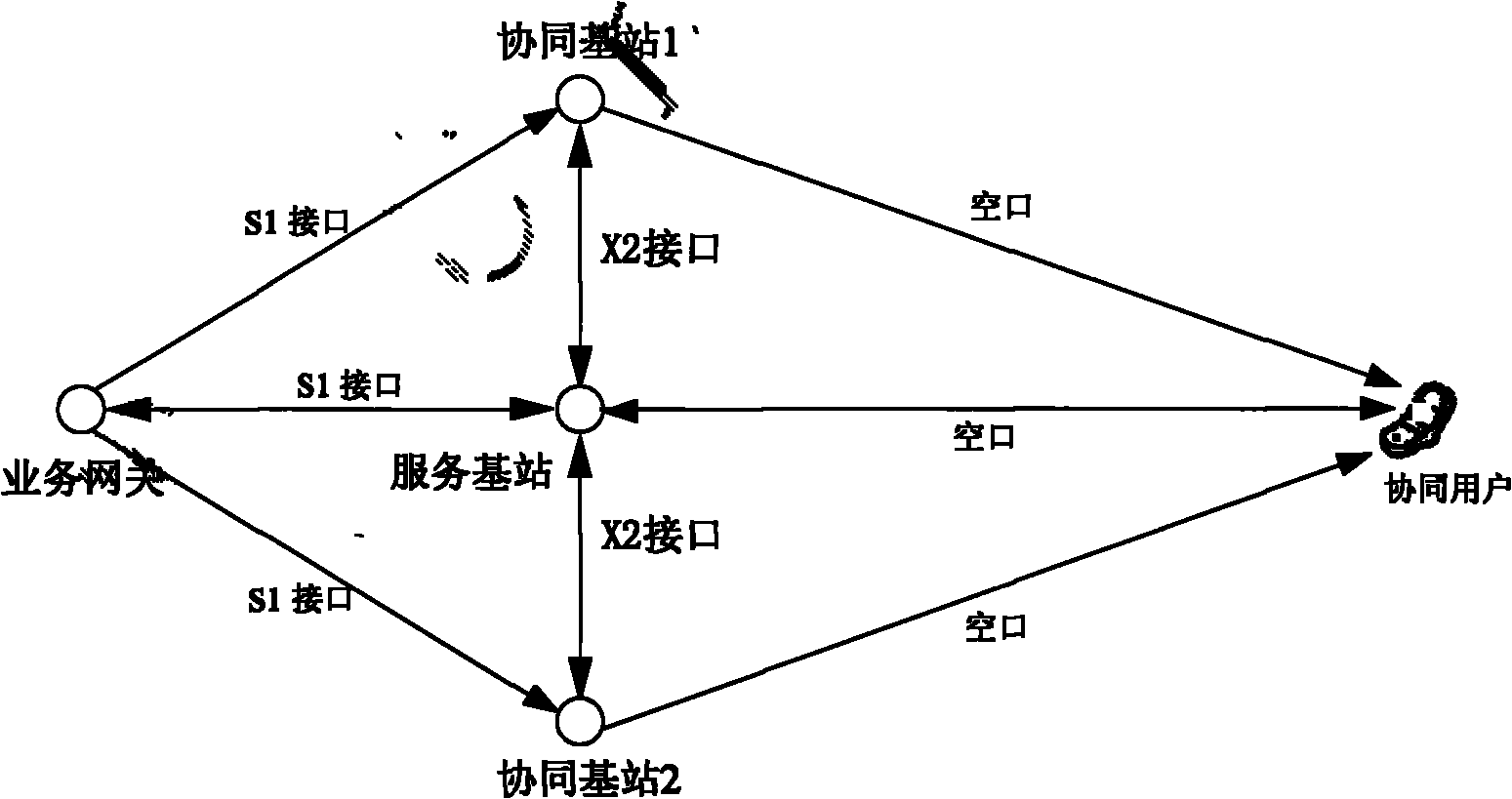
[0070] figure 2 As shown in the figure, it is a schematic diagram of data delivery in scheme 2. The method of scheme 2 is that, for non-cooperative user data, the service gateway sends the data to the user's serving base station through the S1 interface. For the coordinated user data, the serving base station judges the coordinated user, and the method of forming a coordinated group is the same as that in Embodiment 1. The service gateway sends it to all members in the coordinated group through the S1 interface, including the serving base station and each coordinated base station. All the base stations directly receive the coordinated user data from the service gateway, so that there is no need to transmit the downlink data of the coordinated user between the serving base station and the coordinated base station, and the control plane only needs to exchange cooperative control signaling. After the cooperative control signaling interaction is completed, the serving base statio...
example 3
[0080] Scheme 2 is also adopted, and the schematic diagram of data delivery is as follows figure 2 , wherein the functions of the service gateway, the serving base station, the coordinated base station and the coordinated user are the same as those in Example 1.
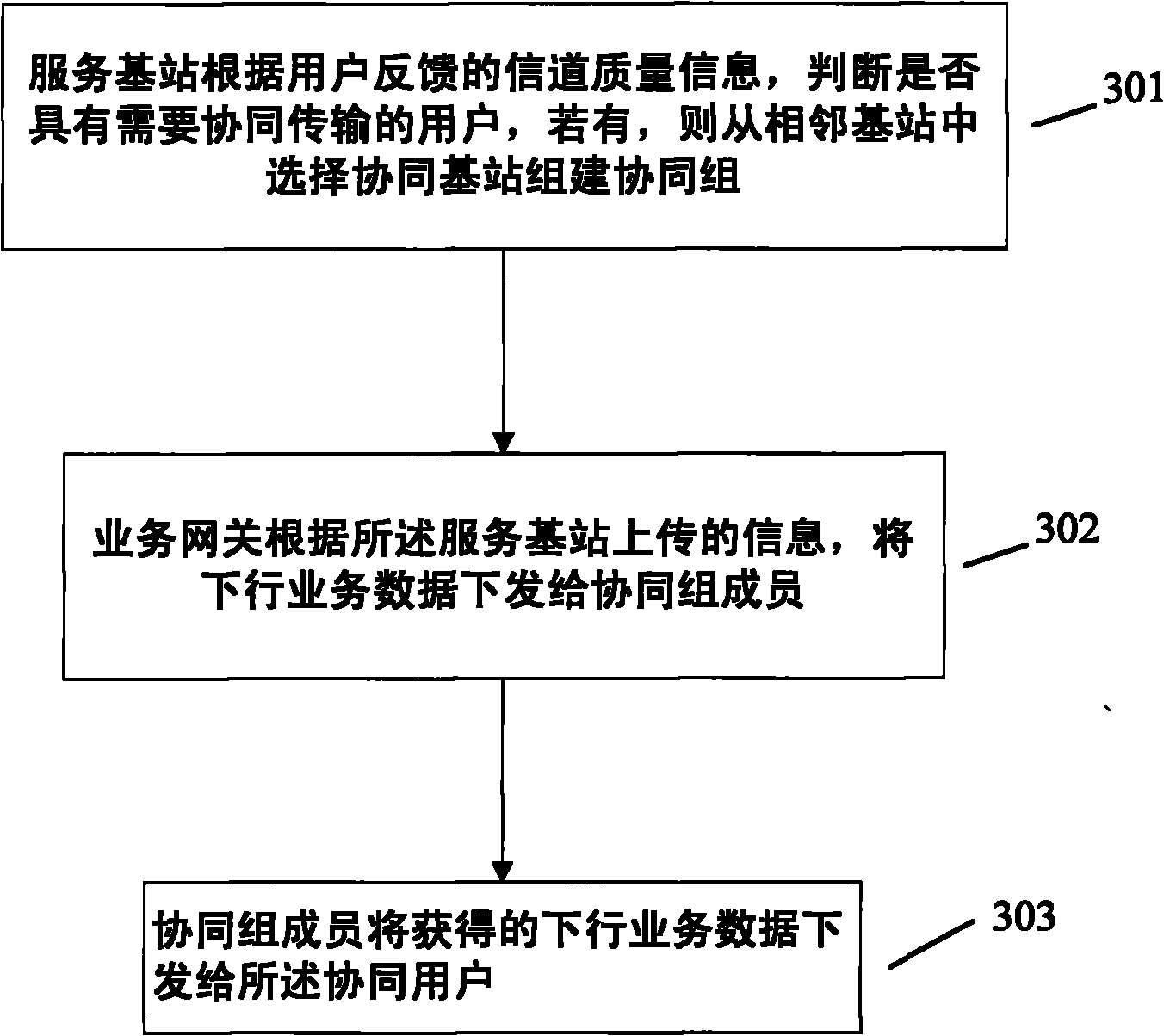
[0081] Flowchart such as Figure 5 As shown, the service gateway transmits the user data to the serving base station of the user through the S1 interface according to the method specified in the current LTE. For the sake of clarity, it is set that the user data received by the serving base station includes the data of user a and the data of user b.
[0082] Based on the channel quality information fed back by users a and b, the serving base station determines that the serving base station itself cannot provide high-quality transmission for user a due to time-varying channels, and needs to perform coordinated transmission for user a, so that user a becomes a cooperative user; user b is still only provided by the ser...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com